丙酮 | 67-64-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
无色易挥发易燃的液体,微有香气。丙酮能与水、乙醇、多元醇、酯、醚、酮、烃、卤代烃等多种极性和非极性溶剂相混溶,是一种典型的溶剂。除棕榈油等少数油类外,几乎所有的油脂都能溶解,并能溶解纤维素、聚甲基丙烯酸、酚醛、聚酯等多种树脂。对环氧树脂溶解能力较差,对聚乙烯、呋喃树脂、聚偏二氯乙烯等树脂不易溶解。虫胶、橡胶、沥青、石蜡等则难以溶解。本品微有毒性,若蒸气浓度不明或超过暴露极限时,应佩戴合适的呼吸器。丙酮对日光和酸碱不稳定,沸点低,挥发性强。
-
丙酮是脂肪族酮类最有代表性的化合物,具有酮类的典型反应。例如,它与亚硫酸氢钠形成无色结晶加成物;与氰化氢反应生成丙酮氰醇[(CH3)2C(OH)CN];在还原剂作用下生成异丙醇与频哪酮;对氧化剂较为稳定,在室温以下不会被硝酸氧化,但用碱性高锰酸钾或铬酸等强氧化剂可使其氧化为乙酸、甲酸、二氧化碳和水。在碱存在下发生双分子缩合反应,生成双丙酮醇。2摩尔丙酮在盐酸、氯化锌或硫酸等酸性催化剂存在下,生成亚异丙基丙酮,再与1摩尔丙酮加成,生成佛尔酮(二亚异丙基丙酮)。3摩尔丙酮在浓硫酸作用下,脱去3摩尔水,生成1,3,5-三甲苯。在石灰、醇钠或氨基钠存在下,缩合生成异佛尔酮(3,5,5-三甲基-2-环己烯-1-酮)。在酸或碱存在下与醛或酮发生缩合反应,生成酮醇、不饱和酮及树脂状物质。与苯酚在酸存在下,缩合成双酚A。丙酮的α-氢原子容易被卤素取代生成α-卤代丙酮;与次卤酸钠或卤素的碱溶液作用生成卤仿。丙酮与Grignard试剂加成反应后水解得到叔醇;亦能与氨及其衍生物如羟胺、肼、苯肼等发生缩合反应。此外,丙酮在500~1000℃时发生热裂化产生乙烯酮;在170~260℃通过硅-铝催化剂生成异丁烯和乙醛;300~350℃时生成异丁烯和乙酸等。
-
丙酮是易燃有毒物品,毒性中等。轻度中毒对眼及上呼吸道黏膜有刺激作用,重度中毒会出现晕厥、痉挛等症状,并可能出现尿中蛋白和红细胞的现象。小鼠暴露于30~40mg/L或150mg/L的丙酮蒸气中2小时后,分别出现侧卧的中毒症状或致死。人体发生中毒时应立即离开现场,呼吸新鲜空气,严重者需送医抢救。空气中最高容许浓度为1000*10^-6。操作现场应保持良好的通风,并穿戴合适的防护用品。
-
丙酮属于低毒类物质,其毒性与乙醇相近。它主要通过中枢神经系统产生麻醉作用,吸入蒸气能引起头痛、眼花和呕吐等症状。空气中的嗅觉界限为3.80mg/m³。频繁接触可导致眼、鼻、舌黏膜炎症。在蒸汽浓度达到9488mg/m³时,在60分钟内会出现头痛、刺激支气管、昏迷等中毒症状;嗅觉阈值在1.2~2.44mg/m³之间。TJ 36-79规定,车间空气中最高容许浓度为360mg/m³。
-
稳定性:丙酮稳定 [23]。
-
禁配物:强氧化剂、强还原剂和碱。
-
聚合危害:不聚合 [25]。
-
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.1
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.67
-
拓扑面积:17.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
制备方法与用途
根据提供的信息,丙酮的主要用途包括:
-
作为溶剂:
-
作为化工原料:
-
在特定行业中的应用:
-
在分析与实验用途:
-
其他应用领域:
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丁酮 butanone 78-93-3 C4H8O 72.1069 丙酮醛 2-oxopropanal 78-98-8 C3H4O2 72.0636 乙醛 acetaldehyde 75-07-0 C2H4O 44.0532 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丙酮18O Aceton-18O 7217-26-7 C3H6O 60.0806 丙醛 propionaldehyde 123-38-6 C3H6O 58.08 丁酮 butanone 78-93-3 C4H8O 72.1069 丙酮醛 2-oxopropanal 78-98-8 C3H4O2 72.0636 乙醛 acetaldehyde 75-07-0 C2H4O 44.0532
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:膦与酮的反应:生成初级氧化膦的途径摘要:审查了膦与羰基化合物反应的早期工作,并提供了有关膦与酮反应的新信息。伯膦氧化物(X)和1-羟基仲膦氧化物(XI)在强酸性介质中形成,两种产物的比例由空间因素决定;前者以受阻酮为主。伯膦氧化物是一类新的化合物。它们在浓缩状态下具有有限的热稳定性,但是在溶液中足够稳定以用作中间体。讨论了该膦和羰基膦反应中氧转移步骤的机理。DOI:10.1016/0040-4020(62)80002-7
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:铑(III)卟啉对水的光催化碳-碳σ键厌氧氧化酮摘要:使用铑(III)卟啉催化剂完成了水对未应变酮的光催化碳-碳σ键氧化反应。催化产生具有α取代基的脂族和环状酮中相应的无碳的一碳羰基化合物和H 2,具有高达30个转换率。在芳族酮中未观察到碳损失。机理研究表明,(Ph 3 P)Rh III(ttp)OH(ttp =四甲苯基卟啉二价阴离子)是碳-碳σ键厌氧氧化的关键中间体。DOI:10.1021/om400672t
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:模块化和一锅立体选择性糖基化策略全合成紫芝多糖九十糖基序摘要:来自药用真菌灵芝的多糖代表了治疗多种疾病的重要辅助治疗剂,包括白细胞减少症和造血损伤。然而,从灵芝多糖中合成长的、支链的、复杂的碳水化合物链仍然是化学合成中的一项具有挑战性的任务。在此,我们首次报道了以糖基原-(1-苯乙烯基)苯甲酸酯为基础,通过一锅立体选择性糖基化策略,从灵芝多糖GSPB70-S中模块化化学合成了具有多种生物活性的九十糖基序。不仅加速了碳水化合物的合成,还减少了化学废物,并避免了基于硫代糖苷的一锅糖基化固有的糖苷配基转移问题。该合成路线还强调了以下关键步骤:(1)基于预激活的一锅糖基化,用于高度立体选择性构建多个1,2-顺式糖苷键,包括三个α- d -GlcN-(1→4)键和一个α- d -Gal-(1→4)键通过试剂N-甲基-N-苯基甲酰胺调节; (2)通过糖基N-苯基三氟乙酰亚胺酯、糖基邻炔基苯甲酸酯和糖基邻-(1-苯基乙烯基)苯甲酸酯的策略组合,在各种直链和支链聚糖片段中正交一锅组装1DOI:10.1021/jacs.4c05188
文献信息
-
Organocatalyzed Kabbe condensation reaction for mild and expeditious synthesis of 2,2‐dialkyl and 2‐spiro‐4‐chromanones作者:Naval P. Kapuriya、Jasmin J. Bhalodia、Mrunal A. Ambasana、Rashmi B. Patel、Atul H. BapodraDOI:10.1002/jhet.4054日期:——An expeditious Kabbe condensation reaction for the synthesis of 2,2‐dialkyl and 2‐spiro‐chroman‐4(1H)‐ones has been developed using pyrrolidine‐butanoic acid in DMSO as bifunctional organocatalyst. Unlike existing methods, this reaction proceeds at room temperature with high yields, rendering it an attractive method to synthesize a vast variety of privileged 4‐chromones.
-
Method development for the determination of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine by the high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry technique作者:Igors Susinskis、Peteris Mekss、Juris HmelnickisDOI:10.1177/1469066718761437日期:2018.8Unsymmetrical dimethyl hydrazine is highly toxic, carcinogenic compound, widely used for organic synthesis and drug development. Therefore, due to its high reactivity, direct analysis is problematic. Current study proposes to use derivatization reaction to increase selectivity and sensitivity of high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method. Different derivatization agents were tested
-
Pd-catalyzed carbonylative access to aroyl phosphonates from (hetero)aryl bromides
-
[EN] IMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF FAAH<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS IMIDAZOLE UTILES COMME INHIBITEURS DE LA FAAH申请人:MERCK & CO INC公开号:WO2009152025A1公开(公告)日:2009-12-17The present invention is directed to certain imidazole derivatives which are useful as inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzeimer Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
-
Preparation of functionalized cyclobutenones and phenolic compounds from α-diazo β-ketophosphonates作者:Rindra Andriamiadanarivo、Bernard Pujol、Bernard Chantegrel、Christian Deshayes、Alain DoutheauDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)61512-5日期:1993.12When heated in refluxing benzene or toluene, α-diazo β-ketophosphonates 2, prepared in three steps from aldehydes or ketones, gave rise to functionalized cyclobutenones 4 or phenolic compounds 5. These products are formed by electrocyclisation respectively of a vinyl or dienylketene, resulting from a Wolff rearrangement.
表征谱图
-
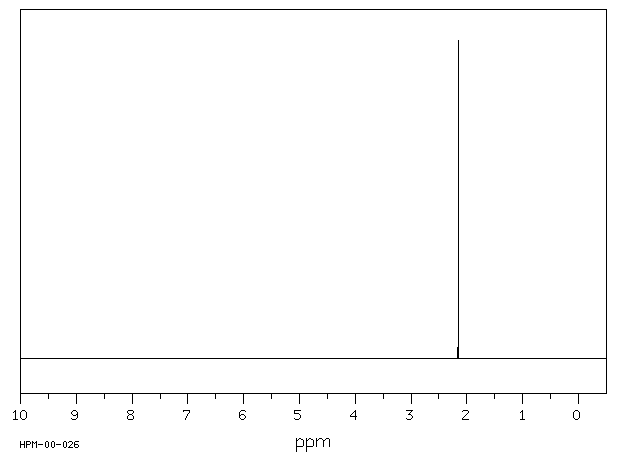
氢谱1HNMR
-
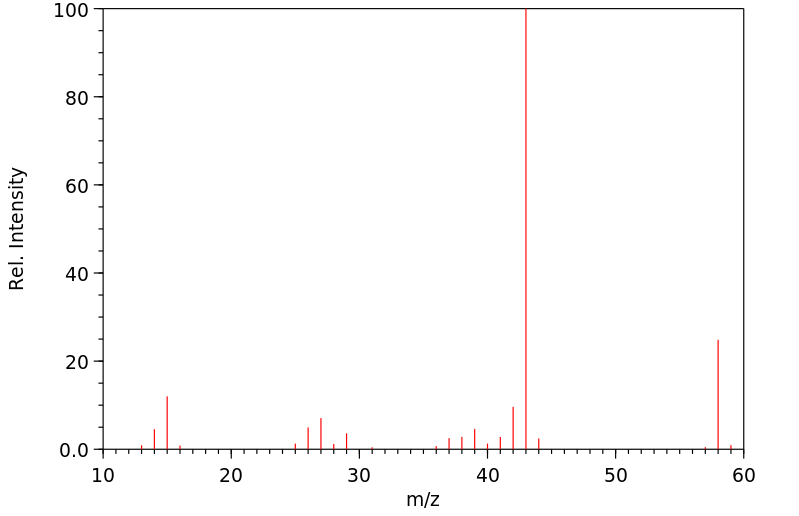
质谱MS
-
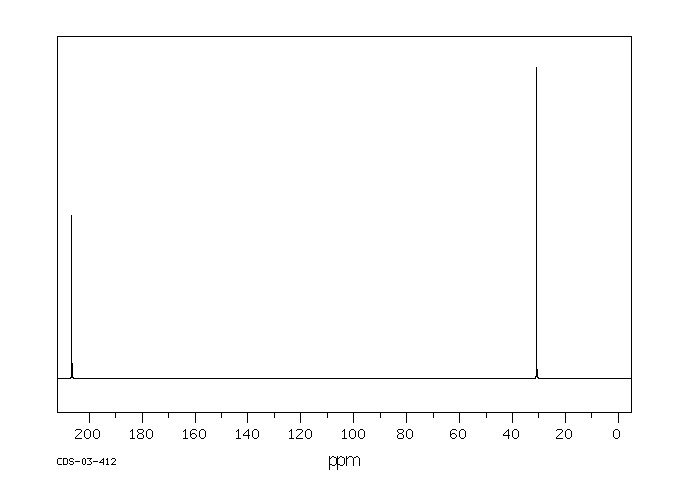
碳谱13CNMR
-
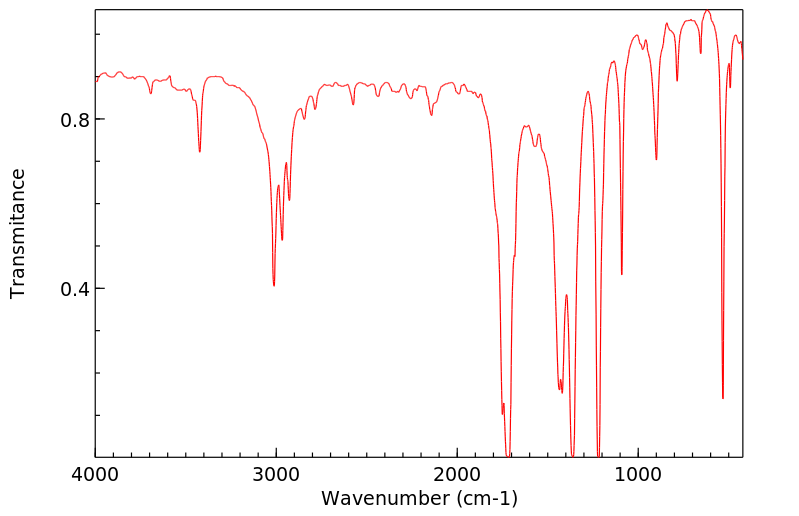
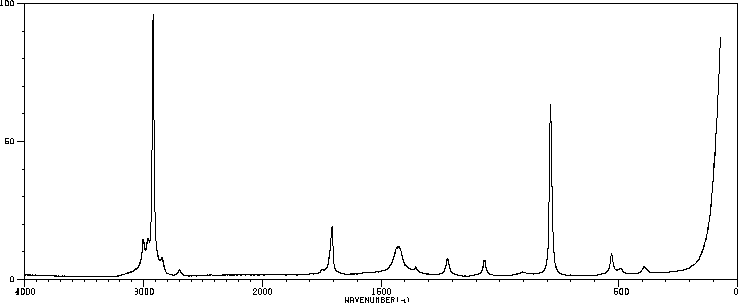
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息