对氯苯胺 | 106-47-8
中文名称
对氯苯胺
中文别名
1-氨基-4-氯苯;4-氯苯胺;对氨基氯苯
英文名称
4-chloro-aniline
英文别名
p-Chloroaniline;para-chloroaniline;p-chloraniline;4-chlorophenylamine;4‐chloroaniline;4-chlorobenzenamine;4-Chloroaniline
CAS
106-47-8
化学式
C6H6ClN
mdl
MFCD00007835
分子量
127.573
InChiKey
QSNSCYSYFYORTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:67-70 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:232 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1,43 g/cm3
-
蒸气密度:4.4 (vs air)
-
闪点:120°C
-
溶解度:2.2克/升
-
LogP:1.83 at 25℃
-
物理描述:P-chloroaniline appears as a white or pale yellow solid. Melting point 69.5°C.
-
颜色/状态:Orthorhombic crystals from alcohol or petroleum ether
-
气味:SLIGHTLY SWEETISH; CHARACTERISTIC AMINE ODOR
-
蒸汽密度:4.41 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:0.071 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:4.30e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:685 °C
-
分解:Energy of exothermic decomposition in range 210-400 °C was measured as 0.633 kJ/g by /diffential scanning calorimetry/, and T(ait24) was determined as 200 °C by adiabatic Dewar tests, with an apparent energy of activation of 124 kJ/mol.
-
燃烧热:-11,000 BTU/LB= -6,000 CAL/G= -250X10+5 J/KG
-
汽化热:12,832.8 gcal/gmole
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5546 at 87 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa= 3.982 at 25 °C (conjugate acid)
-
保留指数:1204;1204;1160;1160;1160;1159;1157;1161
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:26
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
Yields para-chloro-n-hydroxyaniline in rabbit. Yields para-aminophenol in rabbits. Yields para-chloroaniline-n-beta-dextro-glucuronide in rabbit. Yields 2-amino-5-chlorophenol in rabbits. Yields 3-amino-7-chlorophenoxazin-2-one in rabbits. /from table/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
对-氯苯胺通过红褐异胶藻(Chlorella fusca rubra)完全代谢,主要转化为水溶性产物。应用后4周,从藻类中回收了28%的放射性物质,从水相介质中回收了35%。从藻类中分离出的代谢物为对,对'-二氯偶氮氧苯和对,对'-氯偶氮苯,从营养介质中分离出的代谢物为对-氯甲酰胺和对-氯苯酰胺。
p-Chloroaniline is metabolized completely by Chlorella fusca rubra mostly to water-soluble products. 4 wk after application, 28% of the radioactivity was recovered from algae and 35% from aqueous medium. Metabolites isolated were p,p'-dichloroazoxybenzene and p,p'-chloroazobenzene from algae and p-chloro-formanilide and p-chloroanilide from nutrient medium.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
发芽豌豆种子的微粒体部分主要将4-氯苯胺(4-CA)氧化成4-氯硝基苯,尽管在高底物浓度下,(4-氯苯基)羟基胺也是一个主要产物。与4-氯苯胺相比,(4-氯苯基)羟基胺的酶催化氧化速度更快。4-氯苯胺的氧化依赖于过氧化氢,并且当用氧气和烟酸腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸还原酶代替过氧化氢时,反应不会进行。进一步将4-氯硝基苯缓慢氧化成4-氯硝基苯的酶促过程同样依赖于过氧化氢。
Microsomal fraction of germinated pea seeds oxidized 4-chloroaniline (4-CA) primarily to 4-chloronitrosobenzene, although (4-chlorophenyl)hydroxylamine was also a major product at high substrate concn. The enzyme-catalyzed oxidation of (4-chlorophenyl)hydroxylamine was faster than that for 4-chloroaniline. Oxidation of 4-chloroaniline was dependent on hydrogen peroxide & would not proceed when O2 & nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reductase were substituted for hydrogen peroxide. Further slow oxidation of 4-chloronitrosobenzene to 4-chloronitrobenzene was an enzymatic process that was also dependent on hydrogen peroxide.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
The amines undergo a process of metabolism within the organism and real active agents are the metabolites, some of which induce methemaglobinemia while others are carcinogenic. These metabolites generally take the form of hydroxylamines, changing to aminophenols as a form of detoxification. /Amines/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别:4-氯苯胺(PCA)是一种无色至微琥珀色的结晶固体,具有轻微的芳香气味。该化学品可溶于水和常见有机溶剂。PCA用作生产多种产品的中间体,包括农业化学品、偶氮染料和颜料、化妆品和药品。人类暴露:在人类中,意外暴露后30分钟就能检测到血红蛋白加合物,3小时达到最大水平。慢乙酰化个体的形成血红蛋白加合物的能力比快乙酰化个体强。人类的排泄主要通过尿液进行,PCA及其结合物在暴露后30分钟就能出现。排泄主要在前24小时内进行,并在72小时内几乎完全排泄。人类对PCA的职业暴露数据主要来自一些较旧的报告,这些报告是在生产过程中意外暴露于PCA后发生的严重中毒事件。症状包括增加的高铁血红蛋白和硫血红蛋白水平、发绀、贫血的发展以及缺氧引起的变化。PCA具有很强的形成血红蛋白加合物的倾向,它们的测定可以用于监测工作场所暴露于4-氯苯胺的员工的生物监测。有两个国家的报告称,新生儿重症监护室的新生儿出现了严重的高铁血红蛋白血症,这些早产儿暴露于PCA,这是氯己定的分解产物;无意中用于加湿液体中的氯己定在新型孵化器中加热后分解为PCA。一份报告中的三个新生儿(14.5-43.5%的高铁血红蛋白)和另一份报告中的415个新生儿中的33个(在8个月的筛查期间6.5-45.5%的高铁血红蛋白)被发现为高铁血红蛋白阳性。一项前瞻性临床研究表明,不成熟、严重疾病、暴露于PCA的时间以及NADH还原酶的低浓度可能导致了这种情况。
动物研究:PCA被迅速吸收和代谢。PCA的主要代谢途径如下:a)邻位C-羟基化生成2-氨基-5-氯酚,然后硫酸结合生成2-氨基-5-氯苯基硫酸酯,它以原样或经过N-乙酰化生成N-乙酰-2-氨基-5-氯苯基硫酸酯后排出;b)N-乙酰化生成4-氯乙酰苯胺(主要在血液中),进一步转化为4-氯葡萄糖苷苯胺,然后转化为4-氯草酸苯胺(在尿液中);或者c)N-氧化生成4-氯苯基羟胺,进一步转化为4-氯硝基苯(在红细胞中)。PCA的活性代谢物与血红蛋白以及肝脏和肾脏的蛋白质共价结合。动物的排泄主要通过尿液进行,PCA及其结合物在暴露后30分钟就能出现。排泄主要在前24小时内进行,并在72小时内几乎完全排泄。主要的毒性效应是高铁血红蛋白的形成。PCA是比苯胺更有效、更快诱导高铁血红蛋白的物质。PCA还表现出肾毒性和肝毒性。PCA对兔皮肤无刺激性,对兔眼有轻微刺激性。几种测试系统显示PCA有弱致敏潜力。重复暴露于PCA会导致发绀和高铁血红蛋白血症,随后影响血液、肝脏、脾脏和肾脏,表现为血液学参数的变化、脾肿大,以及脾脏、肝脏和肾脏中的中度至重度含铁血黄素沉着,部分伴有髓外造血。这些效应是过度的化合物诱导溶血后的继发性效应,与再生性贫血一致。PCA对雄性大鼠具有致癌性,可诱导脾脏(纤维肉瘤和骨肉瘤)的不寻常和罕见肿瘤,这是苯胺及其相关物质的典型特征。在雌性大鼠中,脾脏肿瘤的前癌阶段频率增加。雄性和雌性大鼠肾上腺嗜铬细胞瘤的发生率增加可能与PCA给药有关。有证据表明,雄性小鼠可能具有致癌性,表现为肝细胞肿瘤和血管肉瘤。PCA在细胞转化试验中显示出转化活性。各种体外遗传毒性测试——沙门氏菌突变试验、小鼠淋巴瘤试验、染色体畸变试验、姐妹染色单体交换的诱导——表明PCA可能具有遗传毒性,尽管结果有时相互矛盾。由于缺乏数据,无法对PCA的体内遗传毒性做出任何结论。没有关于生殖毒性的研究。根据PCA对各种水生生物毒性的有效测试结果,PCA在水生环境中可被归类为中度至高度有毒。因此,不能完全排除对水生生物,特别是底栖物种的潜在风险,特别是在含有大量颗粒物质、抑制快速光矿化的水域中。用大型溞进行的实验表明,随着介质中溶解腐殖质浓度的增加,毒性显著降低,这可能是由于PCA吸附到溶解腐殖质上而降低了生物有效性。
IDENTIFICATION: 4-Chloroaniline (PCA) is a colorless to slightly amber-colored crystalline solid with a mild aromatic odor. The chemical is soluble in water and in common organic solvents. PCA is used as an intermediate in the production of a number of products, including agricultural chemicals, azo dyes and pigments, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products. HUMAN EXPOSURE: In humans, hemoglobin adducts are detectable as early as 30 min after accidental exposure, with a maximum level at 3 hr. Slow acetylating individuals have a higher potency to form hemoglobin adducts compared with fast acetylators. Excretion in humans occurs primarily via the urine, with PCA and its conjugates appearing as early as 30 min after exposure. Excretion takes place mainly during the first 24 h and is almost complete within 72 h. Data on occupational exposure of humans to PCA are mostly from a few older reports of severe intoxications after accidental exposure to PCA during production. Symptoms include increased methemoglobin and sulfhemoglobin levels, cyanosis, the development of anemia, and changes due to anoxia. PCA has a strong tendency to form hemoglobin adducts, and their determination can be used in biomonitoring of employees exposed to 4-chloroaniline in the workplace. There are reports of severe methemoglobinemia in neonates from neonatal intensive care units in two countries where premature babies were exposed to PCA as a breakdown product of chlorohexidine; the chlorohexidine, which had been inadvertently used in the humidifying fluid, broke down to PCA upon heating in a new type of incubator. Three neonates in one report (14.5-43.5% methemoglobin) and 33 of 415 neonates in another report (6.5-45.5% methemoglobin during the 8-month screening period) were found to be methemoglobin positive. A prospective clinical study showed that immaturity, severe illness, time exposed to PCA, and low concentrations of NADH reductase probably contributed to the condition. ANIMAL STUDIES: PCA is rapidly absorbed and metabolized. The main metabolic pathways of PCA are as follows: a) C-hydroxylation in the ortho position to yield 2-amino-5-chlorophenol followed by sulfate conjugation to 2-amino-5-chlorophenyl sulfate, which is excreted as is or after N-acetylation to N-acetyl-2-amino-5-chlorophenyl sulfate; b) N-acetylation to 4-chloroacetanilide (found mainly in blood), which is further transformed to 4-chloroglycolanilide and then to 4-chlorooxanilic acid (found in the urine); or c) N-oxidation to 4-chlorophenylhydroxylamine and further to 4-chloronitrosobenzene (in erythrocytes). Reactive metabolites of PCA bind covalently to hemoglobin and to proteins of liver and kidney. Excretion in animals occurs primarily via the urine, with PCA and its conjugates appearing as early as 30 min after exposure. Excretion takes place mainly during the first 24 hr and is almost complete within 72 hr. The prominent toxic effect is methemoglobin formation. PCA is a more potent and faster methemoglobin inducer than aniline. PCA also exhibits a nephrotoxic and hepatotoxic potential. PCA was found to be non-irritating to rabbit skin and slightly irritating to rabbit eyes. A weak sensitizing potential was demonstrated with several test systems. Repeated exposure to PCA leads to cyanosis and methemoglobinemia, followed by effects in blood, liver, spleen, and kidneys, manifested as changes in hematological parameters, splenomegaly, and moderate to heavy hemosiderosis in spleen, liver, and kidney, partially accompanied by extramedullary hematopoiesis. These effects occur secondary to excessive compound-induced hemolysis and are consistent with a regenerative anemia. PCA is carcinogenic in male rats, with the induction of unusual and rare tumors of the spleen (fibrosarcomas and osteosarcomas), which is typical for aniline and related substances. In female rats, the precancerous stages of the spleen tumors are increased in frequency. Increased incidences of pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland in male and female rats may have been related to PCA administration. There was some evidence of carcinogenicity in male mice, indicated by hepatocellular tumors and hemangiosarcoma. PCA shows transforming activity in cell transformation assays. A variety of in vitro genotoxicity tests Salmonella mutagenicity test, mouse lymphoma assay, chromosomal aberration test, induction of sister chromatid exchange indicate that PCA is possibly genotoxic, although results are sometimes conflicting. Due to lack of data, it is impossible to make any conclusion about PCA's in vivo genotoxicity. No studies are available on reproductive toxicity. From valid test results available on the toxicity of PCA to various aquatic organisms, PCA can be classified as moderately to highly toxic in the aquatic compartment. Therefore, a possible risk to aquatic organisms, particularly benthic species, cannot be completely ruled out, particularly in waters where significant amounts of particulate matter inhibit rapid photomineralization. Experiments with Daphnia magna revealed significantly reduced toxicity with increasing concentrations of dissolved humic materials in the medium, possibly caused by reduced bioavailability of PCA from adsorption to dissolved humic materials.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
癌症分类:B2组可能的人类致癌物
Cancer Classification: Group B2 Probable Human Carcinogen
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicty of para-chloroaniline. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of para-chloroaniline. OVERALL EVALUATION: Group 2B: para-Chloroaniline is possibly carcinogenic to humans.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:对氯苯胺
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:para-Chloroaniline
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:2B组:可能对人类致癌
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 2B: Possibly carcinogenic to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
对氯苯胺可以通过完好无损的皮肤轻易被吸收。
p-Chloroaniline is readily absorbed through the intact skin... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Tomato uptake of 4-chloroaniline from soil increased in direct proportion with amount present in soil. Compound was mostly root-localized, but translocation to stem increased with increasing concentration. In carrots, roots accumulated only slightly more chloroaniline than green parts. 4-Chloroaniline was also taken up by wheat and barley.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
燕麦在6周内从土壤中吸收并转移了1.4%的土壤结合态(14)C-4-氯苯胺;从溶液中的吸收率为1.7-2.3%。将标记化合物以1 ppm的浓度添加到土壤中。在研究的两种土壤类型(富含腐殖质的潜育土和偏棕土)之间,结果只有轻微的差异。
Oats took up and translocated 1.4% of soil-bound (14)C-4-chloroaniline within 6 wk; uptake from solution was 1.7-2.3%. Labeled compound was added to soil at 1 ppm. There were only slight differences in results between 2 soil types (humus-rich gley and parabrown soils) studied.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在给予雄性/Fischer 344/大鼠口服0.3-30 mg/kg bw的(14)C标记化合物(每摩尔5 mCi(0.04 mCi/mg),未指定放射性化学纯度)的0.01 N盐酸溶液后,24小时内,75-85%的剂量通过尿液排出,8-12%通过粪便排出;仅有4%的剂量以未改变的胺形式通过尿液排出,2.5%通过胆汁排出,1%通过粪便排出。七天时,大量的放射性标记物仍然存在于血液细胞中,占总剂量的1-2%。在静脉注射3.0 mg/kg bw的乙醇:丙二醇:水(1:1:8)混合溶液后,4小时内60%的剂量通过尿液排出,6小时内25%通过胆汁排出,8小时内90%通过尿液和粪便排出。初始组织中含量最高的是肌肉>脂肪>皮肤>肝脏>血液……。
In male /Fischer 344/ rats administered (14)C-labelled compound (5 mCi/mmol (0.04 mCi/mg) (radiochemical purity unspecified)) at 0.3-30 mg/kg bw by gavage in 0.01 N hydrochloric acid, 75-85% of the dose was excreted in urine and 8-12% in feces by 24 hr; only 4% was excreted as unchanged amine in urine, 2.5% in bile and 1% in feces. At seven days, appreciable radiolabel was still present in blood cells, accounting for 1-2% of the dose. After an intravenous dose of 3.0 mg/kg bw in ethanol:propylene glycol:water (1:1:8), 60% of the dose was excreted in urine after 4 hr, 25% was excreted in bile after 6 hr, and 90% was eliminated in urine and feces by 8 hr. Initial levels in tissues were highest in muscle >fat >skin >liver >blood... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S16,S36/37,S45,S53,S60,S61,S7
-
危险类别码:R23/24/25,R45,R50/53,R43
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2921420090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2018 6.1/PG 2
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:BX0700000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS06,GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H301 + H311 + H331,H317,H350,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P261,P280,P301 + P310 + P330,P308 + P313,P403 + P233
-
储存条件:1. **储存注意事项**:应储存在阴凉、通风的库房中,并远离火源和热源。包装需密封完好。避免与氧化剂、酸类及食用化学品混放,切勿混合存储。配备相应种类和数量的消防设备。仓库内应备有适当的材料以处理泄漏情况。 2. **包装与储存**:采用铁桶包装,每桶净重200kg。储存在阴凉通风处,防止潮湿和火灾。按有毒危险品规定进行运输和存储。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61766 |
| CAS: | 106-47-8 |
| 中文名称: | 4-氯苯胺 |
| 英文名称: | p-Chloroaniline |
| 别 名: | 对氯苯胺;对氨基氯苯 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 6 ClN;ClC 6 H 4 NH 2 |
| 分子量: | 127.57 |
| 熔 点: | 72.5℃ 沸点:232℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.43 |
| 蒸汽压: | |
| 溶解性: | 溶于热水、多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色结晶或淡黄色固体 |
| 危险标记: | 15(毒害品) |
| 用 途: | 用作染料中间体、药品、农业化学品 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:能经无损的皮肤吸收。能形成高铁血红蛋白血症,并对眼有刺激作用。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:中等毒性。
急性毒性:LD 50 310mg/kg(大鼠经口);360mg/kg(兔经皮);人吸入44mg/m 3 ,最小致死剂量(血液毒作用);人吸入22mg/m 3 ,出现症状。
致突变性:微粒体诱变:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌100ug/皿。非程序DNA合成:大鼠肝5mg/L。
致癌性:IARC致癌性评论:对人可能致癌。
危险特性:遇明火、高热或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。受高热分解,产生有毒的氮氧化物和氯化物气体。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化氮、氯化氢。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法《空气中有害物质的测定方法》,杭士平主编
色谱/质谱法《固体废弃物试验分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译
5.环境标准:
| 前苏联 | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.3mg/m 3 [皮] |
| 前苏联(1977) | 大气质量标准 | 0.01mg/m 3 |
| 前苏联(1975) | 水体中有害物质最高允许浓度 | 0.2mg/L |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,用洁净的铲子收集于干燥净洁有盖的容器中,运至废物处理场所。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:高浓度环境中,佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,应该佩戴自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿紧袖工作服,长统胶鞋。
手防护:戴橡皮手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。及时换洗工作服。工作前不饮酒,用温水洗澡。监测毒物。进行就业前和定期的体检。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。注意手、足和指甲等部位。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者给漱口,饮水,洗胃后口服活性炭,再给以导泻。就医。
灭火方法:雾状水、二氧化碳、砂土、干粉、泡沫。
制备方法与用途
化学性质
对氯苯胺是一种白色或浅黄色晶体,溶于热水,并且易溶于乙醇、乙醚、丙酮及二硫化碳等常用有机溶剂。
用途
作为偶氮染料和色酚AS-LB的中间体,对氯苯胺也是医药利眠宁、非那西丁以及农药的原料。此外,它还用于制彩色胶片成色剂。对氯苯胺可以直接合成除虫脲或通过对氯苯基脲及对氯苯异氰酸酯来合成灭幼脲和除虫脲等品种,还可以通过2-氯-4-氨基苯酚来合成啶蜱脲。该物质也是除草剂莎稗磷和植物生长调节剂杀雄啉(cintofen)的中间体。此外,对氯苯胺在染料、医药及彩色电影胶片成色剂生产中均有应用。
生产方法
- 铁粉还原法:将乙酸水溶液加热至沸,在剧烈搅拌下加入铁粉,再分次加入对硝基氯苯,得到98%纯度的工业品。产率74%。
- 加氢还原法:对硝基氯苯溶于酒精中,以骨架镍为催化剂,在100℃及约4MPa压力下加氢还原。分离溶剂和催化剂后可得成品。
另一种生产方法是使用对氯硝基苯作为原料,兰尼镍作催化剂,乙醇为溶剂,在50~70℃、3.04~3.55 MPa的压力及pH=5~6的条件下进行催化加氢反应,得到产品。
另一种还原方法是对硝基氯苯进行铁粉还原、加氢还原或锌粉还原。具体步骤如下:
- 铁粉还原法:将对氯硝基苯、水和铁屑混合并加热至95℃,滴加浓盐酸调节温度在25℃后继续反应25小时;冷却后加入过量氢氧化钠中和,蒸馏油层即得产品。
- 加氢还原法:将对氯硝基苯与乙醇按质量比1:1.5混合,加入兰尼镍催化剂,在50~70℃、2.94~3.43 MPa压力及pH=5~6条件下通入氢气反应2小时;所得粗品在常压下蒸出乙醇和部分水,再减压蒸馏即得成品。
类别
有毒物品,高毒。急性毒性:口服-大鼠 LD50: 300 毫克/公斤; 口服-小鼠LD50: 100 毫克/公斤。
刺激数据:皮肤-兔 500 毫克/24小时 轻度;眼睛-兔 0.25 毫克/24小时 重度。
可燃性危险特性:遇明火、热或氧化剂燃烧,燃烧释放有毒氮氧化物和氯化物烟雾。
储运特性:库房应通风低温干燥,并与氧化剂及食品添加剂分开存放。
灭火剂:二氧化碳、泡沫、干粉、雾状水。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-氯苯基羟胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)hydroxylamine 823-86-9 C6H6ClNO 143.573 4-氯苯肼 N-4-chlorophenylhydrazine 1073-69-4 C6H7ClN2 142.588 4-氯亚硝基苯 1-chloro-4-nitroso-benzene 932-98-9 C6H4ClNO 141.557 4-氯-N-甲基苯胺 4-chloro-N-methylaniline 932-96-7 C7H8ClN 141.6 3,4-二氯苯胺 3,4-dichloroaniline 95-76-1 C6H5Cl2N 162.018 1-叠氮-4-氯苯 1-azido-4-chlorobenzene 3296-05-7 C6H4ClN3 153.571 对氯苯异氰酸酯 p-chlorphenylisocyanate 104-12-1 C7H4ClNO 153.568 2,4,6-三氯苯胺 2,4,6-trichloroaniline 634-93-5 C6H4Cl3N 196.463 4-氯异硫氰酸苯酯 4-Chlorophenyl isothiocyanate 2131-55-7 C7H4ClNS 169.634 —— 1-p-chlorophenylformamidine 54608-54-7 C7H7ClN2 154.599 N-(4-氯苯)甲酰胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)formamide 2617-79-0 C7H6ClNO 155.584 —— 4-Chlor-N-hydroxymethylanilin —— C7H8ClNO 157.6 N,N’-双-(4-氯-苯基)-肼 N,N'-bis(4-chlorophenyl)hydrazine 953-14-0 C12H10Cl2N2 253.131 1-(4-氯苯基)-2-苯基肼 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-phenylhydrazine 949-88-2 C12H11ClN2 218.686 4,4'-二氯偶氮苯 bis-(4-chloro-phenyl)-diazene 1602-00-2 C12H8Cl2N2 251.115 —— 4-chloroazobenzene 4340-77-6 C12H9ClN2 216.67 —— (E)-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)diazene 21650-51-1 C12H8Cl2N2 251.115 —— N-Isopropyliden-4-chloranilin 40938-43-0 C9H10ClN 167.638 —— bis(p-chlorophenyl)sulfur diimide 2648-43-3 C12H8Cl2N2S 283.181 N-(4-氯苯基)胍 1-(4-chlorophenyl)guanidine 45964-97-4 C7H8ClN3 169.614 1-(4-氯苯基)-3-甲基三氮烯 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methyltriazene 40843-82-1 C7H8ClN3 169.614 4-氯-N-2-丙烯-1-基-苯胺 N-allyl-4-chloroaniline 13519-80-7 C9H10ClN 167.638 - 1
- 2
- 3
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-氯苯基羟胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)hydroxylamine 823-86-9 C6H6ClNO 143.573 4-氯苯肼 N-4-chlorophenylhydrazine 1073-69-4 C6H7ClN2 142.588 N-(4-氯苯基)甲亚胺 4-chloro-N-methylen-aniline 32328-78-2 C7H6ClN 139.584 —— p-chlorophenyl chloramine 57311-92-9 C6H5Cl2N 162.018 4-氯-N-甲基苯胺 4-chloro-N-methylaniline 932-96-7 C7H8ClN 141.6 4-氯亚硝基苯 1-chloro-4-nitroso-benzene 932-98-9 C6H4ClNO 141.557 邻氯苯胺 2-Chloroaniline 95-51-2 C6H6ClN 127.573 2,4-二氯苯胺 2,4-Dichloroaniline 554-00-7 C6H5Cl2N 162.018 4-氯-1,3-苯二胺 4-chloro-1,3-phenylenediamine 5131-60-2 C6H7ClN2 142.588 4-氯-1,2-苯二胺 4-Chloro-1,2-phenylenediamine 95-83-0 C6H7ClN2 142.588 —— (Z)-4-chloro-benzenediazo hydroxide 36966-92-4 C6H5ClN2O 156.572 N-亚磺酰-4-氯苯胺 N-(4-chloro-phenyl)-sulfur imide oxide 13165-68-9 C6H4ClNOS 173.623 1-叠氮-4-氯苯 1-azido-4-chlorobenzene 3296-05-7 C6H4ClN3 153.571 —— p-chloroaniline-N,N-d2 35749-93-0 C6H6ClN 129.557 4-氯-N,N-二甲基苯胺 4-chloro-N,N-dimethylaniline 698-69-1 C8H10ClN 155.627 —— N-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-S-methyl-thiohydroxylamine 103375-60-6 C7H8ClNS 173.666 对氯苯异氰酸酯 p-chlorphenylisocyanate 104-12-1 C7H4ClNO 153.568 —— p-chlorophenyl isoselenocyanate 14223-48-4 C7H4ClNSe 216.528 4-氯二苯胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)aniline 1205-71-6 C12H10ClN 203.671 4-氯苯基氰胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)cyanamide 13463-94-0 C7H5ClN2 152.583 2,4,6-三氯苯胺 2,4,6-trichloroaniline 634-93-5 C6H4Cl3N 196.463 二(4-氯苯基)胺 bis(4-chlorophenyl)amine 6962-04-5 C12H9Cl2N 238.116 4-氯异硫氰酸苯酯 4-Chlorophenyl isothiocyanate 2131-55-7 C7H4ClNS 169.634 乙基氯苯胺 N-ethyl-4-chloro-aniline 13519-75-0 C8H10ClN 155.627 N-(4-氯苯)甲酰胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)formamide 2617-79-0 C7H6ClNO 155.584 —— 4-Chlor-thioformanilid 26060-33-3 C7H6ClNS 171.65 —— 4-Chlor-N-hydroxymethylanilin —— C7H8ClNO 157.6 2,6-二氯苯胺 2,6-Dichloroaniline 608-31-1 C6H5Cl2N 162.018 N,N’-双-(4-氯-苯基)-肼 N,N'-bis(4-chlorophenyl)hydrazine 953-14-0 C12H10Cl2N2 253.131 1-(4-氯苯基)-2-苯基肼 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-phenylhydrazine 949-88-2 C12H11ClN2 218.686 —— (E)-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)diazene 21650-51-1 C12H8Cl2N2 251.115 4,4'-二氯偶氮苯 bis-(4-chloro-phenyl)-diazene 1602-00-2 C12H8Cl2N2 251.115 —— 4-chloroazobenzene 4340-77-6 C12H9ClN2 216.67 —— trans-(4-chloro-phenyl)-phenyl-diazene 6141-95-3 C12H9ClN2 216.67 —— Schwefligsaeure-dichlorid-<4-chlor-phenylimid 6185-77-9 C6H4Cl3NS 228.529 —— bis(p-chlorophenyl)sulfur diimide 2648-43-3 C12H8Cl2N2S 283.181 —— N-Isopropyliden-4-chloranilin 40938-43-0 C9H10ClN 167.638 —— N-(4-chlorophenyl)-SS-dimethylsulphimide 20094-95-5 C8H10ClNS 187.693 —— bis(4-chlorophenylamine) sulfide 13616-65-4 C12H10Cl2N2S 285.197 N-(4-氯苯基)胍 1-(4-chlorophenyl)guanidine 45964-97-4 C7H8ClN3 169.614 N-(2-氨基乙基)-n-(4-氯苯基)胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylenediamine 14088-84-7 C8H11ClN2 170.642 —— 2-(p-Chloranilino)ethanthiol 5891-08-7 C8H10ClNS 187.693 4-氯-N-异丙基苯胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-isopropylamine 770-40-1 C9H12ClN 169.654 双(4-氯苯基)碳二亚胺 bis-(4-chloro-phenyl)-carbodiimide 838-98-2 C13H8Cl2N2 263.126 N1-(4-氯苯基)苯-1,4-二胺 4-amino-4'-chlorodiphenylamine 13065-93-5 C12H11ClN2 218.686 —— 4-chloro-N-propylaniline 73938-86-0 C9H12ClN 169.654 —— 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenylcarbodiimide 53288-64-5 C13H9ClN2 228.681 1-(4-氯苯基)-3-甲基三氮烯 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methyltriazene 40843-82-1 C7H8ClN3 169.614 1,1-二氯-N-(4-氯苯基)甲亚胺 N-dichloromethylene-4-chloroaniline 2771-67-7 C7H4Cl3N 208.474 —— 4-chloro-N-prop-2-ynylaniline 22774-67-0 C9H8ClN 165.622 [(4-氯苯基)氨基]乙腈 2-((4-chlorophenyl)amino)acetonitrile 24889-92-7 C8H7ClN2 166.61 4-氯-N-2-丙烯-1-基-苯胺 N-allyl-4-chloroaniline 13519-80-7 C9H10ClN 167.638 —— (2-chloroethyl)-(4-chlorophenyl)amine 74474-40-1 C8H9Cl2N 190.072 —— 2-(4-chlorophenylamino)ethanol 2933-81-5 C8H10ClNO 171.626 —— N-(2-bromoethyl)-4-chloroaniline 54472-54-7 C8H9BrClN 234.523 4-氯-3-碘苯胺 4-chloro-3-iodoaniline 573764-31-5 C6H5ClIN 253.47 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:选择性 CDK4/6 抑制新型 1,2,3-三唑系吖啶二酮衍生物通过 Rb 磷酸化阻断在乳腺癌模型中诱导 G1/S 细胞周期转变停滞摘要:CDK4 和 CDK6 是初始细胞周期阶段的重要调节剂,一直被认为是抗癌治疗的一个令人兴奋的选择。在本研究中,我们提出了一类新的 1,2,3-三唑系链吖啶二酮衍生物(6a-l)作为选择性 CDK4/6 抑制剂的基于结构的合理设计和合成。作为 1-Phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbaldehydes 的取代衍生物与取代的二甲酮之间的限速反应的结果,制备了标题分子,并通过 IR、1 H、13 C NMR和MS光谱数据。所有分子都经过体外筛选对一组具有不同 Rb 表达状态的不同来源的人乳腺肿瘤细胞系的细胞毒性潜力。在整个系列的共轭六氢吖啶二酮中,6g对 MCF-7、BT-474 和 SK-BR3 细胞系显示出有效的细胞毒性作用,IC 50值分别为 0.173 ± 0.037、0.117 ± 0.025 和 0.136 ± 0.027 μM 此外,CDK 抑制试验表明,化合物6g和6h比该家族的其他DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105377
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Copper-catalyzed conversion of aryl and heteroaryl bromides into the corresponding chlorides摘要:描述了一种合成芳基和杂芳基氯化物的高效方法。在温和反应条件下,芳基和杂芳基溴化物与四甲基氨基氯化铵在铜催化剂存在下顺利反应,产生了相应的氯化物,产率令人满意至优良。DOI:10.1039/c2cc34944b
-
作为试剂:描述:1,4-二甲基-1H-吲哚 、 聚合甲醛 在 sodium benzoate 、 lithium perchlorate 、 对氯苯胺 作用下, 以 水 、 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 20.0h, 以78%的产率得到1,4-二甲基-1H-吲哚-3-甲醛参考文献:名称:吲哚与醛的电化学促成C3-甲酰化和酰化作用摘要:本文报道的是吲哚与各种醛的氧化交叉偶联的有效策略。该策略基于两步转化,通过众所周知的曼尼希型反应和羰基引入的C–N键裂解实现。关键步骤是曼尼希产品的C–N键断裂—是通过电化学实现的。这种策略(包含40多个示例)可确保出色的官能团耐受性以及药物分子的后期功能化。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02433
文献信息
-
Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketimines with Trichlorosilane: Structural Studies作者:Peter Schreiner、Zhiguo Zhang、Parham Rooshenas、Heike HausmannDOI:10.1055/s-0028-1088045日期:——structural and mechanistic studies on the organocatalytic asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketimines with trichlorosilane. Amines were obtained in good yields and moderate enantioselectivities. Both experiment and computation were utilized to provide an improved understanding of the mechanism. amines - Lewis bases - organocatalysis - transfer hydrogenation - trichlorosilane
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
Highly Regio- and Enantioselective Alkoxycarbonylative Amination of Terminal Allenes Catalyzed by a Spiroketal-Based Diphosphine/Pd(II) Complex作者:Jiawang Liu、Zhaobin Han、Xiaoming Wang、Zheng Wang、Kuiling DingDOI:10.1021/jacs.5b07764日期:2015.12.16An enantioselective alkoxycarbonylation-amination cascade process of terminal allenes with CO, methanol, and arylamines has been developed. It proceeds under mild conditions (room temperature, ambient pressure CO) via oxidative Pd(II) catalysis using an aromatic spiroketal-based diphosphine (SKP) as a chiral ligand and a Cu(II) salt as an oxidant and affords a wide range of α-methylene-β-arylamino
-
Synthesis of newer 1,2,3-triazole linked chalcone and flavone hybrid compounds and evaluation of their antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities作者:Rama Kant、Dharmendra Kumar、Drishti Agarwal、Rinkoo Devi Gupta、Ragini Tilak、Satish Kumar Awasthi、Alka AgarwalDOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.02.041日期:2016.5The antiplasmodial and cytotoxic activities of these compounds were also evaluated against human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum strain 3D7 and human hepato-cellular carcinoma cells (Huh-7), respectively. Compounds 10a, 10c, 10d, 12c and 14e showed promising antibacterial activity while compounds 10e, 11d, 11e, 12c, 13a, 13b, 13e, 14a and 14d showed good antifungal activity as compared to the corresponding本研究旨在通过铜催化点击化学合成一类新的抗菌剂和抗疟原虫剂,以提供25种1,4-二取代-1,2,3-三唑的化合物10–14(a – e)。查耳酮和黄酮的衍生物。通过元素分析,IR,1 H NMR,13 C NMR和质谱数据建立了新合成化合物的结构。评价了新合成的化合物对革兰氏阳性细菌(金黄色葡萄球菌,粪肠球菌),革兰氏阴性细菌(大肠杆菌,铜绿假单胞菌,志贺氏菌鲍氏,肺炎克雷伯菌)和抗真菌活性(白色念珠菌,热带念珠菌,近平滑念珠菌,新型隐球菌,皮肤癣菌)以及模具(黑曲霉,烟曲霉)。还分别评估了这些化合物对人疟原虫恶性疟原虫菌株3D7和人肝细胞癌细胞(Huh-7)的抗血浆和细胞毒活性。化合物10a,10c,10d,12c和14e与相应的标准药物相比,化合物10e,11d,11e,12c,13a,13b,13e,14a和14d表现出良好的抗菌活性。发现化合物10b对恶性疟原虫最具活性,而其余化合
-
Synthesis and Anticonvulsant Activity of<i>N</i>-(Substituted)-1-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2-dihydroquinazoline-3(4<i>H</i>)-carboxamides作者:Hemavathi N. Deepakumari、Bidarur K. Jayanna、Maralekere K. Prashanth、Hosakere D. Revanasiddappa、Bantal VeereshDOI:10.1002/ardp.201600024日期:2016.7A series of new N‐(substituted)‐1‐methyl‐2,4‐dioxo‐1,2‐dihydroquinazoline‐3(4H)‐carboxamides were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for their anticonvulsant activity. Most of the synthesized compounds exhibited potent anticonvulsant activities in the maximal electroshock (MES) and pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) test. The most promising compound 4c showed significant anticonvulsant activity with a protective
表征谱图
-
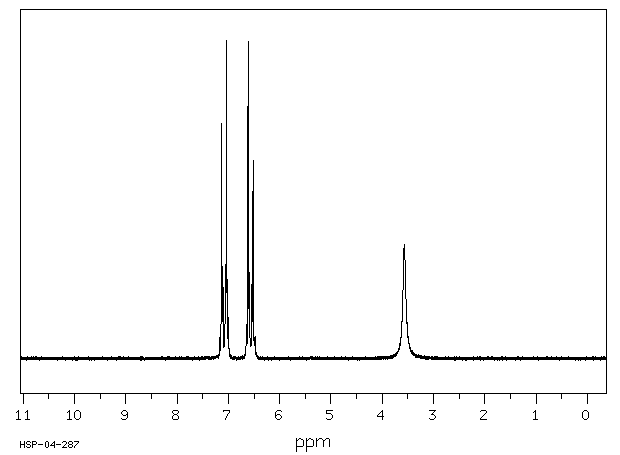
氢谱1HNMR
-
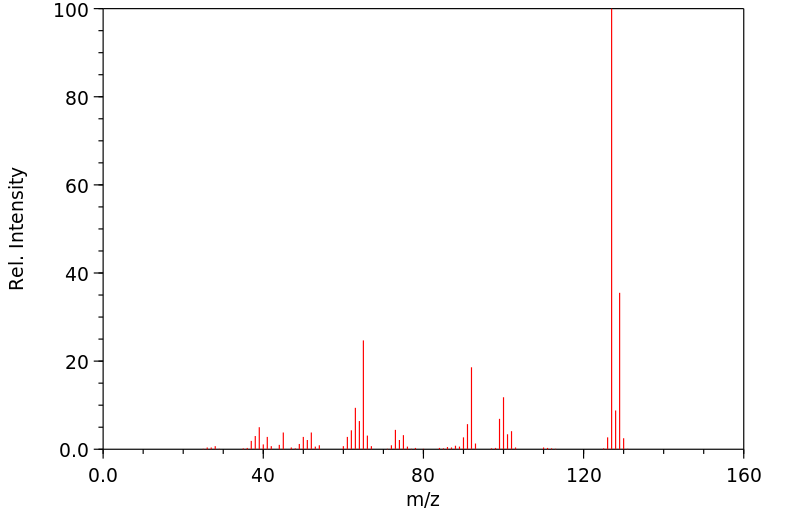
质谱MS
-
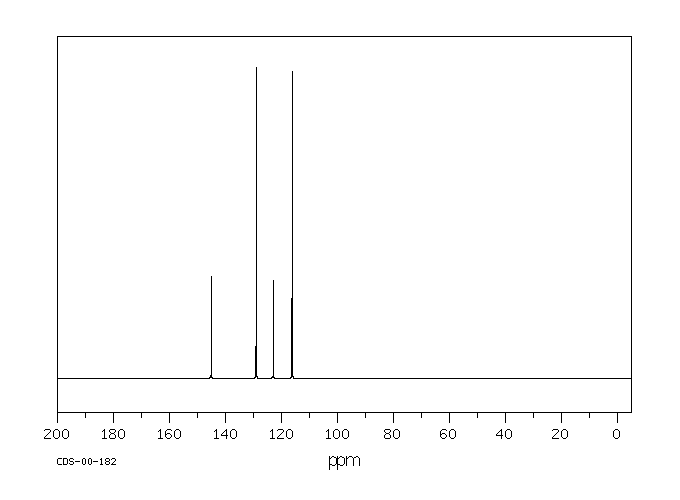
碳谱13CNMR
-
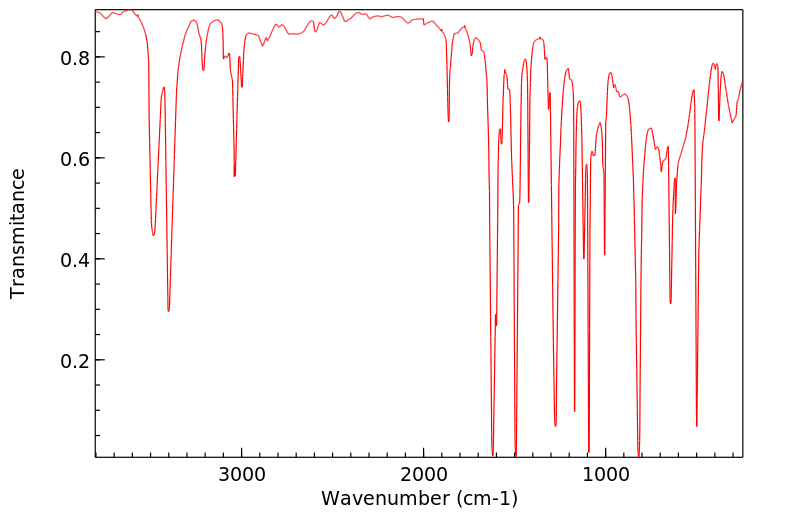
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫