2,4,6-三氯苯酚 | 88-06-2
中文名称
2,4,6-三氯苯酚
中文别名
2,4,6-三氯酚;2,4,6-三氯;2, 4, 6-三氯苯酚
英文名称
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
英文别名
TCP
CAS
88-06-2
化学式
C6H3Cl3O
mdl
MFCD00002172
分子量
197.448
InChiKey
LINPIYWFGCPVIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:64-66 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:246 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.49
-
闪点:99 °C
-
溶解度:0.8g/l
-
物理描述:2,4,6-trichlorophenol appears as yellow to pinkish-orange needles or orange fluffy solid. Strong phenolic odor. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Crystals from ligroin
-
气味:Strong phenolic odor
-
味道:Taste threshold in water: 2.0 ug/l
-
蒸汽压力:0.008 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /hydrogen chloride/.
-
汽化热:14,092.8 g cal/g mole
-
气味阈值:100 ug/L at 30 °C; 1,222 ug/L at 25 °C /Purity not specified/
-
解离常数:pKa = 6.23 at 25 °C
-
保留指数:1335;1326;1330;1327;1339;1349;1346;1331;1346;1360;1349;1367;1331;1335;1320;1325;1326;1336;1349;1315;1387.9
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.7
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
当摄入氯酚时,几乎所有的化合物都会迅速进入人体。氯酚也能通过皮肤迅速进入人体。目前对于吸入含有氯酚的空气时,有多少氯酚会进入人体还知之甚少……其他氯酚(如二氯酚、三氯酚、四氯酚),也会以较为无害的化学物质形式通过尿液排出体外,但它们在体内的停留时间可达数天。/氯酚/
When chlorophenols are eaten, almost all of the compounds quickly enter the body. Chlorophenols also rapidly enter the body through the skin. Little is known about how much of the chlorophenols enter the body if one breathes air containing them... The other chlorophenols (dichlorophenol, trichlorophenols, tetrachlorophenols), which also leave through the urine as less harmful chemicals, can stay in the body for several days. /chlorophenols/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
2,4,6-三氯苯酚在暴露于六氯环己烷的人体尿液中被发现。
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol was found in the urine of humans exposed to hexachlorocyclohexane.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
鸡肉暴露于六氯环己烷后检测出了2,4,6-三氯苯酚。
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol was detected in chicken after exposure to 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
... Corn and pea plants could metabolize pentachlorocyclohexene to the 2,4,6-trichlorophenol isomer.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
人类研究表明,硫酸化和葡萄糖苷酸化是2,4,6-三氯酚(TCP)的主要代谢途径,它以结合代谢物的形式通过尿液排出。通常,2,4,6-TCP会发生生物异构化,转化为其他三氯酚同分异构体,并与葡萄糖醛酸结合。在尿液中检测到的结合物中,大约80%是葡萄糖醛酸。在2,4,6-TCP的孵化过程中产生的代谢物是2,6-二氯-1,4-羟基醌和两种羟基五氯二苯醚的同分异构体。还鉴定出了2,6-二氯-1,4-半醌自由基。(L159)
Human studies indicate that sulfation and glucuronidation are the main metabolic pathways of 2,4,6-TCP, which is excreted in the urine as conjugated metabolites. In general, 2,4,6-TCP undergoes biotic isomerization to other trichlorophenol isomers and conjugation with glucuronic acid. Glucuronic acid accounts for approximately 80% of the conjugates detected in urine. Metabolites generated following incubation of 2,4,6-TCP are 2,6-dichloro-1,4-hydroquinone and two isomers of hydroxypentachlorodiphenyl ether. The 2,6-dichloro-1,4-semiquinone free radical was also identified. (L159)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
识别和使用:2,4,6-三氯苯酚(2,4,6-TCP)是一种无色针状或黄色固体,具有强烈的酚类气味。这种消毒剂曾被用作杀真菌剂、杀菌剂、木材防腐剂、生物杀灭剂,以及生产更高氯代酚的中间体。它在美国目前没有被注册使用,但批准的农药用途可能会定期更改,因此必须咨询联邦、州和地方当局以了解当前批准的用途。人类暴露和毒性:三氯苯酚接触皮肤会引起红肿和水肿,长期暴露可能导致轻至中度的皮肤化学烧伤。对眼睛可引起结膜刺激,有时还会导致角膜损伤和虹膜炎。粉尘对鼻咽有刺激性,系统效应可能类似于酚。三氯苯酚对肺部有刺激性,不能排除长期暴露可能产生肺纤维化的可能性。尿液中2,4,6-TCP水平低(<3.58 ug/g)和高(≥3.58 ug/g)的儿童与父母报告的ADHD风险较高,调整协变量后,与低于检测限的儿童相比。因此得出结论,接触TCP可能会增加儿童行为损害的风险。在努力减少环境暴露/污染的公共卫生工作中,应考虑这些化学品的潜在神经毒性,特别是在仍然普遍使用有机氯农药的国家。根据NTP,2,4,6-三氯苯酚被合理预期为人类致癌物。动物研究:在大鼠中,致死剂量的氯苯酚会产生不安、呼吸速率增加、快速发展的运动无力、震颤、阵挛性惊厥、呼吸困难和中枢神经系统抑制。2,4,6-TCP会产生这些症状,但活动和运动无力不会那么迅速出现。在大鼠中,通过测量肝葡萄糖-6-磷酸酶和血清山梨醇脱氢酶,2,4,6-TCP并未显示出肝毒性。进行了为期两年的致癌生物测试,通过给大鼠和雌性小鼠以及雄性小鼠的饲料中添加2,4,6-TCP。两年后的不良影响包括大鼠两性的外周血白细胞增多和单核细胞增多以及骨髓增生。在小鼠中,常见的肝脏毒性包括单个肝细胞异常、细胞改变的焦点区域以及增生的小叶和结节区域。TCP在雄性大鼠中引起了白血病/淋巴瘤,可能在雌性大鼠和雌性小鼠中也是如此,并在雄性和雌性小鼠中诱导了肝脏肿瘤。2,4,6-TCP对沙门氏菌是非诱变剂,在体外染色体断裂试验中呈阴性,但在V79细胞中产生了数值染色体变化和微核。2,4,6-TCP在CHO细胞和V79细胞中使用3小时处理和20小时采样时间(17小时恢复)诱导结构染色体畸变。在24小时处理后允许4-12小时恢复时间,以及用S9测试2,4,6-TCP时,得到了阳性结果。生态毒性研究:将2,4,6-TCP以单次剂量应用于自然实验池塘的各个舱室中,以研究对生物群的影响。观察到的变化包括在浮游植物之后,水蚤浓度迅速下降至零,污染指标如鞭毛虫和微生物持续增加,以及由于自养和异养种群之间平衡改变而产生的氧气浓度显著下降的次要效应。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol (2,4,6 -TCP) is a colorless needle or yellow solid that has a strong phenolic odor. This germicidal agent was used as a fungicide, bactericide, wood preservative, biocide, and intermediate in production of higher chlorinated phenols. It is not registered for current use in the U.S., but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Trichlorophenols produce redness and edema on skin contact and on prolonged exposure mild to moderate chemical burns of skin of man. In eye they induce conjunctival irritation and sometimes corneal injury and iritis. Dusts are irritating to nose and pharynx and systemic effects presumably resemble phenol. Trichlorophenols can have an irritating effect on the lung, and it cannot be excluded that long-term exposure may produce pulmonary fibrosis. Children with low levels (<3.58 ug/g) and high levels (=3.58 ug/g) of urinary 2,4,6-TCP had a higher risk of parent-reported ADHD compared to children with levels below the limit of detection after adjusting for covariates. It was concluded that exposure to TCP may increase the risk of behavioral impairment in children. The potential neurotoxicity of these chemicals should be considered in public health efforts to reduce environmental exposures/contamination, especially in countries where organochlorine pesticides are still commonly used. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen according to NTP. ANIMAL STUDIES: In rats lethal doses of chlorophenols produce restlessness, increased rate of respiration, rapidly developing motor weakness, tremors, clonic convulsions, dyspnea, and coma. 2,4,6-TCP produces these signs but decreased activity and motor weakness do not appear quite so promptly. 2,4,6-TCP was not hepatotoxic in rats as assessed by measurement of hepatic glucose-6-phosphatase and serum sorbitol dehydrogenase. Carcinogenesis bioassays were conducted by giving 2,4,6-TCP in feed to groups of male and female rats and male mice for two years. Adverse effects at two years were leukocytosis and monocytosis of peripheral blood and hyperplasia of bone marrow in both sexes of rats. In mice, liver toxicity, including individual liver cell abnormalities, focal areas of cellular alteration, and focal and nodular areas of hyperplasia were commonly present. TCP caused leukemias/lymphomas in male rats, and possibly in female rats and female mice as well, and induced liver tumors in male and female mice. 2,4,6-TCP, a non-mutagen to Salmonella, was negative in tests for chromosome breakage in vitro, but did produce numerical chromosome changes and micronuclei in V79 cells. 2,4,6-TCP induces structural chromosome aberrations in CHO cells and in V79 cells using a 3-hr treatment and 20-hr sampling time (17-hr recovery). Positive results were obtained when a recovery time of 4-12 hr was allowed after the 24-hr treatment with 2,4,6-TCP, and when 2,4,6-TCP was tested with S9. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: 2,4,6-TCP was applied at single doses of into compartments of a natural experimental pond to study the effect on biota. Changes seen included a rapid decline of daphnia concentration to zero after phytoplankton, a continuous increase of contamination indicators like flagellates and microorganisms, and a significant decrease in O2 concentration as a secondary effect of the changed balance between autotrophic and heterotrophic populations.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
2,4,6-三氯苯酚是一种胆碱酯酶或乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)抑制剂。胆碱酯酶抑制剂(或“抗胆碱酯酶”)抑制乙酰胆碱酯酶的作用。由于其基本功能,干扰乙酰胆碱酯酶作用的化学物质是强大的神经毒素,在低剂量时会导致过度流涎和流泪,随后是肌肉痉挛,最终导致死亡。神经气体和许多用于杀虫剂的物质已被证明通过结合乙酰胆碱酯酶活性位点的丝氨酸,完全抑制该酶。乙酰胆碱酯酶分解神经递质乙酰胆碱,后者在神经和肌肉接头处释放,以便让肌肉或器官放松。乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制的结果是乙酰胆碱积聚并继续发挥作用,使得任何神经冲动不断传递,肌肉收缩不会停止。最常见的乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂之一是基于磷的化合物,它们被设计成与酶的活性位点结合。结构要求是一个带有两个亲脂性基团的磷原子,一个离去基团(如卤素或硫氰酸盐)以及一个端氧。
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses, followed by muscle spasms and ultimately death. Nerve gases and many substances used in insecticides have been shown to act by binding a serine in the active site of acetylcholine esterase, inhibiting the enzyme completely. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Among the most common acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are phosphorus-based compounds, which are designed to bind to the active site of the enzyme. The structural requirements are a phosphorus atom bearing two lipophilic groups, a leaving group (such as a halide or thiocyanate), and a terminal oxygen.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
分类:B2;可能的人类致癌物。分类依据:基于没有人类数据和动物中的充分证据;即在雄性大鼠中淋巴瘤或白血病的发病率增加,在雄性和雌性小鼠中肝细胞腺瘤或肝癌的发生率增加。人类致癌性数据:无。动物致癌性数据:充分。
CLASSIFICATION: B2; probable human carcinogen. BASIS FOR CLASSIFICATION: Based on no human data and sufficient evidence in animals; namely, increased incidence of lymphomas or leukemia in male rats and hepatocellular adenomas or carcinomas in male and female mice. HUMAN CARCINOGENICITY DATA: None. ANIMAL CARCINOGENICITY DATA: Sufficient.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is limited evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of combined exposures to polychlorophenols or to their sodium salts. There is limited evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. Overall evaluation: Combined exposures to polychlorophenols or to their sodium salts are possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B). /Polychlorophenols/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
2,4,6-三氯苯酚:合理预期为人类致癌物。
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol: reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
大鼠对2,4,6-三氯酚在尿液和粪便中的排泄率进行了研究。6只雄性威斯塔尔大鼠每天通过胃管给药,剂量相当于饮食中2,4,6-三氯酚的1 ppm,持续15天。放射性储存量在3天后达到平台期。在这个水平上,粪便中的排泄量为每日应用剂量的92.5%。停止治疗后,排泄量下降,3天后尿液中为4.3%,粪便中为1.9%。2,4,6-三氯酚被结合,在一定程度上发生了异构化。
The rate of excretion by rats of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in urine and feces was studied. 6 Male wistar rats were dosed daily via stomach tube with a dose corresponding to 1 ppm of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in the diet for 15 days. Storage of radioactivity reached a plateau after 3 days. At this level, excretion in the feces was 92.5% of the daily applied dose. Excretion decr after treatment stopped, reaching 4.3% in the urine and 1.9% in the feces after 3 days. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol was conjugated and to a certain extent isomerized.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
2,4,6-三氯苯酚对整个人类血清及其几种血清蛋白的体外结合能力进行了研究。与白蛋白和血清的结合百分比与分子量相平行,但在对其他蛋白质的结合百分比的排名中并未观察到明确的模式。
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol was investigated for its binding capacities to whole human serum and several human serum proteins in vitro. Percent binding to albumin and serum paralleled molecular wt, but no definite pattern was observed in ranking the percent binding to other proteins.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在给大鼠腹腔注射2,4,6-三氯酚,剂量为25毫克/千克体重后,测量了血液和其它各种组织中的2,4,6-三氯酚浓度。在肾脏中发现了最高的浓度,为每克组织329 ± 117纳摩尔。在血液、大脑、脂肪、肾脏、肝脏和肌肉中的半衰期在1.4到1.8小时之间。
The concentration of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol was measured in the blood and various other tissues of the rat after ip administration of the compound at 25 mg/kg body weight. The highest concentration, 329 + or - 117 nmol per gram of tissue/, was found in the kidney. Half-times were between 1.4 and 1.8 hr in the blood, brain, fat, kidney, liver and muscle.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
来自230名芬兰锯木厂工人的尿液样本被分析,这些工人接触了2,3,4,6-四氯酚(80%)、2,4,6-三氯酚(10-20%)和五氯酚(5%)的混合物,作为氯酚的总和进行检测。样品在工作班次结束时收集。根据工作任务,工人被分为以下暴露组:(I) 主要通过皮肤接触(n=112),(II) 主要通过呼吸道接触(n=34),和(III) 两种途径等量接触(n=84)。工作场所的空气浓度和皮肤接触的时间没有被研究。没有设置对照组;数值与非暴露芬兰人群的水平进行比较,后者的水平低于0.1 umol/L。尿液中氯酚浓度的中位数在主要通过皮肤吸收的工人中为7.8 umol/L(范围0.1至210.9 umol/L),这与主要通过呼吸道接触的工人(中位数浓度0.9 umol/L;范围0.1至13.3 umol/L;p< 0.001)以及两种途径同等重要的工人(1.4 umol/L;范围0.1至47.8 umol/L;p< 0.001)有显著差异。
Urine from 230 Finnish sawmill workers exposed to a combination of 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol (80%), 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (10-20%), and pentachlorophenol (5%), was analyzed for the sum of the three chemicals as chlorophenols. Samples were collected at the end of the work shift. Workers were divided into the following exposure groups according to work tasks: (I) primarily skin exposure (n= 112), (II) primarily respiratory tract exposure (n= 34), and (III) equal exposure by both routes (n= 84). Air concentrations at the workplace and amount of time spent with skin contact were not studied. There was no control group; values were compared to the nonexposed Finnish population level of <0.1 umol/L. Skin absorption was the most effective route of exposure as reflected by urinary chlorophenol concentrations. The median concentration in workers with skin absorption was 7.8 umol/L (range 0.1 to 210.9 umol/L) and was significantly different from that in workers with the respiratory tract as the main route of exposure (median concentration 0.9 umol/L; range 0.1 to 13.3 umol/L; p< 0.001) and from those with both routes of equal importance (1.4 umol/L; range 0.1 to 47.8 umol/L; p< 0.001).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
/2,4,6-三氯苯酚/ ... 在大鼠体内迅速清除,大部分通过尿液排出。在大鼠的饮食中加入了1微克/克的标记酚浓度,持续3天。剂量的82%通过尿液排出,22%通过粪便排出。在最后一次给药后5天内检查的大鼠肝脏、肺或脂肪样本中未检测到放射性三氯苯酚。... 2,4,6-三氯苯酚在兔体内被代谢为3,5-二氯邻苯二酚。在兔体内的研究... 显示,由于2,4,6-三氯苯酚的低pK值,它不会在体内形成硫酸盐结合物。
/2,4,6-Trichlorophenol/ ... cleared rapidly from rats, most of it being excreted in the urine. 1 ug/g concentration of labeled phenol to the diet of rats /was added/ for a 3-day period. Eighty two percent of the dose was excreted in the urine and 22% in the feces. Radioactive trichlorophenol was not detected in liver, lung, or fat samples examined 5 days after the last dose was administered. ... 2,4,6-trichlorophenol is metabolized to 3,5-dichlorocatechol in the rabbit. Studies ... in the rabbit have shown that 2,4,6-trichlorophenol does not form a sulfate conjugate in vivo because of its low pK value.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
危险品标志:Xn,N
-
安全说明:S16,S36/37,S45,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R22,R40,R36/38,R50/53
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29081000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3077 9/PG 3
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:SN1575000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:本品应密封并存放在干燥处。避免明火,受热时会释放有毒的氯化物气体,因此需在通风、低温和干燥的仓库中保存。务必与其他食品原料分开储存和运输。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 2,4,6-三氯苯酚;2,4,6-三氯酚 |
| 化学品英文名称: | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 88-06-2 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 3 C 130 |
| 分子量: | 197.44 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||||
| 化学品名称:2,4,6-三氯苯酚;2,4,6-三氯酚 | |||||
| |||||
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第6.1类毒害品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 吸入、摄入或经皮肤吸收后对身体有害。对眼睛、皮肤、粘膜和上呼吸道有刺激作用。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。有腐蚀性。受高热分解,放出有毒的烟气。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 99 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。小心扫起,避免扬尘,用洁净的铲子收集于干燥净洁有盖的容器中,运至废物处理场所。被污染地面用肥皂或洗涤剂刷洗,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | |
| 储存注意事项: |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度较高时,佩戴防毒口罩。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,应该佩戴防毒面具。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿相应的防护服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防护手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色针状结晶或黄色固体,有强烈的苯酚气味。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 68 |
| 沸点(℃): | 246 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.4901(75/4℃) |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 0.133/76.5℃ |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 99 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 3 C 130 |
| 分子量: | 197.44 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水,易溶于醇、醚、氯仿、甘油、石油醚、二硫化碳。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作染料中间体、杀菌剂、防腐剂,也用作聚酯纤维的溶剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 氧化剂、酸酐、酰基氯。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:820mg/kg(大鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61705 |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | Ⅲ |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。专人保管。保持容器密封。防潮、防晒。应与酸类、氧化剂、食用化工原料等分开存放。操作现场不得吸烟、饮水、进食。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。分装和搬运作业 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 6 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
简介
三氯酚在工业中主要用于生产染料中间体、杀虫剂和防腐剂等产品。由于不达标排放,常出现在焦化、印染、木材防腐等行业中的废水中,并已在自然水体中检测到三氯酚的存在。
2,4,6-三氯酚(2,4,6-TCP)作为一种典型的、广泛应用的工业原料,对人体及水生动植物具有“三致”效应,属于有毒有机污染物,已被美国环保署列为优先控制污染物。
降解方法-
启动SBR反应器:本系统的接种污泥为城镇污水处理厂二次沉淀池的污泥,接种后使SBR反应器的污泥浓度维持在4000~5000mg/L之间。
-
运行时调节操作如下:
- 第一阶段(第0天至36天):驯化系统只引入含有2,4,6-三氯酚的配水,且2,4,6-三氯酚由低浓度向高浓度投加,即从10mg/L增加到80mg/L。每个浓度投加后,当出水检测不到2,4,6-三氯酚时,在提高其进水浓度,直至微生物对氯酚的降解量达到最大,表示第一阶段驯化完毕。
- 第二阶段:维持第一阶段驯化完毕时进水的同时,开始引入蔗糖配水,使SBR反应器内微生物可以逐渐将蔗糖作为共代谢有机碳源。至系统排水检测不到2,4,6-三氯酚,标志着驯化过程完毕,系统进入稳定运行阶段。
SBR反应器在运行过程中,排水比为50%;第一驯化阶段,系统不排放活性污泥,在第二运行阶段开始进行排泥,使系统污泥龄(SRT)维持30~35天,污泥浓度维持4000~5000mg/L左右。第二阶段体系内蔗糖浓度为268mg/L-536mg/L。
驯化期间,开启搅拌以保持SBR反应器处于完全混合状态,并调节气体流量计,维持SBR反应器内溶解氧在1~2mg/L之间。SBR反应器一天运行两个周期,总的水力停留时间(HRT)为16~20小时。
2,4,6-三氯苯酚是一种淡黄色片状结晶,有强烈苯酚气味,熔点64~66℃,沸点246℃,相对密度1.675,易溶于乙醇、丙酮、乙醚、苯、甲苯、四氯化碳等有机溶剂中。
用途- 2,4,6-三氯酚是杀菌剂咪鲜胺和除草剂草枯醚的中间体。
- 它是一种广泛使用的杀虫剂,用于防治昆虫、真菌、植物和细菌。它已成为一种常见的环境污染物和可能的人类致癌物。
- 主要用于杀菌剂、农药、医药中间体。用作染料中间体、杀菌剂、防腐剂,也用作聚酯纤维的溶剂。
其制备方法是将苯酚放入反应器中,通入氯气,前期反应温度60~65℃,后期2~3小时为70~75℃。通氯气结束后保温1小时,通入氯气量为苯酚物质的量的3倍,中途严格跟踪分析,防止氯气过量,然后通入氮气赶除多余的氯气和氯化氢。反应后的粗品经亚硫酸钠处理后蒸馏得产品。
类别上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,4-二氯酚 2,4-dichlorophenol 120-83-2 C6H4Cl2O 163.003 2,6-二氯苯酚 2,6-Dichlorophenol 87-65-0 C6H4Cl2O 163.003 2,4,6-三氯苯甲醚 2,4,6-trichloroanisole 87-40-1 C7H5Cl3O 211.475 邻氯苯酚 2-Chlorophenol 95-57-8 C6H5ClO 128.558 2,3,4,6-四氯酚 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol 58-90-2 C6H2Cl4O 231.893 五氯酚 Pentachlorophenol 87-86-5 C6HCl5O 266.338 2,5-二氯苯酚 2,5-dichlorophenol 583-78-8 C6H4Cl2O 163.003 2,4,6-三氯苯基甲酸酯 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl formate 4525-65-9 C7H3Cl3O2 225.459 对氯苯酚 4-chloro-phenol 106-48-9 C6H5ClO 128.558 2,4-二氯-6-氟苯酚 2,4-dichloro-6-fluoro-phenol 344-21-8 C6H3Cl2FO 180.994 3-溴-2,4,6-三氯苯酚 3-bromo-2,4,6-trichloro-phenol 85117-86-8 C6H2BrCl3O 276.344 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,4-二氯酚 2,4-dichlorophenol 120-83-2 C6H4Cl2O 163.003 2,6-二氯苯酚 2,6-Dichlorophenol 87-65-0 C6H4Cl2O 163.003 2,6-二氯-1,4-氢化喹啉 2,6-dichloro-1,4-benzenediol 20103-10-0 C6H4Cl2O2 179.003 2,4,6-三氯苯甲醚 2,4,6-trichloroanisole 87-40-1 C7H5Cl3O 211.475 邻氯苯酚 2-Chlorophenol 95-57-8 C6H5ClO 128.558 2,3,4,6-四氯酚 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol 58-90-2 C6H2Cl4O 231.893 五氯酚 Pentachlorophenol 87-86-5 C6HCl5O 266.338 3,5-二氯儿茶酚 3,5-dichlorocatechol 13673-92-2 C6H4Cl2O2 179.003 2,4,6-三氯苯乙醚 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl ethyl ether 23399-88-4 C8H7Cl3O 225.502 2,4,6-三氯苯基甲酸酯 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl formate 4525-65-9 C7H3Cl3O2 225.459 —— (2,4,6-trichloro-phenyl)-vinyl ether 938-53-4 C8H5Cl3O 223.486 —— chloromethyl-(2,4,6-trichloro-phenyl)-ether 94637-87-3 C7H4Cl4O 245.92 对氯苯酚 4-chloro-phenol 106-48-9 C6H5ClO 128.558 —— 2,4,6-trichloro-diphenylether 63646-52-6 C12H7Cl3O 273.546 1,3,5-三氯-2-(2,4-二氯苯氧基)苯 2,2',4,4',6-pentachlorobiphenyl ether 104294-16-8 C12H5Cl5O 342.436 2-(2,4,6-三氯苯氧基)乙醇 2-(2,4,6-trichloro-phenoxy)-ethanol 6161-87-1 C8H7Cl3O2 241.501 —— 1,3,5-Trichloro-2-(2-propynyloxy)benzene 17727-28-5 C9H5Cl3O 235.497 2-(2,4,6-三氯苯氧基)乙基溴 2-(2.4.6-Trichlorphenoxy)-ethylbromid 26378-23-4 C8H6BrCl3O 304.398 2-(2,4,6-三氯苯氧基)乙基氯 2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)-ethyl chloride 13001-29-1 C8H6Cl4O 259.947 —— allyl 2,4,6-trichlorophenyl ether 15890-54-7 C9H7Cl3O 237.513 —— 1-Amino-2-(2,4,6-trichlorphenoxy)aethan 26398-84-5 C8H8Cl3NO 240.517 —— (2,4,6-trichloro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile 101495-06-1 C8H4Cl3NO 236.485 —— (2,4,6-trichloro-phenoxy)-acetaldehyde 24535-80-6 C8H5Cl3O2 239.485 4-(2,4,6-三氯苯氧基)苯酚 Hydroxychlornitrofen 68906-24-1 C12H7Cl3O2 289.545 —— 1,2-bis-(2,4,6-trichloro-phenoxy)-ethane 51661-17-7 C14H8Cl6O2 420.934 3-(2,4,6-三氯苯氧基)丙烷-1-胺 3-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)propan-1-amine 1017206-47-1 C9H10Cl3NO 254.543 —— 2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)propyl bromide —— C9H8BrCl3O 318.425 3-溴-2,4,6-三氯苯酚 3-bromo-2,4,6-trichloro-phenol 85117-86-8 C6H2BrCl3O 276.344 1,1'-[氧基二(亚甲基氧基)]二[2,4,6-三氯苯] bis<(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)methyl> ether 60093-93-8 C14H8Cl6O3 436.934 —— 2,4,6-Trichlorphenoxy(trimethyl)silan 1013-45-2 C9H11Cl3OSi 269.63 —— 4-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)butanenitrile —— C10H8Cl3NO 264.539 —— (4-bromo-butyl)-(2,4,6-trichloro-phenyl)-ether —— C10H10BrCl3O 332.452 —— 1,3,5-Trichloro-2-(4-chlorobutoxy)benzene 79096-43-8 C10H10Cl4O 288.001 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Benedikt; Schmidt, Monatshefte fur Chemie, 1883, vol. 4, p. 607摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Electroreduction of Organic Compounds, 34 [1]. Cathodic Dehalogenation of Chloroarenes with Electron-Donating Substituents摘要:氯代芳烃的电化学还原与供电取代基(如氯甲苯、-苯甲醚和-酚)进行研究。在铅或碳阴极下,在各种溶剂支持电解质的电位静态和电流静态条件下进行制备电解。在适当条件下,可能对具有两个或更多氯取代基的化合物进行部分和主要区域选择性的去氯化。尤其是在对位,替换一个单独的氯取代基是困难的。因此,高度有毒和持久的寡氯衍生物可以转化为氯化程度较低的问题较少的化合物。通过电还原,也可以显着降低受氯化酚和Nitrofen®污染的土壤提取物等实际材料的氯含量。DOI:10.1515/znb-2003-1206
-
作为试剂:描述:triethylammonium 5'-O-dimethoxytritylthymidine 3'-H-phosphonate 、 三乙胺 在 五氯酚 、 氯磷酸二苯酯 、 2,4,6-三氯苯酚 、 双(三甲基硫化硅) 作用下, 以 吡啶 为溶剂, 反应 0.67h, 以96%的产率得到5'-O-dimethoxytritylthymidine 3'-H-phosphonodithioate triethylammonium salt参考文献:名称:芳基H-膦酸酯。12.关于制备核苷H-膦酰基硫代酸酯和核苷H-膦二硫代酸酯单酯的合成和(31)P NMR研究。摘要:使用(31)P NMR光谱研究了将核苷H-膦酸酯单酯转化为相应的H-膦酰硫代酸酯和H-膦酰二硫代酸酯衍生物以及该过程可能伴随的副反应。这些提供了对该转化涉及的可能机理的新见解,并构成了开发有效方法的基础,该方法使用容易获得的H-膦酸酯单酯作为原料制备核苷H-膦酰硫代酸酯和核苷H-膦酰二硫代酸酯单酯。DOI:10.1021/jo000729q
文献信息
-
Mechanism of hydrolysis of phosphorylethanolamine diesters. Intramolecular nucleophilic amine participation作者:Robert A. Lazarus、Patricia A. Benkovic、Stephen J. BenkovicDOI:10.1039/p29800000373日期:——Intramolecular displacement reactions at phosphorus have been examined in a series of N-alkyl-O-arylphosphorylethanolamines in water at 35 °C. The examination of the pH–rate profiles and the direct observation by 31P n.m.r. of the reaction products implicate a nucleophilic role for the amine. A rate enhancement of 106–107 is observed. Structure–reactivity correlations derived by changing the pKa of
-
The reactions of unactivated aryl halides with sodium methoxide in HMPA作者:L. Testaferri、M. Tiecco、M. Tingoli、D. Chianelli、M. MontanucciDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)97647-1日期:——Sodium methoxide reacts with dichlorobenzenes in HMPA to give the chloroanisoles as a result of a SNAr process. Excess MeONa then effects the demethylation of the ethers to give the chlorophenols via an SN2 reaction. With tri- and tetrachlorobenzenes the initially formed chloroanisoles can be dealkylated to chlorophenols or can suffer further substitution to give the chlorodimethoxybenzenes; these
-
[EN] AMINO PYRAZINE DERIVATIVES AS PHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL 3-KINASE INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS AMINÉS DE PYRAZINE UTILISABLES EN TANT QU'INHIBITEURS DE LA PHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL 3-KINASE申请人:NOVARTIS AG公开号:WO2015162459A1公开(公告)日:2015-10-29The present invention provides compounds of formula (I) which inhibit the activity of PI 3-kinase gamma isoform, which are useful for the treatment of diseases mediated by the activation of PI 3-kinase gamma isoform.
-
HYDANTOIN DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS KV3 INHIBITORS申请人:Alvaro Giuseppe公开号:US20130267510A1公开(公告)日:2013-10-10The invention provides compounds of formula (I): Said compounds being inhibitors of Kv3 channels and of use in the prophylaxis or treatment of related disorders.该发明提供了化合物的公式(I):所述化合物是Kv3通道的抑制剂,可用于预防或治疗相关疾病。
-
用于预防和治疗心血管疾病的化合物
表征谱图
-
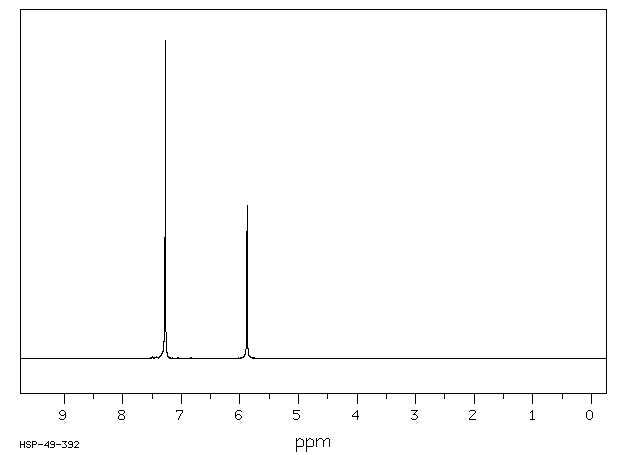
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
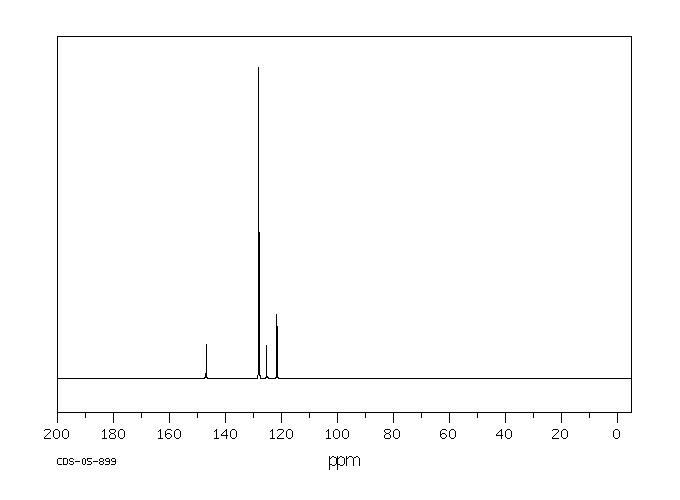
碳谱13CNMR
-
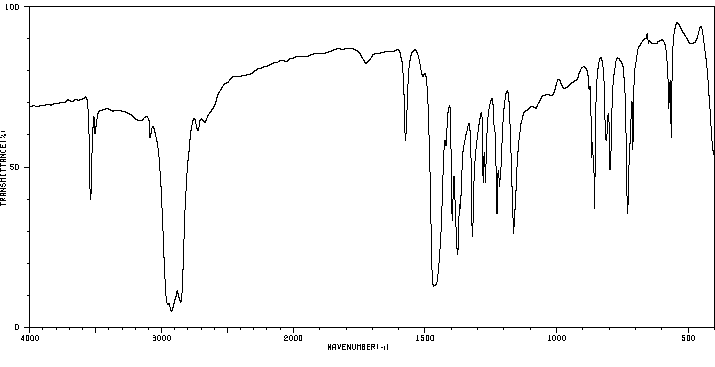
红外IR
-
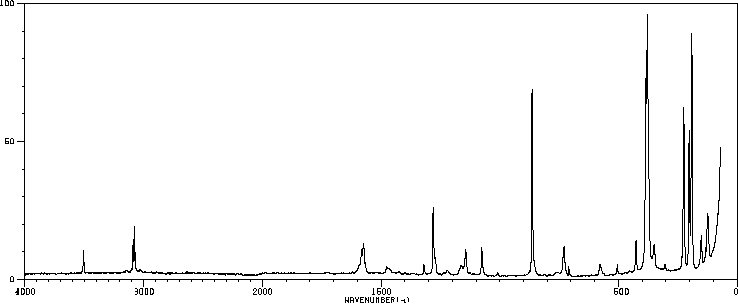
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(2-氯-6-羟基苯基)硼酸
黄柄曲菌素
高香草酸-d3
高香草酸-13C6
高香草酸
高香兰酸乙酯
高辣椒素II
高二氢辣椒素I
香草醛醛肟
香草醛苯腙
香草醛-甲氧基-13C
香草醛-(N-对甲苯基肟)
香草醛
香草酸肼
香草壬酰胺
香草基扁桃酸乙酯
香草吗啉
香草二乙胺
香兰素胺硬脂酸盐
香兰素胺硬脂酸盐
香兰素胺盐酸盐
香兰素丙二醇缩醛
香兰素13C6
香兰素-D3
香兰基乙基醚
香兰基丁醚
顺式-5-正十五碳-8'-烯基间苯二酚
顺式-1-(2-羟基-5-甲基苯基)-2-丁烯-1-酮
顺式-1-(2-羟基-4-甲氧基苯基)-2-丁烯-1-酮
顺-3-氯二氢-5-苯基呋喃-2(3H)-酮
雌二醇杂质1
降二氢辣椒碱
阿诺洛尔
阿瓦醇
阿普斯特杂质
间苯二酚双(二苯基磷酸酯)
间苯二酚-烯丙醇聚合物
间苯二酚-D6
间苯二酚
间苯三酚甲醛
间苯三酚二水合物
间苯三酚
间羟基苯乙基溴
间硝基苯酚
间甲酚紫钠盐
间甲酚与对甲酚和苯酚甲醛树脂的聚合物
间甲酚-D7
间甲酚-D3
间甲酚
间溴苯酚