D-(-)-酒石酸二甲酯 | 608-69-5
中文名称
D-(-)-酒石酸二甲酯
中文别名
(2S,3S)-(-)-酒石酸二甲酯;D-(-)酒石酸二甲酯;二甲基D-酒石酸酯;酒石酸二甲酯
英文名称
Dimethyl D-tartrate
英文别名
D-(-)-dimethyl tartrate;dimethyl (2S,3S)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate
CAS
608-69-5;13171-64-7
化学式
C6H10O6
mdl
——
分子量
178.142
InChiKey
PVRATXCXJDHJJN-IMJSIDKUSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:57-60 °C (dec.)(lit.)
-
比旋光度:-21 º (c=10, H2O)
-
沸点:158 °C0.2 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:1.30
-
闪点:>230 °F
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.67
-
拓扑面积:93.1
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:6
SDS
制备方法与用途
化学性质方面,其熔点为48-50℃,沸点在158℃(15 mmHg)时。用途上,它主要应用于手性药物和手性中间体的合成以及不对称催化领域。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 D-酒石酸 D-tartaric acid 147-71-7 C4H6O6 150.088 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 D-(-)酒石酸二甲酯 dimethyl tartrate 405897-14-5 C6H10O6 178.142 —— (+/-)-monomethyltartaric acid —— C5H8O6 164.115 —— dimethyl (O,O'-dimethyl)-L-tartrate 56145-21-2 C8H14O6 206.196 —— dimethyl 2,3-O-methylene-L-tartrate 137568-30-0 C7H10O6 190.153 —— dimethyl (2R,3R)-2-bromo-3-hydroxysuccinate 749917-66-6 C6H9BrO5 241.038
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:(1R, 3S, 4S)-2-Aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]庚烷-3-羧酸作为有机催化剂促进直接不对称羟醛反应摘要:DOI:10.1002/bkcs.10018
-
作为产物:描述:富马酸二甲酯 在 magnesium(II) perchlorate hexahydrate 、 FeII(OTf)2(tris((5-(triisopropylsilyl)pyridin-2-yl)methyl)amine) 、 双氧水 作用下, 以 水 、 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 1.0h, 以92%的产率得到D-(-)-酒石酸二甲酯参考文献:名称:机械驱动开发用于烯烃与过氧化氢水溶液选择性顺二羟基化的铁催化剂摘要:产物释放是在 Rieske 加氧酶发生的芳烃合成二羟基化反应中的速率决定步骤,被认为是设计用于烯烃合成二羟基化的铁催化剂中需要解决的难题,在有机合成中具有潜在的应用价值。为此,在这项工作中,设计了一种基于 tpa(tpa = 三(2-甲基吡啶基)胺)支架 [FeII(CF3SO3)2(5-tips3tpa)], 1 的新型催化剂. 配体的空间需求被认为是通过隔离金属中心、防止双分子分解路径和促进产物释放来支持高催化活性的关键元素。与有助于螯合产品的路易斯酸协同组合,在温和的实验条件下,使用稍微过量(1.5 当量)的过氧化氢水溶液,在很短的反应时间内,从广泛范围的烯烃的氧化中,1 提供了良好到极好的二醇产物产率(高达 97% 的分离产率)。显示了二烯烃的可预测位点选择性顺式二羟基化。配体的受阻性质也提供了一种独特的工具,该工具已与同位素分析结合使用,以确定活性物质的性质和 H2O2 的活化机制。此外,1DOI:10.1021/jacs.7b07909
-
作为试剂:描述:亚磷酸二甲酯 、 丙烯醛 在 titanium(IV) isopropylate 、 D-(-)-酒石酸二甲酯 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 反应 24.0h, 生成 (1S)-dimethyl [1-hydroxy-2-propenyl] phosphonate 、 (1R)-dimethyl [1-hydroxy-2-propenyl] phosphonate参考文献:名称:Amphidinolide C的C(18)-C(34)片段和Amphidinolide F的C(18)-C(29)片段的合成摘要:报道了amphidinolide C的C(18)-C(34)片段和amphidinolide F的C(18)-C(29)片段的收敛合成。该方法涉及通过交叉复分解、Pd(0)-催化环化和硼氢化-氧化合成常见的中间体四氢呋喃基-β-酮膦酸酯。使用 Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons (HWE) 烯化反应将 β-酮膦酸酯偶联到三个侧链醛上,得到二烯酮,然后用l- selectride还原得到双环内酯 C 和 F 的片段。DOI:10.1021/ol102345v
文献信息
-
An Osmium(III)/Osmium(V) Redox Couple Generating Os<sup>V</sup>(O)(OH) Center for <i>cis</i>-1,2-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>: Os Complex with a Nitrogen-Based Tetradentate Ligand作者:Hideki Sugimoto、Kazuhiro Kitayama、Seiji Mori、Shinobu ItohDOI:10.1021/ja309566c日期:2012.11.212-dihydroxylation of alkenes catalyzed by osmium(VIII) tetroxide (OsO(4)) is a powerful method. However, OsO(4) is quite toxic due to its highly volatile and sublimable nature. Thus, the development of alternative catalysts for cis-1,2-dihydroxylation of alkenes is highly challenging. Our approach involves the use of a nitrogen-based tetradentate ligand, tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (tpa), for an osmium center to对于 1,2-二醇的合成,由四氧化锇 (VIII) (OsO(4)) 催化的烯烃 cis-1,2-dihydroxylation 是一种有效的方法。然而,OsO(4) 由于其高度易挥发和可升华的性质而具有相当大的毒性。因此,开发用于烯烃顺式-1,2-二羟基化的替代催化剂极具挑战性。我们的方法涉及使用基于氮的四齿配体三(2-吡啶基甲基)胺(tpa)作为锇中心开发新的锇催化剂和过氧化氢(H(2)O(2))作为廉价的和环境无害的氧化剂。新的 Os-tpa 复合物作为一种非常有效的周转催化剂,用于水介质中各种烯烃的顺式选择性二羟基化(周转数~1000),并且 H(2)O(2) 氧化剂被正式定量并入产物中(100 % 原子效率)。参与催化循环的反应中间体已被分离出来,并在晶体学上表征为 [Os(III)(OH)(H(2)O)(tpa)](2+) 和 [Os(V)(O)(OH) (tpa)](2+)
-
Osmium(III) and Osmium(V) Complexes Bearing a Macrocyclic Ligand: A Simple and Efficient Catalytic System for<i>cis</i>-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with Hydrogen Peroxide作者:Hideki Sugimoto、Kenji Ashikari、Shinobu ItohDOI:10.1002/asia.201300329日期:2013.9efficient cis‐1,2‐dihydroxylation of alkenes is presented. Unfunctionalized (or aliphatic) alkenes and alkenes/styrenes containing electron‐withdrawing groups are selectively oxidized to the corresponding vicinal diols in good to excellent yields (46–99 %). In the catalytic reactions, the stoichiometry of alkene:H2O2 is 1:1, and thus the oxidant efficiency is very high. For the dihydroxylation of cyclohexene一个简单的协议,它使用[Os III(OH)(H 2 O)(L -N 4 Me 2)](PF 6)2(1 ; L- N 4 Me 2 = N,N'-二甲基-2,11 ‐diaza [3.3](2,6)pyridinophane)作为催化剂,H 2 O 2作为有效顺式的末端氧化剂介绍了烯烃的1,2-二羟基化反应。含有吸电子基团的未官能化(或脂肪族)烯烃和烯烃/苯乙烯被选择性氧化成相应的邻位二醇,收率良好至极佳(46–99%)。在催化反应中,烯烃:H 2 O 2的化学计量为1:1,因此氧化效率非常高。对于环己烯的二羟基化,可以将1的催化量降低至0.01 mol%,以实现5500的极高周转率。活性氧化剂被鉴定为Os V(O)(OH)种类(2)。通过氢过氧化物加合物形成的Os III(OOH)物种。活性氧化剂2 已成功分离并进行了晶体学表征。
-
<i>cis</i>-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with Oxone Catalyzed by Iron Complexes of a Macrocyclic Tetraaza Ligand and Reaction Mechanism by ESI-MS Spectrometry and DFT Calculations作者:Toby Wai-Shan Chow、Ella Lai-Ming Wong、Zhen Guo、Yungen Liu、Jie-Sheng Huang、Chi-Ming CheDOI:10.1021/ja100967g日期:2010.9.29[Fe(III)(L-N(4)Me(2))Cl(2)](+) (1, L-N(4)Me(2) = N,N'-dimethyl-2,11-diaza[3.3](2,6)pyridinophane) is an active catalyst for cis-dihydroxylation of various types of alkenes with oxone at room temperature using limiting amounts of alkene substrates. In the presence of 0.7 or 3.5 mol % of 1, reactions of electron-rich alkenes, including cyclooctene, styrenes, and linear alkenes, with oxone (2 equiv) for[Fe(III)(LN(4)Me(2))Cl(2)](+) (1, LN(4)Me(2) = N,N'-二甲基-2,11-二氮杂[3.3] (2,6)pyridinophane) 是一种活性催化剂,用于在室温下使用有限量的烯烃底物将各种类型的烯烃与 oxone 进行顺式二羟基化。在 0.7 或 3.5 mol % 的 1 存在下,富电子烯烃(包括环辛烯、苯乙烯和线性烯烃)与 oxone(2 当量)反应 5 分钟导致高达 >99% 的底物转化率并提供顺式二醇产品的产率高达 67%,顺式二醇/环氧化物摩尔比高达 16.8:1。对于缺电子烯烃,包括 α,β-不饱和酯和 α,β-不饱和酮,它们与 oxone(2 当量)在 1(3.5 mol%)催化下反应 5 分钟,得到顺式二醇,产率高达 99%高达 >99% 的底物转化率。肉桂酸甲酯 (9.7 g) 与 oxone (1 当量) 的大规模顺式二羟基化得到顺式二醇产物
-
MACROCYCLIC PICOLINAMIDES AS FUNGICIDES申请人:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC公开号:US20130296375A1公开(公告)日:2013-11-07The invention relates to macrocyclic picolinamides of Formula I and their use as fungicides.这项发明涉及式I的大环状吡啶甲酰胺及其作为杀菌剂的应用。
-
Olefin<i>cis</i>-Dihydroxylation and Aliphatic CH Bond Oxygenation by a Dioxygen-Derived Electrophilic Iron-Oxygen Oxidant作者:Sayanti Chatterjee、Tapan Kanti PaineDOI:10.1002/anie.201502229日期:2015.8.3metal–oxygen oxidants to carry out O2‐dependent transformation reactions. However, the selective oxidation of CH and CC bonds by biomimetic complexes using O2 remains a major challenge in bioinspired catalysis. The reactivity of iron–oxygen oxidants generated from an FeII–benzilate complex of a facial N3 ligand were thus investigated. The complex reacted with O2 to form a nucleophilic oxidant, whereas许多含铁酶涉及金属-氧氧化剂,以进行依赖于O 2的转化反应。然而,C的选择性氧化通过仿生络合物H和CC键使用了O 2保持在仿生催化的一个重大挑战。因此研究了由面部N 3配体的Fe II-苯甲酸酯络合物生成的铁-氧氧化剂的反应性。该络合物与O 2反应形成亲核氧化剂,而在路易斯酸的存在下产生被外部底物截获的亲电子氧化剂。基于机理研究,亲核的Fe II有人提议由苯甲酸酯络合物形成–hydroperoxo物种,该复合物在路易斯酸存在下经历杂化OO键裂解,生成Fe IV –oxo–hydroxo氧化剂。亲电子氧化铁可选择性地将硫化物氧化为亚砜,将烯烃氧化为顺式二醇,并羟基化烷烃的CH键,包括环己烷的CH键。
表征谱图
-
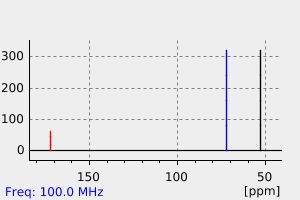
氢谱1HNMR
-
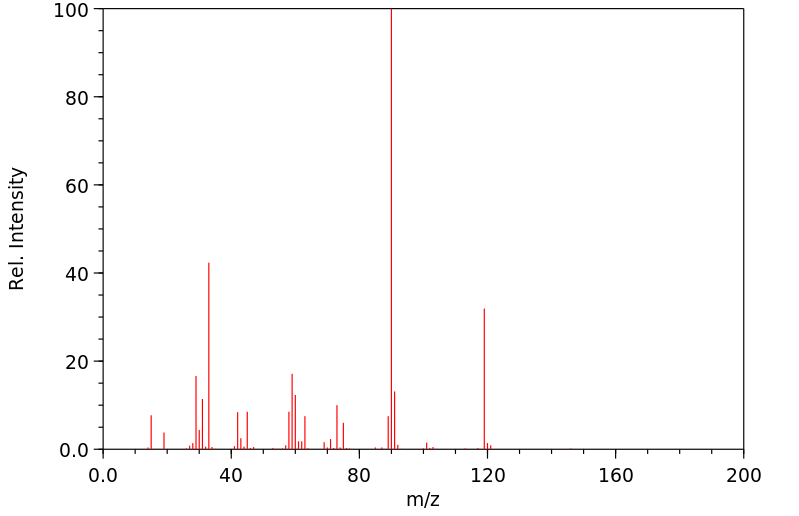
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(R)-2-苯基-3-羟基丙酸
(2S,3R)-2,3-二羟基-3-(2-吡啶基)丙酸乙酯,N-氧化物
麦拉乳酸
阿拉伯碳酸氢二钾
铵;铈(+3)阳离子;(2R,3R)-2,3-二羟基丁烷二酸盐
钡二{8-[3-(2-羟基辛基)-2-环氧乙烷基]辛酸酯}
钠3-脱氧-D-阿拉伯糖-己酮酸酯
钠3-脱氧-D-木糖基-己酮酸酯
钠(3R,5R)-3,5-二羟基-7-[(1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-8-羟基-2,6-二甲基-1,2,6,7,8,8A-六氢-1-萘基]庚酸酯
钠(2S)-2-羟基(13C3)丙酸酯
酮酯
酒石酸锂单水合物
酒石酸铬
酒石酸铜(II)一水
酒石酸钾锑
酒石酸钾
酒石酸钠
酒石酸鐵(III)鉀
酒石酸辛酯钠盐
酒石酸羟吡啶
酒石酸氢钾
酒石酸异丙酯
酒石酸二磺基琥珀酰亚胺酯
酒石酸二琥珀酰亚胺酯
酒石酸二戊酯
酒石酸二仲丁酯
酒石酸二丙酯
辛酸,8-氯-6-羟基-,(6R)-
辛伐他汀钾盐
辛伐他汀钠盐
辛伐他汀酸
超支化BIS-MPA聚酯-64-羟基,4代
西托溴铵
表洛伐他汀羟基酸钠盐
葡萄糖酸镍
葡萄糖酸锶
葡萄糖酸锰
葡萄糖酸汞
葡萄糖酸亚铁
莫那可林J酸
苹果酸镁
苹果酸镁
苹果酸铵盐
苹果酸钙
苹果酸氢钠
苹果酸氢钠
苹果酸根
苹果酸二烯丙酯
苹果酸二乙基己酯
苹果酸乙酯(S)-2-羟基丁二酸1-乙酯(苹果酸杂质S)