2,3-二溴丁烯-1,4-二醇 | 21285-46-1
中文名称
2,3-二溴丁烯-1,4-二醇
中文别名
反式-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇
英文名称
Trans-2,3-dibromo-2-butene-1,4-diol
英文别名
(E)-2,3-dibromo-2-butene-1,4-diol;(E)-2,3-dibromobut-2-ene-1,4-diol;2,3-dibromobut-2-ene-1,4-diol;(E)-2,3-dibromo-but-2-ene-1,4-diol;2,3-dibromo-but-2t-ene-1,4-diol;2,3-Dibrom-but-2t-en-1,4-diol
CAS
21285-46-1
化学式
C4H6Br2O2
mdl
——
分子量
245.898
InChiKey
MELXIJRBKWTTJH-ONEGZZNKSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:112-114 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:318.1±42.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:2.252±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:溶于甲醇
-
物理描述:Crystals or white powder. (NTP, 1992)
-
稳定性/保质期:
如果按照规格使用和储存,则不会分解,请避免接触氧化物。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.1
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:40.5
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
危险性防范说明:P501,P202,P201,P280,P308+P313,P405
-
危险性描述:H341
SDS
反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇 修改号码:2
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: trans-2,3-Dibromo-2-butene-1,4-diol
修改号码: 2
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇
百分比: >99.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 21285-46-1
俗名: trans-2,3-Dibromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butene
分子式: C4H6Br2O2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇 修改号码:2
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-浅黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
114°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度: 溶于: 甲醇
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇 修改号码:2
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
反应性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 溴化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: mmo-sat 33 ug/plate (-S9)
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: EM6910000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装
卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇 修改号码:2
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: trans-2,3-Dibromo-2-butene-1,4-diol
修改号码: 2
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇
百分比: >99.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 21285-46-1
俗名: trans-2,3-Dibromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butene
分子式: C4H6Br2O2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇 修改号码:2
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-浅黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
114°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度: 溶于: 甲醇
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇 修改号码:2
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
反应性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 溴化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: mmo-sat 33 ug/plate (-S9)
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: EM6910000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装
卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
反-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇 修改号码:2
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:脂族的还原性脱卤化VIC具有金属钐-dihalides在甲醇介质摘要:在标题反应,八个VIC -dibromides和三个亚乙烯基二溴化物,得到在室温下相应的脱溴产物(烯烃和炔烃)中性条件和氩气气氛下。2,3-二溴丁二酸衍生物产生过度还原的产物或异常的偶联二聚体。DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(97)82951-6
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:邻二溴代烯烃作为保护炔烃的闭环复分解:大环烯炔的合成方法。摘要:开发了一种访问大环烯炔的新策略。为了阻止不期望的烯-炔环化途径,炔烃通过溴化得到保护,所得的无环vic-(E)-二溴三烯参与选择性的烯-烯闭环易位反应。锌促进的(E)-二溴莫烯的脱保护以高收率提供了大环烯炔。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02595
文献信息
-
Cycloaddition Reactions of Cobalt-Complexed Macrocyclic Alkynes: The Transannular Pauson–Khand Reaction作者:Sedef Karabiyikoglu、Byron A. Boon、Craig A. MerlicDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.7b01369日期:2017.8.4ring-closing metathesis reactions followed by complexation with dicobalt octacarbonyl. Several reaction modalities of these macrocyclic complexes were uncovered. In addition to the first successful transannular Pauson–Khand reactions, other intermolecular and transannular cycloaddition reactions included intermolecular Pauson–Khand reactions, transannular [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions, intermolecular [2Pauson-Khand反应是通过有效的[2 + 2 + 1]二苯甲醚炔烃与烯烃的环加成反应来合成环戊烯酮的有力工具。尽管分子间和分子内的变体是众所周知的,但是该反应的跨环版本是未知的,并且是这项研究的基础。大环烯炔和二烯炔配合物很容易通过钯(II)催化双(乙烯基硼酸酯)的氧化大环化或闭环易位反应,然后与二钴二羰基八羰基配合而合成。这些大环配合物的几种反应方式被发现。除了第一个成功的跨环形波森-汉德反应之外,其他分子间和跨环形环加成反应还包括分子间波森-汉德反应,跨环[4 + 2]环加成反应,分子间[2 + 2 + 2]环加成反应和分子间[2 + 2 +1 + 1]环加成反应。介绍了每个过程的结构和反应要求。
-
Brominated Methanes as Photoresponsive Molecular Storage of Elemental Br<sub>2</sub>作者:Kazumitsu Kawakami、Akihiko TsudaDOI:10.1002/asia.201200322日期:2012.10generation of elemental Br2 from brominated methanes is reported. Br2 was generated by the vaporization of carbon oxides and HBr through oxidative photodecomposition of brominated methanes under a 20 W low‐pressure mercury lamp, wherein the amount and situations of Br2 generation were photochemically controllable. Liquid CH2Br2 can be used not only as an organic solvent but also for the photoresponsive molecular据报道,溴化甲烷可光化学生成元素Br 2。在20 W低压汞灯下,溴化甲烷的氧化光分解使碳氧化物和HBr汽化,从而生成Br 2,其中Br 2的生成量和生成情况可通过化学方法控制。液体CH 2 Br 2不仅可以用作有机溶剂,而且还可以用于Br 2的光敏分子存储,这在各种有机合成和材料科学中都具有巨大的技术优势。通过利用原位生成Br 2的优势由有机溶剂本身,在添加或不添加催化剂的情况下,以高实用产率合成了许多有机溴化合物。此处,溴2,是由CH的光分解产生的2溴2保留了它的反应性溶液中基本上经历相同的反应物作为那些具有的Br溶液进行,即2溶解在CH 2溴2没有光照射制备的。此外,在CH 2 Br 2的光分解过程中产生的HBr也可用于将OH基团取代为Br基团和制备胺的HBr盐。此外,光化学产生的Br 2选自CH 2溴2是可用于天然着色的植物,如红玫瑰花瓣,其中BR的区域选择性光化学漂白2这是从CH光
-
Synthesis and activity studies of analogues of the rat selective toxicant norbormide作者:David Rennison、Sergio Bova、Maurizio Cavalli、Fernanda Ricchelli、Alessandra Zulian、Brian Hopkins、Margaret A. BrimbleDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.02.012日期:2007.4Norbormide [5-(alpha-hydroxy-alpha-2-pyridylbenzyl)-7-(alpha-2-pyridylbenzylidene)-5-norborn ene-2,3-dicarboximide] (NRB, 1), an existing but infrequently used rodenticide, is known to be uniquely toxic to rats but relatively harmless to other rodents and mammals. A series of NRB-related analogues were prepared to investigate the structural features responsible for, and the in vitro biological markers
-
一种(E)-2,3-二溴-2-丁烯-1,4-二醇的制备 方法
-
In situ alcohol oxidation-Wittig reactions作者:Xudong Wei、Richard J.K TaylorDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(98)00592-9日期:1998.5alcohols can be oxidised with activated manganese dioxide in the presence of stabilised Wittig reagents to generate α,β-unsaturated esters directly. This simple procedure, which can also be utilised with diols to give double homologation, is generally useful and particularly valuable if the intermediate aldehydes are difficult to isolate, toxic or prone to isomerisation.
表征谱图
-
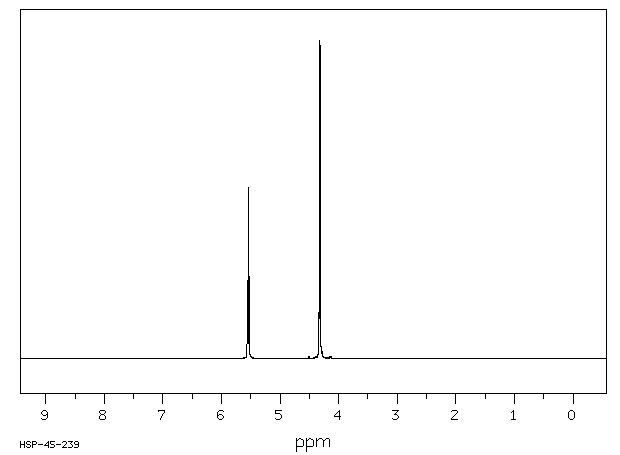
氢谱1HNMR
-
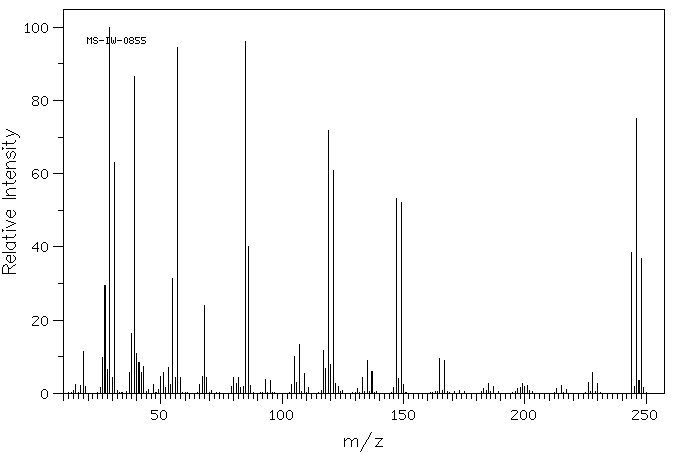
质谱MS
-
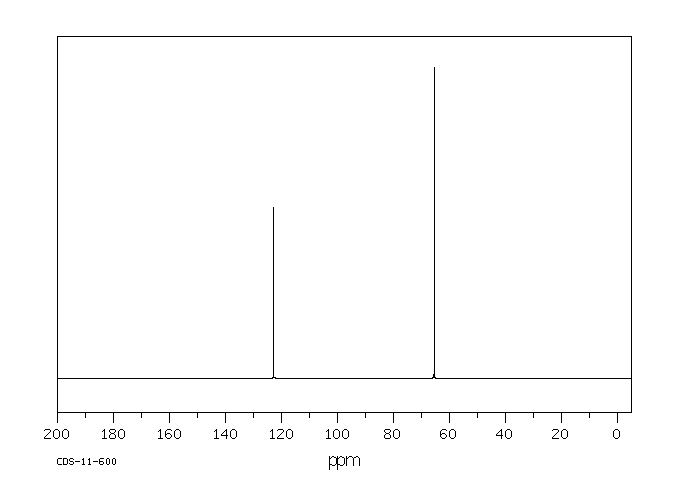
碳谱13CNMR
-
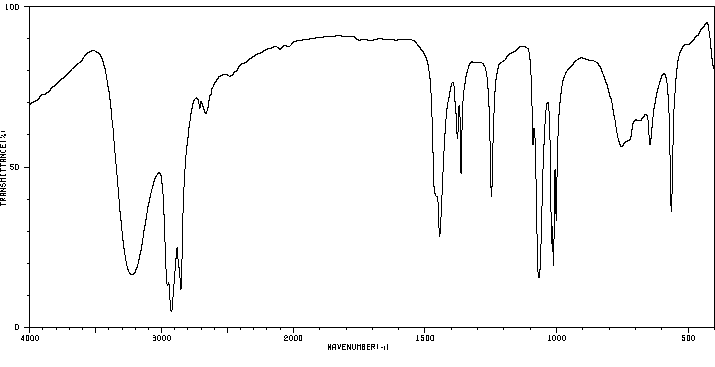
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺-(1S,2S)-1,2-二氢-3-氟邻苯二酚
苏-3-溴-2-丁醇
苏-3-溴-2-丁醇
烯丙基3-氯-2-羟基丙酸酯
溶剂紫36
溴丁醇
水合氯醛
氯醛甜菜碱
氯醛叔丁基半缩醛
氯醛丙基半缩醛
氯二氟乙醛’水合物
氯-(2-氯-3-羟基丙-1-烯基)汞
氘代3-氯-1,2-丙二醇
培氟沙星
四氟乙醇
四氟丙醇
四氟丁二醇
十二氟庚醇
十一氟正己烷-1-醇
六氟异丙醇
六氟丁醇
六氟-1-丙醇
八氟代-1-戊醇
八氟-1,6-己二醇
全氟十醇
全氟-1-辛醇
全氟-1-庚醇
五氟丙醛甲基半缩醛
五氟丙醛水合物
五氟丙醛乙基半缩醛
二溴甘露醇
二氯乙醛水合物
二氯乙氧基合氧钒
二氟乙醛缩半乙醇
乙基3-氟-2-羟基-3-甲基丁酸酯
三溴乙醇
三氟甲基己醇
三氟乙醛缩甲基半醇
三氟乙醛水合物
三氟乙醇
三氟乙基醇-OD
七氟丁醛乙基半缩醛
丁氯醇
rac-2-氯十二烷-1-醇
rac-1-氯十二烷-2-醇
alpha,alpha-二(三氟甲基)-1-氮丙啶甲醇
[2H4]-2-溴-1,3-丙二醇[干冰运输]
[1-氯-3-异丙基氨基-2-丙醇
[1,1-(2)H2]-2-氯乙醇
O-(1,1,3-三氢四氟丙基)-(1-羟基-2,2,2-三氯乙基)甲基膦酸酯