jasmone | 488-10-8
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
jasmone
英文别名
Jasmon;2-Cyclopenten-1-one, 3-methyl-2-(2Z)-2-pentenyl-;3-methyl-2-pent-2-enylcyclopent-2-en-1-one
CAS
488-10-8
化学式
C11H16O
mdl
——
分子量
164.247
InChiKey
XMLSXPIVAXONDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:134-135 °C12 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:0.94 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:225 °F
-
LogP:2.8 at 35℃
-
物理描述:Pale yellowish to straw-coloured oily liquid; odour of jasmine
-
颜色/状态:Oil
-
气味:Odor of jasmine
-
味道:Woody, bitter, tea, with a citrus and floral nuance at 25 ppm
-
溶解度:Slightly soluble in water
-
蒸汽压力:0.029 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritatiing vapors.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4979 at 22 °C
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.2
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.55
-
拓扑面积:17.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
毒理性
识别和使用:茉莉酮是一种淡黄色的粘稠液体(油)。它在精细茉莉花基和花香调的香水中有应用。人类暴露和毒性:茉莉酮在人类志愿者中没有引起皮肤致敏。动物研究:在10只兔子的急性皮肤毒性研究中,给予每只5克/千克的顺式-茉莉酮,并观察了14天。九只动物出现了严重的红斑,所有动物都观察到了中度的水肿。两只兔子发现了焦痂。茉莉酮在豚鼠中既不刺激也不致敏。在兔子眼睛刺激性研究中,最高剂量组显示出强烈的红斑、强烈的分泌物和水肿,在第6天完全消退。其余剂量显示出轻微到中度的红斑和分泌物,在第3天完全消退。茉莉酮在Ames平板掺入和预培养试验中,在添加和不添加代谢活化的情况下,浓度高达2500微克/平板时没有表现出致突变性。在试验中使用的鼠伤寒沙门氏菌菌株是TA98、TA100、TA102、TA1535和TA1537。然而,在中国仓鼠卵巢(CHO)细胞的细胞遗传学试验中,姐妹染色单体交换(SECs)的频率在33.3微摩尔浓度下显著增加,在最高测试剂量100和300微摩尔时也是如此。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Jasmone is a pale yellow, viscous liquid (oil). It is used in perfumery in fine jasmin bases and floral compositions. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Jasmone did not induce dermal sensitization in human volunteers. ANIMAL STUDIES: In an acute dermal toxicity study in 10 rabbits were give 5 g/kg cis-jasmone and observed for 14 days. Severe redness was seen in nine animals and moderate edema was observed in all animals. Eschar was found in two rabbits. Jasmone was not irritating or sensitizing in guinea pigs. In a rabbit eye irritation study, the highest dose group showed strong redness, strong secretion and edema, completely resolving by day 6. The remaining doses showed slight to moderate redness and secretion, completely resolving by day 3. Jasmone was not mutagenic in the Ames plate incorporation and pre-incubation assays with and without metabolic activation at concentrations up to 2500 ug/plate. The strains of Salmonella typhimurium used in the assays were TA98, TA100, TA102, TA1535 and TA1537. However, in a cytogenetic assay in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells frequency of sister-chromatid exchanges (SECs) was significantly increased at concentrations of 33.3 uM and at 100 and 300 uM, the highest dose tested.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 立即急救:确保已经进行了充分的中毒物清除。如果患者停止呼吸,开始人工呼吸,最好使用需求阀复苏器、袋阀面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练操作。如有必要,执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果发生呕吐,让患者前倾或置于左侧(如果可能的话,头部向下),以保持呼吸道畅通,防止吸入。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗帮助。 /毒物A和B/
/SRP:/ Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR if necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on the left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 基本治疗:建立专利气道(如有需要,使用口咽或鼻咽气道)。如有必要,进行吸痰。观察呼吸不足的迹象,如有需要,协助通气。通过非循环呼吸面罩以10至15升/分钟的速度给予氧气。监测肺水肿,如有必要,进行治疗……。监测休克,如有必要,进行治疗……。预期癫痫发作,如有必要,进行治疗……。对于眼睛污染,立即用水冲洗眼睛。在运输过程中,用0.9%的生理盐水(NS)持续冲洗每只眼睛……。不要使用催吐剂。对于摄入,如果患者能够吞咽、有强烈的干呕反射且不流口水,则用温水冲洗口腔,并给予5毫升/千克,最多200毫升的水进行稀释……。在去污后,用干燥的无菌敷料覆盖皮肤烧伤……。/毒药A和B/
/SRP:/ Basic treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if needed. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 mL/kg up to 200 mL of water for dilution if the patient can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 高级治疗:对于昏迷、严重肺水肿或严重呼吸困难的病人,考虑进行口咽或鼻咽气管插管以控制气道。使用气囊面罩装置的正压通气技术可能有益。考虑使用药物治疗肺水肿……。对于严重的支气管痉挛,考虑给予β激动剂,如沙丁胺醇……。监测心率和必要时治疗心律失常……。开始静脉输注D5W TKO /SRP: "保持开放",最低流量/。如果出现低血容量的迹象,使用0.9%的生理盐水(NS)或乳酸钠林格氏液(LR)。对于伴有低血容量迹象的低血压,谨慎给予液体。注意液体过载的迹象……。使用地西泮或劳拉西泮治疗癫痫……。使用丙美卡因氢氯化物协助眼部冲洗……。 /Poisons A and B/
/SRP:/ Advanced treatment: Consider orotracheal or nasotracheal intubation for airway control in the patient who is unconscious, has severe pulmonary edema, or is in severe respiratory distress. Positive-pressure ventilation techniques with a bag valve mask device may be beneficial. Consider drug therapy for pulmonary edema ... . Consider administering a beta agonist such as albuterol for severe bronchospasm ... . Monitor cardiac rhythm and treat arrhythmias as necessary ... . Start IV administration of D5W TKO /SRP: "To keep open", minimal flow rate/. Use 0.9% saline (NS) or lactated Ringer's (LR) if signs of hypovolemia are present. For hypotension with signs of hypovolemia, administer fluid cautiously. Watch for signs of fluid overload ... . Treat seizures with diazepam or lorazepam ... . Use proparacaine hydrochloride to assist eye irrigation ... . /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
人类暴露研究/重复伤害贴片试验被用来确定顺式茉莉酮是否会在人类志愿者中引起皮肤致敏。在诱导阶段,0.5毫升2%顺式茉莉酮的二甲基邻苯二甲酸盐被涂抹在一个封闭的贴片上,并贴在每位志愿者的上臂上,持续24小时。在3周的时间内,诱导应用在周一、周三和周五进行,总共进行了9次应用。在两周的休息期后,一个挑战贴片被贴在一个之前未暴露的部位。贴片像诱导阶段一样贴上,并保持24小时后再移除。对挑战的反应在应用后48小时和72小时进行评分。在测试的54个对象中,没有一个体验到任何致敏反应。
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ Repeated insult patch tests were conducted to determine if cis-jasmone would induce dermal sensitization in human volunteers. During the induction phase, 0.5 mL of 2% cis-jasmone in dimethyl phthalate was applied onto an occlusive patch and applied to the upper arm of each volunteer for 24 hr. Induction applications were made to the same site on Monday, Wednesday and Friday for a total of 9 applications during a 3-week period. Following a two week rest period, a challenge patch was applied to a site previously unexposed. Patches were applied as in the induction phase and kept in place for 24 hr before removal. Reactions to the challenge were scored at 48, and 72 hr after application. None of the 54 subjects tested experienced any sensitization reactions.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29142990
-
RTECS号:GY7301000
-
包装等级:II; III
-
危险类别:4.1
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:请将密封保存,并放置在通风、干燥的环境中。
SDS
顺-茉莉酮 修改号码:6
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: cis-Jasmone
修改号码: 6
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
急性毒性(经口) 第5级
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 吞咽可能有害。
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
若感不适:呼叫解毒中心/医生。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 顺-茉莉酮
顺-茉莉酮 修改号码:6
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
百分比: >92.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 488-10-8
俗名: 3-Methyl-2-(cis-2-peNTenyl)-2-cyclopeNTen-1-one
分子式: C11H16O
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
顺-茉莉酮 修改号码:6
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 135 °C/1.6kPa
闪点: 128°C
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.94
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: skn-rbt LD50:>5 g/kg
orl-rat LD50:5 g/kg
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: GY7301000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
顺-茉莉酮 修改号码:6
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: cis-Jasmone
修改号码: 6
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
急性毒性(经口) 第5级
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 吞咽可能有害。
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
若感不适:呼叫解毒中心/医生。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 顺-茉莉酮
顺-茉莉酮 修改号码:6
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
百分比: >92.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 488-10-8
俗名: 3-Methyl-2-(cis-2-peNTenyl)-2-cyclopeNTen-1-one
分子式: C11H16O
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
顺-茉莉酮 修改号码:6
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 135 °C/1.6kPa
闪点: 128°C
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.94
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: skn-rbt LD50:>5 g/kg
orl-rat LD50:5 g/kg
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: GY7301000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
顺-茉莉酮 修改号码:6
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
概述
茉莉酮学名“3-甲基-2-(2-戊烯基)-2-环戊烯-1-酮”,存在于由茉莉花提取得到的挥发油中,在茉莉油(含约3%)、橙花油、长寿花油、香柠檬油、薄荷油等中均有存在。它可用于配制茉莉香精等。
毒性作为香料可安全用于食品(FDA,§172.515,2000)。
使用限量- 软饮料:10 mg/kg
- 冰淇淋:10 mg/kg
- 糖果:10 mg/kg
- 明胶甜食和布丁:10 mg/kg
顺式-茉莉酮作为一种食品用香料,用于配制香精的各香料成分不得超过在GB 2760中的最大允许使用量和最大允许残留量。
化学性质顺式-茉莉酮为淡黄色油状液体,具有优雅的茉莉花香和芹菜籽香气。其相对密度(d₂²)为0.9437,沸点约为249℃(在134~135℃/1.6×10³Pa时),折射率为1.4979。微溶于水,易溶于乙醇、乙醚和四氯化碳及油脂。天然品存在于茉莉花油、橙花油、香柠檬油等中。
用途GB 2760-1996规定为暂时允许使用的食用香料,主要用于茉莉和薄荷香精的配制。顺茉莉酮是一种很有价值的香料之一,香气很似茉莉花香,是茉莉油的重要香味成分之一,常用于高级茉莉系列化状品香精中。
生产方法顺式-茉莉酮可由7-癸烯在甲醇中,在氢氧化钠存在下环合成2,3-基-环戊烯酮,然后引入甲基而成。工业合成也可通过多种方法实现,例如以3-已烯醇为原料或用甲基乙烯基酮作为起始物等。
二氢茉莉酮是一种略微有色的透明液体,沸点约为230℃(在102℃/0.67kPa时),具有浓郁的花香。化学性质较为稳定,可广泛应用于茉莉系列香精中,并且其工业生产方法多样,其中一种方法是在磷酸存在下,将十一烯酸环化并控制温度和压力,在特定条件下生成顺式8-(+)-烯-5-炔-2-酮,再经加氢制成2,4-二酮。最后在稀碱水溶液中进行分子内缩合而得到顺式茉莉酮。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:有效合成α-氨基酮的α,β-不饱和环状烯酮的形式氨基氰化摘要:通过直接形成CN键将氨基官能团安装在有机分子上是重要的研究目标。为了实现这一目标,开发了1,2-氨基氰化反应。发生通过由环状α的正式偶极环加成来形成吡唑啉的反应中,与锂三甲基甲硅烷β不饱和酮,接着新颖protonolyticÑ 温和的条件下N键裂解。此两步过程以优异的收率提供了各种结构复杂的游离和单烷基化α-氨基酮。DOI:10.1002/anie.201309435
-
作为产物:描述:1,1-ethylenedioxy-3-(cis-hexen-1-yl)-3-(p-toluenesulfonyl)cyclopentane 在 盐酸 、 sodium hydroxide 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 反应 17.0h, 生成 jasmone参考文献:名称:Synthesis ofcis-Jasmoneviathe Retroaldol-aldol Condensation of 3-(cis-3-Hexenyl)-2-cyclopentenone in an Autoclave摘要:cis-茉莉酮是通过2-环戊烯酮高效合成的。将2-环戊烯酮与对甲苯磺酸钠反应,获得3-(对甲苯基磺酰)环戊酮,产率为92.5%。在保护酮之后,用cis-1-溴-3-己烯对磺酮进行烷基化,然后用5%的盐酸在四氢呋喃中进行去磺化,得到3-(cis-3-己烯基)-2-环戊烯酮,产率良好。在不锈钢高压釜中,使用5%氢氧化钠对环戊烯酮进行逆醇缩-醇缩缩合反应,产得cis-茉莉酮,产率为80%。DOI:10.1246/bcsj.55.3931
文献信息
-
Mechanistically Driven Development of an Iron Catalyst for Selective <i>Syn</i>-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with Aqueous Hydrogen Peroxide作者:Margarida Borrell、Miquel CostasDOI:10.1021/jacs.7b07909日期:2017.9.13to be resolved in the design of iron catalysts for olefin syn-dihydroxylation with potential utility in organic synthesis. Toward this end, in this work a novel catalyst bearing a sterically encumbered tetradentate ligand based in the tpa (tpa = tris(2-methylpyridyl)amine) scaffold, [FeII(CF3SO3)2(5-tips3tpa)], 1 has been designed. The steric demand of the ligand was envisioned as a key element to support产物释放是在 Rieske 加氧酶发生的芳烃合成二羟基化反应中的速率决定步骤,被认为是设计用于烯烃合成二羟基化的铁催化剂中需要解决的难题,在有机合成中具有潜在的应用价值。为此,在这项工作中,设计了一种基于 tpa(tpa = 三(2-甲基吡啶基)胺)支架 [FeII(CF3SO3)2(5-tips3tpa)], 1 的新型催化剂. 配体的空间需求被认为是通过隔离金属中心、防止双分子分解路径和促进产物释放来支持高催化活性的关键元素。与有助于螯合产品的路易斯酸协同组合,在温和的实验条件下,使用稍微过量(1.5 当量)的过氧化氢水溶液,在很短的反应时间内,从广泛范围的烯烃的氧化中,1 提供了良好到极好的二醇产物产率(高达 97% 的分离产率)。显示了二烯烃的可预测位点选择性顺式二羟基化。配体的受阻性质也提供了一种独特的工具,该工具已与同位素分析结合使用,以确定活性物质的性质和 H2O2 的活化机制。此外,1
-
Lanthanide replacement in organic synthesis: Luche-type reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones in the presence of calcium triflate作者:Nina V. Forkel、David A. Henderson、Matthew J. FuchterDOI:10.1039/c2gc35619h日期:——calcium-mediated regioselective 1,2-reduction of challenging α,β-unsaturated ketones, such as 2-cyclopententone, is reported. The corresponding allylic alcohols are obtained in very good regioselectivities using Ca(OTf)2 and NaBH4. Furthermore, we have shown that our method can stereoselectively reduce aziridinyl ketones.
-
Ni-Catalyzed Isomerization–Hydrocyanation Tandem Reactions: Access to Linear Nitriles from Aliphatic Internal Olefins作者:Jihui Gao、Jie Ni、Rongrong Yu、Gui-Juan Cheng、Xianjie FangDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.0c04007日期:2021.1.15A highly regioselective nickel-based catalyst system for the isomerization/hydrocyanation of aliphatic internal olefins is described. This benign tandem reaction provides facile access to a wide variety of aliphatic nitriles in good yields with excellent regioselectivities. Thanks to Lewis acid-free conditions, the protocol features board functional groups tolerance, including secondary amine and unprotected
-
Construction of NH‐Unprotected Spiropyrrolidines and Spiroisoindolines by [4+1] Cyclizations of γ‐Azidoboronic Acids with Cyclic <i>N</i> ‐Sulfonylhydrazones作者:Lucía López、María‐Paz Cabal、Carlos ValdésDOI:10.1002/anie.202113370日期:2022.1.10N-sulfonylhydrazones of cyclic ketones are readily transformed into NH-free spirocyclic pyrrolidines and isoindolines by reaction with γ-azidoboronic acids. The transition-metal-free transformation is widely applicable and represents a new disconnection towards spirocyclic pyrrolidines. The application of the reaction in the modification of natural steroids and other biorelevant molecules highlights
-
Synthesis of Pyrethroids and Jasmonoids through Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions作者:Viviana Heguaburu、Florencia Parpal、Ana Paula Paullier、Enrique PandolfiDOI:10.1055/a-1736-1749日期:2022.6The synthesis of jasmone and related jasmonoids and pyrethroids is described. These compounds play a defensive role in plants and share a common cyclopentenone core with variations in the side chains. Jasmone, cinerone, allylrethrone, and derivatives were synthesized through π-allyl palladium cross-coupling of stannane derivatives. With selective hydrogenation, dihydrojasmone, and dihydrocinerone were
表征谱图
-
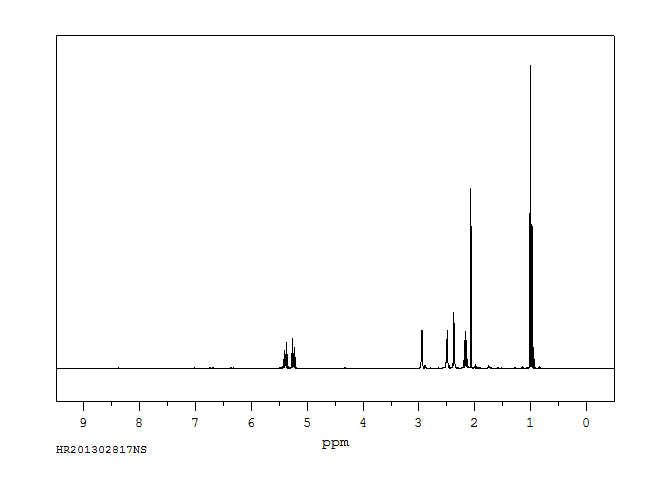
氢谱1HNMR
-
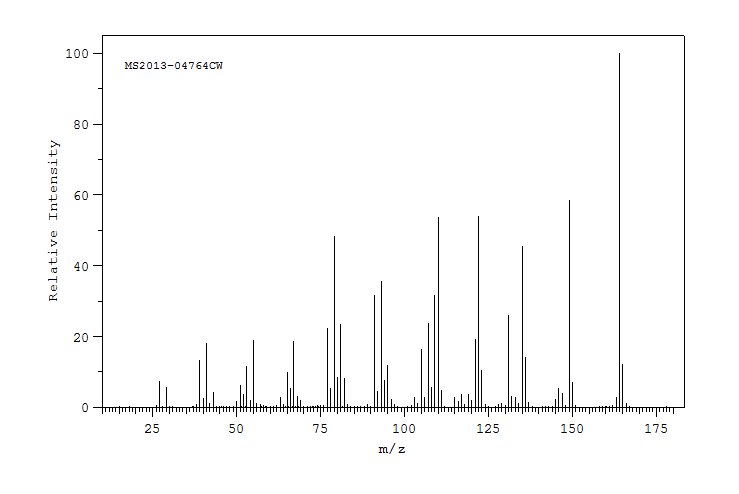
质谱MS
-
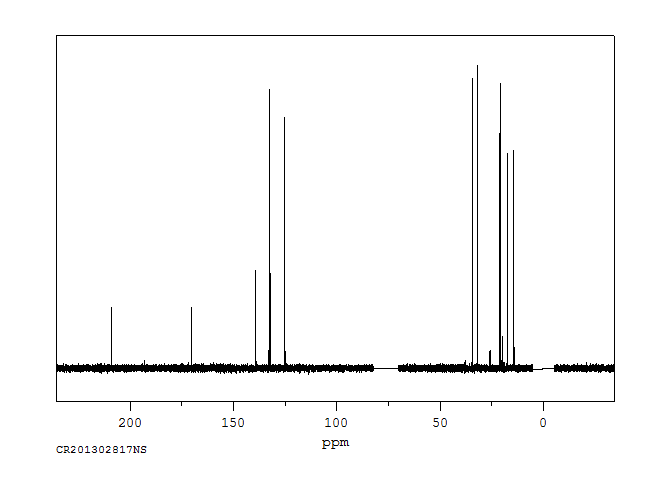
碳谱13CNMR
-
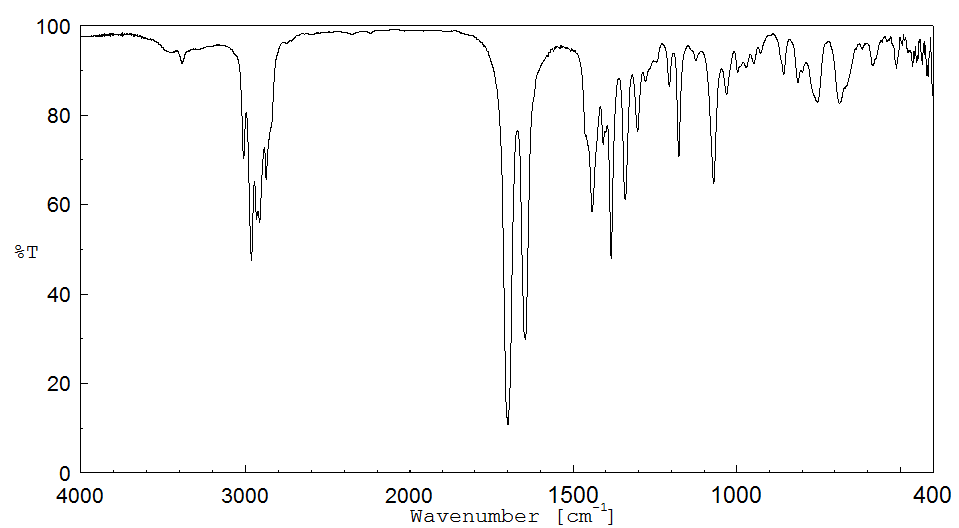
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷