3-(4-乙酰氨基苯基)-3-氧代丙酸乙酯 | 91958-11-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:97.1-99.1 °C
-
沸点:440.2±25.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.203±0.06 g/cm3(Temp: 20 °C; Press: 760 Torr)(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1
-
重原子数:18
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.31
-
拓扑面积:72.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:4
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 3-(4-氨基苯基)-3-氧代丙酸乙酯 4-amino-β-oxobenzenepropanoic acid ethyl ester 61252-00-4 C11H13NO3 207.229 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— ethyl 3-(4-acetylaminophenyl)-3-hydroxypropionate 383663-05-6 C13H17NO4 251.282
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Design, synthesis and RON receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity of new head groups analogs of LCRF-0004摘要:New heteroarylcarboxamide head groups substituted with two aromatic rings analogs of thieno[3,2-b] pyridine-based kinase inhibitor LCRF-0004 were designed and synthesized. Potent inhibitors of RON tyrosine kinase with various level of selectivity for c-Met RTK were obtained. (C) 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.080
-
作为产物:描述:magnesium bis(3-ethoxy-3-oxopropanoate) 、 对乙酰氨基苯甲酸 在 N,N'-羰基二咪唑 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 生成 3-(4-乙酰氨基苯基)-3-氧代丙酸乙酯参考文献:名称:Benzoxazepinones and their use as squalene synthase inhibitors摘要:披露了一种由公式[I]表示的化合物: 1 其中R 1 是可选地取代的1-羧乙基,可选地取代的烷基亚磺酰基,可选地取代的(羧基环烷基)-烷基,—X 1 —X 2 —Ar—X 3 —X 4 —COOH(其中X 1 和X 4 是键或亚烷基,X 2 和X 3 是键,—O—,—S—,Ar是二价芳香族等),R 2 是可选地由酰氧基和/或羟基取代的烷基,R 3 是烷基,W是卤素原子等,或其盐。该化合物具有降低胆固醇活性和降低甘油三酯活性,用于预防或治疗高脂血症。公开号:US20030078251A1
文献信息
-
Discovery of Selective SIRT2 Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents in B-Cell Lymphoma and Other Malignancies作者:Sarwat Chowdhury、Smitha Sripathy、Alyssa A. Webster、Angela Park、Uyen Lao、Joanne H. Hsu、Taylor Loe、Antonio Bedalov、Julian A. SimonDOI:10.3390/molecules25030455日期:——
Genetic ablation as well as pharmacological inhibition of sirtuin 2 (SIRT2), an NAD+-dependent protein deacylase, have therapeutic effects in various cancers and neurodegenerative diseases. Previously, we described the discovery of a dual SIRT1/SIRT2 inhibitor called cambinol (IC50 56 and 59 µM, respectively), which showed cytotoxic activity against cancer cells in vitro and a marked anti-proliferative effect in a Burkitt lymphoma mouse xenograft model. A number of recent studies have shown a protective effect of SIRT1 and SIRT3 in neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases as well as in certain cancers prompting us to initiate a medicinal chemistry effort to develop cambinol-based SIRT2-specific inhibitors devoid of SIRT1 or SIRT3 modulating activity. Here we describe potent cambinol-based SIRT2 inhibitors, several of which show potency of ~600 nM with >300 to >800-fold selectivity over SIRT1 and 3, respectively. In vitro, these inhibitors are found to be toxic to lymphoma and epithelial cancer cell lines. In particular, compounds 55 (IC50 SIRT2 0.25 µM and <25% inhibition at 50 µM against SIRT1 and SIRT3) and 56 (IC50 SIRT2 0.78 µM and <25% inhibition at 50 µM against SIRT1 and SIRT3) showed apoptotic as well as strong anti-proliferative properties against B-cell lymphoma cells.
基因消融以及对SIRT2(一种NAD+依赖性蛋白去乙酰化酶)的药物抑制在各种癌症和神经退行性疾病中具有治疗效果。我们先前描述了一种双重SIRT1/SIRT2抑制剂称为cambinol(IC50分别为56和59微米),在体外对癌细胞显示细胞毒活性,并在Burkitt淋巴瘤小鼠异种移植模型中表现出明显的抗增殖效果。最近的一些研究表明,SIRT1和SIRT3在神经退行性和代谢性疾病以及某些癌症中具有保护作用,促使我们启动了一项药物化学工作,以开发基于cambinol的SIRT2特异性抑制剂,不具有SIRT1或SIRT3调节活性。在这里,我们描述了有效的基于cambinol的SIRT2抑制剂,其中几种显示出约600纳米的效力,对SIRT1和SIRT3的选择性分别为>300至>800倍。在体外,这些抑制剂对淋巴瘤和上皮癌细胞系具有毒性。特别是,化合物55(IC50 SIRT2 0.25微米,在50微米下对SIRT1和SIRT3的抑制<25%)和56(IC50 SIRT2 0.78微米,在50微米下对SIRT1和SIRT3的抑制<25%)显示出对B细胞淋巴瘤细胞具有凋亡以及强烈的抗增殖特性。 -
Copper-catalyzed, silver-mediated formal [3+2] cycloaddition of simple alkynes with β-ketoesters through propargylic C(sp<sup>3</sup>)–H functionalization作者:Zhen-Ting Liu、Xiang-Ping HuDOI:10.1039/c8cc08013e日期:——thus providing a variety of highly functionalized furans in moderate to high yields. This represents the first successful example of the catalytic propargylic cycloaddition of simple alkynes with bisnucleophiles based on the propargylic C(sp3)–H functionalization strategy.
-
BENZOXAZEPINONES AND THEIR USE AS SQUALENE SYNTHASE INHIBITORS申请人:Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd.公开号:EP1292585A1公开(公告)日:2003-03-19
-
[EN] BENZOXAZEPINONES AND THEIR USE AS SQUALENE SYNTHASE INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] BENZOXAZEPINONES ET LEUR UTILISATION COMME INHIBITEURS DE LA SQUALENE SYNTHASE申请人:TAKEDA CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES LTD公开号:WO2001098282A1公开(公告)日:2001-12-27There is disclosed a compound represented by formula (I), wherein R1 is optionally substituted 1-carboxyethyl group, optionally substituted alkyl-sulfonyl group, optionally substituted (carboxy-cycloalkyl)-alkyl group, -X?1-X2-Ar-X3-X4¿-COOH (wherein X?1 and X4¿ are a bond or alkylene group, X?2 and X3¿ are a bond, -O-, -S-, Ar is divalent aromatic group , etc.), R2 is alkyl group optionally substituted with alkanoyloxy group and/or hydroxy group, R3 is alkyl group, and W is halogen atom, etc., or a salt thereof. The compound has the cholesterol lowering activity and the triglyceride lowering activity and is useful for preventing and/or treating hyperlipidemia.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
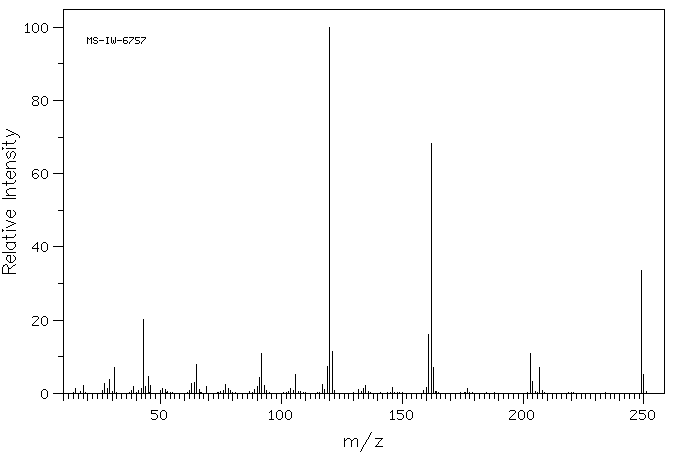
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
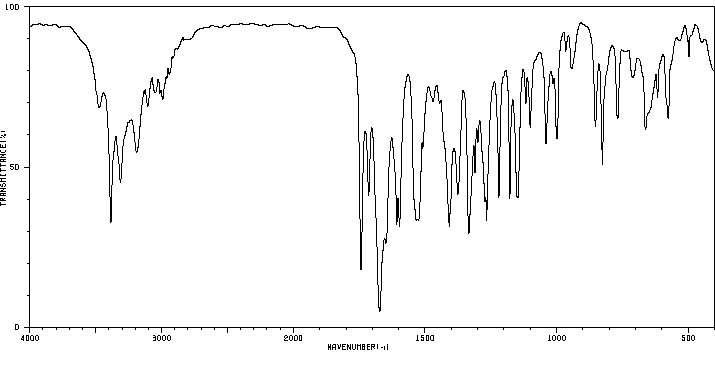
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息