1-(4-羟基苯基)十六烷-1-酮 | 2589-76-6
中文名称
1-(4-羟基苯基)十六烷-1-酮
中文别名
——
英文名称
1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hexadecane-1-one
英文别名
4-hydroxyhexadecanophenone;4-hexadecanoyl phenol;1-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hexadecan-1-one;1-(4-Hydroxy-phenyl)-hexadecan-1-on;4'-Hydroxypalmitophenone;1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hexadecan-1-one
CAS
2589-76-6
化学式
C22H36O2
mdl
——
分子量
332.527
InChiKey
CZYGBHHNNQJSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:84.5-85 °C
-
沸点:470.8±18.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:0.948±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):8.6
-
重原子数:24
-
可旋转键数:15
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.68
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-十六烷基苯酚 4-hexadecylphenol 2589-78-8 C22H38O 318.543
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:1-(4-羟基苯基)十六烷-1-酮 在 hydrazine hydrate 、 草酸 、 4-十二烷基苯磺酸钠盐 、 potassium hydroxide 作用下, 以 水 、 二乙二醇 为溶剂, 20.0~200.0 ℃ 、670.61 Pa 条件下, 反应 7.0h, 生成 bis(2-hydroxy-5-n-hexadecylphenyl)methane参考文献:名称:系列双子烷基酚聚氧乙烯非离子表面活性剂的合成及其临界胶束浓度摘要:成功合成了一系列双子正烷基酚聚氧乙烯表面活性剂(GAP),并通过NMR和FTIR光谱确定了它们的分子结构。使用相同的合成路线,使用工业壬基酚产品和多聚甲醛合成了双基壬基酚聚氧乙烯表面活性剂(GNP),其分子结构也由1表征H-NMR和FTIR光谱。确定了最佳反应条件。通过Wilhelmy平板法和稳态荧光探针法测定GAP的临界胶束浓度(CMC)值。实验结果表明,亲水性聚氧乙烯链和疏水性尾部的长度如何改变CMC值。发现GAP的CMC值比聚乙氧基化烷基酚型的相应常规单尾非离子表面活性剂的CMC值低得多,这表明双子物种具有更好的表面活性。DOI:10.1007/s11743-011-1245-8
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Paranjpe; Phalnikar; Nargund, Journal of the University of Bombay, Science: Physical Sciences, Mathematics, Biological Sciences and Medicine, 1942, vol. 11/A, p. 120,122摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Alkylated phenol series in lacustrine black shales from the Nördlinger Ries, southern Germany作者:Assem O. Barakat、Susan Baumgart、Peter Brocks、Barbara M. Scholz-Böttcher、Jürgen RullkötterDOI:10.1002/jms.3049日期:2012.8Several series of alkylated phenols were detected for the first time in the extractable bitumens of organic matter-rich sediments from the Nördlinger Ries (southern Germany). Most abundant and significant constituents comprise those with n-octadecyl, n-eicosanyl, phytanyl, and iso-pentadecyl and anteiso-pentadecyl substituents. The structures of these compounds are suggested from mass spectrometric and retention time data and coinjection with synthetic standards. Diagenetic alteration of phenolic algal lipids is suggested as a possible way to the formation of these compounds in the Nördlinger Ries sediments. Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
-
COMPOUNDS WITH POTENTIAL ACTIVITY AGAINST LETHAL RADIATIONS. III.<sup>1</sup> BORON TRIFLUORIDE-CATALYZED SYNTHESIS OF HYDROXY ARYL KETONES作者:NG. PH. BUU-HOÏ、JEAN SÉAILLESDOI:10.1021/jo01123a008日期:1955.5
-
Cytotoxicity and Antiestrogenicity of a Novel Series of Basic Diphenylethylenes作者:Jacques Gilbert、Maryse Fuentes、Tiiu Ojasoo、Jean-Christophe Doré、Michel PonsDOI:10.1021/jm950624t日期:1997.3.1On the premise that it is necessary to develop antiestrogens with a higher cytotoxic component in order to reduce the risks of the development of heterogeneous malignant cell populations in breast cancer, we studied a novel series of basic diphenylethylenes, for the most part devoid of estrogenic activity, with low antiestrogenicity but much enhanced cytotoxicity compared to the reference drug tamoxifen. The main structural features associated with cytotoxicity were E isomery, substituents of five to eight carbons on the ethylene bond, and dibasicity.
-
Heinrich, B.; Guillon, D., Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals Science and Technology, Section A: Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 1995, vol. 268, p. 21 - 44作者:Heinrich, B.、Guillon, D.DOI:——日期:——
-
Auwers, Chemische Berichte, 1903, vol. 36, p. 3898作者:AuwersDOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
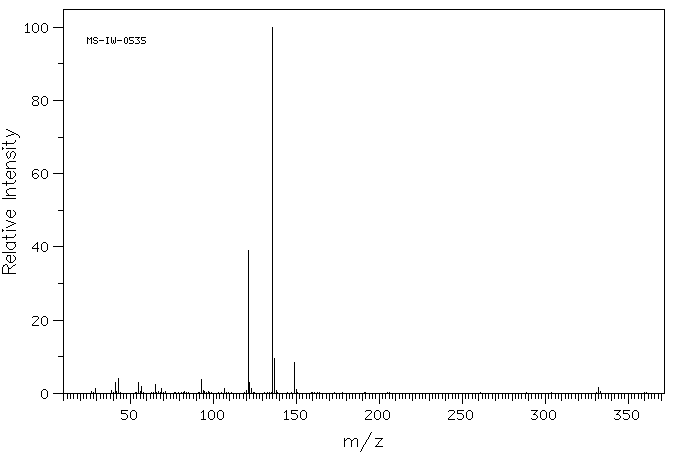
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
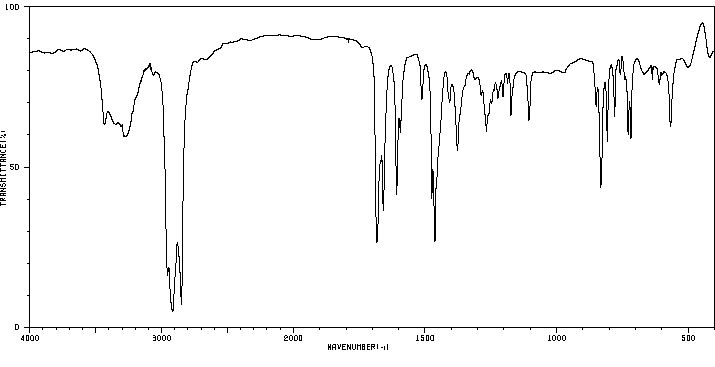
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷