2-乙基-1,3-丁二烯 | 3404-63-5
中文名称
2-乙基-1,3-丁二烯
中文别名
——
英文名称
2-ethyl-1,3-butadiene
英文别名
2-Ethylbutadiene;2-Ethylbutadien;2-Ethyl-butadien-(1,3);2-Ethylbuta-1,3-dien;2-Ethyl-1,3-butadien;3-methylidenepent-1-ene
CAS
3404-63-5
化学式
C6H10
mdl
MFCD00039819
分子量
82.1454
InChiKey
IGLWCQMNTGCUBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-94.9°C (estimate)
-
沸点:72.85°C
-
密度:0.7120
-
保留指数:607;600
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.9
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.333
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2901299090
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:2-硝基-1,3-茚满二酮的氢芳族类似物。摘要:DOI:10.1021/jm00236a021
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Pariselle; Simon, Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l'Academie des Sciences, 1921, vol. 173, p. 88摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Diphosphination of 1,3-Dienes with Diphosphines under Visible-Light-Promoted Photoredox Catalysis作者:Nobutaka Otomura、Koji Hirano、Masahiro MiuraDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03534日期:2018.12.21A diphosphination of 1,3-dienes with tetraaryldiphosphines proceeds under Ir(ppy)3-promoted photoredox catalysis to form the corresponding 1,4-diphosphino-2-butenes in good yields with good regioselectivity. The key to success is the addition of a Br+ additive. Subsequent double bond hydrogenation successfully delivers the 1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane (DPPB) derivatives with uniquely large bite
-
Synthesis, Structure, and Reactions of Stable Titanacyclopentanes作者:Kazushi Mashima、Nozomu Sakai、Hidemasa TakayaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.64.2475日期:1991.8reflections, R=0.053). The reaction of 5 with carbon monoxide afforded spiro[2.4]heptan-5-ones in 98% yield. The thermal decomposition of 5 has been investigated, and possible mechanisms of the reactions have been proposed based on deuterium-labeled experiments. A novel formal reductive elimination of organic ligands giving 1-phenylspiro[2.4]hexane has been observed in the thermolysis of 5b. A structure–reactivity式 Cp*2Ti( C( CHR)CH2)(5a;R=H 和 5b;R=C6H5,Cp*=五甲基环戊二烯基)的钛环化合物是第一种稳定的钛环戊烷,已通过双(五甲基环戊二烯基)的反应制备钛-乙烯配合物 (3) 与亚甲基环丙烷 (4),其结构是基于光谱数据和 X 射线晶体学确定的。配合物 5b 在空间群 P21⁄a(Z=4) 中结晶,具有单元常数,a=21.832(3), b=8.580(1), c=14.759(2) A, β=96.81(1)°, U= 2744.9(6) A3(4261 次反射,R=0.053)。5 与一氧化碳反应得到螺[2.4]庚烷-5-酮,产率为 98%。研究了 5 的热分解,并基于氘标记实验提出了可能的反应机制。在 5b 的热解中观察到了一种新的有机配体的正式还原消除,产生 1-苯基螺[2.4] 己烷。已经讨论了结构-反应性关系。
-
Metal catalysis in organic reactions. Part 13. The reaction of 3-en-1-ynes with trialkylalanes: influence of transition-metal complexes作者:Anna Maria Caporusso、Giampaolo Giacomelli、Luciano LardicciDOI:10.1039/p19810001900日期:——The reaction between trialkylalanes and 3-alkyl-, 4-alkyl-, or 3,4-dialkyl-but-3-en-1-ynes (1) leads to products which correspond to metallation, reduction, and carbalumination processes. The extent of such reactions, and the regio- and stereo-selectivity of the carbalumination, are dependent on the enyne used. A mechanism is proposed involving tautomeric equilibria among several α-unsaturated organoaluminum
-
Cycloaddition of keteniminium with terminal alkynes toward cyclobuteniminium and their use in Diels–Alder reactions作者:Alexandre Lumbroso、Saron Catak、Sarah Sulzer-Mossé、Alain De MesmaekerDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2014.07.059日期:2014.9dienes to afford cyclobutanone derivatives in good yields. A density functional theory (DFT) based computational study has been performed to obtain insight into the nature of the cycloaddition reactions and to investigate the difference in reactivity of cyclobuteniminium salts. Finally, the usefulness of cyclobutanone derivatives has been demonstrated by ring expansion reactions affording lactone, lactame
-
A Series of Crystallographically Characterized Linear and Branched σ-Alkane Complexes of Rhodium: From Propane to 3-Methylpentane作者:Alexander J. Bukvic、Arron L. Burnage、Graham J. Tizzard、Antonio J. Martínez-Martínez、Alasdair I. McKay、Nicholas H. Rees、Bengt E. Tegner、Tobias Krämer、Heather Fish、Mark R. Warren、Simon J. Coles、Stuart A. Macgregor、Andrew S. WellerDOI:10.1021/jacs.1c00738日期:2021.4.7(3-methylpentane). For the linear alkanes propane and hexane, some additional Rh(I)···H–C interactions with the geminal C–H bonds are also evident. The stability of these complexes with respect to alkane loss in the solid state varies with the identity of the alkane: from propane that decomposes rapidly at 295 K to 2-methylbutane that is stable and instead undergoes an acceptorless dehydrogenation to form a bound alkene利用固态分子有机金属(SMOM)技术,特别是固/气单晶到单晶的反应性,一系列通式为[Rh(Cy 2 PCH 2 CH 2 PCy 2 )(η已经制备了n :η (间烷)][BAr F 4 ](烷烃=丙烷、2-甲基丁烷、己烷、3-甲基戊烷;Ar F =3,5-(CF 3 ) 2 C 6 H 3 )。这些新配合物已使用单晶 X 射线衍射、固态核磁共振波谱和 DFT 计算技术进行了表征,并在金属配位位点呈现出多种 Rh(I)·H–C 结合基序:1,2- η 2 :η 2 (2-甲基丁烷)、1,3-η 2 :η 2 (丙烷)、2,4-η 2 :η 2 (己烷)和1,4-η 1 :η 2 (3-甲基戊烷)。对于直链烷烃丙烷和己烷,一些额外的 Rh(I)…H-C 与偕 C-H 键的相互作用也很明显。这些络合物相对于固态烷烃损失的稳定性随烷烃的特性而变化:从在 295 K 下快速分解的丙烷到稳定的 2-
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
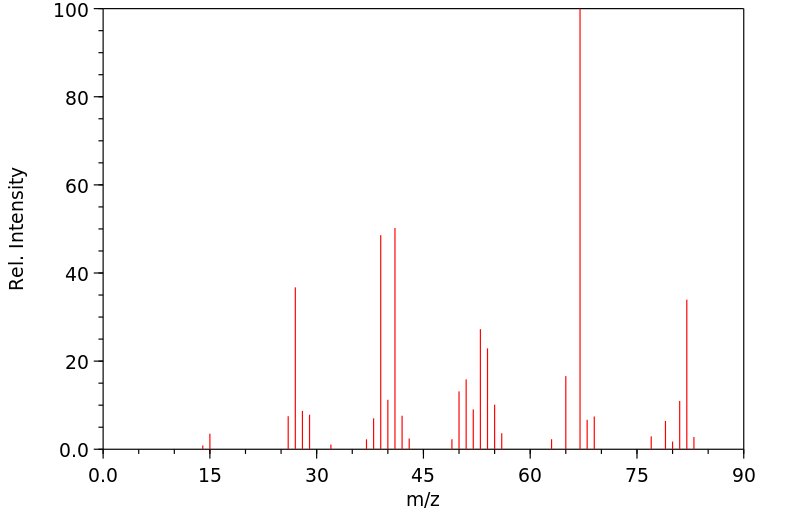
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
高密聚乙烯
香叶醇
顺式3-甲基-2-己烯
顺式-5-癸烯
顺式-5-甲基-2-己烯
顺式-5-庚烯-1-炔
顺式-4-癸烷
顺式-4-甲基-2-戊烯
顺式-4-甲基-2-戊烯
顺式-3-癸烯
顺式-3-甲基-3-己烯
顺式-3-甲基-2-庚烯
顺式-3-戊烯-1-炔
顺式-3,4-二甲基-3-己烯
顺式-3,4-二甲基-2-戊烯
顺式-3,4-二甲基-2-戊烯
顺式-2-甲基-3-己烯
顺式-2-壬烯
顺式-2-丁烯-D1
顺式-1.1.1-三甲基-2-丁烯
顺式-1-甲基-2-环丙基乙烯
顺式-1-甲基-2-乙烯基环戊烷
顺式-1-环戊基-1-辛烯
顺式-1-氘代-3-甲基-1-丁烯
顺式-(9ci)-2,3,3a,7a-四氢-4-(1-甲基乙基)-1H-茚
顺式-(2-丁烯基)环丙烷
顺式,顺式-2,4-己二烯
顺-环辛烯
顺-9-二十一碳烯
顺-6-十三碳烯
顺-5-甲基-1,3,6-庚三烯
顺-4-辛烯
顺-4-壬烯
顺-3-辛烯
顺-3-甲基-2-戊烯
顺-3-壬烯
顺-3-十三碳烯
顺-2-辛烯
顺-2-癸烯
顺-2-戊烯
顺-2-庚烯
顺-2-己烯
顺-2-丁烯
顺-2,2-二甲基-3-己烯
顺-1,3-戊二烯
顺,顺-1,9-环十六烷二烯
顺,顺,顺-环癸-1,3,5-三烯
间戊二烯
间二(4-吡啶基)苯
镁,二-2-丁烯基-