4-氧基-苯氨基-2-巴豆酸 | 555-59-9
物质功能分类
中文名称
4-氧基-苯氨基-2-巴豆酸
中文别名
N-苯基马来酸
英文名称
N-phenylmaleamic acid
英文别名
(Z)-4-oxo-4-(phenylamino)but-2-enoic acid;(Z)-4-anilino-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid
CAS
555-59-9
化学式
C10H9NO3
mdl
——
分子量
191.186
InChiKey
WHZLCOICKHIPRL-SREVYHEPSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:188-190°C
-
沸点:326.92°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:Apparent density 1.418 g/ml at 30°
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.9
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:66.4
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2924299090
-
安全说明:S26
-
储存条件:室温
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-氧-4-苯胺基-2-丁烯酸 3-phenylcarbamoylacrylic acid 37902-58-2 C10H9NO3 191.186 N-苯基马来酰亚胺 N-phenyl-maleimide 941-69-5 C10H7NO2 173.171 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (E)-4-oxo-4-(phenylamino)but-2-enoic acid 4437-08-5 C10H9NO3 191.186 —— methyl (E)-4-oxo-4-(phenylamino)but-2-enoate 87321-69-5 C11H11NO3 205.213 —— N-phenyl-maleamic acid methyl ester 80167-50-6 C11H11NO3 205.213 —— isopropyl N-phenylmaleamate 109096-33-5 C13H15NO3 233.267 —— (Z)-N',N'-dimethyl-N-phenylbut-2-enediamide 112291-06-2 C12H14N2O2 218.255 —— 4-methoxyphenyl N-phenylmaleamate 1229755-24-1 C17H15NO4 297.31 N-苯基马来酰亚胺 N-phenyl-maleimide 941-69-5 C10H7NO2 173.171
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:First Triphenylphosphine PromotedReduction of Maleimides to Succinimides摘要:三苯基膦(TPP)在回流甲醇中能有效地将马来酰亚胺 1a-g 还原成相应的琥珀酰亚胺 2a-g,而且收率很高。据观察,一些从芳香卤素化合物 1h-j 中得到的马来酰亚胺通过该反应转化为相应的琥珀酰亚胺酸甲酯 3a-c。DOI:10.1055/s-2003-40523
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Barakat et al., Journal of the Chemical Society, 1957, p. 4133摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
3-ARYL PROPIOLONITRILE COMPOUNDS FOR THIOL LABELING申请人:UNIVERSITE DE STRASBOURG公开号:US20160145199A1公开(公告)日:2016-05-26The present invention relates to a process for labeling compounds comprising thiol moieties with 3-arylpropiolonitrile compounds, to 3-arylpropiolonitrile compounds substituted with tag moieties and to specific 3-arylpropiolonitrile linkers.
-
Non-hydroxylic clathrate hosts of [4 + 2]π cycloadducts of phencyclone and N-arylmaleimides: recognition of aromatic guests作者:Yasuyuki Yoshitake、Junichi Misaka、Koji Setoguchi、Masaki Abe、Tomohiro Kawaji、Masashi Eto、Kazunobu HaranoDOI:10.1039/b201915a日期:——A series of non-hydroxylic crystalline host compounds, [4 + 2]Ï cycloadducts of phencyclone and N-arylmaleimides having a bicyclo[2.2.1]heptene-7-one system, was synthesized and their inclusion behavior investigated. X-Ray crystal analyses of the inclusion compounds of the N-(1-naphthyl) derivative with butan-2-one, the N-(m-tolyl) derivative with p-xylene, together with the guest-free host and the N-(p-tolyl) derivative with m-xylene indicate that the âspaceâ surrounded by the phenanthrene ring, two phenyl rings and bridge carbonyl of the 1,3-diphenyl-1,3-dihydrocyclopenta[l]phenanthren-2-one moiety plays an important role, not only in the formation of inclusion complexes with the aromatic guests but also in hostâhost interactions. In every case, the N-aryl succinimide assists complex formation with the guests, in which the weak lattice forces due to CâHâ¯Ï and CâHâ¯O interactions are operative. Methyl-substituted benzenes are effectively recognized by the CâHâ¯Ï interactions between the guest molecules and the phenanthrene ring of the hosts.合成了一系列非羟基结晶主客体化合物,即含有二环[2.2.1]庚烯-7-酮体系的苯并环戊烯和N-芳基马来酰亚胺的[4 + 2]π环加成产物,并研究了它们的包埋行为。对N-(1-萘基)衍生物与丁酮、N-(m-甲苯基)衍生物与对二甲苯的包埋化合物,以及无客体的主客体和N-(p-甲苯基)衍生物与米二甲苯的X射线晶体分析表明,1,3-二苯基-1,3-氢环戊烯-2-酮部分中由菲环、两个苯环和桥碳酰基所包围的“空间”在与芳香族客体形成包埋复合物以及主客体之间的相互作用中发挥了重要作用。在每种情况下,N-芳基琥珀酰亚胺都有助于与客体的复合物形成,其中由于C–H⋯π和C–H⋯O相互作用而产生的微弱晶格力起作用。甲基取代的苯类化合物通过客体分子与主客体的菲环之间的C–H⋯π相互作用得到了有效识别。
-
Application of primary halogenated hydrocarbons for the synthesis of 3-aryl and 3-alkyl indolizines作者:Yan Liu、Huayou Hu、Junyu Zhou、Wenhui Wang、Youliang He、Chao WangDOI:10.1039/c7ob00980a日期:——properties that make it suitable for numerous applications in many fields, such as biology, medicine and materials. However, the synthesis of 3-alkyl indolizines from bulky primary halogenated alkanes has not yet been reported. Herein, a transition-metal-free synthetic route to 3-aryl and 3-alkyl indolizines from electron-deficient alkenes, pyridines and primary halogenated hydrocarbons has been reported
-
A facile and economical procedure for the synthesis of maleimide derivatives using an acidic ionic liquid as a catalyst作者:Kai Li、Chao Yuan、Shijun Zheng、Qiang FangDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.06.025日期:2012.8in good yields and high purity from the corresponding maleamic acids using a Brønsted acidic room temperature ionic liquid (RTIL) as a catalyst. The products were obtained through merely a decanting and removal of the solvent, suggesting that this procedure is superior to the conventional routes, in which the strong organic/inorganic acids were used as the catalysts, as well as a complicated post-processing
-
Synthesis and evaluation of novel 2,3,5-triaryl-4H,2,3,3a,5,6,6a-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-d]isoxazole-4,6-diones for advanced glycation end product formation inhibitory activity作者:Anjandeep Kaur、Baldev Singh、Amteshwar Singh JaggiDOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.11.080日期:2013.2substituted N-aryl maleimides 2 leading to the formation of new stereoisomeric 2,3,5-triaryl-4H,2,3,3a,5,6,6a-hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-d]isoxazole-4,6-dione derivatives 3 in excellent yields. The synthesized compounds have been screened for their advanced glycation end (AGE) product formation inhibitory activity on the basis of their ability to inhibit the formation of AGEs in the bovine serum albumin (BSA)-glucose
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
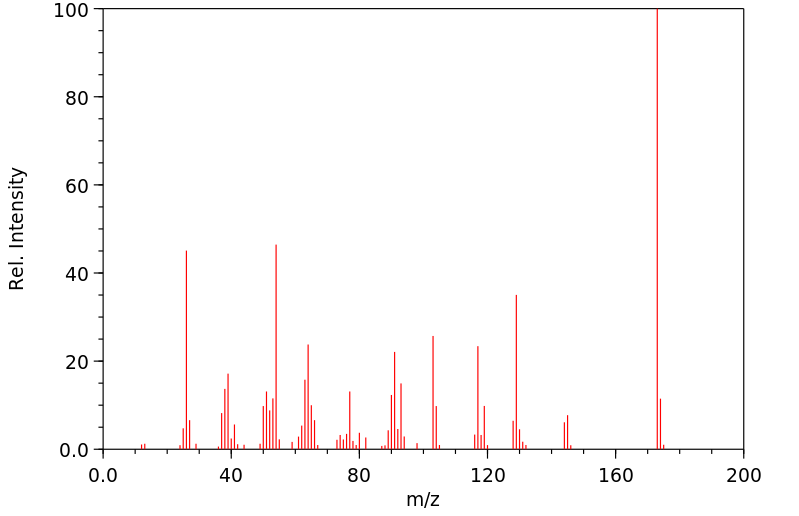
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
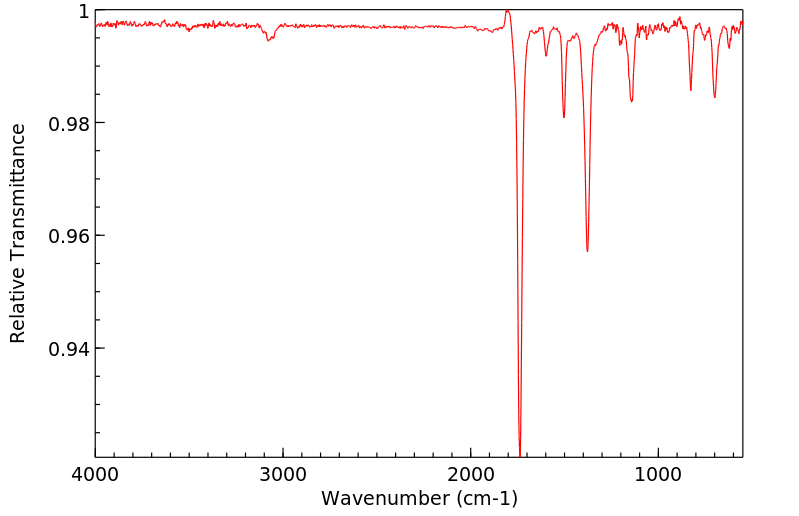
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫