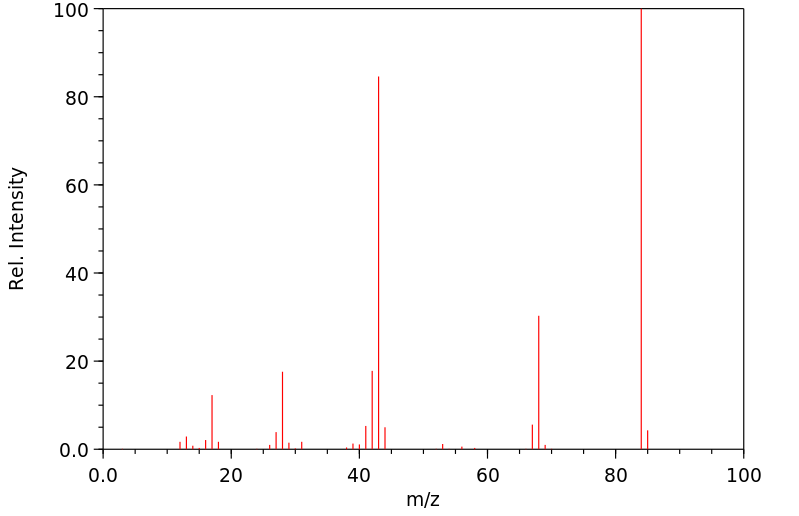
Two new water-soluble copper(II)-dipeptide complexes: [Cu(glygly)(PyTA)]ClO4·1.5H2O (1) and [Cu(glygly)(PzTA)]ClO4·1.5H2O (2) (glygly = glycylglycine anion, PyTA = 2,4-diamino-6-(2′-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine and PzTA = 2,4-diamino-6-(2′-pyrazino)-1,3,5-triazine), utilizing two interrelated DNA base-like ligands (PyTA and PzTA), have been synthesized and characterized. The structure elucidation for 1 performed by single crystal X-ray diffraction showed a one dimensional chain conformation in which the central copper ions arrange in a five-coordinate distorted square-pyramidal geometry. Spectroscopic titration, viscosity and electrophoresis measurements revealed that the complexes bound to DNA via an outside groove binding mode, and cleaved pBR322 DNA efficiently in the presence of ascorbate, probably via an oxidative mechanism with the involvement of ˙OH and ˙O2−. Notably, the complexes exhibited considerable in vitro cytotoxicity against four human carcinoma cell lines (HepG2, HeLa, A549 and U87) with IC50 values ranging from 41.68 to 159.17 μM, in addition to their excellent SOD mimics (IC50 ∼ 0.091 and 0.114 μM). Besides, multispectroscopic evidence suggested their HSA-binding at the cavity containing Trp-214 in subdomain IIA with moderate affinity, mainly via hydrophobic interaction. Further, the molecular docking technique utilized for ascertaining the mechanism and mode of action towards DNA and HSA theoretically verified the experimental results.
两种新的
水溶性
铜(II)二肽配合物:[Cu(甘甘)(PyTA)]ClO4·1.5H2O (1) 和 [Cu(甘甘)(PzTA)]ClO4·1.5H2O (2) (甘甘 = 甘
氨酰甘
氨酸阴离子,PyTA = 2,4-二
氨基-6-(2'-
吡啶基)-
1,3,5-三嗪,PzTA = 2,4-二
氨基-6-(2'-
吡嗪基)-
1,3,5-三嗪),利用两种相关的类DNA碱基
配体(PyTA和PzTA),已合成并表征。通过单晶X射线衍射对1的结构解析显示为一维链状构型,其中央
铜离子排列在五配位扭曲的四角锥几何结构中。光谱滴定、粘度和电泳测量揭示了配合物通过外部沟槽结合模式与DNA结合,并在
抗坏血酸盐存在下高效切割pB
R322 DNA,可能通过涉及˙OH和˙O2-的氧化机制。值得注意的是,配合物对四种人癌
细胞系(HepG2、HeLa、A549和U87)显示出相当大的体外细胞毒性,IC50值范围从41.68到159.17 μM,此外它们还具有优秀的SOD模拟(IC50 ∼ 0.091和0.114 μM)。此外,多光谱证据表明它们在含有Trp-214的亚域IIA腔中与H
SA结合,主要通过疏
水相互作用,具有适度亲和力。进一步,利用分子对接技术理论上验证了实验结果,确定了其对DNA和H
SA的作用机制和模式。