邻氯苯乙酰腈 | 40018-25-5
中文名称
邻氯苯乙酰腈
中文别名
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈;3-(2-氯苯基)-3-氧代乙腈;邻氯苯甲酰乙腈;3-(2-氯苯基)-3-氧代丙腈;2-氯-β-氧代-苯丙烷腈;3(2-氯苯基)-3-氧代丙腈
英文名称
2-Chlorobenzoyl acetonitrile
英文别名
3-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-oxopropanenitrile;2-Chlorobenzoylacetonitrile
CAS
40018-25-5
化学式
C9H6ClNO
mdl
MFCD00051624
分子量
179.606
InChiKey
SBSWHTFHLWSSQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:55-59 °C
-
沸点:302.2±22.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.2364 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
LogP:0.8 at 30℃
-
稳定性/保质期:
常规情况下不会分解,也没有任何危险反应。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.11
-
拓扑面积:40.9
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S22,S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R20/21/22,R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2926909090
-
危险品运输编号:3276
-
包装等级:III
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319
-
储存条件:密封、阴凉、干燥保存
SDS
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈 修改号码:6
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: (2-Chlorobenzoyl)acetonitrile
修改号码: 6
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
急性毒性(经口) 第4级
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 吞咽有害。
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 使用本产品时切勿吃东西,喝水或吸烟。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 食入:若感不适,呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈 修改号码:6
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-氯苯甲酰乙腈
百分比: >97.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 40018-25-5
俗名: 2'-Chloro-2-cyanoacetophenone
分子式: C9H6ClNO
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。冷冻储存。
存放处须加锁。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
热敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈 修改号码:6
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具,自携式呼吸器(SCBA),供气呼吸器等。使用通过政府标准的呼吸器。依
据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防渗手套。
眼睛防护: 护目镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防渗防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 极淡的黄色-灰黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 58°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 乙腈
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx), 氯化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈 修改号码:6
模块 12. 生态学信息
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: (2-Chlorobenzoyl)acetonitrile
修改号码: 6
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
急性毒性(经口) 第4级
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 吞咽有害。
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 使用本产品时切勿吃东西,喝水或吸烟。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 食入:若感不适,呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈 修改号码:6
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-氯苯甲酰乙腈
百分比: >97.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 40018-25-5
俗名: 2'-Chloro-2-cyanoacetophenone
分子式: C9H6ClNO
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。冷冻储存。
存放处须加锁。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
热敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈 修改号码:6
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具,自携式呼吸器(SCBA),供气呼吸器等。使用通过政府标准的呼吸器。依
据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防渗手套。
眼睛防护: 护目镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防渗防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 极淡的黄色-灰黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 58°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 乙腈
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx), 氯化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
2-氯苯甲酰乙腈 修改号码:6
模块 12. 生态学信息
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 邻氯苯乙酮 1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethanone 2142-68-9 C8H7ClO 154.596 (2-氯苯基)-氧代乙腈 2-chlorobenzoyl cyanide 35022-42-5 C8H4ClNO 165.579 2-溴-2'-氯苯乙酮 2-chlorophenacyl bromide 5000-66-8 C8H6BrClO 233.492 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 邻氯苯乙酮 1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethanone 2142-68-9 C8H7ClO 154.596 —— 3-(2-chloro-phenyl)-3-oxo-propionamide —— C9H8ClNO2 197.621 2,2-二氯-1-(2-氯苯基)乙酮 2,2-dichloro-1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethanone 24123-67-9 C8H5Cl3O 223.486 —— (E)-2-(2-chloro-benzoyl)-3-dimethylamino-acrylonitrile 52200-17-6 C12H11ClN2O 234.685 —— 2-bromo-3-(2-chloro-phenyl)-3-oxo-propionamide 1232234-28-4 C9H7BrClNO2 276.517 2-(2-氯苯甲酰基)-3,3-二(甲基硫代)丙烯腈 α-[bis(methylthio)methylene]-2-chloro-β-oxobenzenepropanenitrile 175137-51-6 C12H10ClNOS2 283.803 —— 3-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropanenitrile 84466-39-7 C9H8ClNO 181.622 —— (S)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropanenitrile —— C9H8ClNO 181.622 —— 2-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-phenylaminoacrylonitrile 836684-70-9 C16H11ClN2O 282.729
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:邻氯苯乙酰腈 在 N-氯代丁二酰亚胺 、 硫酸 、 potassium tert-butylate 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 水 为溶剂, 反应 4.0h, 生成 2,2-二氯-1-(2-氯苯基)乙酮参考文献:名称:β-酮酰胺的一锅二氯脱酰胺摘要:描述了一种通过酮裂解使伯-β-酮酰胺二氯化脱酰胺的方法,并且主要在TEMPO存在的情况下提供了一系列α,α-二氯酮。基于对照实验,提出了一种涉及串联二氯化和脱酰胺的机理来解释所观察到的反应性。DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.12.087
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:潜在的抗关节炎药。2.苯甲酰基乙腈和β-氨基肉桂腈。摘要:在大鼠佐剂性关节炎模型中,苯甲酰乙腈和β-氨基肉桂腈显示出有效的抗炎活性。在一系列苯基取代的类似物中,仅邻,间和对氟苯甲酰基乙腈以及间和对氟β-氨基肉桂腈保留了活性。另外,β-氨基-2-和β-氨基-3-噻吩丙烯腈以及β-氧代-2-和β-氧代-3-噻吩丙腈表现出相似的活性。不认为这些试剂通过前列腺素合成酶抑制起作用。还描述了苯甲酰基乙腈的代谢特征。DOI:10.1021/jm00197a020
-
作为试剂:描述:邻氯苯乙酰腈 、 4-(4-(isobutyl)phenyl)butanaldehyde 在 邻氯苯乙酰腈 作用下, 以70的产率得到2-amino-3-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-5-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)ethyl)thiophene参考文献:名称:Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 31, 683-692摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of Urea Derivatives as Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors作者:Gustav Boije af Gennäs、Luca Mologni、Shaheen Ahmed、Mohanathas Rajaratnam、Oriano Marin、Niko Lindholm、Michela Viltadi、Carlo Gambacorti-Passerini、Leonardo Scapozza、Jari Yli-KauhaluomaDOI:10.1002/cmdc.201100168日期:2011.9.5on the development of inhibitors for targeted therapy of these ALK‐positive tumors. Because kinase inhibitors that target the inactive conformation are thought to be more specific than ATP‐targeted inhibitors, we investigated the possibility of using two known inhibitors, doramapimod and sorafenib, which target inactive kinases, to design new urea derivatives as ALK inhibitors. We generated a homology在间变性大细胞淋巴瘤中,涉及间变性淋巴瘤激酶(ALK)激酶结构域的染色体易位通常与核磷蛋白基因的5'部分融合,会产生高度致癌的ALK融合蛋白,从而破坏这些细胞的细胞周期,凋亡和分化。细胞。最近在患有非小细胞肺癌,乳腺癌和结直肠癌的患者中发现了其他涉及ALK的融合癌蛋白,例如棘皮动物微管相关蛋白4-ALK。最近的研究集中在针对这些ALK阳性肿瘤的靶向治疗的抑制剂的开发上。由于靶向无活性构象的激酶抑制剂被认为比针对ATP的抑制剂更具特异性,因此我们研究了使用两种已知的靶向无活性激酶的抑制剂doramapimod和sorafenib的可能性,设计新的尿素衍生物作为ALK抑制剂。我们在其活性位点与多拉吡莫德或索拉非尼复合的非活性构象中生成了ALK的同源模型。结果阐明了为什么doramapimod是一种弱抑制剂,为什么sorafenib不抑制ALK。使用ALK的同源性模型对市售化合物进行的虚拟筛选产
-
Cu(II)‐Mediated C−C/C−O Bond Formation via C−H/C−C Bond Cleavage: Access to Benzofurans Using Amide as a Traceless Directing Group作者:Shuling Yu、Ningning Lv、Zhanxiang Liu、Yuhong ZhangDOI:10.1002/adsc.201901316日期:2020.1.7A copper‐mediated synthesis of 2,3‐disubstituted benzofurans with the assistance of an 8‐aminoquinolyl auxiliary is described from readily available benzamides and benzoylacetonitriles. In this reaction, the C−C bond is successfully constructed via C−H activation, and C−O bond is subsequently formed at the original position of the amide group in a one‐pot manner. The amide directing group is detached
-
Chlorophosphines as auxiliary ligands in ruthenium-catalyzed nitrile hydration reactions: application to the preparation of β-ketoamides作者:Rebeca González-Fernández、Pedro J. González-Liste、Javier Borge、Pascale Crochet、Victorio CadiernoDOI:10.1039/c5cy02142a日期:——heteroaryl or alkyl group). In the reaction medium, the coordinated chlorophosphines readily undergo hydrolysis to generate the corresponding phosphinous acids PR2OH, which are well-known “cooperative” ligands for this catalytic transformation. Among the complexes employed, best results were obtained with [RuCl2(η6-p-cymene)P(4-C6H4F)2Cl}]. Performing the catalytic reactions at 40 °C with 2 mol% of this腈成酰胺,在中性条件下的水的催化水合,已使用一系列芳烃-钌(的研究II含有市售chlorophosphines作为辅助配位体)配合物,即化合物将[RuCl 2(η 6 - p(-cymene) PR 2 Cl)](R =芳基,杂芳基或烷基)。在反应介质中,配位的氯膦易于水解生成相应的次膦酸PR 2 OH,次膦酸PR 2 OH是该催化转化的众所周知的“配合”配体。中所采用的复合物,用将[RuCl获得最好的结果2(η 6 - p-cymene)P(4-C 6 H 4 F)2 Cl}]。在40°C下用2 mol%的这种络合物进行催化反应,可以将各种有机腈以高收率和较短时间选择性地转化为相应的伯酰胺。的应用将[RuCl 2(η 6 - p -cymene)P(4-C 6 H ^ 4 F)2氯}]在合成有用β酮酰胺的制备也提出。
-
Copper‐Catalyzed Synthesis of Substituted 4‐Quinolones using Water as a Benign Reaction Media: Application for the Construction of Oxolinic Acid and BQCA作者:Babasaheb Sopan Gore、Chein Chung Lee、Jessica Lee、Jeh‐Jeng WangDOI:10.1002/adsc.201900286日期:2019.7.11−NO2, −SO2Ar, and −COAr were also successful. In addition, reaction with heterocyclic compounds such as 3‐(3‐bromothiophen‐2‐yl)‐3‐oxopropanenitrile proceeded smoothly to afford tetrahydrothieno[3,2‐b]pyridine‐6‐carbonitrile analogues. The practicality of the designed protocol was confirmed by gram scale synthesis of two derivatives.
-
Formal [3+2] Annulation of Copper‐Allenylidenes with 3‐Oxo‐3‐Arylpropanenitriles: Synthesis of Tetrasubstituted Furans作者:De Zhong、Feng Jiang、Siyong Shen、Lan Wang、Wei Wang、Yongjun Wu、Yumei Xiao、Hongchao GuoDOI:10.1002/adsc.202000929日期:2020.11.18The copper‐catalyzed decarboxylative [3+2] annulation of ethynyl benzoxazinanones with 3‐oxo‐3‐arylpropanenitriles has been developed, producing tetrasubstituted furan derivatives in moderate to high yield. This reaction was generally compatible with a wide range of substrates. Notably, the intermediate copper‐allenylidenes worked as a C2 synthon in the cycloaddition reaction.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
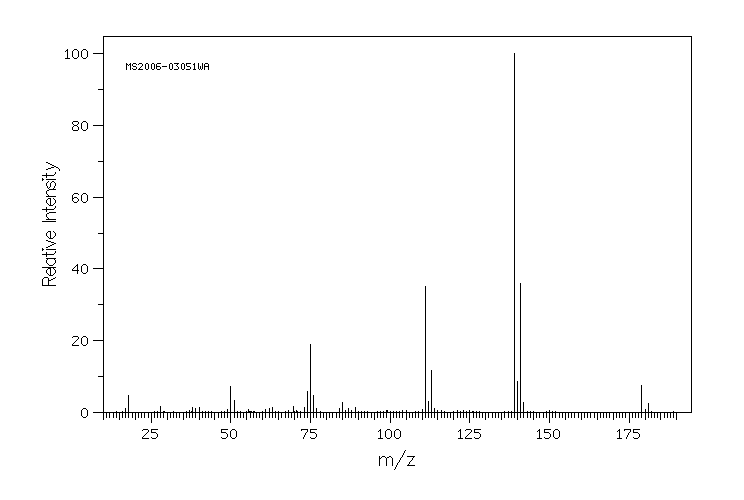
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
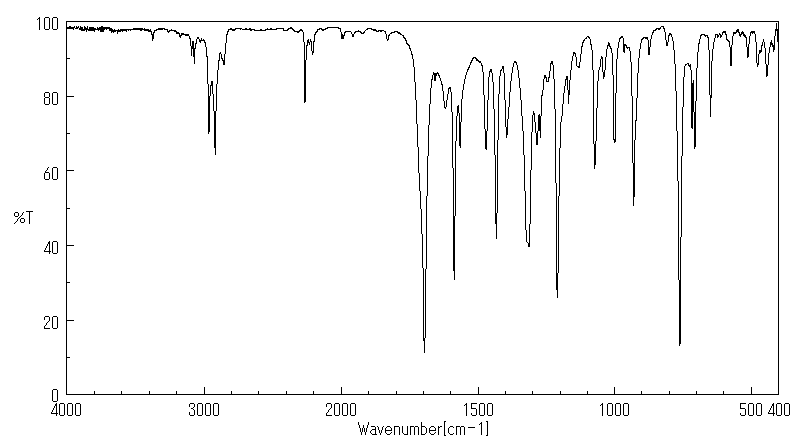
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷