对苯二酚 | 123-31-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:172-175 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:285 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.32
-
蒸气密度:3.81 (vs air)
-
闪点:165 °C
-
溶解度:在水中的溶解度50 mg/mL,澄清
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: 15-min ceiling 2, IDLH 50; OSHA PEL: TWA 2; ACGIH TLV: TWA 2 (adopted).
-
LogP:0.59 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Hydroquinone appears as light colored crystals or solutions. May irritate the skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Mildly toxic by ingestion or skin absorption.
-
颜色/状态:White crystals
-
气味:Odorless
-
味道:A slightly bitter taste in aqueous solutions
-
蒸汽密度:3.81 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1.9X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
可燃,在空气中见光容易变成褐色,碱性溶液中氧化更快。
-
中等毒性。在动物实验中,反复给予30-50毫克/千克剂量可引起急性黄色肝萎缩,除了严重损伤肾脏外,并能导致异常的色素沉着。因此,有时用它涂在人体局部可以去除雀斑。服用1克对苯二酚会引起食道刺激,产生耳鸣、恶心、呕吐、腹痛和虚脱;服用5克则可致死。此外,长期接触对二苯酚蒸气、粉尘或烟雾会刺激皮肤、黏膜,并可能引起眼水晶体浑浊。操作现场空气中最高允许浓度为2毫克/立方米。生产设备应封闭,操作人员需穿戴好防护用具。
-
在动物试验中,反复给予30~50毫克/千克剂量时,则可引起急性黄色肝萎缩,除了导致严重的肝损伤外,并能引发异常的色素沉着。服用1克本品时,会刺激食道,引起耳鸣、恶心、呕吐、腹痛和虚脱;服用5克则可能致死。
-
氢醌有毒且可燃。氢醌还原性很强,极易被氧化成对苯醌。氢醌可通过皮肤引起中毒。动物经口致死量为0.08~0.2克/千克。人若口服1克以上会出现急性中毒症状;59克则可能致命。
-
稳定。
-
禁配物:酰基氯、酸酐、碱、强氧化剂、强酸。
-
避免接触的条件:光照、空气接触。
-
聚合危害:不会聚合。
-
-
自燃温度:960 °F (516 °C)
-
燃烧热:-2.74X10+3 kJ/mol
-
电离电位:7.95 eV
-
折光率:Index of refraction = 1.632 at 25 °C
-
解离常数:pKa = 10.85 at 25 °C
-
碰撞截面:128.79 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: stepped-field]
-
保留指数:1334;1327;1334
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.6
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:40.5
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露限值:Ceiling: 2 mg/m3 [15-minute]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:9
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:50 mg/m3
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39,S61
-
危险类别码:R40,R43,R22,R68,R50,R41
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2907221000
-
危险品运输编号:2662
-
危险类别:9
-
RTECS号:MX3500000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS05,GHS07,GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H302,H317,H318,H341,H351,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P273,P280,P305 + P351 + P338 + P310,P308 + P313
-
储存条件:1. 采用聚乙烯塑料袋包装,每袋5kg,4袋装一木箱;或使用圆木箱内衬塑料袋包装,每桶50kg。应存放在阴凉、干燥处,避免日光直射和潮湿,防潮并注意防热。根据有毒物品的规定进行运输与储存。 2. 储存时请注意:存放于阴凉且通风良好的仓库中,并远离火源和热源。包装需密封,确保不与空气接触。应将该物质与其他氧化剂、酸类、碱类及食用化学品分开存放,避免混合存储。同时配备相应的消防设备,并在储区准备合适材料以处理泄漏情况。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61725 |
| CAS: | 123-31-9 |
| 中文名称: | 1,4-苯二酚 |
| 英文名称: | p-Dihydroxybenzene;p-Hydroquinone |
| 别 名: | 对苯二酚;氢醌 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 6 O 2 ;HOC 6 H 4 OH |
| 分子量: | 110.11 |
| 熔 点: | 170.5℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.33; |
| 蒸汽压: | 165℃ |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水,易溶于乙醇、乙醚 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色结晶 |
| 危险标记: | 15(毒害品) |
| 用 途: | 制取黑白显影剂、蒽醌染料、偶氮染料、橡胶防老剂、稳定剂和抗氧剂 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。 健康危害:毒性比酚大,对皮肤、粘膜有强烈的腐蚀作用,可抑制中枢神经系统或损害肝、皮肤功能。 急性中毒:吸入高浓度蒸气,可致头痛、头昏、乏力、视物模糊、肺水肿等;误服可出现头痛、头晕、耳鸣、苍白、紫绀、恶心、呕吐、腹育、呼吸困难、心动过速、尺厥、谵妄和虚脱 ,严重者呕血、血尿、溶血性黄疸,甚至可致死。 慢性影响:长期低浓度吸入,可致头痛、头晕、咳嗽、食欲减退、恶心、呕吐等。皮肤可引起皮炎。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
急性毒性:LD50 320mg/kg(大鼠经口);人经口5000mg/kg,死亡。 刺激性:人经皮:250mg (24小时),轻度刺激。 亚急性和慢性毒性:动物亚急性中毒表现为溶血性黄疸、贫血、白细胞增多、红细胞脆性增加、低血糖、皮毛无光泽和明显的恶病质。 致突变性:微生物致突变性:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌2umol/皿。微核试验:人淋巴细胞75umol/L。性染色体缺失和不分离:人淋巴细胞6mg/kg。DNA损伤:人骨髓500mol/L。 生殖毒性:大鼠经口最低中毒剂量(TDL0):2500mg/kg(孕1~22天),致植入后的死亡率(51天,雄性),影响睾丸、附睾、输精管、前列腺、精囊等,对雄性生育指数有影响。 致癌性:IARC致癌性评论:动物不明确,人类无可靠数据。
危险特性:遇明火、高热可燃。与强氧化剂可发生反应。受高热分解放出有毒的气体。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法,参照《分析化学手册》(第四分册,色谱分析),化学工业空气中:样品经滤器收集后,用酸洗脱,再用高压液相色谱法测定(NIOSH法)高效液相色谱法测定焦化废水中的酚类化合物[刊]/张万让等//新疆环境保护1989,(1).-49~52
5.环境标准:
| 前苏联(1975) | 作业环境空气中有害物质的允许浓度 | 2mg/m 3 |
| 前苏联(1978) | 地面水中最高容许浓度 | 0.2mg/L |
| 前苏联(1975) | 污水排放标准 | 0.5mg/L |
| 水中嗅觉阈浓度 | 5mg/L |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警标志,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,避免扬尘,用清洁的铲子收集于干燥净洁有盖的容器中,运至废物场所。也可以用大量水冲洗,经稀释的洗水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 废弃物处置方法:用焚烧法。焚烧炉排出的气体通过洗涤器除去有害成份。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:空气中浓度超标时,必须佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带自给式呼吸器。 眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。 防护服:穿相应的防护服。 手防护:戴防化学品手套。 其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,彻底清洗。单独存入被毒物污染的衣服,洗后再用。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去污染的衣着,用甘油、聚乙烯乙二醇或聚乙烯乙二醇和酒精混合液(7:3)抹擦。然后用水彻底冲洗。或立即用水冲洗至少15分钟。就医。 眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗至少15分钟。就医。 吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 食入:患者清醒时立即给饮植物油15~30ml。催吐,尽快彻底洗胃。就医。
废弃物处置方法:用焚烧法。焚烧炉排出的气体通过洗涤器除去有害成份。
制备方法与用途
对苯二酚又称氢醌或1.4-苯二酚,分子式C6H6O2,分子量为110.11。无色或白色结晶,在空气中暴露易变色;其水溶液在空气中能氧化成褐色,碱性介质中氧化速度更快。熔点为170~171℃,沸点为285~287℃,相对密度为1.33215,在水中UVλmax为288nm。对苯二酚易溶于热水、乙醇及乙醚,微溶于苯。它化学性质活泼,容易被氧化,并可发生酯化和取代等反应。
用途对苯二酚是一种重要的有机显影剂,需在较强碱性溶液中才能发挥作用。其还原速度较米吐尔缓慢,但影像一旦显现,则密度增长迅速,能获得较大反差。27~29℃温度下显影最快,低于15℃时变缓,低于5℃则几乎停止。多用可使照片产生暖色调。主要用于普通照相显影剂、物理显影及再显影还原剂,并常与菲尼酮和米吐尔混合使用。
用途对苯二酚是除草剂喹禾灵、吡氟禾草灵、噻唑禾草灵、噁唑禾草灵、氟吡氯禾草灵、乳氟禾草灵的中间体,也是医药和染料中间体。对苯二酚及其烷基化物广泛用作单体贮运过程中的阻聚剂,常用浓度约为200ppm。对苯二酚一甲醚是食用油抗氧剂BHA的中间体;对苯二酚二甲醚用作染料、有机颜料和香料的中间体;而对苯二酚二乙醚则用于制备感光色素及染料,还用于合成N,N'-二苯基对苯二胺,后者是橡胶及汽油的抗氧剂和抗臭剂。
用途除了上述应用,对苯二酚还可用于比色法测定磷、镁、铌、铜、硅和砷等元素;在铱的极谱法和容量法中测定其含量;作为杂多酸的还原剂;铜和金的还原剂;检验磷酸盐、钨酸盐、硝酸盐、亚硝酸盐、硒和碲等物质;用作显影剂及抗氧剂,用于化肥工业中的脱硫剂以及尿素增效剂。
生产方法对苯二酚传统上采用苯胺法生产,但目前工业上还发展了邻苯二酚联产法、异丙苯法和双酚A法。我国当前主要使用苯胺法进行工业化生产。具体步骤如下:首先在硫酸介质中用二氧化锰氧化苯胺生成对苯醌;然后经铁粉还原产生对苯二酚,随后通过浓缩、脱色、结晶及干燥工序最终制得成品。工业级对苯二酚含量需≥99%,而照相级的则要求≥99.5%。
生产方法 类别有毒物品
- 毒性分级:高毒
-
急性毒性
- 大鼠口服LD50: 320 毫克/公斤;
- 小鼠口服LD50: 245 毫克/公斤
-
刺激数据
- 皮肤接触(人):5%浓度导致重度刺激
可燃性危险特性
- 明火下可燃,遇氧化剂或氢氧化钠反应;燃烧时释放出刺激性烟雾
储运特性
- 应存放在通风、低温和干燥的仓库中
- 须与氧化剂及食品添加剂分开存放
使用二氧化碳、泡沫灭火器、干粉灭火器、砂土或雾状水进行扑灭。
职业健康标准- 时间加权平均浓度(TWA):2 毫克/立方米
- 短时间接触极限(STEL):4 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 苯酚 phenol 108-95-2 C6H6O 94.113 间苯二酚 recorcinol 108-46-3 C6H6O2 110.112 邻苯二酚 benzene-1,2-diol 120-80-9 C6H6O2 110.112 4-甲氧基苯酚 4-methoxy-phenol 150-76-5 C7H8O2 124.139 对苯二甲醚 1,4-dimethoxybezene 150-78-7 C8H10O2 138.166 1,2,4-苯三酚 1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene 533-73-3 C6H6O3 126.112 —— O-phenylhydroxylamine 4846-21-3 C6H7NO 109.128 苯甲醚 methoxybenzene 100-66-3 C7H8O 108.14 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 苯酚 phenol 108-95-2 C6H6O 94.113 4-甲氧基苯酚 4-methoxy-phenol 150-76-5 C7H8O2 124.139 对苯二甲醚 1,4-dimethoxybezene 150-78-7 C8H10O2 138.166 1,2,4-苯三酚 1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene 533-73-3 C6H6O3 126.112 1,2,4,5-四羟基苯 1,2,4,5-benzenetetrol 636-32-8 C6H6O4 142.111 苯甲醚 methoxybenzene 100-66-3 C7H8O 108.14
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Sarauw, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1881, vol. 209, p. 109摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Goldberg, Journal fur praktische Chemie (Leipzig 1954), 1879, vol. <2> 19, p. 362,378摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:1-(2-氯乙基)-1H-吡唑 在 (1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride 、 癸二酸 、 溴 、 potassium acetate 、 potassium carbonate 、 对苯二酚 、 sodium iodide 、 sodium hydroxide 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 1,4-二氧六环 、 二氯甲烷 、 水 为溶剂, 反应 25.0h, 生成参考文献:名称:SALT-INDUCIBLE KINASES (SIK) INHIBITORS AND METHODS OF USES THEREOF摘要:The disclosure provides for compounds, compositions, and methods for modulating or inhibiting SIK.公开号:WO2024104441A1
文献信息
-
Additives and products including oligoesters申请人:——公开号:US20030199593A1公开(公告)日:2003-10-23The present invention relates to oligoesters and their use or the creation of additives. Oligoester containing additives and/or oligoesters themselves may be used for formulating pharmaceutical preparations, cosmetics or personal care products such as shampoos and conditioners. These oligoesters are particularly useful for the creation of multi-purpose additives that can impart conditioning, long substantivity and/or UV protection. Individual oligoesters and oligoester mixtures are described.本发明涉及寡酯及其用途或添加剂的制备。含有寡酯的添加剂和/或寡酯本身可用于配制药物制剂、化妆品或个人护理产品,如洗发水和护发素。这些寡酯对于制备能够赋予调理、长效性和/或紫外线保护的多功能添加剂特别有用。描述了单独的寡酯和寡酯混合物。
-
Deoxygenation of Polyhydroxybenzenes: An Alternative Strategy for the Benzene-Free Synthesis of Aromatic Chemicals作者:Chad A. Hansen、J. W. FrostDOI:10.1021/ja0176346日期:2002.5.1e requires 2 enzyme-catalyzed and 2 chemical steps. By contrast, synthesis of hydroquinone using the shikimate pathway and intermediacy of quinic acid requires 18 enzyme-catalyzed steps and 1 chemical step. Methylation of triacetic acid lactone, cyclization, and regioselective deoxygenation of phloroglucinol methyl ether affords resorcinol. Given the ability to synthesize triacetic acid lactone from在葡萄糖和芳香族化学品(如连苯三酚、对苯二酚和间苯二酚)之间建立了新的合成联系。这种方法的核心是从 1,2,3,4-四羟基苯、羟基氢醌和间苯三酚甲基醚中去除一个氧原子,分别形成连苯三酚、氢醌和间苯二酚。脱氧是通过起始多羟基苯的 Rh 催化氢化,然后是推定的二氢中间体的酸催化脱水来完成的。连苯三酚合成包括将葡萄糖转化为肌醇,氧化为肌 2-肌糖,脱水为 1,2,3,4-四羟基苯,以及脱氧形成连苯三酚。通过 myo-2-inosose 合成连苯三酚需要 4 个酶催化和 2 个化学步骤。为了比较,通过没食子酸中间体和莽草酸途径从葡萄糖合成连苯三酚需要至少 20 个酶催化步骤。一种新的对苯二酚的无苯合成采用将葡萄糖转化为 2-脱氧青蟹肌糖,将该肌糖脱水为羟基氢醌,然后脱氧形成对苯二酚。通过 2-脱氧青蟹肌糖合成氢醌需要 2 个酶催化和 2 个化学步骤。相比之下,使用莽草酸途径和奎尼酸中间体合成对苯二酚需要
-
[EN] PREPARATION AND USES OF REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES SCAVENGER DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] PRÉPARATION ET UTILISATIONS DE DÉRIVÉS PIÉGEURS D'ESPÈCES RÉACTIVES DE L'OXYGÈNE申请人:XW LAB INC公开号:WO2019033330A1公开(公告)日:2019-02-21Compounds of Formula (I) a or (I) b: including certain quinone derivatives, and the corresponding pharmaceutical compositions, which may serve to modulate ferroptosis in a subject. Also disclosed herein are the preparations of these compounds and pharmaceutical compositions and their potential uses in the manufacture of a medicament in reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a cell and for preventing, treating, ameliorating certain related disorder or a disease.
-
New Drug Delivery System for Crossing the Blood Brain Barrier申请人:Lipshutz H. Bruce公开号:US20070203080A1公开(公告)日:2007-08-30New ubiquinol analogs are disclosed, as well as methods of using these compounds to deliver drug moieties to the body.新的泛醌类似物被披露,以及利用这些化合物将药物基团输送到人体的方法。
-
Efficient synthesis of α-substituted-α-arylmethyl phosphonates using trichloroacetimidate C C coupling method作者:Walid Fathalla、Pavel Pazdera、Samir El-Rayes、Ibrahim.A.I. AliDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2018.02.033日期:2018.4A simple convenient protocol for the synthesis of diethyl α,α-diaryl methylphosphonate derivatives 5a-f, 6b-f, 7a-f and 8a-f, diethyl α-alkenyl α-aryl methylphosphonates 9a-d and 10a-d and α-(oxoalkyl) α-aryl methylphosphonate 11a-d and 12a-d is described. Trichloroacetimidates 3a-d were treated with activated arenes, styrene, allyltrimethylsilane or silylenol ethers C-nucleophiles in the presence
表征谱图
-
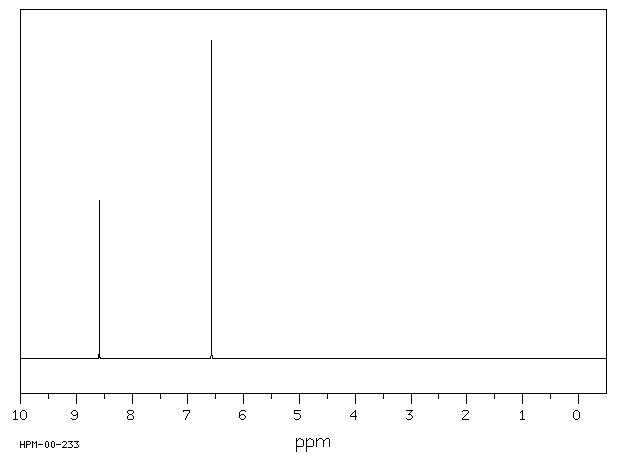
氢谱1HNMR
-
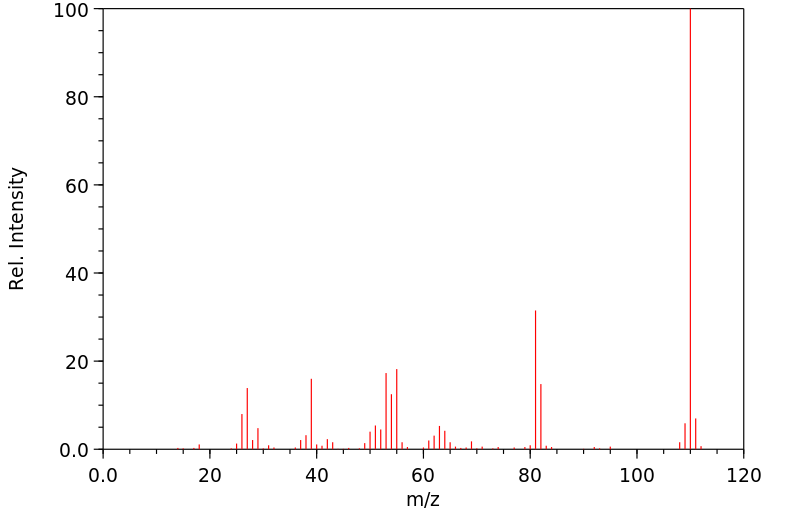
质谱MS
-
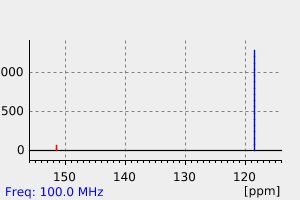
碳谱13CNMR
-
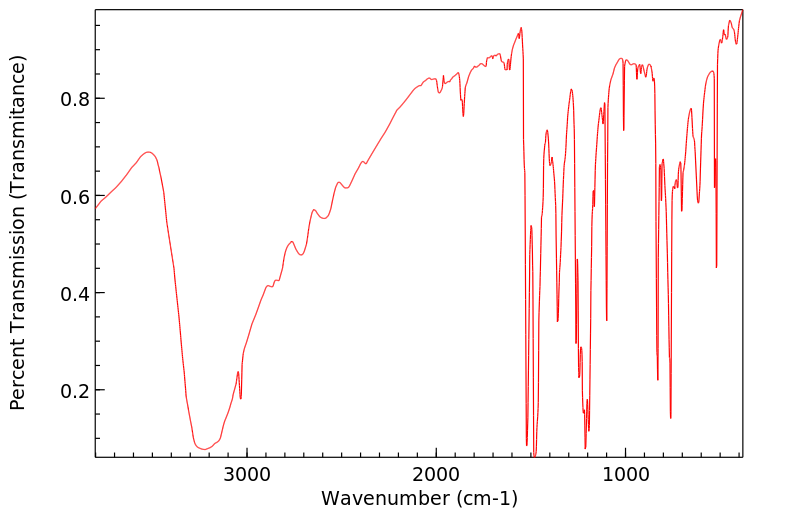
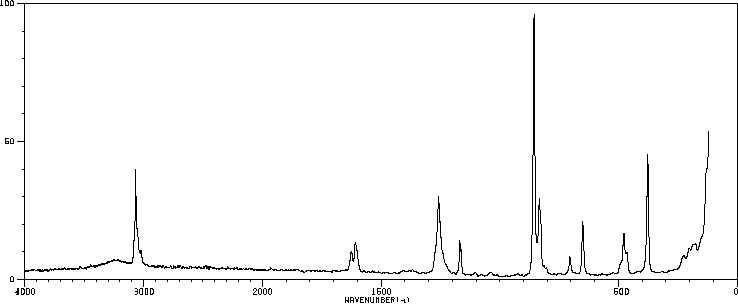
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息