氯乙酸 | 79-11-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:63 °C
-
沸点:189 °C
-
密度:1.4043 g/cm3(Temp: 40 °C)
-
物理描述:Chloroacetic acid, solid is a colorless to light-brown crystalline material. It is soluble in water and sinks in water. Combustible. It is transported as a molten liquid and therefore can cause thermal burns. It is toxic by ingestion, skin absorption and inhalation of dust. It is corrosive to metals and tissue.
-
颜色/状态:Monoclinic prisms
-
气味:Strong vinegar-like odor
-
闪点:259 °F (126 °C) (Closed cup)
-
溶解度:In water, 8.58X10+5 mg/L at 25 °C
-
蒸汽密度:3.26 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:6.5X10-2 mm Hg (8.68X10-3 kPa) at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:9.26e-09 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
具有很强的腐蚀性,能腐蚀皮肤,破坏所有非贵重金属、橡胶和木材等。酸性比醋酸强。无色或淡黄色结晶,带有刺激性气味,容易吸湿。它溶于水和乙醇、乙醚等多种有机溶剂。
-
氯乙酸非常活泼,酸性强于乙酸(Ka=1.4×10^-3)。其乙醇溶液在紫外线照射下会分解为甲醇、乙醛和氯化氢。氯乙酸及其碱金属盐中的氯原子容易在水溶液中被取代。当氯乙酸在回流的水溶液中时,它逐渐发生水解生成乙醇酸;若存在碱性物质,则会加速这一过程。该化合物与氨、胺、肼或苯酚反应时能生成相应的α-取代乙酸,并且容易与各种醇作用形成酯类。氯乙酸还能够与磷酰氯反应生成酰氯化合物,同时在碘的存在下进行氯化反应可生成二氯乙酸和三氯乙酸。
-
氯乙酸稳定。
-
避免接触强氧化剂、强碱或强还原剂。
-
应避免潮湿空气的环境。
-
不会发生聚合。
-
-
自燃温度:>932 °F (>500 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions: Carbon oxides, hydrogen chloride gas.
-
腐蚀性:...extremely corrosive and will cause serious chemical burns.
-
燃烧热:-715.9 kJ/mol (alpha-chloroacetic acid)
-
汽化热:250 Btu/Lb = 139 cal/g = 5.82X10+5 J/kg
-
表面张力:35.17 dyn/cm at 100 °C
-
气味阈值:0.01 ppm, 0.042 mg/cu m
-
解离常数:pKa = 2.87
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.2
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1
-
安全说明:S16,S23,S26,S36,S37,S45,S61
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1751 6.1/PG 2
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29154000
-
危险类别:6.1
-
危险品标志:T
-
危险类别码:R34,R25,R50
-
RTECS号:AF8575000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风良好的专用库房内,并实行“双人收发、双人保管”制度。 - 远离火种和热源,库温不超过32℃,相对湿度不超过80%。 - 包装应密封。 - 应与氧化剂、还原剂、碱类及食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。 - 配备相应的消防器材。 - 储存区应备有合适的材料以收容泄漏物。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 81603 |
| CAS: | 79-11-8 |
| 中文名称: | 氯乙酸 |
| 英文名称: | Chloroacetic acid;Monoehloroac |
| 别 名: | 氯醋酸;一氯醋酸 |
| 分子式: | C 2 H 3 Cl 2 O;ClCH 2 COOH |
| 分子量: | 94.49 |
| 熔 点: | 63℃ 沸点:189℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.58; |
| 蒸汽压: | 0.67kPa/71.5℃ 闪点:126℃ |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水、乙醇、乙醚、氯仿、二硫化碳 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色结晶,有潮解性 |
| 危险标记: | 20(酸性腐蚀品) |
| 用 途: | 用于制农药和作有机合成中间体 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:接触氯乙酸烟雾,可有眼部疼痛、流泪、羞明、结膜充血等症状及上呼吸道刺激症状。皮肤接触本品溶液后,出现水疱伴有剧痛,随后,水疱吸收,出现过度角化,经数次脱皮治愈。经常接触本品酸雾者有头痛、头晕现象。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属中等毒类。
急性毒性:LD 50 76mg/kg(大鼠经口);255mg/kg(小鼠经口)LC 50 180mg/m 3 (大鼠吸入)
亚急性和慢性毒性:大鼠饲料中含1%的氯乙酸时,在200天实验期内,生长缓慢,发现肝糖元增加,其它无特殊损害。
危险特性:遇明火、高热可燃。与强氧化剂可发生反应。受高热分解产生有毒的腐蚀性气体。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢、光气。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
液-液萃取气相色谱法《水和废水标准检验法》(20版)
5.环境标准:
前苏联 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 1mg/m 3
前苏联(1975)污水排放标准 100mg/L
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
隔离泄漏污染区,限制出入。建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿防酸碱工作服。不要直接接触泄漏物,用洁清的铲子收集于干燥净洁有盖的容器中,运至废物处理场所。也可以用大量水冲洗,经稀释的洗水放入废水系统。大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其烟雾时,应该佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿工作服(防腐材料制作)。
手防护:戴橡皮手套。
其它:工作后,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即用水冲洗至少15分钟。若有灼伤,就医治疗。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗至少15分钟。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者立即漱口,给饮牛奶或蛋清。就医。
灭火方法:雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、砂土。
制备方法与用途
工业生产氯乙酸主要有三种主要方法。
-
乙酸氯化法:在碘、磷、硫或磷和硫的卤化物等催化剂存在下,用氯气将乙酸直接氯化而得。除生成氯乙酸外,还有深度氯化的副产物如二氯乙酸、三氯乙酸。此方法原料消耗较低,工艺简单,氯乙酸产率可达92%。
-
三氯乙烯水合法:以93%的硫酸为催化剂,在约160-180℃下反应。这种方法可得高纯度的氯乙酸,产率可达90%,但副产盐酸较多。
-
氯乙醇氧化法:在60℃用60%的硝酸氧化,收率超过90%。北美洲以乙酸氯化法为主,西欧则偏爱三氯乙烯水合法。我国采用乙酸氯化法生产:将定量的冰醋酸加入反应锅中,并以冰醋酸重量的3.5%硫黄粉作为催化剂进行预热至90℃以上,开始通入适量氯气,两只反应锅串联通氯,主锅控制温度为98±2℃,副锅为85-90℃。通氯速度约70kg/h,待反应锅内物料的相对密度达到1.350(80℃)时即到达终点。将反应物抽至酸罐,冷却结晶。液相包括少量乙酸、二氯乙酸、氯化硫和少量氯乙酸,分离出结晶体后,在38℃以下把母液抽尽即可得到成品。每吨产品约产生150公斤母液,可进一步氯化制成二氯乙酸、二氯乙酸甲酯及氯仿。三氯乙烯水合法同时进行水的加成和水解:反应温度160-180℃,保持硫酸浓度在93%,控制三氯乙烯与水的比例。硫酸消耗不超过50kg,副产30%盐酸2.57吨。工业品氯乙酸为无色或略带淡黄色结晶体。原料消耗定额:冰醋酸(98%)730kg/t、氯气860kg/t、硫磺26kg/t。
经过上述方法之一制备的氯乙酸可通过精制进一步纯化,通常使用氯仿、四氯化碳、苯或水进行重结晶。然后将产物放入真空干燥器中用五氧化二磷或浓硫酸干燥,并在真空或干燥氮气中储存。
合成制备方法-
工业生产氯乙酸的主要方法:
- 采用碘、磷、硫或磷和硫的卤化物等催化剂,通过氯气将乙酸直接氯化而得。副产物包括二氯乙酸及三氯乙酸。
- 使用93%硫酸为催化剂,在160-180℃下进行三氯乙烯水合法,可获得高纯度的氯乙酸,产率可达90%,但会产生较多盐酸。
- 在60℃用60%硝酸氧化法生成氯乙醇,其收率超过90%。此方法在北美洲以乙酸氯化法为主,在西欧则偏好三氯乙烯水合法。我国使用乙酸氯化法制备:将冰醋酸加入反应锅并添加3.5%的硫黄粉作为催化剂进行预热至90℃以上,开始通入适量氯气。主锅控制温度为98±2℃,副锅保持在85-90℃,通氯速度约70kg/h。待物料密度达到1.350(80℃)时即完成反应。随后将反应物抽至酸罐冷却结晶分离出结晶体,并在38℃以下抽尽母液获得成品。
这些方法中的每一种都有其特定的优势和应用领域,具体选择哪种方法取决于实际生产条件与需求。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 二氯乙酸 dichloro-acetic acid 79-43-6 C2H2Cl2O2 128.943 氯乙酸甲酯 methyl chloroacetate 96-34-4 C3H5ClO2 108.525 溶剂黄146 acetic acid 64-19-7 C2H4O2 60.0526 一溴一氯乙酸 bromochloroacetic acid 5589-96-8 C2H2BrClO2 173.394 三氯乙酸 trichloroacetic acid 76-03-9 C2HCl3O2 163.388 氯乙酸乙酯 chloroacetic acid ethyl ester 105-39-5 C4H7ClO2 122.551 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 二氯乙酸 dichloro-acetic acid 79-43-6 C2H2Cl2O2 128.943 氯乙酸甲酯 methyl chloroacetate 96-34-4 C3H5ClO2 108.525 —— 2-chloro-O-deuterio-acetic acid 1837-59-8 C2H3ClO2 95.4897 溶剂黄146 acetic acid 64-19-7 C2H4O2 60.0526 一溴一氯乙酸 bromochloroacetic acid 5589-96-8 C2H2BrClO2 173.394 三氯乙酸 trichloroacetic acid 76-03-9 C2HCl3O2 163.388 氯乙酸乙酯 chloroacetic acid ethyl ester 105-39-5 C4H7ClO2 122.551
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Panizzon, Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1932, vol. 15, p. 1191摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Synthesis of Monochloroacetic Acid from Ethylene Chlorohydrin摘要:The possibility of preparing monochloroacetic acid by oxidation of ethylene chlorohydrin with nitric acid was examined.DOI:10.1023/b:rjac.0000012682.03958.d4
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:10.1016/j.bmcl.2024.129857摘要:DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2024.129857
文献信息
-
腈及其相应胺的制造方法申请人:中国石油化工股份有限公司公开号:CN104557610B公开(公告)日:2018-04-27本发明涉及一种腈的制造方法,与现有技术相比,具有氨源用量显著降低、环境压力小、能耗低、生产成本低、腈产物的纯度和收率高等特点,并且能够获得结构更为复杂的腈。本发明还涉及由该腈制造相应胺的方法。
-
Allenone-Mediated Racemization/Epimerization-Free Peptide Bond Formation and Its Application in Peptide Synthesis作者:Zhengning Wang、Xuewei Wang、Penghui Wang、Junfeng ZhaoDOI:10.1021/jacs.1c04614日期:2021.7.14peptide synthesis (SPPS). The robustness of the allenone-mediated peptide bond formation was showcased incisively by the synthesis of carfilzomib, which involved a rare racemization-/epimerization-free N to C peptide elongation strategy. Furthermore, the successful synthesis of the model difficult peptide ACP (65–74) on a solid support suggested that this method was compatible with SPPS. This method combines
-
안트라센 유도체 화합물 및 이를 포함하는 유기전계발광소자申请人:SFC CO., LTD. 에스에프씨 주식회사(120060087061) Corp. No ▼ 135511-0105889BRN ▼134-81-54429公开号:KR102121583B1公开(公告)日:2020-06-10본 발명은 신규한 유기전계발광 화합물에 관한 것으로서, 하기 [화학식 1] 내지 [화학식 2]로 표시되는 화합물인 것을 특징으로 하고, 본 발명에 따른 유기전계발광 화합물은 높은 유리전이온도를 가져서 열적 안정성이 우수함과 동시에 이를 유기전계발광소자에 채용시 저전압 구동, 고휘도, 고색순도 및 장수명을 나타내는 유기전계발광소자의 구현이 가능하다. [화학식 1] [화학식 2]
-
Rational design, synthesis and evaluation of new azido-ester structures as green energetic plasticizers作者:Nasser Sheibani、Narges Zohari、Reza Fareghi-AlamdariDOI:10.1039/d0dt02250k日期:——Computer-aided molecular design (CAMD) is a well-known tool for the theoretical assessment of chemical structures before their experimental synthesis. In this study, we used this method to consider the important criteria for a chemical structure as an energetic plasticizer for an energetic azido binder. The number of new azido-ester structures were initially designed, and their physicochemical and计算机辅助分子设计(CAMD)是在化学合成实验之前对化学结构进行理论评估的著名工具。在这项研究中,我们使用这种方法来考虑化学结构作为高能叠氮基粘合剂的高能增塑剂的重要标准。新叠氮基酯结构的数量最初设计,并测定其物理化学和能量性质通过通过分子动力学模拟和基于机器学习的方法进行理论计算。考虑到几个标准之间的平衡,然后选择,合成和表征了这些理论化学结构中的两个(包括GTAA(甘油三(叠氮基乙酸酯))和TEGBAA(三乙二醇双(叠氮基乙酸酯))。实验和理论结果的比较,以评估这些新型叠氮基酯增塑剂的理化性质,表明两种方法之间可以接受。最后,使用流变学和DSC分析研究了这两种新型叠氮基酯增塑剂对缩水甘油叠氮化物聚合物(GAP)的流变学和热学性能的相容性和效率,并与一些常见的高能增塑剂进行了比较。
-
[EN] PROCESSES FOR THE PREPARATION OF FUNGICIDAL COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] PROCÉDÉS DE PRÉPARATION DE COMPOSÉS FONGICIDES申请人:GILEAD APOLLO LLC公开号:WO2018161008A1公开(公告)日:2018-09-07Provided herein are processes for the preparation of stereomerically enriched compounds of Formulas I-014, I-020, I-064, I-074, I-082, I-089, I-090, I-095, I-171, I-181, I-184, I-186, I-189, I-191, I-192, I-193, I-205, I-206, I-208, I-211, I-212, I-213, I-220, I-229, I-231, I-233, I-234, I-246, I-251, I-258, I-259, I-262, I-263, I-285, I-323 and I-400. The compounds described herein exhibit activity as pesticides and are useful, for example, in methods for the control of fungal pathogens and diseases caused by fungal pathogens in plants. A preferred process is directed to preparing a stereomerically enriched compound of Formula V-1 or V-2-F by assymetrical reduction in the presence of a chiral organometallic catalyst.本文提供了制备具有I-014、I-020、I-064、I-074、I-082、I-089、I-090、I-095、I-171、I-181、I-184、I-186、I-189、I-191、I-192、I-193、I-205、I-206、I-208、I-211、I-212、I-213、I-220、I-229、I-231、I-233、I-234、I-246、I-251、I-258、I-259、I-262、I-263、I-285、I-323和I-400的立体富集化合物的方法。本文描述的化合物表现出作为杀虫剂的活性,并且在例如用于控制植物中由真菌病原体引起的真菌病害的方法中是有用的。一种首选的方法是通过在手性有机金属催化剂存在下进行不对称还原来制备具有V-1或V-2-F式的立体富集化合物。
表征谱图
-
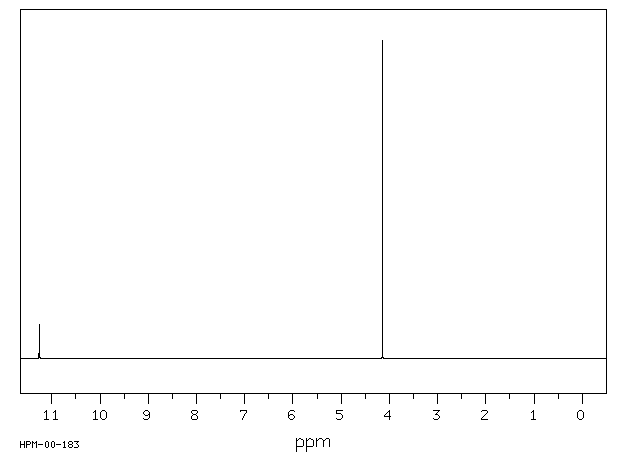
氢谱1HNMR
-
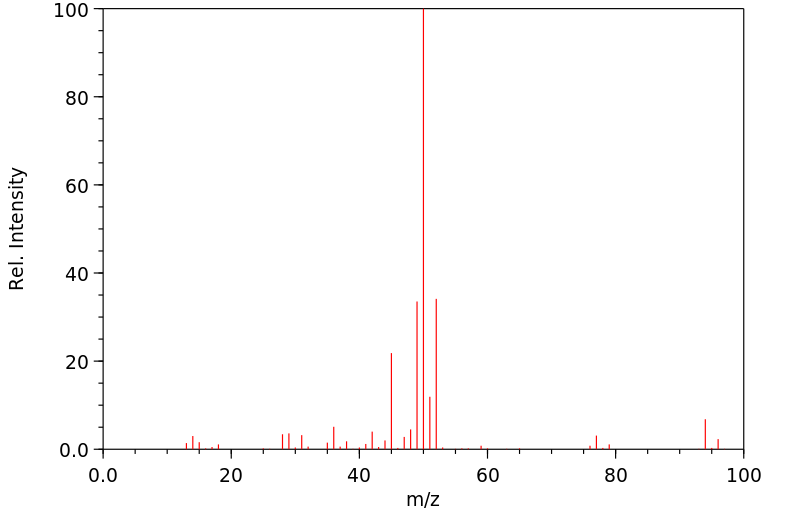
质谱MS
-
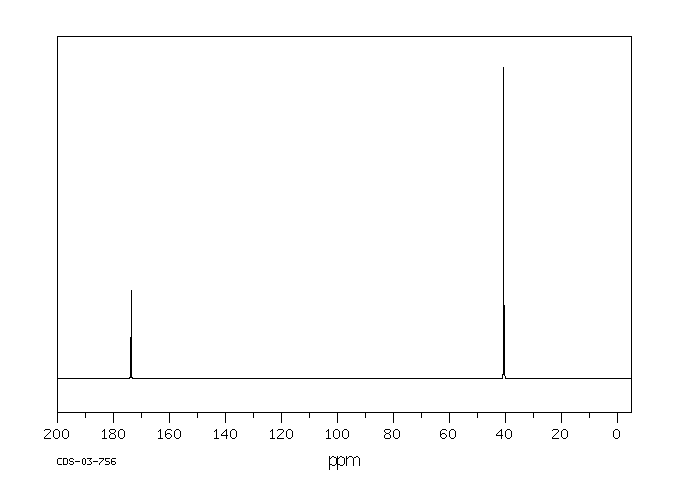
碳谱13CNMR
-
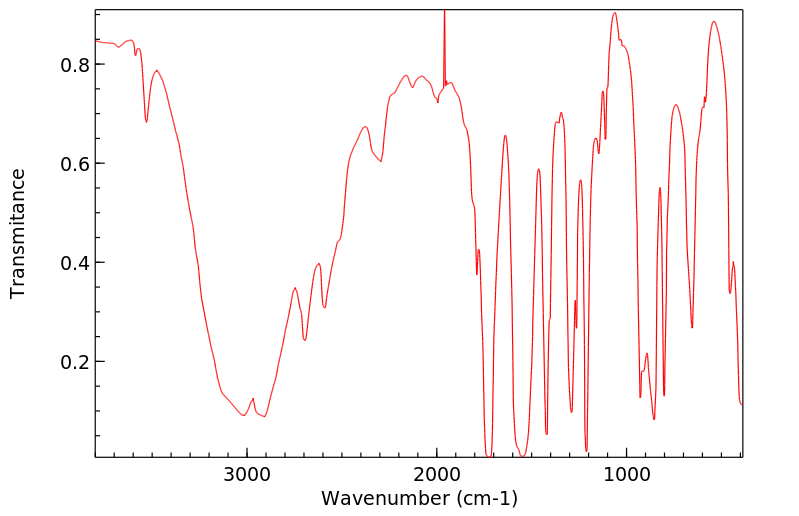
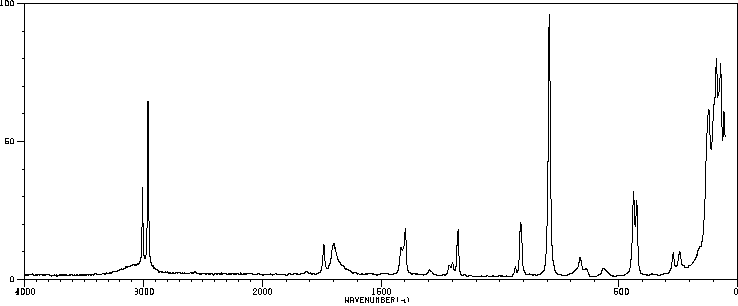
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息