烟酸丁酯 | 6938-06-3
中文名称
烟酸丁酯
中文别名
烟酸正丁酯;3-吡啶甲酸丁酯
英文名称
n-butyl nicotinate
英文别名
butyl nicotinate;Nicotinsaeure-butylester;Nicotinsaeure-n-butylester;butyl pyridine-3-carboxylate
CAS
6938-06-3
化学式
C10H13NO2
mdl
——
分子量
179.219
InChiKey
DQULIMIQTCDUAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:252 °C
-
密度:1.06
-
闪点:113 °C
-
LogP:2.270
-
溶解度:0.01 M
-
保留指数:1384
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.3
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.4
-
拓扑面积:39.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2933399090
-
RTECS号:QT0875000
-
危险性防范说明:P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319
-
储存条件:应存放在室温、密封且干燥的环境中。
SDS
Butyl Nicotinate Revision number: 5
SAFETY DATA SHEET
Section 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product name: Butyl Nicotinate
Revision number: 5
Section 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
GHS classification
PHYSICAL HAZARDS Not classified
HEALTH HAZARDS
Skin corrosion/irritation Category 2
Category 2A
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARDS Not classified
GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
Pictograms or hazard symbols
Signal word Warning
Hazard statements Causes skin irritation
Causes serious eye irritation
Precautionary statements:
Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
[Prevention]
Wear protective gloves/eye protection/face protection.
IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses,
[Response]
if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
IF ON SKIN: Gently wash with plenty of soap and water.
If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Take off contaminated clothing and wash before reuse.
Section 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substance/mixture: Substance
Components: Butyl Nicotinate
Percent: >98.0%(GC)
CAS Number: 6938-06-3
Synonyms: Nicotinic Acid Butyl Ester
C10H13NO2
Chemical Formula:
Section 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Inhalation: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
Butyl Nicotinate
Section 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Skin contact: Remove/Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Gently wash with plenty of
soap and water. If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Eye contact: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present
and easy to do. Continue rinsing. If eye irritation persists: Get medical
advice/attention.
Ingestion: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. Rinse mouth.
A rescuer should wear personal protective equipment, such as rubber gloves and air-
Protection of first-aiders:
tight goggles.
Section 5. FIRE-FIGHTING MEASURES
Suitable extinguishing Dry chemical, foam, water spray, carbon dioxide.
media:
Unsuitable extinguishing Solid streams of water
media:
Specific hazards arising Take care as it may decompose upon combustion or in high temperatures to
from the chemical: generate poisonous fume.
Precautions for firefighters: Fire-extinguishing work is done from the windward and the suitable fire-extinguishing
method according to the surrounding situation is used. Uninvolved persons should
evacuate to a safe place. In case of fire in the surroundings: Remove movable
containers if safe to do so.
Special protective When extinguishing fire, be sure to wear personal protective equipment.
equipment for firefighters:
Section 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, Use personal protective equipment. Keep people away from and upwind of spill/leak.
protective equipment and Entry to non-involved personnel should be controlled around the leakage area by
emergency procedures: roping off, etc.
Environmental precautions: Prevent product from entering drains.
Methods and materials for Sweep dust to collect it into an airtight container, taking care not to disperse it.
containment and cleaning Adhered or collected material should be promptly disposed of, in accordance with
up: appropriate laws and regulations.
Section 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling
Technical measures: Handling is performed in a well ventilated place. Wear suitable protective equipment.
Prevent dispersion of dust. Wash hands and face thoroughly after handling.
Use a local exhaust if dust or aerosol will be generated.
Advice on safe handling: Avoid contact with skin, eyes and clothing.
Conditions for safe storage, including any
incompatibilities
Storage conditions: Keep container tightly closed. Store in a cool and dark place.
Store away from incompatible materials such as oxidizing agents.
Packaging material: Comply with laws.
Section 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS / PERSONAL PROTECTION
Engineering controls: Install a closed system or local exhaust as possible so that workers should not be
exposed directly. Also install safety shower and eye bath.
Personal protective equipment
Respiratory protection: Dust respirator. Follow local and national regulations.
Hand protection: Protective gloves.
Safety glasses. A face-shield, if the situation requires.
Eye protection:
Skin and body protection: Protective clothing. Protective boots, if the situation requires.
Section 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Physical state (20°C): Solid
Clear
Form:
Butyl Nicotinate
Section 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Colour: Colorless - Pale yellow
Odour: No data available
pH: No data available
Melting point/freezing point:No data available
Boiling point/range: 252°C
Flash point: No data available
Flammability or explosive
limits:
Lower: No data available
Upper: No data available
Relative density: 1.06
Solubility(ies):
[Water] No data available
[Other solvents] No data available
Section 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Stable under proper conditions.
Chemical stability:
Possibility of hazardous No special reactivity has been reported.
reactions:
Incompatible materials: Oxidizing agents
Hazardous decomposition Carbon monoxide, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
products:
Section 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Acute Toxicity: ipr-mus LDLo:63 mg/kg
Skin corrosion/irritation: No data available
Serious eye No data available
damage/irritation:
Germ cell mutagenicity: No data available
Carcinogenicity:
IARC = No data available
NTP = No data available
Reproductive toxicity: No data available
RTECS Number: QT0875000
Section 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Ecotoxicity:
No data available
Fish:
Crustacea: No data available
No data available
Algae:
Persistence / degradability: No data available
No data available
Bioaccumulative
potential(BCF):
Mobility in soil
Log Pow: No data available
No data available
Soil adsorption (Koc):
Henry's Law No data available
constant(PaM3/mol):
Section 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Recycle to process, if possible. Consult your local regional authorities. You may be able to dissolve or mix material
with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber system.
Observe all federal, state and local regulations when disposing of the substance.
Section 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
Hazards Class: Does not correspond to the classification standard of the United Nations
Butyl Nicotinate
Section 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
UN-No: Not listed
Section 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
Safe management ordinance of dangerous chemical product (State Council announces on January 26, 2002
and revised on February 16,2011): Safe use and production, the storage of a dangerous chemical, transport,
loading and unloading were prescribed.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
SAFETY DATA SHEET
Section 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product name: Butyl Nicotinate
Revision number: 5
Section 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
GHS classification
PHYSICAL HAZARDS Not classified
HEALTH HAZARDS
Skin corrosion/irritation Category 2
Category 2A
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARDS Not classified
GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
Pictograms or hazard symbols
Signal word Warning
Hazard statements Causes skin irritation
Causes serious eye irritation
Precautionary statements:
Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
[Prevention]
Wear protective gloves/eye protection/face protection.
IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses,
[Response]
if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
IF ON SKIN: Gently wash with plenty of soap and water.
If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Take off contaminated clothing and wash before reuse.
Section 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substance/mixture: Substance
Components: Butyl Nicotinate
Percent: >98.0%(GC)
CAS Number: 6938-06-3
Synonyms: Nicotinic Acid Butyl Ester
C10H13NO2
Chemical Formula:
Section 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Inhalation: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
Butyl Nicotinate
Section 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Skin contact: Remove/Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Gently wash with plenty of
soap and water. If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Eye contact: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present
and easy to do. Continue rinsing. If eye irritation persists: Get medical
advice/attention.
Ingestion: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. Rinse mouth.
A rescuer should wear personal protective equipment, such as rubber gloves and air-
Protection of first-aiders:
tight goggles.
Section 5. FIRE-FIGHTING MEASURES
Suitable extinguishing Dry chemical, foam, water spray, carbon dioxide.
media:
Unsuitable extinguishing Solid streams of water
media:
Specific hazards arising Take care as it may decompose upon combustion or in high temperatures to
from the chemical: generate poisonous fume.
Precautions for firefighters: Fire-extinguishing work is done from the windward and the suitable fire-extinguishing
method according to the surrounding situation is used. Uninvolved persons should
evacuate to a safe place. In case of fire in the surroundings: Remove movable
containers if safe to do so.
Special protective When extinguishing fire, be sure to wear personal protective equipment.
equipment for firefighters:
Section 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, Use personal protective equipment. Keep people away from and upwind of spill/leak.
protective equipment and Entry to non-involved personnel should be controlled around the leakage area by
emergency procedures: roping off, etc.
Environmental precautions: Prevent product from entering drains.
Methods and materials for Sweep dust to collect it into an airtight container, taking care not to disperse it.
containment and cleaning Adhered or collected material should be promptly disposed of, in accordance with
up: appropriate laws and regulations.
Section 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling
Technical measures: Handling is performed in a well ventilated place. Wear suitable protective equipment.
Prevent dispersion of dust. Wash hands and face thoroughly after handling.
Use a local exhaust if dust or aerosol will be generated.
Advice on safe handling: Avoid contact with skin, eyes and clothing.
Conditions for safe storage, including any
incompatibilities
Storage conditions: Keep container tightly closed. Store in a cool and dark place.
Store away from incompatible materials such as oxidizing agents.
Packaging material: Comply with laws.
Section 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS / PERSONAL PROTECTION
Engineering controls: Install a closed system or local exhaust as possible so that workers should not be
exposed directly. Also install safety shower and eye bath.
Personal protective equipment
Respiratory protection: Dust respirator. Follow local and national regulations.
Hand protection: Protective gloves.
Safety glasses. A face-shield, if the situation requires.
Eye protection:
Skin and body protection: Protective clothing. Protective boots, if the situation requires.
Section 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Physical state (20°C): Solid
Clear
Form:
Butyl Nicotinate
Section 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Colour: Colorless - Pale yellow
Odour: No data available
pH: No data available
Melting point/freezing point:No data available
Boiling point/range: 252°C
Flash point: No data available
Flammability or explosive
limits:
Lower: No data available
Upper: No data available
Relative density: 1.06
Solubility(ies):
[Water] No data available
[Other solvents] No data available
Section 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Stable under proper conditions.
Chemical stability:
Possibility of hazardous No special reactivity has been reported.
reactions:
Incompatible materials: Oxidizing agents
Hazardous decomposition Carbon monoxide, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
products:
Section 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Acute Toxicity: ipr-mus LDLo:63 mg/kg
Skin corrosion/irritation: No data available
Serious eye No data available
damage/irritation:
Germ cell mutagenicity: No data available
Carcinogenicity:
IARC = No data available
NTP = No data available
Reproductive toxicity: No data available
RTECS Number: QT0875000
Section 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Ecotoxicity:
No data available
Fish:
Crustacea: No data available
No data available
Algae:
Persistence / degradability: No data available
No data available
Bioaccumulative
potential(BCF):
Mobility in soil
Log Pow: No data available
No data available
Soil adsorption (Koc):
Henry's Law No data available
constant(PaM3/mol):
Section 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Recycle to process, if possible. Consult your local regional authorities. You may be able to dissolve or mix material
with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber system.
Observe all federal, state and local regulations when disposing of the substance.
Section 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
Hazards Class: Does not correspond to the classification standard of the United Nations
Butyl Nicotinate
Section 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
UN-No: Not listed
Section 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
Safe management ordinance of dangerous chemical product (State Council announces on January 26, 2002
and revised on February 16,2011): Safe use and production, the storage of a dangerous chemical, transport,
loading and unloading were prescribed.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 烟酸 nicotinic acid 59-67-6 C6H5NO2 123.111
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Synthesis and structures of 1,2,4-triazoles derivatives摘要:A series of novel 1,2,4-triazole derivatives were synthesized, and their structures were characterized by IR, UV-Vis, FL, NMR, ESI-MS, and elemental analysis. In the meanwhile, the single crystal structures of 3,4-diethyl-5-(4-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazole and 3,4-dimethyl-5-(o-hydroxyphenyl)-1,2,4-triazole were determined by X-ray diffraction.DOI:10.1134/s1070363215030330
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Hukushima, Nippon Kagaku Kaishi/Journal of the Chemical Society of Japan, 1940, vol. 61, p. 121,123摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Zr‐MOF‐808 as Catalyst for Amide Esterification作者:Beatriz Villoria‐del‐Álamo、Sergio Rojas‐Buzo、Pilar García‐García、Avelino CormaDOI:10.1002/chem.202003752日期:2021.3.8esterification. Comparing with previously reported homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts, Zr‐MOF‐808‐P can promote the reaction for a wide range of primary, secondary and tertiary amides with n‐butanol as nucleophilic agent. Different alcohols have been employed in amide esterification with quantitative yields. Moreover, the catalyst acts as a heterogeneous catalyst and could be reused for at least five
-
Efficient Palladium-Catalyzed Alkoxycarbonylation of <b><i>N</i></b>-Heteroaryl Chlorides - A Practical Synthesis of Building Blocks for Pharmaceuticals and Herbicides作者:Matthias Beller、Wolfgang Mägerlein、Adriano Indolese、Christine FischerDOI:10.1055/s-2001-14576日期:——The alkoxycarbonylation of various N-heteroaryl chlorides was examined in detail. Studies of the butoxycarbonylation of 2- and 3-chloropyridine revealed the importance of selecting both the right phosphine ligand and ligand concentration in order to obtain efficient conversion and selectivity. Amongst the different ligands tested, 1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane (dppb) and 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene (dppf) led to the most efficient palladium catalyst systems for the conversion of 2- and 4-chloropyridines and similar heteroaryl chlorides. The best catalytic systems for the alkoxycarbonylation of less activated substrates, such as 3-chloropyridines, were found to be those containing 1,4-bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)butane. Good to excellent yields of a number of N-heterocyclic carboxylic acid esters were realized by applying the appropriate ligand in the right concentration at low catalyst loadings (0.005-0.5 mol% Pd). For the first time catalyst turnover numbers (TON) of up to 13,000 were obtained for the carbonylation of a (hetero)aryl chloride.详细研究了各种N-杂芳基氯化物的烷氧羰基化反应。对2-和3-氯吡啶的丁氧羰基化研究发现,为了获得高效的转化率和选择性,选择合适的膦配体及其浓度至关重要。在测试的不同配体中,1,4-双(二苯基膦)丁烷(dppb)和1,1'-双(二苯基膦)二茂铁(dppf)为2-和4-氯吡啶及类似杂芳基氯化物提供了最高效的钯催化体系。对于活性较低的底物,如3-氯吡啶,最佳催化体系是含有1,4-双(二环己基膦)丁烷的体系。通过在低催化负载量(0.005-0.5摩尔% 钯)下使用适当浓度的合适配体,实现了多种N-杂环羧酸酯的良好至优异产率。对于(杂)芳基氯化物的羰基化反应,首次获得了高达13,000的催化剂周转数(TON)。
-
Carbonylation of Aryl Chlorides with Oxygen Nucleophiles at Atmospheric Pressure. Preparation of Phenyl Esters as Acyl Transfer Agents and the Direct Preparation of Alkyl Esters and Carboxylic Acids作者:Donald A. Watson、Xuexiang Fan、Stephen L. BuchwaldDOI:10.1021/jo800907e日期:2008.9.19A mild, functional group tolerant method of the preparation of phenyl esters from aryl chlorides via palladium-catalyzed carbonylation is described using atmospheric pressure of carbon monoxide. Phenyl esters are shown to be useful acylating agents, delivering libraries of carbonyl derivatives, including alkyl, allyl and thioesters, under very mild conditions. Direct preparation of alkyl esters and
-
Ir<sup>III</sup>-Catalyzed direct syntheses of amides and esters using nitriles as acid equivalents: a photochemical pathway作者:Ranadeep TalukdarDOI:10.1039/d0nj00002g日期:——unprecedented IrIII[df(CF3)ppy]2(dtbbpy)PF6-catalyzed simple photochemical process for direct addition of amines and alcohols to the relatively less reactive nitrile triple bond is described herein. Various amides and esters are synthesized as the reaction products, with nitriles being the acid equivalents. A mini-library of different types of amides and esters is made using this mild and efficient process, which本文描述了空前的Ir III [df(CF 3)ppy] 2(dtbbpy)PF 6催化的简单光化学过程,用于将胺和醇直接加成到反应性较小的腈三键上。合成了各种酰胺和酯作为反应产物,其中腈是酸的当量。使用这种温和有效的方法可以制得不同类型的酰胺和酯的小型文库,该方法在可见光照射下(λ = 445 nm)仅使用1 mol%的光催化剂。该反应策略对于克级合成也是有效的。
-
Efficient Carbonylation of Aryl and Heteroaryl Bromides using a Palladium/Diadamantylbutylphosphine Catalyst作者:Helfried Neumann、Anne Brennführer、Peter Groß、Thomas Riermeier、Juan Almena、Matthias BellerDOI:10.1002/adsc.200606044日期:2006.7A general palladium-catalyzed alkoxycarbonylation of aryl and heteroaryl bromides has been developed in the presence of bulky monodentate phosphines. Studies of the butoxycarbonylation of three model substrates revealed the advantages of di-1-adamantyl-n-butylphosphine compared to other ligands. In the presence of this catalyst system various bromoarenes provided the corresponding benzoic acid derivatives
表征谱图
-
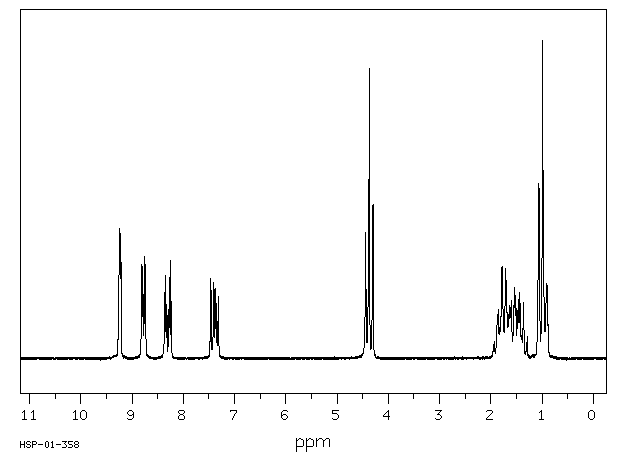
氢谱1HNMR
-
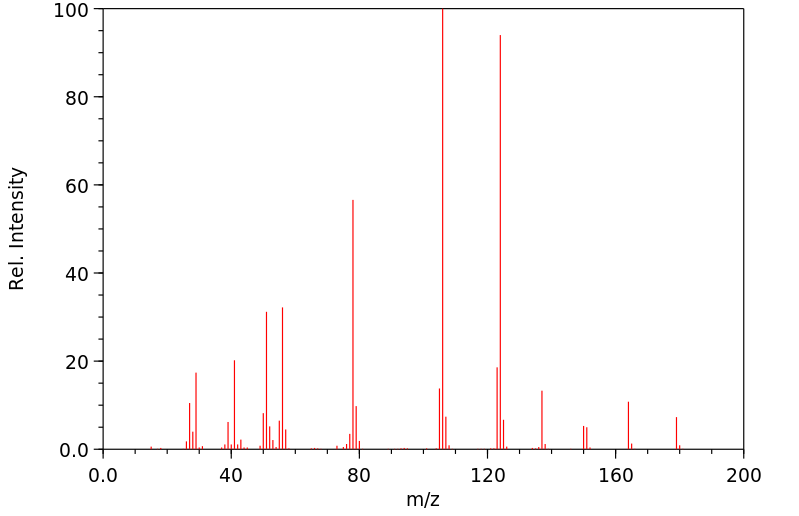
质谱MS
-
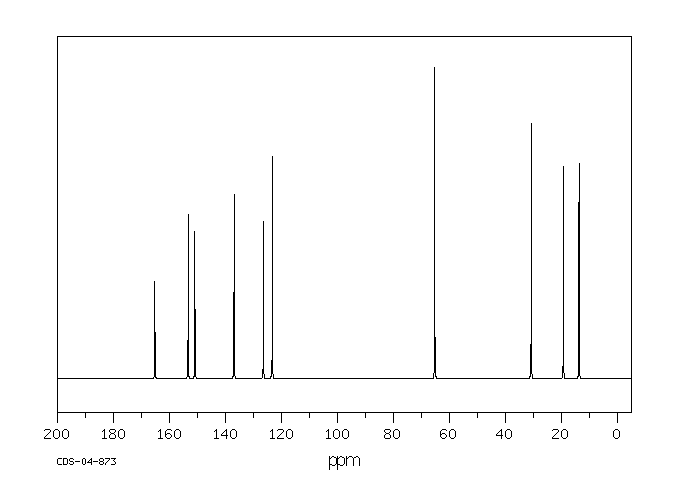
碳谱13CNMR
-
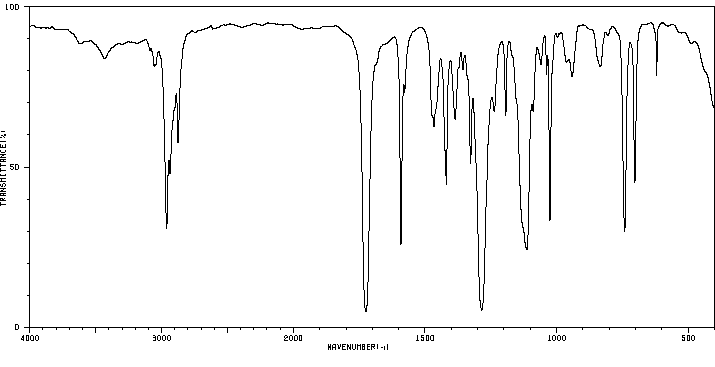
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-氨氯地平-d4
(R,S)-可替宁N-氧化物-甲基-d3
(R)-(+)-2,2'',6,6''-四甲氧基-4,4''-双(二苯基膦基)-3,3''-联吡啶(1,5-环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-N'-亚硝基尼古丁
(R)-DRF053二盐酸盐
(5E)-5-[(2,5-二甲基-1-吡啶-3-基-吡咯-3-基)亚甲基]-2-亚磺酰基-1,3-噻唑烷-4-酮
(5-溴-3-吡啶基)[4-(1-吡咯烷基)-1-哌啶基]甲酮
(5-氨基-6-氰基-7-甲基[1,2]噻唑并[4,5-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺)
(2S,2'S)-(-)-[N,N'-双(2-吡啶基甲基]-2,2'-联吡咯烷双(乙腈)铁(II)六氟锑酸盐
(2S)-2-[[[9-丙-2-基-6-[(4-吡啶-2-基苯基)甲基氨基]嘌呤-2-基]氨基]丁-1-醇
(2R,2''R)-(+)-[N,N''-双(2-吡啶基甲基)]-2,2''-联吡咯烷四盐酸盐
(1'R,2'S)-尼古丁1,1'-Di-N-氧化物
黄色素-37
麦斯明-D4
麦司明
麝香吡啶
鲁非罗尼
鲁卡他胺
高氯酸N-甲基甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸,吡啶
高奎宁酸
马来酸溴苯那敏
马来酸氯苯那敏-D6
马来酸左氨氯地平
顺式-双(异硫氰基)(2,2'-联吡啶基-4,4'-二羧基)(4,4'-二-壬基-2'-联吡啶基)钌(II)
顺式-二氯二(4-氯吡啶)铂
顺式-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯铬氯化物
顺式-1-(4-甲氧基苄基)-3-羟基-5-(3-吡啶)-2-吡咯烷酮
顺-双(2,2-二吡啶)二氯化钌(II) 水合物
顺-双(2,2'-二吡啶基)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
顺-二氯二(吡啶)铂(II)
顺-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
韦德伊斯试剂
非那吡啶
非洛地平杂质C
非洛地平
非戈替尼
非布索坦杂质66
非尼拉朵
非尼拉敏
雷索替丁
阿雷地平
阿瑞洛莫
阿扎那韦中间体
阿培利司N-6
阿伐曲波帕杂质40
间硝苯地平
间-硝苯地平
镉,二碘四(4-甲基吡啶)-
锌,二溴二[4-吡啶羧硫代酸(2-吡啶基亚甲基)酰肼]-