环氧乙烷 | 75-21-8
中文名称
环氧乙烷
中文别名
氧化伸乙基;氧化乙烯;EO;虫菌畏;一氧三环;恶烷
英文名称
oxirane
英文别名
ethylene oxide;oxyethylene;propylene oxide
CAS
75-21-8
化学式
C2H4O
mdl
MFCD00014482
分子量
44.0532
InChiKey
IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−111 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:10.7 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.882 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
介电常数:14.0(-4℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 1.8 mg/m3 (1 ppm) (ACGIH), 0.18 mg/m3 (0.1 ppm), 5 ppm/10 min (NIOSH).
-
LogP:-0.30
-
物理描述:Ethylene oxide appears as a clear colorless gas with an ethereal odor with a flash point below 0°F. Liquid less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. May polymerize exothermically if heated or contaminated. If the polymerization takes place inside a container, the container may rupture violently. Vapors very toxic. Vapors irritate the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Prolonged skin contact may result in delayed burns. Used to make other chemicals, as a fumigant and industrial sterilant.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless ... gas at ordinary room temp and pressure; liquid below 12 °C
-
气味:Sweet
-
闪点:-20 °F (-29 °C) (closed cup)
-
溶解度:Miscible (NTP, 1992)
-
蒸汽密度:1.49 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1,310 mm Hg at 25 °C (extrapolated)
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.48X10-4 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:7.60e-14 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
环氧乙烷液体是一种良好的有机溶剂。它容易爆炸,当空气中环氧乙烷含量在3%至80%之间时,会形成爆炸性混合气体,遇火即可能发生燃烧或爆炸。若将环氧乙烷与水按1:22的比例混合,则不再具有易燃(爆)性。环氧乙烷与镁、银及其化合物接触时可生成乙炔并引发爆炸。为确保安全使用,通常需添加淬火剂进行稀释。
-
环氧乙烷可以发生聚合反应,但通常聚合过程较为缓慢且主要发生在液体状态下。在聚合过程中会释放一定能量。某些催化剂的存在可能会加速这一过程。环氧乙烷的聚合产物可能是黄色油状物或类似树胶的固体物质,并能溶于水和多种有机溶剂中,还原硝酸银后呈现特定反应。其化学性质活泼,容易进行开环反应,并能够与多种化合物发生加成反应,比如与水生成乙二醇、与醇类生成乙二醇单醚、与苯酚形成苯氧基乙醇以及与无机酸如硝酸生成乙二醇二硝酸酯。此外,环氧乙烷还能聚合为聚乙二醇。
-
在体内,环氧乙烷可转化为甲醛、乙二醇和乙二酸等物质。它对中枢神经系统具有麻醉作用,并能刺激黏膜并损害细胞原浆。小鼠吸入其致死浓度约为1.5 mg/L,大鼠则为2.63 mg/L。人吸入高浓度蒸汽后会迅速出现麻醉症状,产生恶心、呕吐等症状。遇到中毒情况应立即撤离现场,进行吸氧和人工呼吸等急救措施。若皮肤被污染,应用大量清水或3%硼酸溶液冲洗15分钟以上,并做好保暖措施后送往医院诊治。
-
环氧乙烷相对稳定。
-
请远离高温和光照条件。
-
聚合反应可能带来安全隐患。
-
-
自燃温度:804 °F (429 °C)
-
分解:Liquid ethylene oxide is not detonable, but the vapor may be readily initiated into explosive decomposition.
-
粘度:9.45X10-3 mPa.s (25 °C, gas) and 0.254 mPa.s (10 °C, liquid)
-
燃烧热:1280.9 kJ/mol (liquid); 1306.1 kJ/mol (gas)
-
汽化热:24.75 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
电离电位:10.56 eV
-
聚合:Precautions designed to prevent explosive polymerization of ethylene oxide are discussed, including rigid exclusion of acids, covalent halides such as aluminium, iron (III), and tin (IV) chloride, basic materials like alkali hydroxides, ammonia, amines, metallic potassium, and catalytically active solids such as aluminium or iron oxides or rust.
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 257.0 [ppm]; Odor Threshold High: 690.0 [ppm]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 420 ppm)
-
折光率:Inex of refraction: 1.3597 at 7 °C/D
-
保留指数:417 ;417 ;405.3 ;405 ;400 ;405 ;400
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.1
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:12.5
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
Ethylene oxide reacts with glutathione to form cysteine derivatives, forms ethylene glycol by epoxide hydrolase with subsequent metabolism of the glycol, and reacts with chloride to form 2-chloroethanol. The relative importance of these pathways is undefined. Ethylene glycol glutathione conjugates are metabolites of ethylene oxide. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在成年雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠、雄性瑞士CD-1小鼠和雄性家兔中,将20或60毫克/千克环氧乙烷作为蒸馏水中的溶液注射到大鼠和小鼠的尾静脉中,或者在家兔的边缘静脉中注射。部分动物在吸入室暴露于200 ppm的环氧乙烷。动物被安置在代谢笼中,收集0-6小时和6-24小时的尿液样本。尿液样本分析了2-羟基乙基硫酸酯、N-乙酰-S-羧甲基-L-半胱氨酸、S-(2-羟基乙基)-L-半胱氨酸、S-羧甲基-L-半胱氨酸和乙二醇。观察到了环氧乙烷代谢分布的种间差异。排泄产物模式在注射剂量之间没有显著差异。大鼠(n=5)以2-羟基乙基硫酸酯(31%)和乙二醇(6%)的形式消除了37%的环氧乙烷;小鼠(n=10)将19.3%的环氧乙烷转化为2-羟基乙基硫酸酯(8.3%)、S-2-羟基乙基-L-半胱氨酸(5.8%)、S-羧甲基-L-半胱氨酸(1.9%)和乙二醇(3.3%)。家兔(n=3)仅以乙二醇的形式排除了2%的环氧乙烷。在大鼠中,更多的2-羟基乙基硫酸酯在6-24小时期间被排出,而更多的乙二醇在0-6小时期间被排出。在小鼠中,两个收集期间等量的3-羟基乙基硫酸酯被排出,而更多的乙二醇在6-24小时期间被排出。家兔在0-6小时期间没有排尿。相对于暴露方式,环氧乙烷的尿液代谢物排泄没有观察到定性差异。
In adult male Sprague-Dawley rats, male Swiss CD-1 mice, and male rabbits, 20 or 60 mg/kg ethylene oxide as a solution in distilled water was injected into the caudal vein in rats and mice or in the marginal vein in rabbits. Some animals were exposed to 200 ppm ethylene oxide in inhalation chambers. The animals were housed in metabolism cages, and urine samples were collected at 0-6 hr and 6-24 hr. The urine samples were analyzed for 2-hydroxyethylmercapturic acid, N-acetyl-S-carboxy-methyl-L cysteine, S-(2-hydroxyethyl)-L-cysteine, S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine, and ethylene glycol. Species-related differences in the metabolic disposition of ethylene oxide were observed. Excretion product patterns did not differ significantly between injected doses. Rats (n= 5) eliminated 37% of ethylene oxide as 2-hydroxyethylmercapturic acid (31%) and ethylene glycol (6%); mice (n= 10) converted 19.3% of the ethylene oxide to 2-hydroxyethylmercapturic acid (8.3%), S-2-hydroxyethyl-L-cysteine (5.8%), S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine (1.9%), and ethylene glycol (3.3%). The rabbits (n= 3) excreted only 2% of the ethylene oxide, primarily as ethylene glycol. In rats, larger amounts of 2-hydroxyethylmercapturic acid were excreted in the 6-24 hr period, and larger amounts of ethylene glycol were excreted in the 0-6 hr period. In mice, equal amounts of 3-hydroxyethylmercapturic acid were excreted in the two collection periods and larger amounts of ethylene glycol were excreted in the 6-24 hr period. No urine was voided by the rabbits in the 0-6 hr period. No qualitative differences in urinary metabolite excretion of ethylene oxide were observed relative to the method of exposure.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
In the presence of water and chloride, ethylene oxide is hydrolyzed to 2-chloroethanol and ethylene glycol. The glycol is further metabolized to oxalate, formic acid and CO2.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在给予大鼠静脉注射1至10毫克/公斤的剂量后,24小时内,35%的剂量以2-羟基乙基巯基尿酸(2-HEMA)的形式在尿液中排出。在不同的乙烯浓度下进行吸入暴露后,24小时尿液中的2-HEMA水平与乙烯氧化物的暴露水平呈线性关系。
Within 24 hours following iv treatment 35% of the administered doses ranging from 1 to 10 mg/kg to the rat were excreted as 2-hydroxyethyl-mercapturic acid (2-HEMA) in the urine. After inhalation exposure to different ethylene oxide concentrations, the 2-HEMA levels determined in 24 hr-urine were linearly related to ethylene oxide exposure levels.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在动物和人类中,环氧乙烷有两种代谢途径,都被认为是解毒途径。首先是水解为乙二醇,随后转化为草酸、甲酸和二氧化碳。其次是与谷胱甘肽结合,随后的代谢步骤产生S-(2-羟基乙基)半胱氨酸(S-(2-羧甲基)半胱氨酸)和N-乙酰化衍生物(即N-乙酰-S-(2-羟基乙基)半胱氨酸(和N-乙酰-S-(2-羧甲基)半胱氨酸))……。在大鼠和小鼠中,与谷胱甘肽结合的途径似乎占主导地位;在较大的物种(兔子、狗)中,环氧乙烷的转化主要是通过乙二醇的水解途径……。环氧乙烷还可能来自乙烯的代谢……。首先为大鼠开发了一个基于生理学的药代动力学(PBPK)模型,用于吸入环氧乙烷的剂量学,包括环氧乙烷与血红蛋白和DNA的结合以及组织分布、代谢途径(即通过环氧水合酶的水解和通过谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶的结合)和肝脏及肝外谷胱甘肽的消耗……。然后将该模型进行了改进并扩展到小鼠和人类……。模拟表明,在大鼠、小鼠和人类中,分别约有80%、60%和20%会通过谷胱甘肽结合途径代谢……。这与观察到大鼠、小鼠和人类的theta类谷胱甘肽S-转移酶(GSTT1)酶活性水平一致,顺序为小鼠>大鼠>人类。在大鼠和小鼠中,GSTT1活性在肝脏中最高,其次是肾脏和睾丸。大鼠大脑以及大鼠和小鼠的肺与其它组织相比含有少量活性(小鼠大脑的酶活性未检查)。环氧乙烷是人类GSTT1酶的底物……。
In animals and humans, there are two routes of ethylene oxide catabolism, both of which are considered to be detoxification pathways. The first involves hydrolysis to ethylene glycol, with subsequent conversion to oxalic acid, formic acid, and carbon dioxide. The second involves conjugation with glutathione, with subsequent metabolic steps yielding S-(2-hydroxyethyl)cysteine (S-(2-carboxymethyl)cysteine) and N-acetylated derivatives (ie, N-acetyl-S-(2-hydroxyethyl)cysteine (and N-acetyl-S-(2-carboxymethyl)cysteine)) ... . The route involving conjugation with glutathione appears to predominate in rats and mice; in larger species (rabbits, dogs), the conversion of ethylene oxide is primarily via hydrolysis through ethylene glycol ... . Ethylene oxide may also be formed from the metabolism of ethylene ... . A physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for the dosimetry of inhaled ethylene oxide was first developed for rats and included binding of ethylene oxide to hemoglobin and DNA in addition to tissue distribution, metabolic pathways (ie, hydrolysis by epoxide hydrolase and conjugation by glutathione-S-transferase), and depletion of hepatic and extra-hepatic glutathione ... . The model was then refined and extended to mice and humans ... . Simulations indicate that in mice, rats, and humans, about 80%, 60%, and 20%, respectively, would be metabolized via glutathione conjugation ... . This is consistent with observed levels of theta-class glutathione S-transferase (GSTT1) enzyme activity in the order mice > rats > humans. In rats and mice, GSTT1 activity was highest in the liver, followed by the kidney and testes. Rat brain and rat and mouse lung contained small amounts of activity compared with other tissues (enzyme activity in mouse brain was not examined). Ethylene oxide is a substrate for the human GSTT1 enzyme ... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别:环氧乙烷是一种无色、高反应性的气体,在室温和常压下。它用于制造乙二醇和表面活性剂。环氧乙烷还用作医疗材料和其他热敏感产品的灭菌剂。人类暴露:环氧乙烷通过肺部迅速吸收、分布,并代谢为乙二醇和谷胱甘肽结合物。环氧乙烷可以通过皮肤从气态或水溶液中吸收,并在全身均匀分布。环氧乙烷是一种烷基化剂,能形成蛋白质和DNA加合物。血红蛋白加合物已被用于生物监测。根据主要在职业暴露人群中的研究,环氧乙烷是一种眼睛、呼吸和皮肤的刺激物,也是一种致敏剂。在暴露于相对较高浓度的工人中观察到神经学效应(主要是感觉运动多发性神经病)。最可能的最大暴露途径和人类健康的关注点是吸入空气。有一些证据表明,在职业暴露人群的流行病学研究中,环氧乙烷暴露与血液癌症的发展有关,但数据限制排除了明确的结论。有一致的证据表明,环氧乙烷已在暴露的工人中诱导了裂变变化。动物/植物研究:在啮齿类动物和狗中,环氧乙烷的急性吸入毒性较低。在吸入研究中,环氧乙烷已诱导出多种肿瘤(例如,白血病、淋巴瘤、大脑、肺)。环氧乙烷在体外和体内测试的所有谱系水平上诱导基因突变。它还在实验动物中诱导生殖细胞突变和裂变效应。在实验动物中,环氧乙烷在高于与癌症和其他非癌(即神经学)效应相关浓度的浓度下,在存在和不存在母体毒性时对胎儿有毒;仅在非常高的浓度下(约1600 mg/m3以上)具有致畸性。关于环氧乙烷在人类中的生殖效应(主要是自发性流产)的流行病学研究证据有限。在实验动物中,在非肿瘤效应中,生殖效应发生在最低浓度(>90 mg/m3)。这些包括窝大小减少、着床后损失增加、精子形态改变以及精子计数和活力的变化。关于重复暴露于环氧乙烷的非肿瘤效应的研究数据有限,过去主要集中在化合物的致癌性上。在动物研究报告中,影响主要局限于血液和神经系统。
IDENTIFICATION: Ethylene oxide is a colorless, high reactive gas at room temperature and pressure. It used in the manufacture of ethylene glycol and surfactants. It used in the manufacture of surfactants. Ethylene oxide is also used as a sterilant for health care materials and other heat-sensitive products. HUMAN EXPOSURE: Ethylene oxide is rapidly taken up via the lungs, distributed, and metabolized to ethylene glycol and to glutathione conjugates. Ethylene oxide can be absorbed though the skin from the gas phase or from aqueous solutions and is uniformly distributed throughout the body. Ethylene oxide is an alkylating agent and forms protein and DNA adducts. Hemoglobin adducts have been used for biomonitoring. Based on studies primarily in occupationally exposed populations, ethylene oxide is an ocular, respiratory, and dermal irritant and a sensitizing agent. Neurological effects (primarily sensorimotor polyneuropathy) have been observed in workers exposed to relatively high concentrations. The route of likely greatest exposure and focus of the human health is inhalation from air. There is some evidence of an association between exposure to ethylene oxide and the development of haematological cancers in epidemiological studies of occupationally exposed populations, limitations of the data preclude definitive conclusions. There is consistent evidence that ethylene oxide has induced clastogenic changes in exposed workers. ANIMAL/PLANT STUDIES: The acute inhalation toxicity of ethylene oxide in rodents and dogs is low. In inhalation studies, ethylene oxide has induced a wide range of tumours (e.g., leukaemia, lymohoma, brain, lung). Ethylene oxide induces gene mutations at all phylogenetic levels tested in vitro and in vivo. It also induces germ cell mutations and clastogenic effects in experimental animals. In experimental animals, ethylene oxide is fetotoxic in the presence and absence of maternal toxicity at concentrations higher than those associated with cancer and other non-cancer (i.e., neurological) effects; it is teratogenic only at very high concentrations (above about 1600 mg/m3). Evidence from epidemiological studies of reproductive effects (primarily spontaneous abortions) of ethylene oxide in humans is limited. In experimental animals, among non-neoplastic effects, reproductive effects occur at lowest concentration (>90 mg/m3). These include reductions in litter size, increased post-implantation losses, alterations in sperm morphology, and changes in sperm count and motility. Available data on the non-neoplastic effects of repeated exposure to ethylene oxide in studies are limited, with past focus being primarily on the carcinogenicity of the compound. Reported effects in studies in animals were restricted primarily to those on the hematological and nervous systems.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
环氧乙烷是一种烷基化剂。它通过结合巯基、羟基、氨基和羧基,向蛋白质、DNA和RNA中加入烷基基团,阻止正常细胞代谢并最终杀死细胞。实验室动物中环氧乙烷的致癌性很可能主要是由于其直接对DNA和RNA进行烷基化。在活体中,环氧乙烷暴露引起了大鼠和小鼠脾T淋巴细胞的Hprt位点的突变(增加5到5.6倍)。
Ethylene oxide is an alkylating agent. The addition of alkyl groups to proteins, DNA, and RNA by binding to the sulfhydryl and hydroxyl, amino, and carboxyl groups, prevents normal cellular metabolism and ultimately kills cells. It is likely that the carcinogenicity of ethylene oxide in laboratory animals arises primarily as a result of its direct alkylation of DNA and RNA. In vivo exposure to ethylene oxide induced mutations (5- to 5.6-fold) at the Hprt locus in splenic T-lymphocytes in rats and mice.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
A2; 怀疑的人类致癌物。
A2; Suspected human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
评估:对于乙烯氧化物的致癌性,人类中的证据有限。在实验动物中,乙烯氧化物的致癌性有足够的证据。在做出总体评估时,工作组考虑了以下支持性证据。乙烯氧化物是一种直接作用的烷基化剂,它:(1)在暴露工人的外周淋巴细胞和骨髓细胞中诱导敏感、持续、剂量相关的染色体畸变和姐妹染色单体交换以及微核频率的增加;(2)在人类和实验动物中都与淋巴系统和造血系统的恶性肿瘤有关;(3)在暴露的人类中诱导剂量相关的血红蛋白加合物的频率增加,在暴露的啮齿动物中诱导DNA和血红蛋白加合物的数量剂量相关的增加;(4)在暴露的啮齿动物生殖细胞中诱导基因突变和可遗传的易位;(5)在所有谱系水平上都是一种强力的诱变剂和裂变剂。总体评估:乙烯氧化物对人类是致癌的(第1组)。
Evaluation: There is limited evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of ethylene oxide. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of ethylene oxide. In making the overall evaluation, the Working Group took into consideration the following supporting evidence. Ethylene oxide is a directly acting alkylating agent that: (1) induces a sensitive, persistent dose-related increase in the frequency of chromosomal aberrations and sister chromatid exchange in peripheral lymphocytes and micronuclei in bone marrow cells of exposed workers; (2) has been associated with malignancies of the lymphatic and hematopoietic system in both humans and experimental animals; (3) induces a dose related increase in the frequency of hemoglobin adducts in exposed humans and dose related increases in the numbers of adducts in DNA and hemoglobin in exposed rodents; (4) induces gene mutations and heritable translocations in germ cells of exposed rodents; and (5) is a powerful mutagen and clastogen at all phylogenetic levels. Overall evaluation: Ethylene oxide is carcinogenic to humans (Group 1).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
环氧乙烷:已知是一种人类致癌物。
Ethylene Oxide: known to be a human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
这项研究报告在这里检查了通过直接测定血液中环氧乙烷(EO)浓度来研究雄性B6C3F1小鼠的环氧乙烷剂量学。在单一4小时的仅鼻子吸入暴露(0、50、100、200、300或400 ppm EO)期间,测量了稳态血液EO浓度。此外,为了评估谷胱甘肽(GSH)消耗在之前在小鼠中观察到的可饱和代谢中的作用,测量了肝脏、肺、肾脏和睾丸中的GSH浓度。发现血液EO浓度在暴露浓度达到200 ppm时线性增加。在超过200 ppm的暴露浓度下观察到明显的亚线性血液剂量学。观察到与EO暴露浓度依赖性相关的组织GSH水平降低,肝脏和肺的GSH水平在EO暴露浓度为100 ppm或更高时显著降低。结果还表明,GSH的消耗很可能是小鼠中EO非线性剂量学的责任,并且GSH的消耗与关于小鼠暴露于EO的剂量率效应的报告相符。
The study reported here examined the dosimetry of ethylene oxide (EO) in male B6C3F1 mice by direct determination of blood EO concentrations. Steady-state blood EO concentrations were measured during a single 4-hr nose-only inhalation exposure (0, 50, 100, 200, 300, or 400 ppm EO). In addition, glutathione (GSH) concentrations were measured in liver, lung, kidney, and testis to assess the role of the GSH depletion in the saturable metabolism previously observed in mice. Blood EO concentrations were found to increase linearly with exposure concentration up to 200 ppm. Markedly sublinear blood dosimetry was observed at exposure concentrations exceeding 200 ppm. An EO exposure concentration-dependent reduction in tissue GSH levels was observed, with both liver and lung GSH levels significantly depressed at EO exposure concentrations of 100 ppm or greater. /The/ results also indicate that depletion of GSH is likely responsible for nonlinear dosimetry of EO in mice and that GSH depletion corresponds with reports of dose-rate effects in mice exposed to EO.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
这项研究的目标是检查香烟吸烟与源自EO的血红蛋白加合物之间的关系,并调查谷胱甘肽转移酶(GSTM1和GSTT1)的无效基因型是否改变了这些剂量的内剂量。血红蛋白加合物N-(2-羟基乙基)缬氨酸(HEVal)是由EO形成的,GST基因型是通过从16名非吸烟者和32名吸烟者(每天一至两包)获得的血液样本确定的。吸烟信息通过问卷获得,血浆可替宁水平通过免疫分析确定。谷胱甘肽转移酶无效基因型(GSTM1和GSTT1)通过PCR确定。HEVal水平随着香烟吸烟剂量的增加而增加(基于自我报告和可替宁水平)。HEVal水平也有相关性。GSTM1无效基因型对HEVal没有显著影响。然而,当根据吸烟状况或可替宁水平进行正常化时,GSTT1无效个体的HEVal水平显著升高。功能性GSTT1的缺失估计会使来自香烟烟雾的EO内剂量增加50-70%。
... The objectives of this study were to examine the relationship between cigarette smoking and hemoglobin adducts derived from ... EO and to investigate whether null genotypes for glutathione transferase (GSTM1 and GSTT1) alter the internal dose of these agents. The hemoglobin adduct ... N-(2-hydroxyethyl)valine (HEVal), which is formed from EO, and GST genotypes were determined in blood samples obtained from 16 nonsmokers and 32 smokers (one to two packs/day). Smoking information was obtained by questionnaire, and plasma cotinine levels were determined by immunoassay. Glutathione transferase null genotypes (GSTM1 and GSTT1) were determined by PCR. ... HEVal levels increased with increased cigarette smoking dose (both self-reported and cotinine-based). ... HEVal levels were also correlated. ... GSTM1 null genotypes had no significant impact on HEVal. However, HEVal levels were significantly elevated in GSTT1-null individuals when normalized to smoking status or cotinine levels. ... The lack of a functional GSTT1 is estimated to increase the internal dose of EO derived from cigarette smoke by 50-70%.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在将小鼠暴露于含有1,2-(3)H-环氧乙烷蒸气的空气中75分钟后,24小时内消除了90-95%的放射性。在脾脏的蛋白质部分中发现了剩余放射性的最高浓度;肝脏、肾脏、肺和睾丸中的含量较少。
AFTER EXPOSURE OF MICE TO MIXT OF 1,2-(3)H-ETHYLENE OXIDE VAPOR IN AIR FOR 75 MIN, 90-95% OF RADIOACTIVITY WAS ELIMINATED IN 24 HR. HIGHEST CONCN OF RESIDUAL RADIOACTIVITY WERE FOUND IN PROTEIN FRACTIONS OF SPLEEN; SMALLER AMT OCCURRED IN LIVER, KIDNEY, LUNG & TESTIS.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
通过静脉注射放射性碳14标记的环氧乙烷,结果显示在接触后20分钟到4小时内,睾丸、附睾和其他器官中的放射性碳浓度高于血液中的浓度。在接触结束24小时后,附睾中仍能检测到放射性。
Iv injection of (14)C-labeled ethylene oxide indicated that (14)C concn in the testicle, epididymis and other organs were higher than those in the blood when measured 20 min to 4 hr after exposure. Radioactivity was still present in the epididymis 24 hr after exposure had ended.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:C
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: <0.1 ppm (0.18 mg/m3), Ceiling: 5 ppm (9 mg/m3) [10-min/day]
-
危险等级:2.3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:800 ppm
-
危险品标志:F,F+,T
-
安全说明:S16,S23,S24/25,S36/37,S45,S53
-
危险类别码:R45
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2910100000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2037 2.3
-
危险类别:2.3
-
RTECS号:KX2450000
-
包装等级:O52
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS04,GHS06,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H220,H280,H315,H319,H331,H335,H340,H350
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P210,P261,P305 + P351 + P338,P311,P410 + P403
-
储存条件:1. 储存注意事项: - 存放于阴凉、通风的易燃气体专用库房。 - 远离火种和热源,避免光照。 - 库温不宜超过30℃。 - 与酸类、碱类、醇类及食用化学品分开存放,禁止混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备。 2. 设备应密封,防止跑、冒、滴、漏,并加强通风设施。操作人员需穿戴防护用具,高浓度环境中应佩戴活性炭口罩或压缩空气、压缩厌氧呼吸面具。装置附近应配置水龙头及淋浴设备。空气中最高容许浓度为0.001g/m³。
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Recoverable polymer-bound homogeneous catalysts for catalytic chain transfer process摘要:本文披露了新型聚合物-挂链配体、包含这些配体的金属配合物,以及利用这些配合物作为链转移催化剂来控制在自由基聚合过程中产生的寡聚物和聚合物材料的分子量。根据本文披露的工艺制备的材料具有显著降低的颜色,使其适用于广泛的颜色关键终端用途,包括汽车涂料。公开号:US08030422B2
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:的Ag /的制备和粒度的影响的α-Al 2个ö 3催化剂乙烯环氧化摘要:当前,对于工业乙烯环氧化,α-氧化铝负载的银催化剂是唯一选择的催化剂。我们展示了一种生产这些具有不同银粒径的催化剂的新颖方法,但没有改变可能影响催化性能的其他关键参数,例如载体比表面积或金属前体。α-氧化铝用草酸银溶液浸渍,然后干燥并在不同的气体气氛和不同的温度下进行处理,以调节银的粒径在20-500 nm范围内。根据文献结果,20nm的颗粒比70nm的颗粒具有更低的周转频率,而更大的颗粒具有恒定的周转频率。但是,当以恒定转化率测量时,选择性与粒度无关。这是第一次以恒定转化率报道了粒径对乙烯环氧化选择性的影响。这是通过一种生产负载型银催化剂的新方法使之成为可能的,我们希望该方法也适用于带有其他载体的银催化剂以及其他负载型金属催化剂的制备。DOI:10.1016/j.jcat.2017.10.001
-
作为试剂:描述:二乙烯基砜 、 氯仿 在 环氧乙烷 、 四乙基溴化铵 、 对苯二酚 作用下, 反应 5.0h, 生成 (3,3,3-trichloro-propane-1-sulfonyl)-ethene 、 bis-(3,3,3-trichloro-propyl) sulfone参考文献:名称:Nerdel,F. et al., Chemische Berichte, 1968, vol. 101, p. 1407 - 1413摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Synthesis of Spiroacetal Pheromones via Metalated Hydrazones作者:Dieter Enders、Walter Dahmen、Eleonore Dederichs、Winfried Gatzweiler、Peter WeusterDOI:10.1055/s-1990-27080日期:——The synthesis of simple alkyl substituted spiroacetals by α,α′-alkylation of metalated acetone dimethylhydrazone with appropriate electrophiles and subsequent acid catalyzed cleavage and ring closure of the products is described.
-
Synthesis of multi-substituted 1,2,4-triazoles utilising the ambiphilic reactivity of hydrazones作者:Haruo Matsuzaki、Norihiko Takeda、Motohiro Yasui、Mayuko Okazaki、Seishin Suzuki、Masafumi UedaDOI:10.1039/d1cc05326d日期:——The synthesis of N-alkyl-1H-1,2,4-triazoles from N,N-dialkylhydrazones and nitriles via formal [3+2] cycloaddition including the C-chlorination/nucleophilic addition/cyclisation/dealkylation sequence was developed. This sequential reaction utilising the in situ generation of hydrazonoyl chloride based on the ambiphilic reactivity of hydrazones afforded a variety of multi-substituted N-alkyl-triazoles
-
Process for preparing alkylene glycols申请人:Stankowiak Achim公开号:US20060199980A1公开(公告)日:2006-09-07The invention relates to a process for preparing alkylene glycols by hydration of alkylene oxides in the presence of polyalkylene glycol dialkyl ethers of the formula R 1 —O—[—(CH 2 CH 2 O) m (CH(CH 3 )CH 2 )—O] n —R 2 in which m=0-100, n=0-100, where n+m is at least equal to 1, R 1 is a C 1 - to C 6 -alkyl radical, R 2 is a C 1 - to C 6 -alkyl radical, where R 2 may be different from R 1 , with the proviso that for at least 50 mol % of the polyalkylene glycol dialkyl ether m+n is greater than or equal to 11.
-
4' SUBSTITUTED COMPOUNDS HAVING 5-HT6 RECEPTOR AFFINITY申请人:Dunn Robert公开号:US20080318941A1公开(公告)日:2008-12-25The present disclosure provides compounds having affinity for the 5-HT 6 receptor which are of the formula (I): wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 5 , R 6 , B, D, E, G, Q, x and n are as defined herein. The disclosure also relates to methods of preparing such compounds, compositions containing such compounds, and methods of use thereof.本公开提供了具有亲和力的化合物,其对5-HT 6 受体具有亲和力,其化学式为(I): 其中R1、R2、R5、R6、B、D、E、G、Q、x和n如本文所定义。本公开还涉及制备这种化合物的方法、含有这种化合物的组合物以及使用这些化合物的方法。
-
A convenient synthesis of nitro-substituted 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2<i>H</i>)-one 1,1-dioxides (nitrosaccharins)作者:Walfred S. Saari、John E. SchweringDOI:10.1002/jhet.5570230456日期:1986.7Nitro-substituted 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one 1,1-dioxides (nitrosaccharins) have been synthesized by amminolysis of nitro 2-chlorosulfonylbenzoate esters. This method appears to have advantages over the original procedure of oxidation of an ortho-toluenesulfonamide.
表征谱图
-
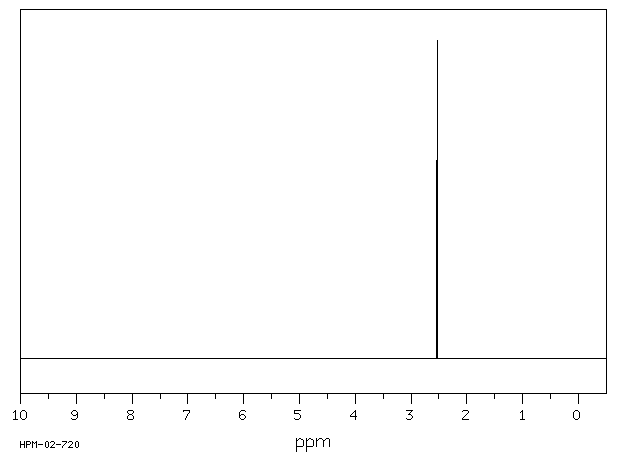
氢谱1HNMR
-
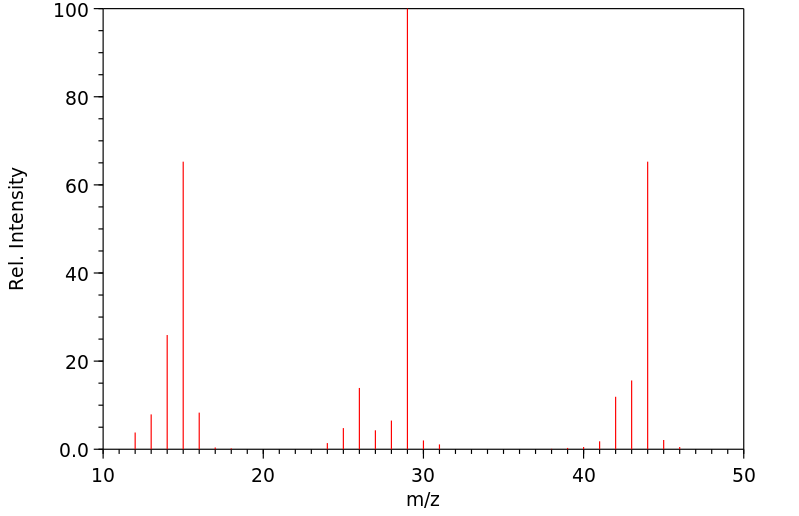
质谱MS
-
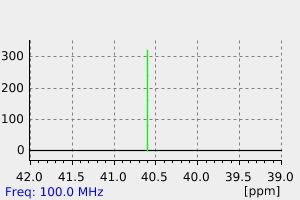
碳谱13CNMR
-
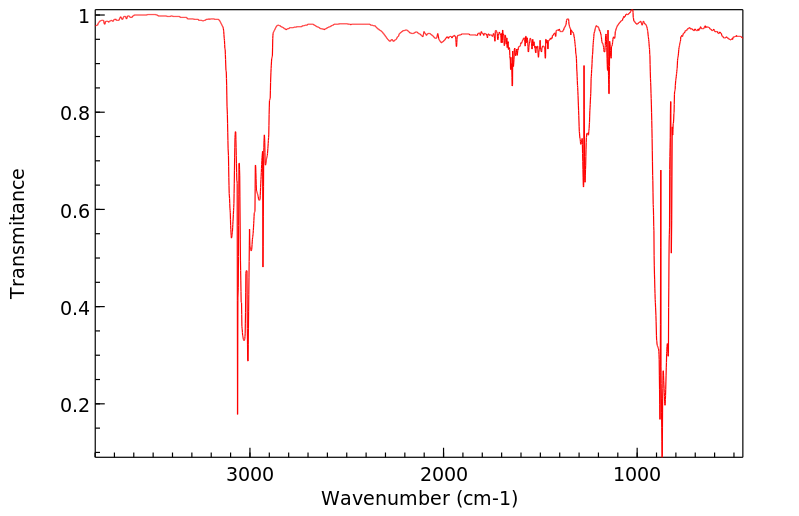
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-4-氯-1,2-环氧丁烷
顺式-环氧琥珀酸氢钾
顺式-1-环己基-2-乙烯基环氧乙烷
顺-(2S,3S)甲基环氧肉桂酸酯
雌舞毒蛾引诱剂
阿洛司他丁
辛基缩水甘油醚
试剂(3S,6S)-(-)-3,6-Diisopropyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione
表氰醇
螺[环氧乙烷-2,2-三环[3.3.1.1~3,7~]癸烷]
蛇根混合碱
benzene oxide
聚碳酸丙烯酯
聚依他丁
羟基乙醛
缩水甘油基异丁基醚
缩水甘油基十六烷基醚
缩水甘油
硬脂基醇聚氧乙烯聚氧丙烯醚
硅烷,三甲基[(3-甲基噁丙环基)乙炔基]-,顺-
盐酸司维拉姆
甲醛与(氯甲基)环氧乙烷,4,4-(1-甲基乙亚基)双酚和2-甲基苯酚的聚合物
甲醛与(氯甲基)环氧乙烷,4,4'-(1-甲基乙亚基)二[苯酚]和4-(1,1,3,3-四甲基丁基)苯酚的聚合物
甲醇环氧乙烷与壬基酚的聚合物
甲胺聚合物与(氯甲基)环氧乙烷
甲硫代环氧丙烷
甲基环氧氯丙烷
甲基环氧巴豆酸酯
甲基环氧乙烷与环氧乙烷和十六烷基或十八烷基醚的聚合物
甲基环氧乙烷与[(2-丙烯基氧基)甲基]环氧乙烷聚合物
甲基环氧丙醇
甲基环氧丙烷
甲基N-丁-3-烯酰甘氨酸酸酯
甲基7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-2,4-二烯-1-羧酸酯
甲基3-环丙基-2-环氧乙烷羧酸酯
甲基1-氧杂螺[2.5]辛烷-2-羧酸酯
甲基(2S,3R)-3-丙基-2-环氧乙烷羧酸酯
甲基(2R,3S)-3-丙基-2-环氧乙烷羧酸酯
甲基(2R,3R)-3-环丙基-2-环氧乙烷羧酸酯
环氧溴丙烷
环氧氯丙烷与双酚A、4-(1,1-二甲乙基)苯酚的聚合物
环氧氯丙烷-d5
环氧氯丙烷-D1
环氧氯丙烷-3,3’-亚氨基二丙胺的聚合物
环氧氯丙烷-2-13C
环氧氯丙烷
环氧氟丙烷
环氧树脂(环氧氯丙烷和二乙二醇)
环氧树脂
环氧柏木烷