2-氯-6-硝基苯甲醛 | 6361-22-4
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:69-71 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:298.8±25.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.485±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
稳定性/保质期:
避免强氧化剂、强碱。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:62.9
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2913000090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:请将药品存放在密闭、阴凉干燥处保存。
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-氯-6-硝基甲苯 6-chloro-2-nitrotoluene 83-42-1 C7H6ClNO2 171.583 2-氯-6-硝基苯甲醇 (2-chloro-6-nitrobenzene)methanol 50907-57-8 C7H6ClNO3 187.583 6-氯-2-硝基溴苄 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzyl bromide 56433-01-3 C7H5BrClNO2 250.479 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-氯-6-硝基苯甲醇 (2-chloro-6-nitrobenzene)methanol 50907-57-8 C7H6ClNO3 187.583 —— 2-chloro-6-nitrophenyl acetylene 947409-39-4 C8H4ClNO2 181.578 —— 2-(2-Bromoethynyl)-1-chloro-3-nitrobenzene 1353714-60-9 C8H3BrClNO2 260.474 2-氨基-6-氯苯甲醛 2-amino-6-chlorobenzaldehyde 35490-90-5 C7H6ClNO 155.584 —— N'-[1-(2-Chloro-6-nitro-phenyl)-meth-(E)-ylidene]-hydrazinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester 128153-91-3 C10H10ClN3O4 271.66
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Synthesis of Indoles from o,β-Dinitrostyrenes via Indium/Acetic Acid-Mediated Reductive Heterocyclizations摘要:Reductive heterocyclization reactions of various 1-nitro-2-(2-nitroaryl)ethenes to indoles were investigated. In the presence of indium/AcOH in toluene or benzene, 1-nitro-2-(2-nitroaryl)ethenes were cyclized to give corresponding indoles in good yields.DOI:10.3987/com-12-12605
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:DE107501摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
[EN] SULFONAMIDE COMPOUNDS HAVING TRPM8 ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS SULFONAMIDES AYANT UNE ACTIVITÉ D'ANTAGONISTE DE TRPM8申请人:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP公开号:WO2012124825A1公开(公告)日:2012-09-20Sulfonamide compounds having TRPM8 antagonistic activity are provided. A sulfonamide compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a prodrug thereof: (I) wherein Ring A is bicyclic aromatic heterocycle comprised of (a) pyridine is condensed with benzene; or (b) pyridine is condensed with monocyclic aromatic heterocycle, and Ring A binds to a sulfonylamino moiety on a carbon atom adjacent to a nitrogen atom of the pyridine ring constituting Ring A, Ring B is (a) monocyclic or bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; (b) monocyclic or bicyclic alicyclic hydrocarbon; (c) monocyclic or bicyclic aromatic heterocycle; or (d) monocyclic or bicyclic non-aromatic heterocycle, Ring C is (a) benzene; or (b) monocyclic aromatic heterocycle, and other symbols are the same as defined in the specification.
-
Improved glucose tolerance in rats treated with oxazolidinediones作者:Rodney C. Schnur、Malcolm MorvilleDOI:10.1021/jm00155a030日期:1986.55-(2-Chloro-6-methoxyphenyl)oxazolidine-2,4-dione (49) is the most potent agent selected from a series of 5-substituted oxazolidinediones that were found to cause improvements in glucose tolerance in previously fasted rats and potentiation of insulin release in response to a glucose challenge. These compounds were unique in not producing hypoglycemia below the normal fasting glycemia levels. Substituent
-
[EN] 1,2,4 -TRIAZOLES AS ALLOSTERIC MODULATORS OF MGLU5 RECEPTOR ACTIVITY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA OF DEMENTIA<br/>[FR] 1,2,4-TRIAZOLES COMME MODULATEURS ALLOSTÉRIQUES DE L'ACTIVITÉ DES RÉCEPTEURS MGLU5 POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE LA SCHIZOPHRÉNIE OU DE LA DÉMENCE申请人:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT公开号:WO2013083741A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-13This invention relates to compounds of formula (I) their use as positive allosteric modulators of mGlu5 receptor activity, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods of using the same as agents for treatment and/or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders associated with glutamate dysfunction such as schizophrenia or cognitive decline such as dementia or cognitive impairment. A, B, X, R1, R2, R3 have meanings given in the description.这项发明涉及公式(I)化合物的用途,它们作为mGlu5受体活性的正变构调节剂,包含这些化合物的药物组合物,以及使用它们作为治疗和/或预防与谷氨酸功能障碍相关的神经和精神障碍的方法,如精神分裂症或认知衰退,例如痴呆或认知障碍。A、B、X、R1、R2、R3的含义在描述中给出。
-
Inhibitors of the Detoxifying Enzyme of the Phytoalexin Brassinin Based on Quinoline and Isoquinoline Scaffolds作者:M. Pedras、Abbas Abdoli、Vijay Sarma-MamillapalleDOI:10.3390/molecules22081345日期:——
The detoxification of the phytoalexin brassinin to indole-3-carboxaldehyde and S-methyl dithiocarbamate is catalyzed by brassinin oxidase (BOLm), an inducible fungal enzyme produced by the plant pathogen Leptosphaeria maculans. Twenty-six substituted quinolines and isoquinolines are synthesized and evaluated for antifungal activity against L. maculans and inhibition of BOLm. Eleven compounds that inhibit BOLm activity are reported, of which 3-ethyl-6-phenylquinoline displays the highest inhibitory effect. In general, substituted 3-phenylquinolines show significantly higher inhibitory activities than the corresponding 2-phenylquinolines. Overall, these results indicate that the quinoline scaffold is a good lead to design paldoxins (phytoalexin detoxification inhibitors) that inhibit the detoxification of brassinin by L. maculans.
植物病原体Leptosphaeria maculans产生的可诱导真菌酶 brassinin 氧化酶 (BOLm) 催化了植物抗毒素brassinin向indole-3-carboxaldehyde和S-甲基二硫代氨基甲酸的解毒。合成了二十六种取代喹啉和异喹啉,并评估了它们对L. maculans的抑菌活性和对BOLm的抑制作用。报道了十一种抑制BOLm活性的化合物,其中3-乙基-6-苯基喹啉显示出最高的抑制效果。一般来说,取代的3-苯基喹啉比相应的2-苯基喹啉显示出显著更高的抑制活性。总的来说,这些结果表明喹啉支架是设计paldoxins(植物抗毒素解毒抑制剂)的良好先导,可以抑制L. maculans对brassinin的解毒。 -
Vasicine from Adhatoda vasica as an organocatalyst for metal-free Henry reaction and reductive heterocyclization of o-nitroacylbenzenes作者:Sushila Sharma、Manoranjan Kumar、Vinod Bhatt、Onkar S. Nayal、Maheshwar S. Thakur、Neeraj Kumar、Bikram Singh、Upendra SharmaDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.09.095日期:2016.11Vasicine, a quinazoline alkaloid, from the leaves of Adhatoda vasica, has been utilized as an efficient catalyst for metal and base free Henry reaction of various aldehydes with nitro alkanes. The method can be used in the synthesis of various β-nitro alcohols under mild reaction conditions without use of hazardous organic solvents and expensive catalysts. Vasicine is also applied successfully for
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
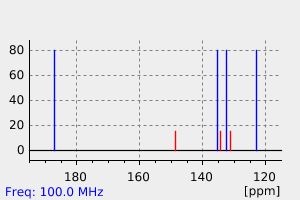
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息