4-溴苯酚 | 106-41-2
物质功能分类
中文名称
4-溴苯酚
中文别名
4-溴酚;对溴酚;对溴苯酚;溴酚
英文名称
4-bromo-phenol
英文别名
4-hydroxybromobenzene;p-bromophenol;para-bromophenol;4-Bromophenol
CAS
106-41-2
化学式
C6H5BrO
mdl
MFCD00002313
分子量
173.009
InChiKey
GZFGOTFRPZRKDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:61-64 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:235-236 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.84
-
闪点:235-238°C
-
溶解度:14g/l
-
最大波长(λmax):282nm(EtOH)(lit.)
-
颜色/状态:Tetragonal bipyramidal crystals from chloroform or ether
-
蒸汽压力:1.17X10-2 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.51e-07 atm-m3/mole
-
解离常数:pKa = 9.17
-
保留指数:1256;1256;1274;1312;1274;1252;1256;1274
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.6
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
溴苯在大鼠体内引起肝脏和肝脏外毒性。这种毒性与大鼠体内的肝脏、肺和肾脏中存在的共价结合物质的产生有关。溴苯的主要代谢物之一,对溴苯酚,已被证明能够在体内引起肝脏、肺和肾脏中共价结合物质的产生,但其本身并不具有毒性。对溴苯酚是由肝脏、肺和肾脏微粒体中的溴苯形成的,随后被代谢为4-溴儿茶酚和共价结合物质。肝脏微粒体现场生成的溴苯-3,4-氧化物,可通过肾脏、肝脏和肺细胞质解毒。结果表明,溴苯引起的肾脏毒性可能不是由溴苯-3,4-氧化物或对溴苯酚的活性代谢物介导的。相比之下,溴苯-3,4-氧化物可能在溴苯给药后观察到的肺毒性中发挥作用。然而,在肝脏外组织中发现的共价结合物质可能来源于溴苯-3,4-氧化物或对溴苯酚的活性代谢物,这些物质可能是由这些组织直接形成或从肝脏运输过来的。
Bromobenzene causes hepatic and extrahepatic toxicity in rats. Toxicity is related to the presence of covalently bound material in these tissues. A major bromobenzene metabolite, p-bromophenol, has been shown to give rise to covalently bound material in liver, lung and kidney in vivo, but is not toxic. p-Bromophenol is formed from bromobenzene in liver, lung and kidney microsomes and is subsequently metabolized to 4-bromocatechol and covalently bound material. Bromobenzene-3,4-oxide generated in situ by liver microsomes, is detoxified by kidney, liver and lung cytosol. The results suggest that the kidney toxicity caused by bromobenzene is probably not mediated by either bromobenzene-3,4-oxide or the reactive metabolites of p-bromophenol. In contrast, bromobenzene-3, 4-oxide may play a role in the lung toxicity observed after bromobenzene administration. However, the covalently bound material found in extrahepatic tissues may be derived from both bromobenzene-3,4-oxide or the reactive metabolites of p-bromophenol, which may be formed directly by these tissues or transported there from the liver.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
4-溴苯酚和4-溴邻苯二酚是在体内和离体大鼠肝细胞中作为溴苯的代谢产物形成的。这两种代谢产物可能对溴苯的肝毒性有潜在的贡献。在用苯巴比妥处理的大鼠中分离出的肝细胞代谢溴苯,在2小时内形成0.12到0.17毫摩尔浓度的4-溴苯酚和4-溴邻苯二酚,使用的溴苯浓度为1到3毫摩尔。
4-Bromophenol and 4-bromocatechol are formed as metabolites of bromobenzene in vivo and in isolated rat hepatocytes. Both of these metabolites may potentially contribute to the hepatotoxicity of bromobenzene. Bromobenzene metabolism in hepatocytes isolated from phenobarbital-treated rats forms 0.12 to 0.17 mM 4-bromophenol and 4-bromocatechol in 2 hr, with 1 to 3 mM bromobenzene.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
p-溴酚的微粒体代谢物被分离并鉴定为6-(谷胱甘肽-S-基)-4-溴儿茶酚。p-溴酚在大鼠肝微粒体中部分代谢为4-溴儿茶酚。儿茶酚会自动氧化成相应的醌或半醌,这些物质可以共价结合到微粒体蛋白上,或者,在谷胱甘肽存在的情况下,形成谷胱甘肽结合物。超氧化物歧化酶通过防止超氧阴离子介导的4-溴儿茶酚氧化来抑制这些反应。因此,在谷胱甘肽的存在下,超氧化物歧化酶导致结合物形成减少,相应的4-溴儿茶酚水平增加。增加p-溴酚体外共价结合的条件(即,苯巴比妥治疗和谷胱甘肽的缺失)并未导致体内毒性。因此,p-溴酚的化学活性代谢物在溴苯介导的肝毒性中不起作用。
A microsomal metabolite of p-bromophenol was isolated and identified as 6-(glutathion-S-yl)-4-bromocatechol. p-Bromophenol is metabolized in rat liver microsomes in part to 4-bromocatechol. The catechol undergoes autooxidation to the corresponding quinone or semiquinone, which can either covalently bind to microsomal protein or, in the presence of glutathione, form a glutathione conjugate. Superoxide dismutase inhibited these reactions by preventing the superoxide anion-mediated oxidation of 4-bromocatechol. Thus, in the presence of glutathione, superoxide dismutase caused a decrease in conjugate formation with a corresponding increase in 4-bromocatechol levels. Conditions which increased the in vitro covalent binding of p-bromophenol (namely, phenobarbital treatment and the absence of glutathione) did not cause toxicity in vivo. Thus, chemically reactive metabolite(s) of p-bromophenol do not play a role in bromobenzene-mediated hepatotoxicity.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
溴苯代谢在诱导了苯巴比妥的大鼠的孤立肝细胞和肝脏微粒体中以及在活体诱导了苯巴比妥的大鼠中进行了研究。在用溴苯孵育孤立的大鼠肝细胞时,产生的代谢物轮廓随着肝细胞浓度的不同而有所差异。在肝细胞浓度较低(0.5 x 10+6细胞/mL)时,4-溴苯酚是主要的代谢物,而在较高的肝细胞浓度(2.0和5.0 x 10+6细胞/mL)时,溴苯-3,4-二氢二醇是主要的代谢物。在大鼠肝脏微粒体的孵育中,4-溴苯酚是主要的代谢物。在活体中,3-和4-溴苯酚更为主要,形成的二氢二醇非常少。4-溴儿茶酚,作为一种潜在的溴苯有毒代谢物,在活体以及孤立肝细胞和微粒体中都有形成。然而,儿茶酚形成的机制不同,这是通过溴苯对位上氘标记的保留来确定的。在微粒体中,4-溴苯酚是4-溴儿茶酚的主要前体代谢物。在孤立肝细胞中,尽管4-溴苯酚作为溴儿茶酚前体的相对贡献随着肝细胞浓度的不同而有所差异,但在所有浓度下,溴苯-3,4-二氢二醇都是主要的前体。在活体中,与孤立肝细胞一样,4-溴儿茶酚主要是通过溴苯-3,4-二氢二醇形成的。
The metabolism of bromobenzene has been examined in isolated hepatocytes and liver microsomes from phenobarbital-induced rats and in phenobarbital-induced rats in vivo. The metabolite profile produced upon incubation of isolated rat hepatocytes with bromobenzene differed with the hepatocyte concentration. At a low hepatocyte concentration (0.5 x 10+6 cells/mL), 4-bromophenol was the major metabolite, while at higher hepatocyte concentrations (2.0 and 5.0 x 10+6 cells/mL) bromobenzene-3,4-dihydrodiol was the major metabolite. 4-Bromophenol was the primary metabolite in incubations with rat liver microsomes. In vivo, 3- and 4-bromophenol were more predominant, with very little dihydrodiol formed. 4-Bromocatechol, a potentially toxic metabolite of bromobenzene, was formed in vivo as well as in isolated hepatocytes and microsomes. However, the mechanism of catechol formation differed, as determined by the retention of a deuterium label at the para position of bromobenzene. In microsomes, 4-bromophenol was the predominant precursor metabolite of 4-bromocatechol. In isolated hepatocytes, although the relative contribution of 4-bromophenol as the bromocatechol precursor differed with hepatocyte concentration, bromobenzene-3,4-dihydrodiol was the predominant precursor at all concentrations. In vivo, as in isolated hepatocytes, 4-bromocatechol was formed primarily via bromobenzene-3,4-dihydrodiol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
4-Bromophenol has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-(4-bromophenoxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
/SRP:/ 立即急救:确保已经进行了充分的中毒物清除。如果患者停止呼吸,开始人工呼吸,最好使用需求阀复苏器、袋阀面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练操作。如有必要,执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果发生呕吐,让患者前倾或置于左侧(如果可能的话,头部向下),以保持呼吸道畅通,防止吸入。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗帮助。 /毒物A和B/
/SRP:/ Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR if necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on the left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 基本治疗:建立专利气道(如有需要,使用口咽或鼻咽气道)。如有必要,进行吸痰。观察呼吸不足的迹象,如有需要,辅助通气。通过非循环呼吸面罩以10至15升/分钟的速度给予氧气。监测肺水肿,如有必要,进行治疗……。监测休克,如有必要,进行治疗……。预防癫痫发作,如有必要,进行治疗……。对于眼睛污染,立即用水冲洗眼睛。在运输过程中,用0.9%的生理盐水(NS)持续冲洗每只眼睛……。不要使用催吐剂。对于摄入,如果患者能吞咽、有强烈的干呕反射且不流口水,则用温水冲洗口腔,并给予5毫升/千克,最多200毫升的水进行稀释……。在去污后,用干燥的无菌敷料覆盖皮肤烧伤……。/毒药A和B/
/SRP:/ Basic treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if needed. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 mL/kg up to 200 mL of water for dilution if the patient can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 高级治疗:对于无意识、严重肺水肿或严重呼吸困难的病人,考虑进行口咽或鼻咽气管插管以控制气道。使用气囊面罩装置的正压通气技术可能有益。考虑使用药物治疗肺水肿……。对于严重的支气管痉挛,考虑给予β激动剂,如沙丁胺醇……。监测心率和必要时治疗心律失常……。开始静脉输注D5W /SRP: "保持开放",最低流量/。如果出现低血容量的迹象,使用0.9%生理盐水(NS)或乳酸林格氏液。对于伴有低血容量迹象的低血压,谨慎给予液体。注意液体过载的迹象……。使用地西泮或劳拉西泮治疗癫痫……。使用丙美卡因氢氯化物协助眼部冲洗……。 /Poisons A and B/
/SRP:/ Advanced treatment: Consider orotracheal or nasotracheal intubation for airway control in the patient who is unconscious, has severe pulmonary edema, or is in severe respiratory distress. Positive-pressure ventilation techniques with a bag valve mask device may be beneficial. Consider drug therapy for pulmonary edema ... . Consider administering a beta agonist such as albuterol for severe bronchospasm ... . Monitor cardiac rhythm and treat arrhythmias as necessary ... . Start IV administration of D5W /SRP: "To keep open", minimal flow rate/. Use 0.9% saline (NS) or lactated Ringer's if signs of hypovolemia are present. For hypotension with signs of hypovolemia, administer fluid cautiously. Watch for signs of fluid overload ... . Treat seizures with diazepam or lorazepam ... . Use proparacaine hydrochloride to assist eye irrigation ... . /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
内分泌调节/... 苯酚、4-溴苯酚(4-BP)、2,4-二溴苯酚(2,4-DBP)、2,4,6-三溴苯酚(2,4,6-TBP)和4-叔丁基苯酚(叔-BP)的雌激素样活性/被特征化为/使用雌激素依赖性人乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7。4-BP、2,4-DBP和4-叔-BP都与雌激素受体(ER)结合,其亲和力大约比17 beta-雌二醇(17 beta-E)低10,000倍。当在1 uM的浓度下测试时,2,4,6-TBP只能取代43%的放射性标记雌激素,而苯酚对ER没有亲和力。4-叔-BP刺激细胞生长并诱导雌激素调节蛋白,如孕酮受体(PgR)和pS2。然而,尽管溴代苯酚与ER结合,但它们并没有刺激细胞生长或增加PgR或pS2的水平,也没有降低17 beta-E诱导的pS2水平。相反,4-BP、2,4-DBP和部分4-叔-BP通过一种看似ER独立的机制减少了17 beta-E刺激的细胞生长。
/ENDOCRINE MODULATION/ ... The estrogen-like activity of phenol, 4-bromophenol (4-BP), 2,4-dibromophenol (2,4-DBP), 2,4,6-tribromophenol (2,4,6-TBP) and 4-tert-butylphenol (tert-BP) /was characterized/ using the estrogen-dependent human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. 4-BP, 2,4-DBP and 4-tert-BP all bind to the estrogen receptor (ER) with approximately 10,000-fold less affinity than 17 beta-estradiol (17 beta-E). 2,4,6-TBP was only able to displace 43% of radiolabelled estrogen when tested at concentrations up to 1 uM, whereas phenol had no affinity for the ER. 4-tert-BP stimulated cell growth and induced estrogen-regulated proteins such as the progesterone receptor (PgR) and pS2. The brominated phenols, however, although binding to the ER, did not stimulate cell growth or increase the levels of the PgR or pS2, or reduce the level of 17 beta-E induced pS2. On the contrary, 4-BP, 2,4-DBP and partly 4-tert-BP reduced 17 beta-E-stimulated cell growth apparently by an ER independent mechanism.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/替代测试和体外测试/
本研究评估了十九种多溴联苯醚(BDEs)、五种羟基化多溴联苯醚(OH-BDEs)、一种甲氧基化多溴联苯醚(CH(3)O-BDE)、四溴双酚-A(TBBPA)、其二溴丙烷醚衍生物(TBBPA-DBPE)以及溴化酚/茴香醇2,4,6-三溴苯酚(TBP)、4-溴苯酚(4BP)和2,4,6-三溴茴香醚(TBA)对H295R人类肾上腺皮质癌细胞中类固醇生成酶芳香化酶(CYP19)的催化活性的潜在影响。研究的浓度范围是0.5到7.5微摩尔;暴露时间为24小时。6-OH-BDE47和6-OH-BDE99在浓度分别大于2.5微摩尔和大于5微摩尔时,显示出对芳香化酶活性的抑制作用。然而,6-OH-BDE47在浓度大于2.5微摩尔时也引起了细胞毒性(基于线粒体MTT还原和乳酸脱氢酶泄漏[LDH])的统计学显著增加,这可能部分解释了对芳香化酶活性的明显抑制作用。与6-OH-BDE47相比,甲氧基类似物(6-CH(3)O-BDE47)没有引起细胞毒性效应,而芳香化酶的显著抑制作用仍然存在。TBP在0.5到7.5微摩尔的浓度范围内引起了芳香化酶活性的浓度依赖性诱导(在7.5微摩尔时最大诱导倍数为3.8倍)。当OH-基团取代CH(3)O-基团,或者当这个OH-基团附近的溴原子不存在时,这种诱导作用并未观察到...
/ALTERNATIVE and IN VITRO TESTS/ /The/ study assessed the potential effects of nineteen polybrominated diphenyl ethers (BDEs), five hydroxylated BDEs (OH-BDEs), one methoxylated BDE (CH(3)O-BDE), tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBPA), its dibromopropane ether derivative (TBBPA-DBPE), and the brominated phenols/anisols 2,4,6-tribromophenol (TBP), 4-bromophenol (4BP) and 2,4,6-tribromoanisole (TBA) on the catalytic activity of the steroidogenic enzyme aromatase (CYP19) in H295R human adrenocortical carcinoma cells. Effects were studied in the concentration range from 0.5 to 7.5 uM; exposures were for 24 hr. Both 6-OH-BDE47 and 6-OH-BDE99 showed an inhibitory effect on aromatase activity at concentrations >2.5 uM and >5 uM, respectively. However, 6-OH-BDE47 also caused a statistically significant increase in cytotoxicity (based on mitochondrial MTT reduction and lactate dehydrogenase-leakage [LDH]) at concentrations >2.5 uM that could explain in part the apparent inhibitory effect on aromatase activity. Compared to 6-OH-BDE47, the methoxy analog (6-CH(3)O-BDE47) did not elicit a cytotoxic effect, whereas significant inhibition of aromatase remained. TBP caused a concentration-dependent induction of aromatase activity between 0.5 and 7.5 uM (with a maximum of 3.8-fold induction at 7.5 uM). This induction was not observed when a OH- group replaced the CH(3)O- group or when bromine atoms adjacent to this OH- group were absent...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R22,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2908199090
-
危险品运输编号:2811
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
RTECS号:SJ7960000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 应储存在阴凉、通风良好的库房中。 - 远离火源和热源。 - 包装需密封保存。 - 与氧化剂及食用化学品分开存放,避免混存。 - 配备相应的消防器材。 - 储区应准备合适的材料以处理泄漏物。
制备方法与用途
应用
4-溴苯酚是一种含溴化合物。在医药、染料、农药、香料、颜料、增塑剂、阻燃剂的生产过程中,含溴化合物发挥着重要作用。例如,在医药行业中,它们用于制造多种镇静剂和消毒剂,并作为抗菌药物的中间体。
理化性质4-溴苯酚(对溴苯酚)可从乙醚或三氯甲烷中析出四面双锥形结晶。熔点为66.4℃,微量水分会使熔点显著降低。沸点为238℃,在118.2℃时的饱和蒸汽压为1.46kPa,相对密度为1.840(15/4℃)。它溶于水、三氯甲烷,并易溶于乙醇、乙醚和冰醋酸,还能溶解于7份水中。
制备在三口瓶中,加入苯酚(4.33g, 0.046mmol)、TBAB(7.45g, 0.023mmol)、KBr(8.26g, 0.069mmol)和1,2-二氯乙烷(20mL),在40℃下搅拌。随后,在反应液中加入三光气(17.80g, 0.060mmol)的1,2-二氯乙烷(40mL)溶液,待反应完成后,用少量水洗涤反应物并蒸发以得到产品7.40g。该产品的收率为93%,纯度通过HPLC测得为99%。
用途4-溴苯酚在有机合成中常用作STille反应试剂,在制药工业中也有应用,并可作为杀虫剂和阻燃剂的中间体。
生产方法4-溴苯酚可通过苯酚溴化获得。具体步骤包括:将溴素、二硫化碳溶液加入到苯酚与二硫化碳的混合液中,然后在5℃以下开始缓慢添加,在搅拌下2小时内完成反应。将反应物蒸馏去除二硫化碳后,再进行减压分馏,收集145-150℃(3.32-3.99kPa)馏分即可得到产品。产率为80-84%。
类别有毒物品
毒性分级高毒
急性毒性口服:小鼠LD₅₀: 523毫克/公斤;腹腔:小鼠LD₅₀: 411毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性遇明火可燃,燃烧时释放有毒溴化物烟雾。
储运特性库房应通风、低温干燥,并与氧化剂和食品添加剂分开存放。
灭火剂 职业标准短期暴露极限(STEL)为0.3毫克/立方米。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 间溴苯酚 3-Bromophenol 591-20-8 C6H5BrO 173.009 4-溴苯甲醚 1-bromo-4-methoxy-benzene 104-92-7 C7H7BrO 187.036 2-溴苯酚 2-Bromophenol 95-56-7 C6H5BrO 173.009 —— 4-bromophenyl formate 4525-62-6 C7H5BrO2 201.019 4-溴苯乙醚 4-bromoethoxybenzene 588-96-5 C8H9BrO 201.063 4,4'-二溴二苯醚 4,4'-dibromodiphenyl ether 2050-47-7 C12H8Br2O 328.003 4-溴联苯醚 4-Bromodiphenyl ether 101-55-3 C12H9BrO 249.107 三溴苯酚 2,4,6-tribromophenol 118-79-6 C6H3Br3O 330.801 1-溴-4-(甲氧基甲氧基)苯 p-methoxymethoxybromobenzene 25458-45-1 C8H9BrO2 217.062 4-溴苯基炔丙基醚 1-bromo-4-(prop-2-ynyloxy)benzene 33133-45-8 C9H7BrO 211.058 4-n-丙氧基溴苯 1-bromo-4-propoxybenzene 39969-56-7 C9H11BrO 215.09 4-(烯丙氧基)-1-溴苯 4-(allyloxy)bromobenzene 25244-30-8 C9H9BrO 213.074 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 间溴苯酚 3-Bromophenol 591-20-8 C6H5BrO 173.009 4-溴苯甲醚 1-bromo-4-methoxy-benzene 104-92-7 C7H7BrO 187.036 —— O-(4-bromophenyl)hydroxylamine 65440-82-6 C6H6BrNO 188.024 2-溴苯酚 2-Bromophenol 95-56-7 C6H5BrO 173.009 4-溴邻苯二酚 1-bromo-3,4-dihydroxybenzene 17345-77-6 C6H5BrO2 189.008 2,4-二溴苯酚 2,4-dibromophenol 615-58-7 C6H4Br2O 251.905 —— 4-bromophenyl formate 4525-62-6 C7H5BrO2 201.019 —— bromomethyl 4-bromophenyl ether 121824-53-1 C7H6Br2O 265.932 4-溴苯乙醚 4-bromoethoxybenzene 588-96-5 C8H9BrO 201.063 4-乙烯氧基溴苯 4-bromophenyl vinyl ether 1005-61-4 C8H7BrO 199.047 —— 1-bromo-4-ethynyloxybenzene 6686-67-5 C8H5BrO 197.031 4-溴联苯醚 4-Bromodiphenyl ether 101-55-3 C12H9BrO 249.107 4,4'-二溴二苯醚 4,4'-dibromodiphenyl ether 2050-47-7 C12H8Br2O 328.003 —— 4-bromophenyl chloromethyl ether 35657-04-6 C7H6BrClO 221.481 —— 1-bromo-4-(fluoromethoxy)benzene 496052-51-8 C7H6BrFO 205.026 三溴苯酚 2,4,6-tribromophenol 118-79-6 C6H3Br3O 330.801 1-溴-4-(甲氧基甲氧基)苯 p-methoxymethoxybromobenzene 25458-45-1 C8H9BrO2 217.062 2-(4-溴苯氧基)乙醇 2-(4-bromophenoxy)ethanol 34743-88-9 C8H9BrO2 217.062 —— (4-Bromophenoxy)-dichlorophosphane 97680-24-5 C6H4BrCl2OP 273.881 4-n-丙氧基溴苯 1-bromo-4-propoxybenzene 39969-56-7 C9H11BrO 215.09 4-溴苯基炔丙基醚 1-bromo-4-(prop-2-ynyloxy)benzene 33133-45-8 C9H7BrO 211.058 —— 4-bromophenyl methylthiomethyl ether 63316-81-4 C8H9BrOS 233.129 1-溴-4-异丙氧基苯 1-bromo-4-isopropoxybenzene 6967-88-0 C9H11BrO 215.09 1-溴-4-(2-氟乙氧基)苯 1-bromo-4-(2-fluoroethoxy)benzene 332-47-8 C8H8BrFO 219.053 —— 1,1’-[methylenebis(oxy)]bis[4-bromobenzene] 69984-32-3 C13H10Br2O2 358.029 4-溴苯基 2-氯乙基醚 1-bromo-4-(2-chloroethoxy)benzene 55162-34-0 C8H8BrClO 235.508 1-溴-4-(二氟甲氧基)苯 1-bromo-4-(difluoromethoxy)benzene 5905-69-1 C7H5BrF2O 223.017 1-(2-溴氧基)-4-溴苯 1-bromo-4-(2-bromoethoxy)benzene 18800-30-1 C8H8Br2O 279.959 —— 2-(4-bromophenoxy)acetaldehyde 134671-56-0 C8H7BrO2 215.046 2-(4-溴苯氧基)乙胺 2-(4-bromophenoxy)ethanamine 26583-55-1 C8H10BrNO 216.077 4-(4-溴苯氧基)苯酚 4-(4-bromophenoxy)phenol 13320-48-4 C12H9BrO2 265.106 4-溴苯氧基乙腈 (4-bromophenoxy)acetonitrile 39489-67-3 C8H6BrNO 212.046 4-(烯丙氧基)-1-溴苯 4-(allyloxy)bromobenzene 25244-30-8 C9H9BrO 213.074 1-溴-4-(4-苯氧基苯氧基)苯 p-(p-phenoxyphenoxy)bromobenzene 54590-36-2 C18H13BrO2 341.204 —— (Z)-1-bromo-4-(prop-1-en-1-yloxy)benzene 205981-40-4 C9H9BrO 213.074 间溴苯甲醚 3-methoxyphenyl bromide 2398-37-0 C7H7BrO 187.036 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:形成轴向手性非C2对称联芳基的肽催化片段偶联。摘要:我们已经证明具有路易斯基本残基β-二甲基氨基丙氨酸(Dmaa)的小,模块化,四聚体肽能够对萘酚和带有酯的醌进行熵选择性偶联,以产生具有良好收率和对映选择性的非C2对称BINOL型支架。该研究最终以不对称合成类似于3,3'-双取代BINOL的骨架取代支架(如(R)-TRIP),重结晶后具有良好的(94:6 er)至优异的(> 99.9:0.1 er)对映选择性,以及修饰最小的非甾体类抗炎药(NSAID)萘普生的非对映选择性净芳基化。DOI:10.1002/anie.201913563
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Authenrieth; Muehlinghaus, Chemische Berichte, 1907, vol. 40, p. 748摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:2,2-dimethyl-5-(4-nitrobenzylidene)-1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione 、 (E)-4-cyanobenzalacetone 在 奎宁胺 、 4-溴苯酚 作用下, 以 氯仿 为溶剂, 反应 96.0h, 生成 4-(3,3-dimethyl-11-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,5,9-trioxo-2,4-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecan-7-yl)benzonitrile 、 4-(3,3-dimethyl-11-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,5,9-trioxo-2,4-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecan-7-yl)benzonitrile参考文献:名称:通过有机催化三组分反应不对称合成多取代螺[5,5]十一烷-1,5,9-三酮摘要:作为一种重要的方法,非对称多米诺三组分Knoevanagel-Diels-Alder加成反应(ATCDA)已被用于从普通起始原料构建复杂的产物。在本报告中,研究了许多典型的有机胺催化剂,以实现烯酮2,醛3和Meldrum酸4的高效不对称三组分反应。各种药理学上多取代的螺[5,5]十一烷-1,5,9-三酮一锅得到9 g的9-氨基-9-脱氧表位-奎宁促进,中等至良好的收率(高达81%),具有极好的非对映异构体(> 99:1 dr)和对映选择性(高达97 %ee)。同时,根据控制实验和分析数据,提出了该反应双重活性的合理机理。DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2011.01.037
文献信息
-
Expanding the Scope of Hypervalent Iodine Reagents for Perfluoroalkylation: From Trifluoromethyl to Functionalized Perfluoroethyl作者:Václav Matoušek、Jiří Václavík、Peter Hájek、Julie Charpentier、Zsófia E. Blastik、Ewa Pietrasiak、Alena Budinská、Antonio Togni、Petr BeierDOI:10.1002/chem.201503531日期:2016.1.4A series of new hypervalent iodine reagents based on the 1,3‐dihydro‐3,3‐dimethyl‐1,2‐benziodoxole and 1,2‐benziodoxol‐3‐(1H)‐one scaffolds, which contain a functionalized tetrafluoroethyl group, have been prepared, characterized, and used in synthetic applications. Their corresponding electrophilic fluoroalkylation reactions with various sulfur, oxygen, phosphorus, and carbon‐centered nucleophiles
-
[EN] HYPERVALENT IODINE CF2CF2X REAGENTS AND THEIR USE<br/>[FR] RÉACTIFS CF2CF2X À BASE D'IODE HYPERVALENT ET LEUR UTILISATION申请人:ETH ZUERICH公开号:WO2016019475A1公开(公告)日:2016-02-11A hypervalent iodine of formula (I) or formula (II) wherein R is a nucleophile and a method for their production is described. Such compounds can be used for fluoroethylation of compounds carrying a reactive group. A preferred compound carrying a reactive group is cystein in any environment such as peptide targets.
-
Cyclopropyl derivative lipoxygenase inhibitors申请人:Abbott Laboratories公开号:US05037853A1公开(公告)日:1991-08-06Certain carbocyclic aryl- and heterocyclic aryl-substituted cyclopropyl N-hydroxyureas, N-hydoroxycarboxamides, and N-acyl-N-hydroxyamides inhibit 5- and/or 12-lipoxygenase and are useful in the treatment of inflammatory disease states.某些含环丙基N-羟基脲、N-羟基羧酰胺和N-酰基-N-羟基酰胺的碳环芳基和杂环芳基取代物抑制5-和/或12-脂氧合酶,在治疗炎症性疾病状态中具有用处。
-
BENZOTHIOPHENE INHIBITORS OF RHO KINASE申请人:Kahraman Mehmet公开号:US20080021026A1公开(公告)日:2008-01-24The present invention relates to compounds and methods which may be useful as inhibitors of Rho kinase for the treatment or prevention of disease.本发明涉及化合物和方法,这些化合物和方法可能作为Rho激酶的抑制剂在治疗或预防疾病方面有用。
-
NEW STRIGOLACTONE ANALOGUES AND THE USE THEREOF FOR THE TREATMENT OF PLANTS申请人:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE公开号:US20150141255A1公开(公告)日:2015-05-21A compound of general formula (I): in which X represents O, S, NH or an N-alkyl radical, R 1 and R 2 , identical or different, each represent H or a C 1 -C 10 hydrocarbon radical, R 1 and R 2 not both representing H, R 3 represents a C 1 -C 10 hydrocarbon radical, and R represents a phenyl radical monosubstituted or disubstituted by a substituent Y and, if applicable, a substituent Z, chosen from Cl, Br, I and CF 3 , or R represents a C═R 4 (R 5 ) radical in which R 4 represents an hydrocarbon radical and R 5 represents a linear or branched, saturated or unsaturated, hydrocarbon radical, optionally substituted, a COR 6 group or a CO 2 R 6 group, where R 6 represents a hydrogen atom or a linear or branched, saturated or unsaturated, hydrocarbon radical. This compound can be used for the treatment of higher plants for controlling their growth and architecture.通式(I)的化合物: 其中X代表O、S、NH或N-烷基基团,R1和R2,相同或不同,各自代表H或C1-C10烃基,R1和R2不同时代表H,R3代表C1-C10烃基,R代表被取代基团Y和如适用的取代基团Z选择自Cl、Br、I和CF3的苯基单取代或双取代基团,或R代表C═R4(R5)基团,其中R4代表烃基团,R5代表线性或支链、饱和或不饱和、可选择取代的烃基团、COR6基团或CO2R6基团,其中R6代表氢原子或线性或支链、饱和或不饱和的烃基团。该化合物可用于治疗高等植物,控制其生长和结构。
表征谱图
-
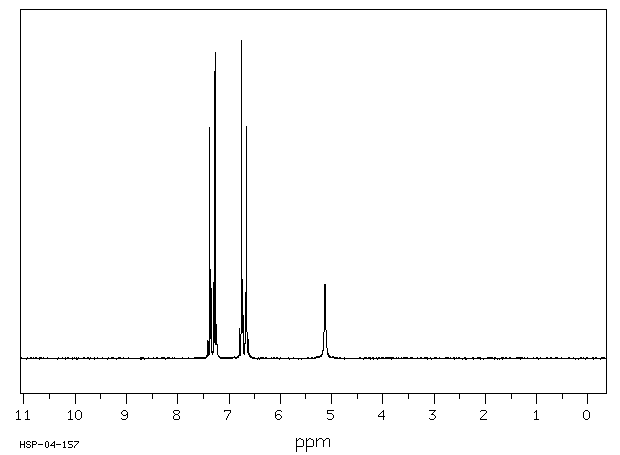
氢谱1HNMR
-
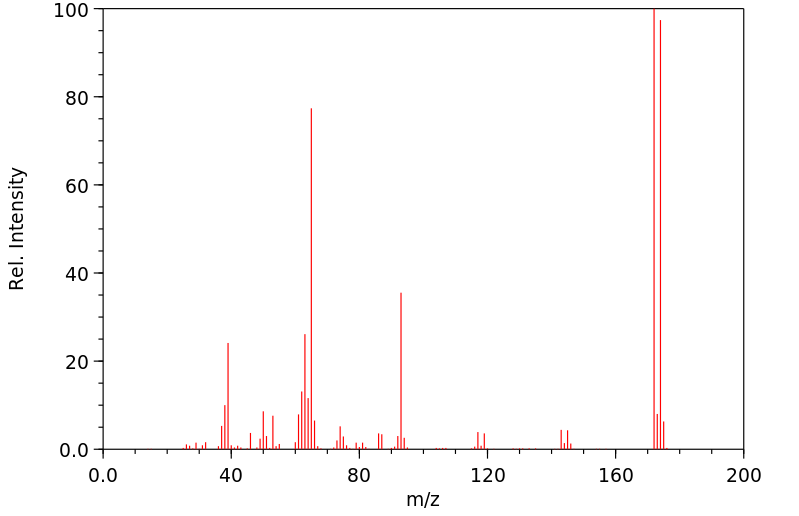
质谱MS
-
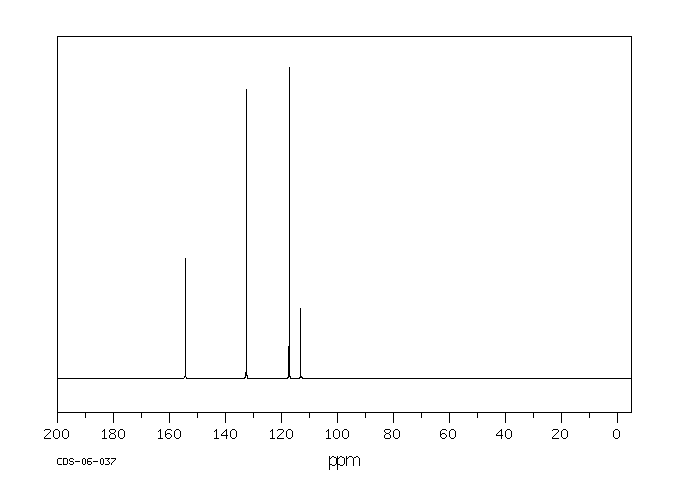
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(2-氯-6-羟基苯基)硼酸
黄柄曲菌素
高香草酸-d3
高香草酸-13C6
高香草酸
高香兰酸乙酯
高辣椒素II
高二氢辣椒素I
香草醛醛肟
香草醛苯腙
香草醛-甲氧基-13C
香草醛-(N-对甲苯基肟)
香草醛
香草酸肼
香草壬酰胺
香草基扁桃酸乙酯
香草吗啉
香草二乙胺
香兰素胺硬脂酸盐
香兰素胺硬脂酸盐
香兰素胺盐酸盐
香兰素丙二醇缩醛
香兰素13C6
香兰素-D3
香兰基乙基醚
香兰基丁醚
顺式-5-正十五碳-8'-烯基间苯二酚
顺式-1-(2-羟基-5-甲基苯基)-2-丁烯-1-酮
顺式-1-(2-羟基-4-甲氧基苯基)-2-丁烯-1-酮
顺-3-氯二氢-5-苯基呋喃-2(3H)-酮
雌二醇杂质1
降二氢辣椒碱
阿诺洛尔
阿瓦醇
阿普斯特杂质
间苯二酚双(二苯基磷酸酯)
间苯二酚-烯丙醇聚合物
间苯二酚-D6
间苯二酚
间苯三酚甲醛
间苯三酚二水合物
间苯三酚
间羟基苯乙基溴
间硝基苯酚
间甲酚紫钠盐
间甲酚与对甲酚和苯酚甲醛树脂的聚合物
间甲酚-D7
间甲酚-D3
间甲酚
间溴苯酚