6-mercaptopurine | 6112-76-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:>300 °C(lit.)
-
溶解度:不溶的
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:Yellow crystalline powder
-
气味:Nearly odorless
-
蒸汽压力:1.27X10-8 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
碰撞截面:125.5 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:85.2
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S22,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R22,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29335995
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:UP0400000
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335,H351,H361
-
储存条件:请将药品存放在避光、阴凉干燥的地方,并密封保存。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 6-巯基嘌呤 一水合物
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
6-Purinethiol
6-Thiohypoxanthine
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
皮肤刺激 (类别2)
眼刺激 (类别2A)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P302 + P352 如与皮肤接触,用大量肥皂和水冲洗受感染部位.
P304 + P340 如吸入,将患者移至新鲜空气处并保持呼吸顺畅的姿势休息.
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P332 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激:求医/ 就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊.
P362 脱掉沾染的衣服,清洗后方可重新使用。
储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P405 存放处须加锁。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: 6-Purinethiol
别名
6-Thiohypoxanthine
: C5H4N4S · H2O
分子式
: 170.19 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Mercaptopurine
-
CAS 号 6112-76-1
EC-编号 200-037-4
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 硫氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
将人员撤离到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 粉末
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: > 300 °C - lit.
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂, 强碱, 强酸
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 老鼠 - 1,250 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
3 - GroUP 3: Not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans (Mercaptopurine)
生殖毒性
实验室试验表明有畸胎生成效应
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: UP0400000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
巯嘌呤(Mercaptopurine,简称6-MP),又称6-巯基嘌呤、巯基嘌呤或巯唑嘌呤,是一种硫嘌呤类化疗药物和免疫抑制剂。
适应症巯嘌呤主要用于急性白血病(包括急性粒细胞白血病和急性淋巴细胞白血病)的维持治疗。此外,它也被用于治疗恶性葡萄胎、绒毛膜上皮癌、真红细胞增多症、银屑病关节炎以及炎症性肠病(如克罗恩病和溃疡性结肠炎)。有研究表明,巯嘌呤在体外具有抗副结核分枝杆菌活性。
作用机理作为一种嘌呤类似物,巯嘌呤属于嘌呤拮抗剂类的抗代谢药物。它通过抑制酰胺转移酶来干扰嘌呤核苷酸合成;抑制次黄嘌呤核苷酸转化为腺嘌呤核苷酸及黄嘌呤核苷酸、鸟嘌呤核苷酸的过程;还能够抑制烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD+)的合成,并引起脱氧腺苷三磷酸(dATP)和脱氧鸟苷三磷酸(dGTP)水平下降。这些作用使得巯嘌呤能有效抑制DNA的合成,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的生长。
生物活性6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) Monohydrate 是一种广泛使用的抗白血病药和免疫抑制剂,能够通过将巯嘌呤甲基转移酶代谢产物整合到 DNA 和 RNA 中来抑制嘌呤从头合成。
体外研究Mercaptopurine 被广泛应用治疗恶性肿瘤、风湿性疾病、皮肤病、炎性肠道疾病以及实体器官移植排斥反应。它通过抑制磷酸核糖焦磷酸酰胺转移酶 (PRPP酰胺转移酶),抑制嘌呤核苷酸的合成和代谢,而 PRPP酰胺转移酶是嘌呤和嘧啶生物合成过程中的限速酶。这会改变 RNA 和 DNA 的合成与功能。Mercaptopurine 还干扰了核苷互变现象和糖蛋白的合成。
化学性质单水合物为微黄色结晶粉末,熔点在312-314℃之间,易溶于碱性溶液,略溶于热水,不溶于水、丙酮或乙醚。
用途6-巯基嘌呤是溶癌呤和硫唑嘌呤的中间体,并可作为抗肿瘤药物使用。它也是一种免疫抑制剂,用于治疗白血病。此外,还适用于儿科非霍奇金淋巴瘤、真红细胞增多症及银屑病关节炎。
生产方法上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 7-(dimethylamino)methyl-6-mercaptopurine 119056-59-6 C8H11N5S 209.275 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 6-硫代-2-羟基嘌呤 6-thioxanthine 2002-59-7 C5H4N4OS 168.179 6-硫代-7,9-二氢-3H-嘌呤-2,8-二酮 6-Thiouric acid 2002-60-0 C5H4N4O2S 184.178 嘌呤 purine 120-73-0 C5H4N4 120.114 —— 7-(dimethylamino)methyl-6-mercaptopurine 119056-59-6 C8H11N5S 209.275 —— 7-(diethylamino)methyl-6-mercaptopurine 119087-39-7 C10H15N5S 237.329
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:6-mercaptopurine 在 O-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate 、 三乙胺 、 2,3-二氯-5,6-二氰基-1,4-苯醌 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 、 二甲基亚砜 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 21.33h, 生成 [3-hexadecanoyloxy-2-[11-(7H-purin-6-yldisulfanyl)undecanoylamino]propyl] hexadecanoate参考文献:名称:Branched-chain and dendritic lipids for nanoparticles摘要:脂质纳米颗粒(LNPs)用于药物传递应用主要来源于天然脂质。合成脂质,特别是那些包含支链碳氢化合物和超支链碳氢化合物结构的合成脂质,可能具有增强的亲脂性和流动性,从而导致LNPs稳定。基于丝氨醇二酯的碳氢化合物锚点是从线性Cn(n = 14、16、18)和支链(n = 16)酸与Boc保护的丝氨醇反应制备而成。这些二酯在亚胺二乙酸酰胺骨架上进一步二聚,提供了八种支链和树枝状脂质锚点。对这些核心结构的衍生物进行改性,提供了八种PEG-脂质和七种硫嘌呤连接的脂质-药物共轭物。LNPs是通过将混合脂质在乙醇中稀释成水介质中进行微流体混合来制备的。脂质-药物共轭物包含5 mol%的磷胆碱和5 mol%的商业PEG-脂质,形成硫嘌呤药物负载为15 wt%的LNPs。制备的PEG-脂质以1.5 mol%的浓度作为表面稳定剂,添加到含有dsDNA脂质体复合物的LNPs中。通过监测粒径来评估LNPs在不同储存条件下的稳定性。对于来自脂质-硫嘌呤共轭物和PEG-脂质系统的LNPs,有强有力的初步证据表明,碳氢化合物支链导致LNPs稳定。四种脂质-药物共轭物配方在细胞培养条件(10%血清,37°C)下稳定,评估了这些LNPs相对于培养基中的游离硫嘌呤对两种细胞系的毒性。观察到的毒性与LNPs的细胞摄取和细胞内硫嘌呤的还原释放一致。DOI:10.1139/cjc-2016-0462
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Mercapto heterocycles and method of making摘要:公开号:US02697709A1
-
作为试剂:描述:sodium hydroxide 、 6-巯基嘌呤(一水合物) 、 2-hydroxy-3-[4-diphenylmethyl-1-piperazinyl]propyl chloride 在 氮 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 、 methanol-dichloromethane 、 6-mercaptopurine 、 正戊烷 作用下, 以 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 25.0~80.0 ℃ 、17.77 kPa 条件下, 反应 72.58h, 以to give the title compound (0.35 g, 15.0%), mp 105°-110° C. (dec)的产率得到6-[2-Hydroxy-3-(1-(diphenylmethyl)piperazin-4-yl)propan-1-yl]thiopurine Hemihydrate参考文献:名称:6-Substituted purinyl piperazine derivatives useful as cardiotonic and摘要:本文描述了6-取代嘌呤基哌嗪衍生物及其合成方法。这些6-取代嘌呤基哌嗪衍生物可用作心脏强心剂和抗心律失常剂。公开号:US04876257A1
文献信息
-
[EN] TREATMENT OR PROPHYLAXIS OF PROLIFERATIVE CONDITIONS<br/>[FR] TRAITEMENT OU PROPHYLAXIE D'ÉTATS PROLIFÉRATIFS申请人:UNIV DUNDEE公开号:WO2010125350A1公开(公告)日:2010-11-04The invention relates to novel compounds for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of cancers and other proliferative conditions that are for example characterized by cells that express cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) and allelic variants thereof. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more such compounds for use in medical therapy, for example in the treatment of prophylaxis of cancers or other proliferative conditions, as well as methods for treating cancers or other conditions in human or non-human animal patients. The invention also provides methods for identifying novel compounds for use in the treatment of prophylaxis of cancers and other proliferative conditions that are for example characterized by cells that express CYP1 B1 and allelic variants thereof. The invention also provides a method for determining the efficacy of a compound of the invention in treating cancer.
-
Detoxication of Sulfur Half-Mustards by Nucleophilic Scavengers: Robust Activity of Thiopurines作者:Jinyun Liu、K. Leslie Powell、Howard D. Thames、Michael C. MacLeodDOI:10.1021/tx900190j日期:2010.3.15Sulfur mustard and monofunctional analogues (half-mustards, 2-[chloroethyl] alkyl sulfides) react as electrophiles, damaging cellular macromolecules, and thus are potentially subject to scavenging by nucleophilic agents. We have determined rate constants for the reaction of four purine derivatives that contain nucleophilic thiol moieties with several sulfur-half-mustards. Three of these compounds, 2,6-dithiopurine自第一次世界大战以来,硫芥(双(2-氯乙基)硫化物)一直用于化学战,是众所周知的剧毒起泡剂。在长期低水平暴露后,它被认为是一种致癌物质,并且已知会在 DNA 中形成链间交联。由于易于合成,硫和氮芥作为恐怖分子的潜在化学威胁剂目前受到关注。硫芥和单功能类似物(半芥末,2-[氯乙基] 烷基硫化物)作为亲电试剂反应,破坏细胞大分子,因此可能会被亲核试剂清除。我们已经确定了四种含有亲核硫醇部分的嘌呤衍生物与几种半硫芥的反应速率常数。这些化合物中的三种,2,6-二硫嘌呤、2,6-二硫脲酸、和 9-methyl-6-mercaptopurine,与亲电子芥子化合物表现出容易的反应。在接近中性的 pH 值下,这些硫嘌呤是芥末亲电试剂的亲核清除剂,比其他低分子量硫醇(如N-乙酰半胱氨酸和谷胱甘肽。通过数值积分技术计算的进展曲线表明,等摩尔浓度的硫嘌呤显着减少了对表锍离子的总体暴露,这是硫芥子气溶解在水溶液中时产生的主要反应性亲电子试剂。
-
8-arylalkyl- and申请人:Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.公开号:US05705499A1公开(公告)日:1998-01-06Disclosed are novel 8-arylalkyl-5,11-dihydro-6H-dipyrido\x9b3,2-b:2',3'-e!\x9b1,4!diazepines. These are useful in the treatment of HIV-1 infection.公开的是新型的8-芳基烷基-5,11-二氢-6H-二吡啶[3,2-b:2',3'-e]![1,4]二氮杂环。这些化合物在治疗HIV-1感染中是有用的。
-
[EN] PYRROLOTRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES AS PI3K INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE PYRROLOTRIAZINONE EN TANT QU'INHIBITEURS DE PI3K申请人:ALMIRALL SA公开号:WO2012146666A1公开(公告)日:2012-11-01New pyrrolotriazinone derivatives having the chemical structure of formula (I) are disclosed; as well as process for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising them and their use in therapy as inhibitors of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases (PI3Ks).
-
一种具有杀虫作用的芳基吡唑嘌呤类化合物、 制备方法及应用
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
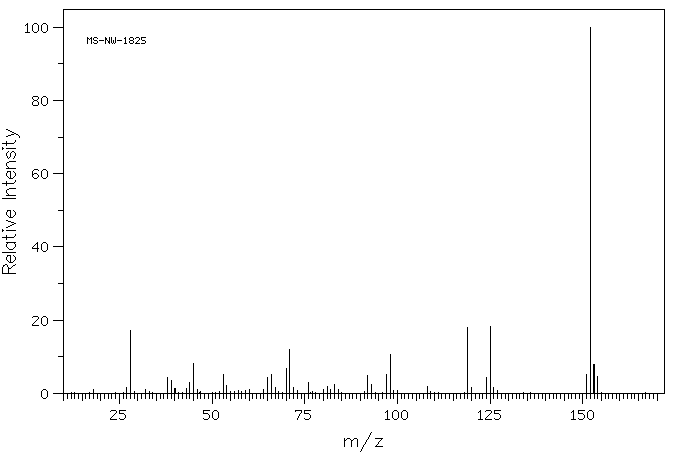
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
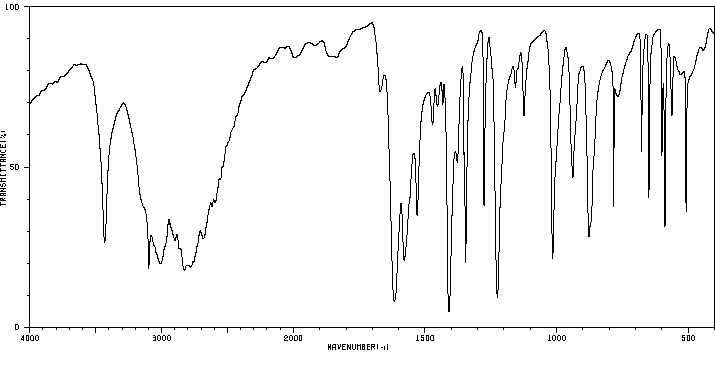
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息