9,9-二甲基芴 | 4569-45-3
中文名称
9,9-二甲基芴
中文别名
9,9'-二甲基芴
英文名称
9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene
英文别名
9,9-dimethylfluorene;9,9-Dimethyl-fluoren
CAS
4569-45-3
化学式
C15H14
mdl
MFCD00114670
分子量
194.276
InChiKey
ZHQNDEHZACHHTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:96°C
-
沸点:287 °C
-
密度:1.040±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
最大波长(λmax):301nm(EtOH)(lit.)
-
保留指数:1573.2
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 在常温常压下保持稳定。
- 主要存在于烟气中。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.4
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.2
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R20/21/22
-
海关编码:2902909090
-
危险性防范说明:P280,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302
-
储存条件:常温、避光、通风干燥处,密封保存。
SDS
Section I.Chemical Product and Company Identification
Chemical Name 9,9-Dimethylfluorene
Portland OR
Synonym 9H-Fluorene, 9,9-dimethyl- (CA INDEX NAME)
Chemical Formula C15H14
4569-45-3
CAS Number
Section II. Composition and Information on Ingredients
Chemical Name CAS Number Percent (%) TLV/PEL Toxicology Data
9,9-Dimethylfluorene 4569-45-3 Min. 98.0 (GC) Not available. Not available.
Section III. Hazards Identification
No specific information is available in our data base regarding the toxic effects of this material for humans. However,
Acute Health Effects
exposure to any chemical should be kept to a minimum. Skin and eye contact may result in irritation. May be harmful if
inhaled or ingested. Always follow safe industrial hygiene practices and wear proper protective equipment when handling
this compound.
Chronic Health Effects CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS : Not available.
MUTAGENIC EFFECTS : Not available.
TERATOGENIC EFFECTS : Not available.
DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available.
Repeated or prolonged exposure to this compound is not known to aggravate existing medical conditions.
Section IV. First Aid Measures
Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15
Eye Contact
minutes. Get medical attention.
Skin Contact In case of contact, immediately flush skin with plenty of water. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Wash clothing
before reuse. Thoroughly clean shoes before reuse. Get medical attention.
If the victim is not breathing, perform mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or
Inhalation
waistband. If breathing is difficult, oxygen can be administered. Seek medical attention if respiration problems do not
improve.
Ingestion INDUCE VOMITING by sticking finger in throat. Lower the head so that the vomit will not reenter the mouth and throat.
Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. If the victim is not breathing, perform mouth-to-mouth
resuscitation. Examine the lips and mouth to ascertain whether the tissues are damaged, a possible indication that the toxic
material was ingested; the absence of such signs, however, is not conclusive.
Section V. Fire and Explosion Data
Not available.
May be combustible at high temperature. Auto-Ignition
Flammability
Flash Points Flammable Limits Not available.
Not available.
Combustion Products These products are toxic carbon oxides (CO, CO2).
Fire Hazards
Not available.
Risks of explosion of the product in presence of mechanical impact: Not available.
Explosion Hazards
Risks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available.
Fire Fighting Media
SMALL FIRE: Use DRY chemical powder.
LARGE FIRE: Use water spray, fog or foam. DO NOT use water jet.
and Instructions
Consult with local fire authorities before attempting large scale fire-fighting operations.
Continued on Next Page
9,9-Dimethylfluorene
Section VI. Accidental Release Measures
Spill Cleanup Use a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning the spill by rinsing any
contaminated surfaces with copious amounts of water. Consult federal, state, and/or local authorities for assistance on
Instructions
disposal.
Section VII. Handling and Storage
Handling and Storage Keep away from heat. Mechanical exhaust required. When not in use, tightly seal the container and store in a dry, cool
place. Avoid excessive heat and light. Do not breathe dust.
Information
Always store away from incompatible compounds such as oxidizing agents.
Section VIII. Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below recommended
Engineering Controls
exposure limits. If user operations generate dust, fume or mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants
below the exposure limit.
Splash goggles. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a
Personal Protection
specialist BEFORE handling this product. Be sure to use a MSHA/NIOSH approved respirator or equivalent.
Exposure Limits Not available.
Section IX. Physical and Chemical Properties
Solid. (White crystal.) Solubility
Physical state @ 20°C Not available.
Not available.
Specific Gravity
194.27
Molecular Weight Partition Coefficient Not available.
Boiling Point Not available. Vapor Pressure Not applicable.
97°C (206.6°F) Not available.
Melting Point Vapor Density
Not available. Volatility Not available.
Refractive Index
Not available.
Critical Temperature Not available. Odor
Viscosity Not available. Taste Not available.
Section X. Stability and Reactivity Data
Stability
This material is stable if stored under proper conditions. (See Section VII for instructions)
Conditions of Instability Avoid excessive heat and light.
Incompatibilities
Reactive with oxidizing agents.
Section XI. Toxicological Information
Not available.
RTECS Number
Routes of Exposure Eye Contact. Ingestion. Inhalation.
Not available.
Toxicity Data
Chronic Toxic Effects CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS : Not available.
MUTAGENIC EFFECTS : Not available.
TERATOGENIC EFFECTS : Not available.
DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available.
Repeated or prolonged exposure to this compound is not known to aggravate existing medical conditions.
Acute Toxic Effects No specific information is available in our data base regarding the toxic effects of this material for humans. However,
exposure to any chemical should be kept to a minimum. Skin and eye contact may result in irritation. May be harmful if
inhaled or ingested. Always follow safe industrial hygiene practices and wear proper protective equipment when handling this
compound.
Section XII. Ecological Information
Not available.
Ecotoxicity
Not available.
Environmental Fate
Continued on Next Page
9,9-Dimethylfluorene
Section XIII. Disposal Considerations
Waste Disposal Recycle to process, if possible. Consult your local regional authorities. You may be able to dissolve or mix material with a
combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber system. Observe all
federal, state and local regulations when disposing of the substance.
Section XIV. Transport Information
DOT Classification Not a DOT controlled material (United States).
PIN Number Not applicable.
Proper Shipping Name Not applicable.
Packing Group (PG) Not applicable.
DOT Pictograms
Section XV. Other Regulatory Information and Pictograms
TSCA Chemical Inventory This product is NOT on the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) inventory. The following notices are required by 40
CFR 720.36 (C) for those products not on the inventory list:
(EPA)
(i) These products are supplied solely for use in research and development by or under the supervision of a technically
qualified individual as defined in 40 CFR 720.0 et sec.
(ii) The health risks of these products have not been fully determined. Any information that is or becomes available will be
supplied on an MSDS sheet.
WHMIS Classification Not controlled under WHMIS (Canada).
(Canada)
EINECS Number (EEC) Not available.
EEC Risk Statements Not available.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
制备方法与用途
用途:医药中间体,也是合成光电材料的重要中间体。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 9-甲基芴 9-methylfluorene 2523-37-7 C14H12 180.249 —— 9-(chloromethyl)-9-methylfluorene 118716-48-6 C15H13Cl 228.721 9,9-二甲基-2-溴芴 2-bromo-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene 28320-31-2 C15H13Br 273.172 2-氨基-9,9-二甲基芴 9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-amine 108714-73-4 C15H15N 209.291 9-羟基-9-甲基芴 9-methyl-9H-fluoren-9-ol 6311-22-4 C14H12O 196.249 芴 9H-fluorene 86-73-7 C13H10 166.222 —— tert-butyl 9-methylfluorene-9-percarboxylate 104835-55-4 C19H20O3 296.366 9-芴酮 9-fluorenone 486-25-9 C13H8O 180.206 —— 2-(biphenyl-2-yl)-2-propanol 4635-81-8 C15H16O 212.291 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 13,13-dimethyl-13H-indeno[1,2-b]anthracene 1205546-01-5 C23H18 294.396 3-溴-9,9-二甲基芴 3-bromo-9,9-dimethylfluorene 1190360-23-6 C15H13Br 273.172 9,9-二甲基-2-溴芴 2-bromo-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene 28320-31-2 C15H13Br 273.172 2,7-二溴-9,9-二甲基芴 2,7-dibromo-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene 28320-32-3 C15H12Br2 352.068 2,7-二羟基-9,9-二甲基芴 9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diol 221010-68-0 C15H14O2 226.275 9H-芴-2-醇,9,9-二甲基- 9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-ol 959246-70-9 C15H14O 210.276 —— 2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-9,9-dimethylfluorene 1514864-65-3 C21H17F 288.364 —— 2,7-Bis(chloromethyl)-9,9-dimethylfluorene 765314-49-6 C17H16Cl2 291.22 —— 9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diamine —— C15H16N2 224.305 2-氨基-9,9-二甲基芴 9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-amine 108714-73-4 C15H15N 209.291 —— 8-bromo-13,13-dimethyl-13H-indeno[1,2-b]anthracene 1258514-92-9 C23H17Br 373.292 1-(9,9-二甲基芴-2-基)乙酮 2-acetyl-9,9-dimethyl-fluorene 72322-75-9 C17H16O 236.313 —— 9,9-Dimethylfluorene-2-carbonyl chloride 765314-57-6 C16H13ClO 256.732 N-[1,1'-联苯-4-基]-9,9-二甲基-9H-芴-2-胺 N-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-amine 897671-69-1 C27H23N 361.486 9,9-二甲基芴-2-甲酸 9,9-dimethylfluorene-2-carboxylic acid 28320-62-9 C16H14O2 238.286 7-溴-9,9-二甲基-9H-芴-2-醇 7-bromo-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-ol 1256619-51-8 C15H13BrO 289.172 —— 2-acetamido-9,9-dimethylfluorene 63021-04-5 C17H17NO 251.328 —— 7-bromo-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-amine 28320-34-5 C15H14BrN 288.187 —— 6,11-dibromo-13,13-dimethyl-13H-indeno[1,2-b]anthracene 1214723-20-2 C23H16Br2 452.188 2-硝基-9,9-二甲基芴 9,9-dimethyl-2-nitro-9H-fluorene 605644-46-0 C15H13NO2 239.274 —— 9,9-dimethyl-2,7-dinitro-9H-fluorene 28320-58-3 C15H12N2O4 284.271 —— 6,8,11-tribromo-13,13-dimethyl-13H-indeno[1,2-b]anthracene 1258514-93-0 C23H15Br3 531.084 —— 6-bromo-13,13-dimethyl-11-phenyl-13H-indeno[1,2-b]anthracene 1214723-05-3 C29H21Br 449.39 —— 9,9-dimethyl-γ-oxo-9H-fluorene-2-butanoic acid methyl ester 358626-87-6 C20H20O3 308.377 —— 2,9,9-trimethyl-3,9-dihydrocyclopenta[b]fluorene 1415359-01-1 C19H18 246.352 —— 13,13-dimethyl-6H-indeno[1,2-b]anthracen-11(13H)-one 1258867-78-5 C23H18O 310.395 —— 2-(9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene-2-carbonyl)benzoic acid 72834-16-3 C23H18O3 342.394 9,9-二甲基-2-溴-7-硝基芴 2-bromo-7-nitro-9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene 28320-33-4 C15H12BrNO2 318.17 —— 2-Jodo-9,9-dimethyl-7-nitrofluoren 28320-37-8 C15H12INO2 365.17 —— 2,7-bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-9,9-dimethylfluorene 1204429-63-9 C27H20Cl2O4S2 543.491 9,9-二甲基芴-2,7-二硼酸频哪酯 2,2'-(9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane) 325129-69-9 C27H36B2O4 446.202 —— 13,13-dimethyl-6H-indeno[1,2-b]anthracene-6,11(13H)-dione 1196107-82-0 C23H16O2 324.379 —— 2,9,9-trimethyl-2,3-dihydrocyclopenta[b]fluoren-1(9H)-one 1415358-99-4 C19H18O 262.351 —— 1,2,9,9-tetramethyl-3,9-dihydrocyclopenta[b]fluorene 1415690-68-4 C20H20 260.379 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:基于构象受限的 peri 样 4,5-二取代芴二硫属化物的谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶模拟物摘要:谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 (GPx) 通过谷胱甘肽氧化调节细胞过氧化物水平。基于 4,5-二取代芴二硒化物、它们的氧化物和二碲化物的 GPx 模拟物显示出与二硫属元素键的构象限制一致的催化活性。DOI:10.1039/d1ob02153b
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:692. 2'-(1-羟基-1-甲基乙基)-二苯基-2-羧酸的内酯的异构化摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9570003477
文献信息
-
Selective Transformation of Strychnine and 1,2-Disubstituted Benzenes by C–H Borylation作者:Yutaro Saito、Kotono Yamanoue、Yasutomo Segawa、Kenichiro ItamiDOI:10.1016/j.chempr.2020.02.004日期:2020.4as natural products, pharmaceuticals, and π-conjugated systems are at the heart of constructing and modifying organic molecules, whereby the selectivity and predictability are of the utmost importance. Herein, we report the highly C3-selective C–H borylation of strychnine along with olefin isomerization, catalyzed by an iridium complex with a diphosphine ligand. This method enabled us to rapidly produce
-
A Metal‐Free Direct Arene C−H Amination作者:Tao Wang、Marvin Hoffmann、Andreas Dreuw、Edina Hasagić、Chao Hu、Philipp M. Stein、Sina Witzel、Hongwei Shi、Yangyang Yang、Matthias Rudolph、Fabian Stuck、Frank Rominger、Marion Kerscher、Peter Comba、A. Stephen K. HashmiDOI:10.1002/adsc.202100236日期:2021.6.8The synthesis of aryl amines via the formation of a C−N bond is an essential tool for the preparation of functional materials, active pharmaceutical ingredients and bioactive products. Usually, this chemical connection is only possible by transition metal-catalyzed reactions, photochemistry or electrochemistry. Here, we report a metal-free arene C−H amination using hydroxylamine derivatives under benign
-
Fine tuning of emission color of iridium(iii) complexes from yellow to red via substituent effect on 2-phenylbenzothiazole ligands: synthesis, photophysical, electrochemical and DFT study作者:Ming Li、Hui Zeng、Yanyan Meng、Huiqin Sun、Song Liu、Zhiyun Lu、Yan Huang、Xuemei PuDOI:10.1039/c1dt10305a日期:——Four novel iridium(III) complexes bearing biphenyl (7a–7c) or fluorenyl (7d) modified benzothiazole cyclometallate ligands are synthesized. In comparison with the yellow parent complex, bis(2-phenylbenzothiozolato-N,C2′) iridium(III) (acetylacetonate) [(pbt)2Ir(acac)] (λPLmax = 557 nm, φPL = 0.26), 7a–7d show 20–43 nm bathochromic shifted orange or red phosphorescence in solution, with maximum photoluminescence (PL) quantum yield of 0.62, and PL lifetime of 1.8–2.0 μs. Meanwhile, the resulting complexes also exhibit intense orange or red phosphorescence of λPLmax = 588–611 nm in solid films. The complex 7c with two tert-butyl substituents possesses the highest phosphorescent efficiency both in dilute solution and thin solid films, therefore may be a prospective candidate for both doping and host emitting electrophosphorescent material. Furthermore, despite the observation of severe oxygen quenching for 7a–7d in solution, 7a and 7c even show efficient emission intensity quenching by oxygen in their solid state due to the existence of void channels in crystals; consequently, they are promising molecular oxygen sensor reagents. Electrochemical measurement and DFT calculation results suggest that all these chelates own declined LUMOs of 0.1 eV relative to that of (pbt)2Ir(acac) owing to the contribution of the phenyl substituents; whereas only 7d shows a more destabilized HOMO (∼0.1 eV) compared with the parent chelate.合成了四种新型铱(III)配合物,分别带有改性的联苯(7a-7c)或芴基(7d)苯并噻唑环金属配体。与黄色母体配合物 bis(2-苯基苯并噻唑-N,C2')铱(III)(乙酰丙酮)[(pbt)2Ir(acac)](λPLmax=557 nm, φPL=0.26)相比,7a-7d在溶液中表现出橙色或红色磷光,最大发射波长红移20-43 nm,最大光致发光(PL)量子产率为0.62,PL寿命为1.8-2.0μs。同时,所得配合物在固态薄膜中也显示出强烈的橙色或红色磷光,最大发射波长为588-611 nm。具有两个叔丁基取代基的配合物7c在稀溶液和薄固态薄膜中都具有最高的磷光效率,因此可能是掺杂和主体发光电磷光材料的有前景的候选材料。此外,尽管在溶液中观察到7a-7d的严重氧猝灭,但7a和7c甚至在固态下由于晶体中存在空隙通道而表现出有效的氧猝灭发射强度;因此,它们是有前景的分子氧传感器试剂。电化学测量和DFT计算结果表明,由于苯基取代基的贡献,所有这些螯合物相对于(pbt)2Ir(acac)的LUMOs下降了0.1 eV;而只有7d的HOMO(约0.1 eV)比母体螯合物更不稳定。
-
Photocatalytic C–H Amination of Aromatics Overcoming Redox Potential Limitations作者:Tatsuya Morofuji、Gun Ikarashi、Naokazu KanoDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00822日期:2020.4.3report the photocatalytic C–H amination of aromatics overcoming redox potential limitations. Radical cations of aromatic compounds are generated photocatalytically using Ru(phen)3(PF6)2, which has a reduction potential at a high oxidation state (Ered(RuIII/RuII) = +1.37 V vs SCE) lower than the oxidation potentials of aromatic substrates (Eox = +1.65 to +2.27 V vs SCE). The radical cations are trapped
-
Synthesis and properties of alkynethiolate gold(i) complexes作者:Nora Lardiés、Inocencio Romeo、Elena Cerrada、Mariano Laguna、Peter J. SkabaraDOI:10.1039/b708966j日期:——A series of alkynethiolate gold(I) derivatives have been synthesised by the cleavage of 4-monosubstituted 1,2,3-thiadiazoles in the presence of strong bases. The syntheses of the 1,2,3-thiadiazoles with p-cyanophenyl, p-tolyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl and 9,9-dimethylfluoren-2-yl fragments are also described. All the complexes have been characterised by spectroscopic techniques and the complexes [Au(p-CH3–C6H4–CC–S)PPh3], [Au(3-C4H3S–CC–S)PPh3] and PPN[Au(p-CH3–C6H4–CC–S)(C6F5)] by X-ray analysis. The electrochemically polymerizable mononuclear bis(alkynethiolate) gold(I) complex PPN[Au(3-C4H3S–CC–S)2] is also described, including its electropolymerization and electrochemical properties.
表征谱图
-
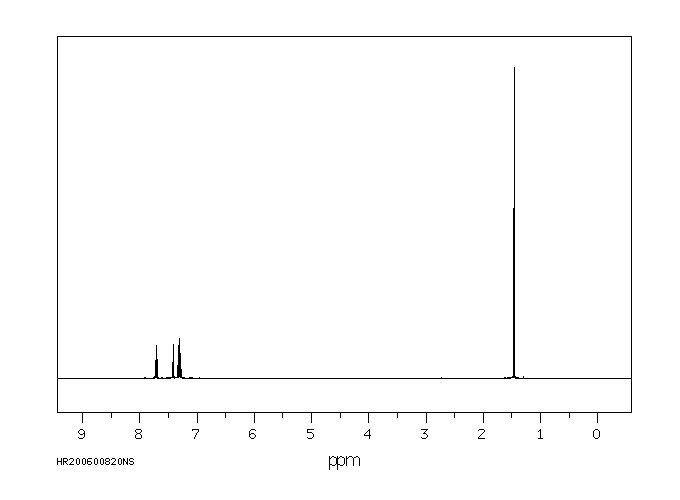
氢谱1HNMR
-
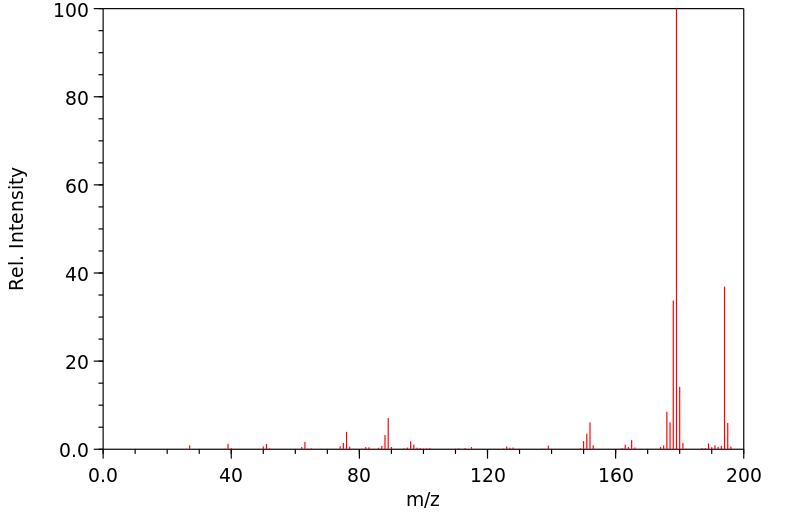
质谱MS
-
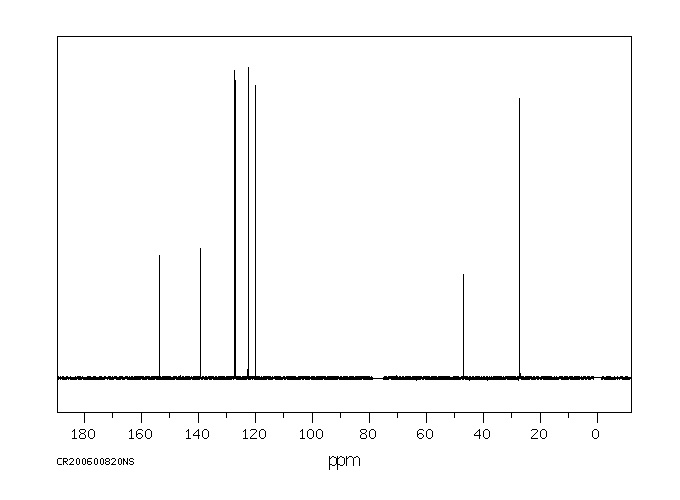
碳谱13CNMR
-
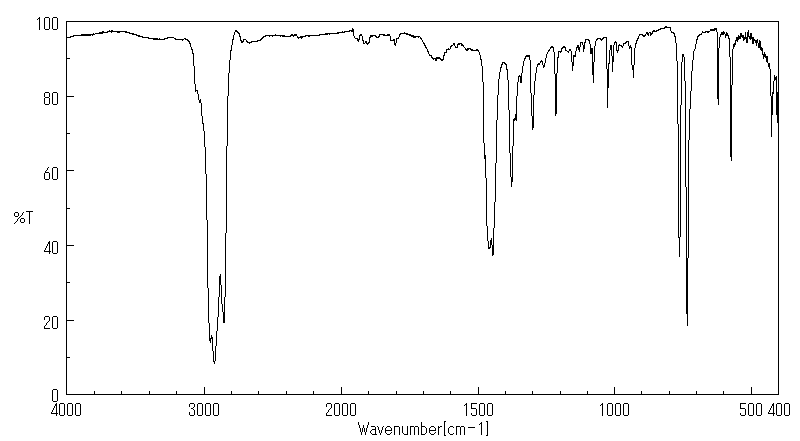
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-2-N-Fmoc-氨基甲基吡咯烷盐酸盐
(2S,4S)-Fmoc-4-三氟甲基吡咯烷-2-羧酸
黎芦碱
鳥胺酸
魏因勒卜链接剂
雷迪帕韦二丙酮合物
雷迪帕韦中间体6
雷迪帕韦
雷迪帕维中间体
雷迪帕维中间体
雷尼托林
锰(2+)二{[乙酰基(9H-芴-2-基)氨基]氧烷负离子}
醋酸丁酸纤维素
达托霉素杂质
赖氨酸杂质4
试剂9,9-Dioctyl-9H-fluoren-2-amine
螺[环戊烷-1,9'-芴]
螺[环庚烷-1,9'-芴]
螺[环己烷-1,9'-芴]
螺[3.3]庚烷-2,6-二-(2',2'',7',7''-四碘螺芴)
螺-(金刚烷-2,9'-芴)
螺(环己烷-1,9'-芴)-3-酮
藜芦托素
荧蒽 反式-2,3-二氢二醇
草甘膦-FMOC
英地卡胺
苯芴醇杂质A
苯甲酸-(芴-9-基-苯基-甲基酯)
苯甲酸-(9-苯基-芴-9-基酯)
苯并[b]芴铯盐
苯并[a]芴酮
苯基芴胺
苯基(9-苯基-9-芴基)甲醇
苯(甲)醛,9H-芴-9-亚基腙
苯(甲)醛,4-羟基-3-甲氧基-,(3-甲基-9H-茚并[2,1-c]吡啶-9-亚基)腙
芴甲氧羰酰胺
芴甲氧羰酰基高苯丙氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基肌氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基环己基甘氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基正亮氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基D-环己基甘氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基D-Β环己基丙氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基-O-三苯甲基丝氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基-D-正亮氨酸
芴甲氧羰酰基-6-氨基己酸
芴甲氧羰基-高丝氨酸内酯
芴甲氧羰基-缬氨酸-1-13C
芴甲氧羰基-叔丁基二甲基硅-D-丝氨酸
芴甲氧羰基-beta-赖氨酰酸(叔丁氧羰基)
芴甲氧羰基-S-叔丁基-L-半胱氨酸五氟苯基脂