D-葡萄糖-二乙基缩硫醛 | 1941-52-2
中文名称
D-葡萄糖-二乙基缩硫醛
中文别名
D-葡萄糖二乙基缩硫醛
英文名称
D-glucose diethyl mercaptal
英文别名
D-glucose diethyl dithioacetal;diethyl dithioacetal D-glucose;(2R,3R,4S,5R)-6,6-bis(ethylsulfanyl)hexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
CAS
1941-52-2
化学式
C10H22O5S2
mdl
——
分子量
286.414
InChiKey
BTOYCPDACQXQRS-LURQLKTLSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:126-130 °C
-
沸点:398.77°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.3416 (rough estimate)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.7
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:9
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:152
-
氢给体数:5
-
氢受体数:7
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn,Xi
-
安全说明:S24/25
-
危险类别码:R20/21/22,R36/38,R63,R21,R62,R46
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29400000
SDS
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— O2-methyl-D-glucose diethyl dithioacetal 3767-34-8 C11H24O5S2 300.441 —— S-ethyl-1-thio-D-glucitol 109062-48-8 C8H18O5S 226.294 D-葡萄糖,2,3,4,5,6-戊-O-甲基-,二乙基二硫代缩醛(9CI) penta-O-methyl-aldehydo-D-glucose diethyl dithioacetal 91414-42-5 C15H32O5S2 356.548 —— 6-O-benzoyl-D-glucose diethyl dithiacetal 60405-33-6 C17H26O6S2 390.522 —— 6-O-(methoxyphenylmethyl)-D-glucose diethyl dithioacetal 106450-86-6 C18H30O6S2 406.565
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Identification of catabolic pathway for 1-deoxy-D-sorbitol in Bacillus licheniformis摘要:1-Deoxy-D-sorbitol, the 1-deoxy analogue of D-sorbitol, has been detected in human urine as well as in natural herbs and spices. Although there are sporadic reports about 1-deoxy-D-sorbitol dehydrogenase, the complete catabolic pathway of 1-deoxy-D-sorbitol remains unsolved. Informed by the promiscuous activities of fructose-6-phosphate aldolase (FSA) which is involved in the sorbitol (glucitol) utilization (gut) operon and guided by the large scale bioinformatics analysis, we predicted and then experimentally verified the gut operon encoded by Bacillus licheniformis ATCC14580 is responsible for the catabolism of both D-sorbitol and 1-deoxy-D-sorbitol by in vitro activity assays of pathway enzymes, in vivo growth phenotypes, and transcriptomic studies. Moreover, the phylogenetic distribution analysis suggests that the D-sorbitol and 1-deoxy-D-sorbitol catabolic gene cluster is mostly conserved in members of Firmicutes phylum.DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.11.072
-
作为产物:描述:葡萄糖 生成 D-葡萄糖-二乙基缩硫醛参考文献:名称:PAZUR J. H.; MISKIEL F. J.; LIU B., J. CHROMATOGR., 396,(1987) 139-147摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Bromodimethylsulfonium bromide (BDMS) mediated dithioacetalization of carbohydrates under solvent-free conditions作者:Abu T. Khan、Md. Musawwer KhanDOI:10.1016/j.carres.2010.07.044日期:2010.10A variety of diethyl dithioacetals of sugars can be prepared in very good yields by the reaction of various monosaccharides with ethanethiol in the presence of 3 mol% bromodimethylsulfonium bromide (BDMS) at 0-5 degrees C. Similarly, dipropyl dithioacetal derivatives can also be obtained in good yields using propanethiol under identical reaction conditions. These dithioacetal derivatives were characterized
-
THE OXIDATION OF SUGAR ACETALS AND THIOACETALS BY ACETOBACTER SUBOXYDANS作者:D. T. Williams、J. K. N. Jones、N. J. Dennis、R. J. Ferrier、W. G. OverendDOI:10.1139/v65-123日期:1965.4.1The oxidation by Acetobacter suboxydans of several aldose dimethylacetals and diethyldithioacetals has been achieved. Isolation and characterization of the ketose products showed that the oxidation...
-
Regioselective Synthesis of Difluorinated <i>C</i>-Furanosides Involving a Debenzylative Cycloetherification作者:Julien A. Delbrouck、Valentin N. Bochatay、Abdellatif Tikad、Stéphane P. VincentDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01878日期:2019.7.19A highly regioselective synthesis of valuable gem-difluorinated C-furanosides from unprotected aldoses via a debenzylative cycloetherification (DBCE) reaction induced by diethylaminosulfur trifluoride is descibed. The scope and limitations of this DBCE reaction are described using a series of commercially available pentoses and hexoses to afford, without selective protection/deprotection sequences
-
Prodrugs of L-cysteine as protective agents against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. 2-(Polyhydroxyalkyl)- and 2-(polyacetoxyalkyl)thiazolidine-4(R)-carboxylic acids作者:Jeanette C. Roberts、Herbert T. Nagasawa、Richard T. Zera、Robert F. Fricke、David J. W. GoonDOI:10.1021/jm00393a034日期:1987.10prodrugs of L-cysteine (1a-h) were synthesized by the condensation of the sulfhydryl amino acid with naturally occurring aldose monosaccharides containing three, five, and six carbon atoms. The resulting 2-(polyhydroxyalkyl)thiazolidine-4(R)-carboxylic acids (TCAs) are capable of releasing L-cysteine and the sugars by nonenzymatic ring opening and hydrolysis. Thus, when added to rat hepatocyte preparations通过巯基氨基酸与天然存在的含三个,五个和六个碳原子的醛糖单糖的缩合,合成了八个L-半胱氨酸的前药(1a-h)。所得的2-(聚羟基烷基)噻唑烷-4(R)-羧酸(TCA)能够通过非酶开环和水解而释放L-半胱氨酸和糖。因此,当将它们添加到体外大鼠肝细胞制剂中时,这些TCA(1.0 mM)相对于对照组将细胞谷胱甘肽(GSH)的水平提高了1.2-2.1倍。基于这一发现,在小鼠模型中测试了半胱氨酸前药作为对乙酰氨基酚诱导的肝毒性的保护剂。衍生自D-核糖和L-半胱氨酸的TCA(RibCys,1d)显示了该系列的最大治疗前景,存活率为100%(12/12),而未经治疗的为17%。但是,这些前药对大鼠肝细胞中GSH产生的刺激程度与对小鼠的保护程度无关,这表明药代动力学参数必须在体内超越。为了评估脂质溶解度增加的效果,我们通过在缩合反应中使用过乙酰化醛糖制备了前药2a-c。然而,这些化合物对小鼠表现出急性毒性
-
[EN] A NOVEL PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SGLT-2 INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] NOUVEAU PROCÉDÉ DE PRÉPARATION D'INHIBITEURS DE SGLT-2申请人:PHARMATHEN SA公开号:WO2020001812A1公开(公告)日:2020-01-02The present invention relates to a novel process for the preparation of SGLT-2 inhibitors via addition of a hydroxymethylene group in an open chain intermediate, readily accessible from D-glucose.
表征谱图
-
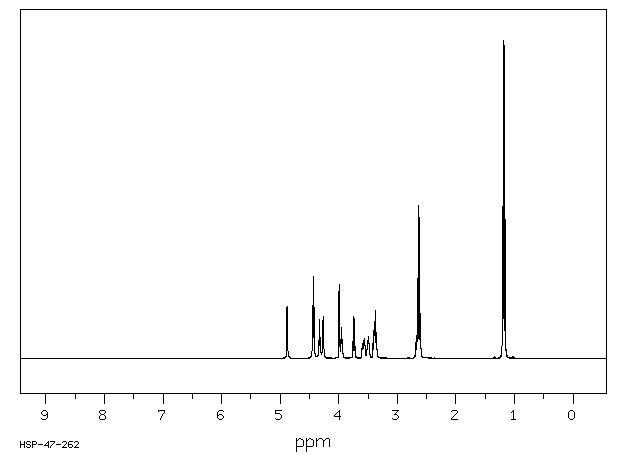
氢谱1HNMR
-
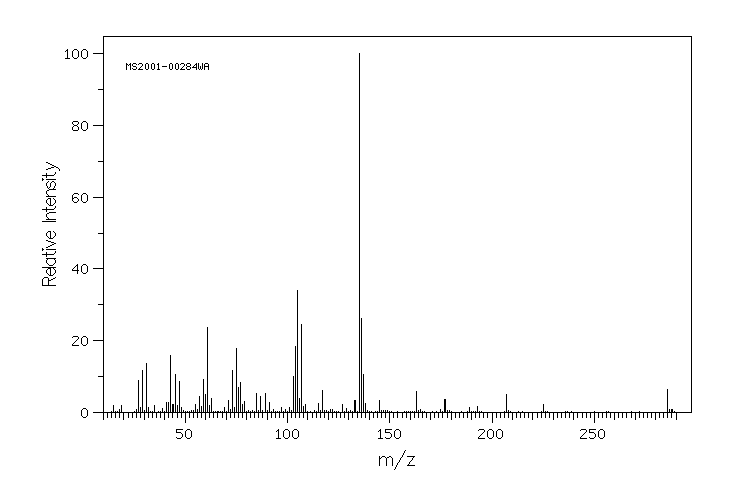
质谱MS
-
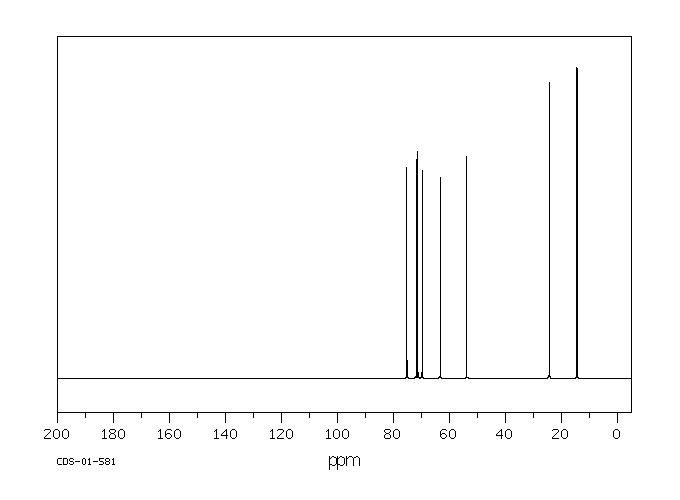
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷