N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 | 16284-60-9
物质功能分类
中文名称
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸
中文别名
2-[(3-甲基丁酰基)氨基]乙酸
英文名称
isovalerylglycine
英文别名
N-isovaleryl glycine;N-isovaleroylglycine;2-(3-methylbutanoylamino)acetic acid
CAS
16284-60-9
化学式
C7H13NO3
mdl
MFCD00059629
分子量
159.185
InChiKey
ZRQXMKMBBMNNQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:105°C
-
沸点:371.8±25.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.097±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:可溶于DMSO(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
物理描述:Solid
-
碰撞截面:155.1 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.5
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.714
-
拓扑面积:66.4
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
危险等级:IRRITANT
-
安全说明:S22,S24/25
-
海关编码:2924199090
-
WGK Germany:3
-
危险性防范说明:P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H319
-
储存条件:室温
SDS
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: N-Isovalerylglycine
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): N-异戊酰氨基乙酸
百分比: >97.0%(T)
CAS编码: 16284-60-9
俗名: N-Isovaleroylglycine
分子式: C7H13NO3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
105°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: N-Isovalerylglycine
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): N-异戊酰氨基乙酸
百分比: >97.0%(T)
CAS编码: 16284-60-9
俗名: N-Isovaleroylglycine
分子式: C7H13NO3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
105°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:N-异戊酰氨基乙酸 在 lithium aluminium tetrahydride 、 盐酸 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 乙醚 为溶剂, 反应 10.0h, 生成 2-[(3-methylbutyl)amino]ethanol hydrochloride参考文献:名称:WO2007/108968摘要:公开号:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:N-酰基甘氨酸:通过选定的离子监测在尿中进行气相色谱质谱鉴定和测定。摘要:合成了11种生物学上有意义的N-酰基甘氨酸,并研究了其三甲基甲硅烷基衍生物的气相色谱和质谱性质。每种N-酰基甘氨酸作为N,O-双-(三甲基甲硅烷基)-可得到清晰且可重现的气相色谱峰。 N-酰基甘氨酸。通过使用这些衍生物,已经开发出灵敏且特定的离子监测方法,用于测定人尿中的N-酰基甘氨酸。DOI:10.1002/bms.1200061007
文献信息
-
Repurposing the 3‐Isocyanobutanoic Acid Adenylation Enzyme SfaB for Versatile Amidation and Thioesterification作者:Mengyi Zhu、Lijuan Wang、Jing HeDOI:10.1002/anie.202010042日期:2021.1.25molecules with novel skeletons, but also to identify the enzymes that catalyze diverse chemical reactions. Exploring the substrate promiscuity and catalytic mechanism of those biosynthetic enzymes facilitates the development of potential biocatalysts. SfaB is an acyl adenylate‐forming enzyme that adenylates a unique building block, 3‐isocyanobutanoic acid, in the biosynthetic pathway of the diisonitrile
-
METHODS FOR USING AND BIOMARKERS FOR AMPK-ACTIVATING COMPOUNDS申请人:Hitoshi Yasumichi公开号:US20150087673A1公开(公告)日:2015-03-26Disclosed are methods of using AMPK-activating compounds, for example, in the treatment of cancer and disorders of vascular flow. Also disclosed are biomarkers for AMPK and uses thereof, for example, in the diagnosis and treatment of AMPK-linked disorders. In certain embodiments, the AMPK-activating compounds have the structural formula wherein E, J, T, D 1 , D 2 , D 3 , the ring system denoted by “B”, T, R 3 , R 4 , w and x are as described herein.
-
Enzymatic Characterization and Elucidation of the Catalytic Mechanism of a Recombinant Bovine Glycine<i>N</i>-Acyltransferase作者:Christoffel P. S. Badenhorst、Maritza Jooste、Alberdina A. van DijkDOI:10.1124/dmd.111.041657日期:2012.2Glycine conjugation, a phase II detoxification process, is catalyzed by glycine N -acyltransferase (GLYAT; E.C. 2.3.1.13). GLYAT detoxifies various xenobiotics, such as benzoic acid, and endogenous organic acids, such as isovaleric acid, which makes GLYAT important in the management of organic acidemias in humans. We cloned the open reading frame encoding the bovine ortholog of GLYAT from bovine liver mRNA into the bacterial expression vector pColdIII. The recombinant enzyme was expressed, partially purified, and enzymatically characterized. Protein modeling was used to predict Glu226 of bovine GLYAT to be catalytically important. This was assessed by constructing an E226Q mutant and comparing its enzyme kinetics to that of the wild-type recombinant bovine GLYAT. The Michaelis constants for benzoyl-CoA and glycine were determined and were similar for wild-type recombinant GLYAT, E226Q recombinant GLYAT, and GLYAT present in bovine liver. At pH 8.0, the E226Q mutant GLYAT had decreased activity, which could be compensated for by increasing the reaction pH. This suggested a catalytic mechanism in which Glu226 functions to deprotonate glycine, facilitating nucleophilic attack on the acyl-CoA. The recombinant bovine GLYAT enzyme, combined with this new understanding of its active site and reaction mechanism, could be a powerful tool to investigate the functional significance of GLYAT sequence variations. Eventually, this should facilitate investigations into the impact of known and novel sequence variations in the human GLYAT gene.甘氨酸缀合是 II 期解毒过程,由甘氨酸 N-酰基转移酶 (GLYAT;E.C. 2.3.1.13) 催化。 GLYAT 可以解毒各种外源性物质(例如苯甲酸)和内源性有机酸(例如异戊酸),这使得 GLYAT 在人类有机酸血症的治疗中发挥着重要作用。我们将牛肝脏 mRNA 中编码 GLYAT 的牛直系同源物的开放阅读框克隆到细菌表达载体 pColdIII 中。表达、部分纯化重组酶并进行酶学表征。使用蛋白质模型来预测牛 GLYAT 的 Glu226 具有重要的催化作用。这是通过构建 E226Q 突变体并将其酶动力学与野生型重组牛 GLYAT 的酶动力学进行比较来评估的。测定了苯甲酰辅酶A和甘氨酸的米氏常数,并且与野生型重组GLYAT、E226Q重组GLYAT和牛肝脏中存在的GLYAT相似。在 pH 8.0 时,E226Q 突变体 GLYAT 的活性降低,这可以通过提高反应 pH 值来补偿。这表明 Glu226 具有使甘氨酸去质子化的催化机制,促进对酰基辅酶 A 的亲核攻击。重组牛 GLYAT 酶,结合对其活性位点和反应机制的新认识,可能成为研究 GLYAT 序列变异功能意义的有力工具。最终,这将有助于研究人类 GLYAT 基因中已知和新的序列变异的影响。
-
Indazole derivatives申请人:Ohta Yoshihisa公开号:US20070117856A1公开(公告)日:2007-05-24The present invention provides a compound represented by Formula (I): [wherein R 1 represents CONR 1a R 1b (wherein R 1a and R 1b may be the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, substituted or unsubstituted ararkyl or a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, or R 1a and R 1b are combined together with the adjacent nitrogen atom thereto to form a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group) or the like, R 2 represents a hydrogen atom, CONR 2a R 2b (wherein R 2a and R 2b may be the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, substituted or unsubstituted ararkyl or a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, or R 2a and R 2b are combined together with the adjacent nitrogen atom thereto to form a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group), NR 2c R 2d (wherein R 2c and R 2d may be the same or different and each represents a hydrogen atom, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkanoyl, substituted or unsubstituted aroyl, substituted or unsubstituted heteroaroyl, substituted or unsubstituted ararkyl, substituted or unsubstituted lower alkylsulfonyl or substituted or unsubstituted lower arylsulfonyl) or the like].本发明提供了一个由公式(I)表示的化合物:[其中R1表示CONR1aR1b(其中R1a和R1b可以相同或不同,每个表示氢原子,取代或未取代的较低烷基,取代或未取代的芳基,取代或未取代的芳基烷基或取代或未取代的杂环基,或R1a和R1b与相邻的氮原子结合形成取代或未取代的杂环基)或类似物,R2表示氢原子,CONR2aR2b(其中R2a和R2b可以相同或不同,每个表示氢原子,取代或未取代的较低烷基,取代或未取代的芳基,取代或未取代的芳基烷基或取代或未取代的杂环基,或R2a和R2b与相邻的氮原子结合形成取代或未取代的杂环基),NR2cR2d(其中R2c和R2d可以相同或不同,每个表示氢原子,取代或未取代的较低烷基,取代或未取代的较低烷酰基,取代或未取代的芳酰基,取代或未取代的杂环芳酰基,取代或未取代的芳基烷基磺酰基或取代或未取代的较低芳基磺酰基)或类似物]。
-
Protein kinase inhibitors申请人:Shiotsu Yukimasa公开号:US20060281789A1公开(公告)日:2006-12-14The present invention provides a protein kinase inhibitor (excluding c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor) which comprises, as an active ingredient, an indazole derivative represented by Formula (I) (wherein R 1 represents substituted or unsubstituted aryl or a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
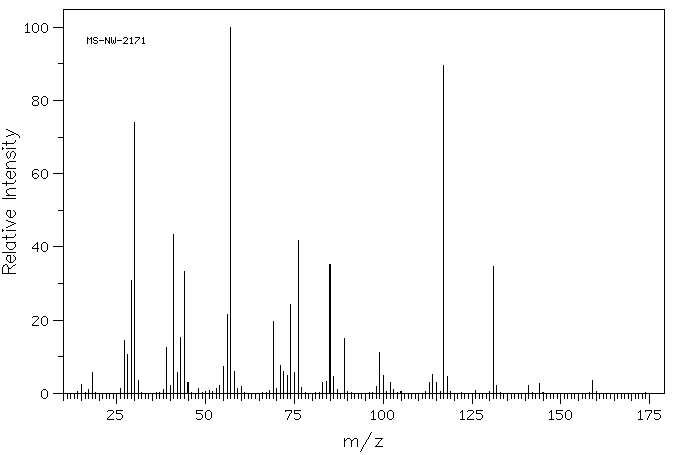
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
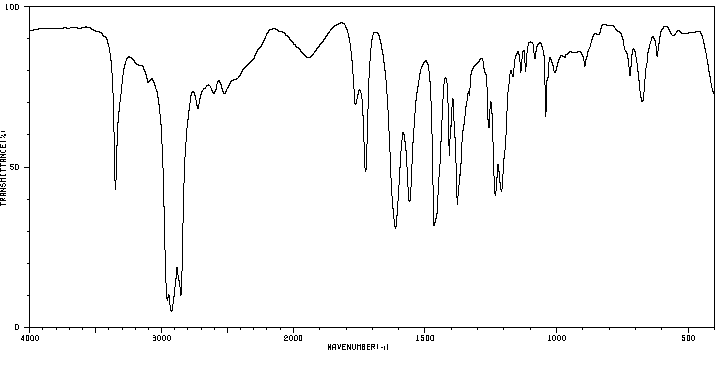
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸