γ-muurolene | 24268-39-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:272.1±20.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:0.89±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.3
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.73
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (-)-菊酯D germacrene D 23986-74-5 C15H24 204.356 —— (4R,4aS,8aR)-6-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-1,2,3,4,4a,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalen-1-one 94425-73-7 C14H22O 206.328 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (1S,4aS,8aR)-1-异丙基-4,7-二甲基-1,2,4A,5,6,8A-六氢萘 (-)-α-muurolene 10208-80-7 C15H24 204.356 —— ε-Muurolen 1136-29-4 C15H24 204.356 —— (+)-ε-Cadinen 1080-67-7 C15H24 204.356 —— (1R,4S,7R,10S)-1,4-dimethyl-8-isopropylidenetricyclo<5.3.0.0.4,10>decane 917773-17-2 C15H24 204.356 —— (1R,10R)-zonarene 41929-05-9 C15H24 204.356
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Westfelt,L., Acta Chemica Scandinavica (1947), 1966, vol. 20, p. 2852 - 2864摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Germacrene D, a key intermediate of cadinene group compounds and bourbonenes摘要:DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)88136-3
文献信息
-
A Multiproduct Terpene Synthase from <i>Medicago truncatula</i> Generates Cadalane Sesquiterpenes via Two Different Mechanisms作者:Stefan Garms、Tobias G. Köllner、Wilhelm BolandDOI:10.1021/jo100917c日期:2010.8.20Terpene synthases are responsible for a large diversity of terpene carbon skeletons found in nature. The multiproduct sesquiterpene synthase MtTPS5 isolated from Medicago truncatula produces 27 products from farnesyl diphosphate (1, FDP). In this paper, we report the reaction steps involved in the formation of these products using incubation experiments with deuterium-containing substrates; we determined
-
Selectivity of Fungal Sesquiterpene Synthases: Role of the Active Site's H-1α Loop in Catalysis作者:Fernando López-Gallego、GraysonT. Wawrzyn、Claudia Schmidt-DannertDOI:10.1128/aem.01811-10日期:2010.12
ABSTRACT Sesquiterpene synthases are responsible for the cyclization of farnesyl pyrophosphate into a myriad of structurally diverse compounds with various biological activities. We examine here the role of the conserved active site H-α1 loop in catalysis in three previously characterized fungal sesquiterpene synthases. The H-α1 loops of Cop3, Cop4, and Cop6 from
Coprinus cinereus were altered by site-directed mutagenesis and the resultant product profiles were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and compared to the wild-type enzymes. In addition, we examine the effect of swapping the H-α1 loop from the promiscuous enzyme Cop4 with the more selective Cop6 and the effect of acidic or basic conditions on loop mutations in Cop4. Directed mutations of the H-α1 loop had a marked effect on the product profile of Cop3 and Cop4, while little to no change was shown in Cop6. Swapping of the Cop4 and Cop6 loops with one another was again shown to influence the product profile of Cop4, while the product profile of Cop6 remained identical to the wild-type enzyme. The loop mutations in Cop4 also implicate specific residues responsible for the pH sensitivity of the enzyme. These results affirm the role of the H-α1 loop in catalysis and provide a potential target to increase the product diversity of terpene synthases.摘要 倍半萜合酶负责将焦磷酸法呢基环化成具有各种生物活性的结构多样的化合物。我们在此研究了保守的活性位点 H-α1 环在三个先前表征的真菌倍半萜合成酶催化作用中的作用。Cop3、Cop4 和 Cop6 的 H-α1 环来自于 Coprinus cinereus 通过定点突变改变了这些酶的 H-α1 环,并用气相色谱-质谱法分析了所得到的产物图谱,并将其与野生型酶进行了比较。此外,我们还研究了将杂合酶 Cop4 的 H-α1 环与选择性更强的 Cop6 互换的效果,以及酸性或碱性条件对 Cop4 环突变的影响。H-α1 环的定向突变对 Cop3 和 Cop4 的产物特征有明显影响,而 Cop6 几乎没有变化。Cop4 和 Cop6 环路的相互交换再次证明会影响 Cop4 的产物特征,而 Cop6 的产物特征则与野生型酶保持一致。Cop4 的环突变还牵涉到负责该酶 pH 敏感性的特定残基。这些结果肯定了 H-α1 环在催化中的作用,并为增加萜烯合成酶的产物多样性提供了一个潜在的目标。 -
Diversity of sesquiterpene synthases in the basidiomycete<i>Coprinus cinereus</i>作者:Sean Agger、Fernando Lopez-Gallego、Claudia Schmidt-DannertDOI:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06717.x日期:2009.6of sesquiterpene synthases identified in plants, less than a handful of unique sesquiterpene synthases have been described from fungi. Here we describe the functional characterization of six sesquiterpene synthases (Cop1 to Cop6) and two terpene-oxidizing cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (Cox1 and Cox2) from Coprinus cinereus. The genes were cloned and, except for cop5, functionally expressed in Escherichia真菌是生物活性次生代谢物的丰富来源,而形成蘑菇的真菌(蘑菇纲)尤其以合成大量具有生物活性且通常具有细胞毒性的倍半萜类次生代谢物而闻名。与在植物中鉴定出的大量倍半萜合酶相比,从真菌中发现的独特倍半萜合酶少于少数。在这里,我们描述了来自鬼伞的六种倍半萜合酶(Cop1 到 Cop6)和两种萜烯氧化细胞色素 P450 单加氧酶(Cox1 和 Cox2)的功能表征。基因被克隆,除了 cop5,在大肠杆菌和/或酿酒酵母中功能性表达。Cop1 和 Cop2 各自合成锗烯 A 作为主要产物。Cop3 被鉴定为一种 α-muurolene 合酶,一种以前没有描述过的酶,而 Cop4 合成 delta-cadinene 作为其主要产物。Cop6 最初被注释为单丁二烯合酶同系物,但发现它可以催化 α-铜烯的高度特异性合成。cop6 和它旁边的两个单加氧酶基因的共表达产生含氧的 α-铜烯衍生物,包括铜苯酚,这表明
-
Polovinka, M. P.; Mamatyuk, V. I.; Korchagina, D. V., Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1991, vol. 27, # 5.2, p. 863 - 882作者:Polovinka, M. P.、Mamatyuk, V. I.、Korchagina, D. V.、Sal'nikov, G. E.、Gatilov, Yu. V.、et al.DOI:——日期:——
-
The revised structure of sclerosporin, a sporogenic substance of sclerotinia fructicola. The total synthesis of (±)-sclerosporin作者:Masato Katayama、Shingo Marumo、Hiroyuki HattoriDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)81749-9日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
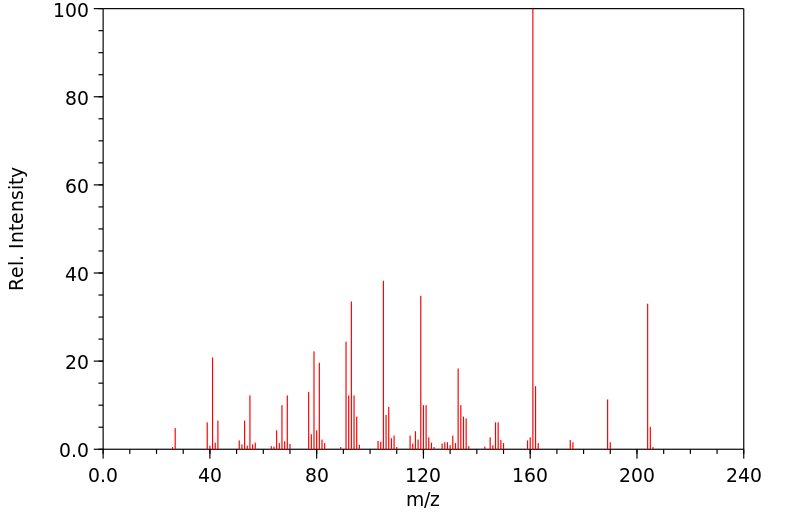
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息