吡啶-2,3-二醇 | 16867-04-2
中文名称
吡啶-2,3-二醇
中文别名
2,3-二羟基吡啶;2,3-吡啶二醇;2,3-二氯-5-三氯甲基吡啶;2,3-羟基吡啶
英文名称
dihydroxypyridine
英文别名
2,3-Dihydroxypyridine;pyridine-2,3-diol;3-hydroxy-1H-pyridin-2-one
CAS
16867-04-2;84719-32-4
化学式
C5H5NO2
mdl
MFCD00006271
分子量
111.1
InChiKey
GGOZGYRTNQBSSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:245 °C (dec.) (lit.)
-
沸点:208.19°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.3113 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:245°C
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.1
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:49.3
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xn,Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R40,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29333999
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:UV1146700
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
SDS
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 3-甲氧基-2(1H)-吡啶酮 3-methoxy-1H-pyridin-2-one 20928-63-6 C6H7NO2 125.127 1-甲基-3-羟基-2(1H)-吡啶酮 1-methyl-3-hydroxy-2(1H)-pyridinone 19365-01-6 C6H7NO2 125.127 3-乙氧基吡啶-2-醇 3-ethoxypyridin-2-ol 909854-16-6 C7H9NO2 139.154 —— 1-ethyl-3-hydroxy-2(1H)-pyridinone 90037-19-7 C7H9NO2 139.154
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:JP5736201摘要:公开号:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:v. Schickh et al., Chemische Berichte, 1936, vol. 69, p. 2593,2604摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] NOVEL ANTIVIRAL COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] NOUVEAUX COMPOSÉS ANTIVIRAUX申请人:PHARMARESOURCES SHANGHAI CO LTD公开号:WO2012065062A1公开(公告)日:2012-05-18The present invention relates to a compound of formula I: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein the symbols are as defined in the specification; a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, a method for treating or preventing a viral infection such as HIV using the same.本发明涉及一种化合物I的化学式:或其药用可接受的盐,其中符号如规范中定义;包括相同化合物的药物组合物,以及使用该化合物治疗或预防病毒感染,如HIV的方法。
-
Exploration of zinc-binding groups for the design of inhibitors for the oxytocinase subfamily of M1 aminopeptidases作者:Sofia Tsoukalidou、Magdalini Kakou、Ioannis Mavridis、Despoina Koumantou、Vito Calderone、Marco Fragai、Efstratios Stratikos、Athanasios Papakyriakou、Dionisios VourloumisDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2019.115177日期:2019.12of the enzymes via strong interactions with the catalytic zinc(II) atom and, while achieving increased potency, they suffer in selectivity. Continuing our earlier efforts on weaker zinc(II) binding groups (ZBG), like the 3,4-diaminobenzoic acid derivatives (DABA), we herein synthesized and biochemically evaluated analogues of nine potentially weak ZBGs, based on differential substitutions of functionalizedM1氨基肽酶的催产素酶亚家族由三个成员ERAP1,ERAP2和IRAP组成,这些成员起着重要的生物学作用,包括在驱动人类免疫应答的抗原肽的产生中发挥关键作用。它们代表了免疫系统药理学控制的新兴目标,尽管缺乏选择性抑制剂阻碍了这些努力。大多数以前探索的小分子结合剂通过与催化性锌(II)原子的强相互作用而靶向酶的活性位点,并且在获得增强的效价的同时,它们也具有选择性。继续我们先前对弱锌(II)结合基团(ZBG)(如3,4-二氨基苯甲酸衍生物(DABA))的研究,我们在此合成并通过生物化学方法评估了9种潜在的弱ZBG的类似物,基于官能化的吡啶酮和吡啶硫酮骨架,烟酸,异烟酸,氨基苯甲酸和肼基苯甲酸的差异取代。两种类似物与金属蛋白酶(MMP-12)的结晶学分析显示出意料之外的结合拓扑,与观察到的亲和力一致。我们的结果表明,该化合物作为ERAP1,ERAP2和IRAP抑制剂的效力主要是由占据活性位点的特异性口袋及其在酶中的正确方向决定的。
-
[EN] SMALL MOLECULE INHIBITORS OF NF-kB INDUCING KINASE<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS À PETITE MOLÉCULE DE KINASE INDUISANT NF-KB申请人:JANSSEN PHARMACEUTICA NV公开号:WO2020239999A1公开(公告)日:2020-12-03The present invention relates to compounds that inhibit NIK and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of using the same. These compounds and pharmaceutical compositions are envisaged to be useful for preventing or treating diseases such as cancer (such as B-cell malignancies including leukemias, lymphomas and myeloma), inflammatory disorders, autoimmune disorders, immunodermatologic disorders such as palmoplantar pustulosis and hidradenitis suppurativa, and metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes.本发明涉及抑制NIK的化合物,以及包含这些化合物的药物组合物和使用方法。这些化合物和药物组合物预期能用于预防或治疗癌症(如包括白血病、淋巴瘤和多发性骨髓瘤的B细胞恶性肿瘤)、炎症性疾病、自身免疫疾病、免疫皮肤病学疾病(如掌跖脓疱病和化脓性汗腺炎)以及代谢紊乱疾病(如肥胖和糖尿病)。
-
Non-imidazole benzodiazepine inhibitors of farnesyl protein transferase申请人:Bristol-Myers Squibb Company公开号:US06458783B1公开(公告)日:2002-10-01Inhibition of farnesyl transferase, which is an enzyme involved in ras oncogene expression, is effected by compounds of the formulas their enantiomers, diastereomers, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs and solvates thereof.抑制法尼基转移酶,这是一种参与ras癌基因表达的酶,可以通过具有上述公式化合物、它们的对映异构体、非对映异构体以及药物可接受的盐、前药和溶剂化物来实现。
-
Selective synthesis of mono- and distannylpyridines from chloropyridinols via an SRN1 mechanism作者:Gustavo F. Silbestri、Marcos J. Lo Fiego、María T. Lockhart、Alicia B. ChopaDOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2010.08.032日期:2010.11selective two-step synthesis of either mono- or distannylated pyridines from commercially available pyridinols, involving its conversion to the corresponding diethyl pyridyl phosphates (pyDEP) followed by the reaction with Me3SnNa in liquid ammonia, is described. The results obtained clearly indicate that the reactions proceed through an unimolecular radical nucleophilic substitution mechanism (SRN1) with
表征谱图
-
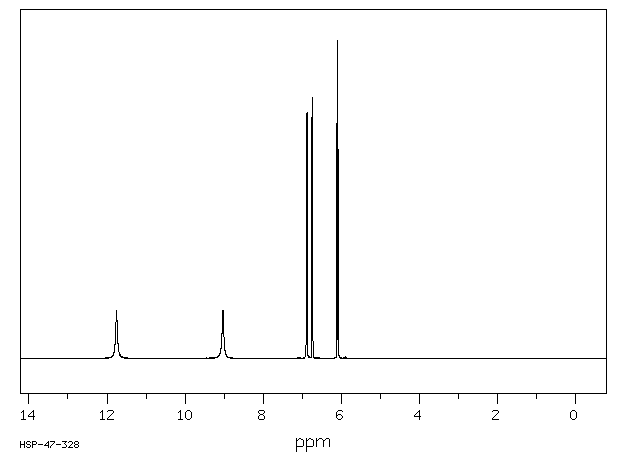
氢谱1HNMR
-
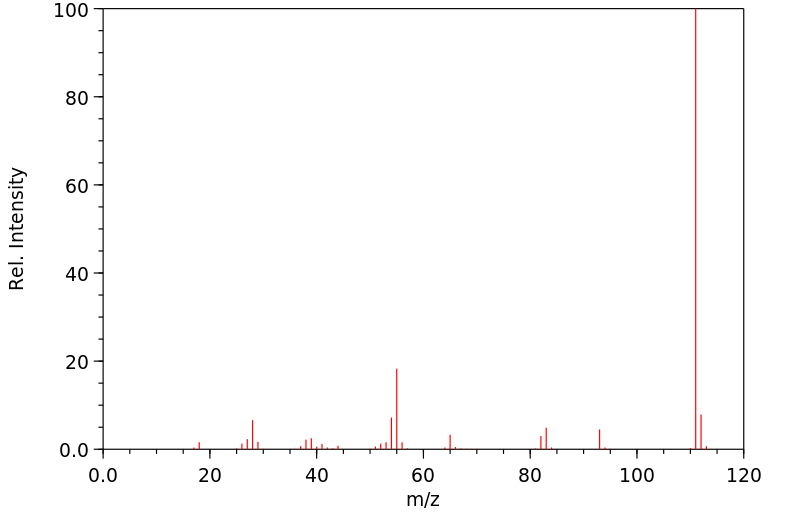
质谱MS
-
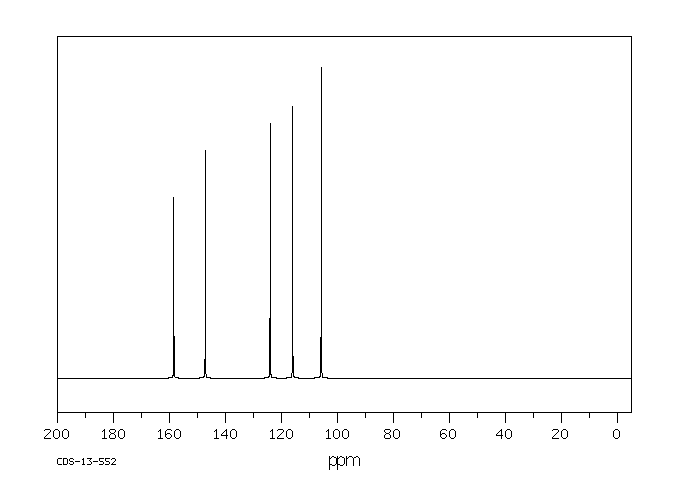
碳谱13CNMR
-
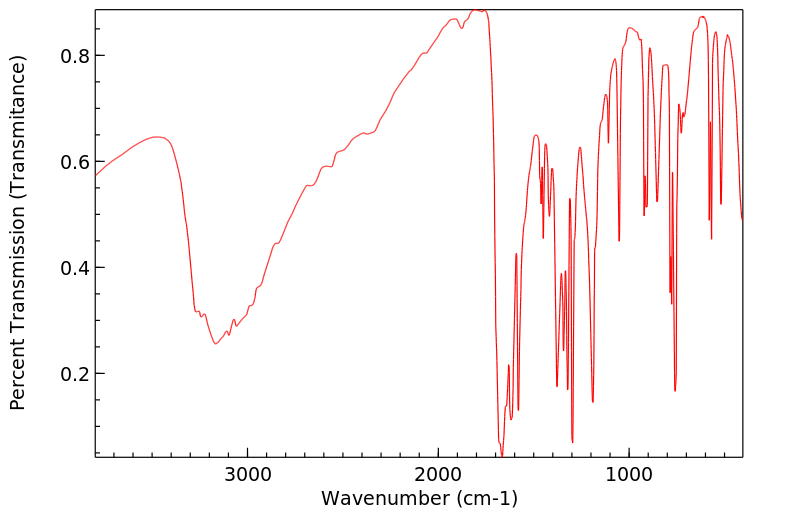
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-氨氯地平-d4
(R,S)-可替宁N-氧化物-甲基-d3
(R)-(+)-2,2'',6,6''-四甲氧基-4,4''-双(二苯基膦基)-3,3''-联吡啶(1,5-环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-N'-亚硝基尼古丁
(R)-DRF053二盐酸盐
(5E)-5-[(2,5-二甲基-1-吡啶-3-基-吡咯-3-基)亚甲基]-2-亚磺酰基-1,3-噻唑烷-4-酮
(5-溴-3-吡啶基)[4-(1-吡咯烷基)-1-哌啶基]甲酮
(5-氨基-6-氰基-7-甲基[1,2]噻唑并[4,5-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺)
(2S,2'S)-(-)-[N,N'-双(2-吡啶基甲基]-2,2'-联吡咯烷双(乙腈)铁(II)六氟锑酸盐
(2S)-2-[[[9-丙-2-基-6-[(4-吡啶-2-基苯基)甲基氨基]嘌呤-2-基]氨基]丁-1-醇
(2R,2''R)-(+)-[N,N''-双(2-吡啶基甲基)]-2,2''-联吡咯烷四盐酸盐
(1'R,2'S)-尼古丁1,1'-Di-N-氧化物
黄色素-37
麦斯明-D4
麦司明
麝香吡啶
鲁非罗尼
鲁卡他胺
高氯酸N-甲基甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸,吡啶
高奎宁酸
马来酸溴苯那敏
马来酸氯苯那敏-D6
马来酸左氨氯地平
顺式-双(异硫氰基)(2,2'-联吡啶基-4,4'-二羧基)(4,4'-二-壬基-2'-联吡啶基)钌(II)
顺式-二氯二(4-氯吡啶)铂
顺式-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯铬氯化物
顺式-1-(4-甲氧基苄基)-3-羟基-5-(3-吡啶)-2-吡咯烷酮
顺-双(2,2-二吡啶)二氯化钌(II) 水合物
顺-双(2,2'-二吡啶基)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
顺-二氯二(吡啶)铂(II)
顺-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
韦德伊斯试剂
非那吡啶
非洛地平杂质C
非洛地平
非戈替尼
非布索坦杂质66
非尼拉朵
非尼拉敏
雷索替丁
阿雷地平
阿瑞洛莫
阿扎那韦中间体
阿培利司N-6
阿伐曲波帕杂质40
间硝苯地平
间-硝苯地平
镉,二碘四(4-甲基吡啶)-
锌,二溴二[4-吡啶羧硫代酸(2-吡啶基亚甲基)酰肼]-