代谢
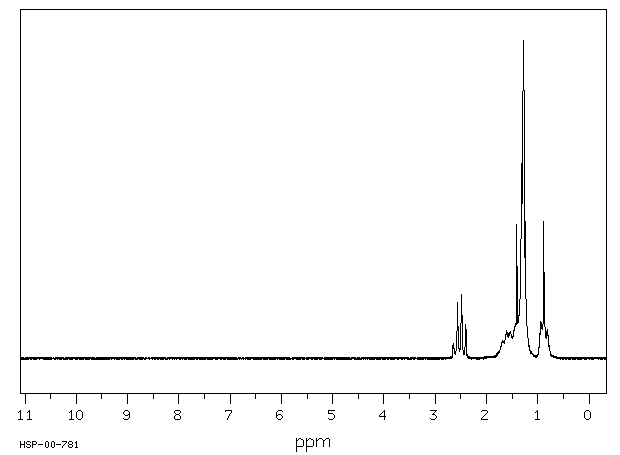
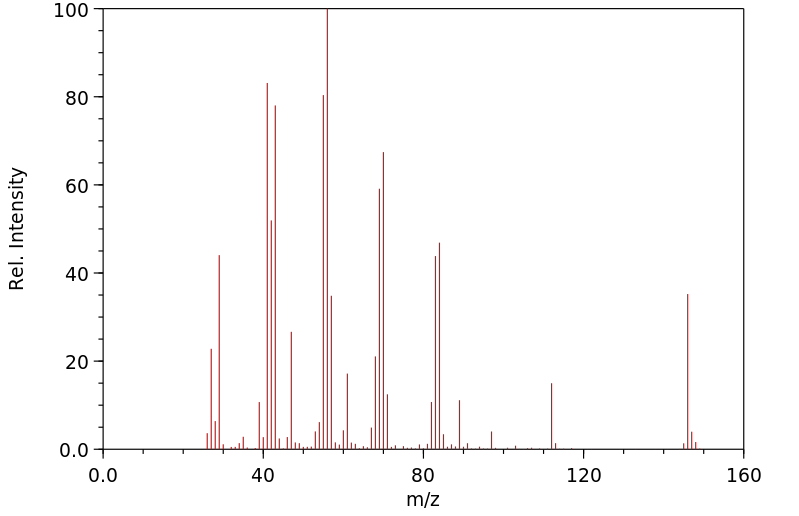
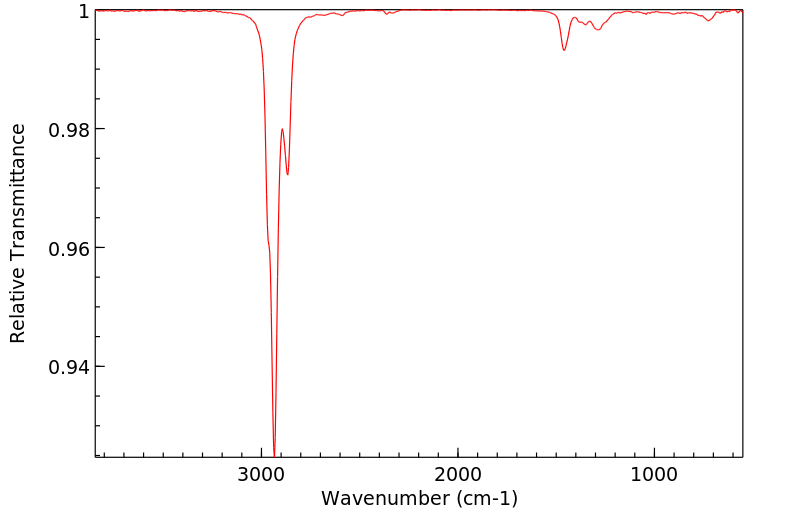
简单的脂肪族和芳香族硫醇在哺乳动物中发生S-甲基化反应,生成相应的甲硫醚或硫化合物。甲基化反应由细胞质中的硫嘌呤甲基转移酶和微粒体中的硫醇甲基转移酶催化,两个反应都需要S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸作为甲基供体。硫嘌呤甲基转移酶存在于人肝、肾和红细胞中;这种酶的首选底物包括芳香族和杂环硫醇。脂肪族硫醇的S-甲基化由微粒体硫醇甲基转移酶催化,生成的甲硫醚(硫化合物)代谢物会经历S-氧化,产生作为尿液产物的甲亚砜和甲砜类似物。硫醇可能会与谷胱甘肽和其他内源性硫醇物质反应形成混合二硫键。据报道,微粒体和细胞质硫醇转移酶都能催化混合二硫键的形成。生成的混合二硫键可以经过还原回到硫醇,氧化脱硫,或者通过中间体硫代硫酸盐和亚硫酸酸氧化成磺酸。在循环中的主要形式可能是与白蛋白形成的混合二硫键。/简单硫醇/
Simple aliphatic and aromatic thiols undergo S-methylation in mammals to produce the corresponding methyl thioether or sulfide. Methylation is catalysed by thiopurine methyltransferase in the cytoplasm and thiol methyltransferase in microsomes, and both reactions require S-adenosyl-l-methionine as a methyl group donor. Thiopurine methyltransferase is present in human liver, kidney, and erythrocytes; preferential substrates for this enzyme include aromatic and heterocyclic thiols. S-Methylation of aliphatic thiols is catalysed by microsomal thiol methyltransferase, and the resulting methyl thioether (sulfide) metabolite would undergo S-oxidation to give the methyl sulfoxide and methyl sulfone analogues as urinary products. Thiols may react with glutathione and other endogenous thiol substances to form mixed disulfides. Both microsomal and cytoplasmic thioltransferasess have been reported to catalyse the formation of mixed disulfides. The resulting mixed disulfides can undergo reduction back to thiols, oxidative desulfuration, or oxidation to a sulfonic acid via the intermediate thiosulfinate and sulfinic acids. The principal form in the circulation would probably be a mixed disulfide formed with albumin. /Simple thiols/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)