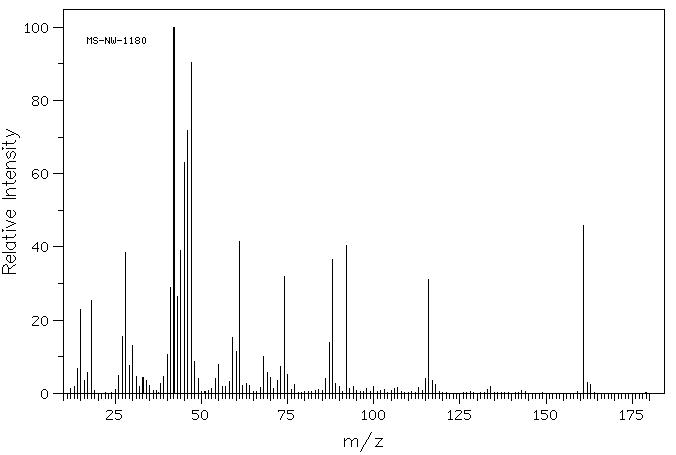
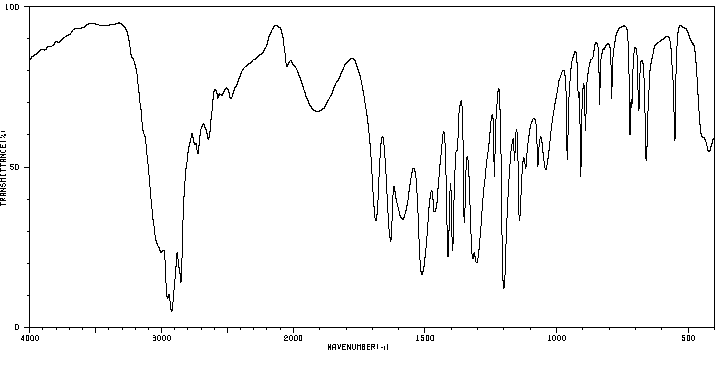
代谢
碳水化合物代谢途径包括乙酰化、脱羧和亚砜化,导致形成药理学上不活跃的碳水化合物衍生物。由于亚砜化能力的遗传多态性,代谢存在显著变异性。两种细胞质酶负责碳水化合物的代谢:半胱氨酸二氧酶和苯丙氨酸4-羟化酶。减少的代谢可能导致碳水化合物暴露增加,这解释了可能影响碳水化合物代谢酶的多态性患者在临床反应上的变异性。通常认为亚砜化是碳水化合物的主要代谢途径,然而,一组研究人员发现了一种新的尿液代谢物,S-(羧甲基硫基)-L-半胱氨酸(CMTC)。在这项研究中,服用碳水化合物的患者的尿液中没有发现半胱氨酰亚砜代谢物。
Metabolic pathways for carbocisteine include acetylation, decarboxylation, and sulfoxidation, leading to the formation of pharmacologically inactive carbocisteine derivatives. Significant variability exists in metabolism due to genetic polymorphism in sulfoxidation capacity. Two cytosolic enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of carbocisteine: cysteine dioxygenase and phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase. Reduced metabolism can cause increased exposure to carbocisteine, explaining variable clinical response between patients who may polymorphisms affecting the enzymes responsible for carbocisteine metabolism. It is generally accepted that sulfodixation is the main metabolic pathway of carbocisteine, however, one group of researchers found a novel urinary metabolite, S-(carboxymethylthio)-L-cysteine (CMTC). No cysteinyl sulfoxide metabolites were found in the urine of patients taking carbocisteine in this study.
来源:DrugBank