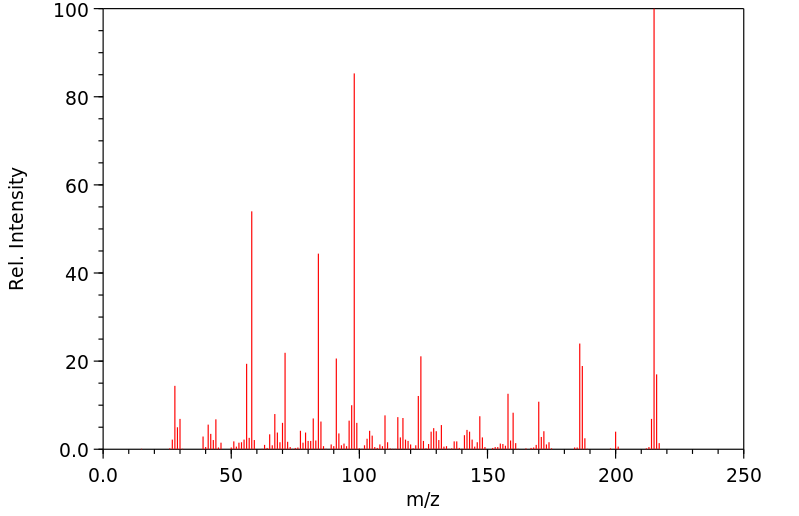
毒理性
芬坎法明作为一种间接的多巴胺激动剂。它通过一种与安非他命相似的机制释放多巴胺,但产生这种效果的效力比右旋安非他命低10倍。这种药物似乎能抑制多巴胺转运体(DAT),后者负责将多巴胺从突触中移除。DAT的抑制阻止了多巴胺和去甲肾上腺素被突触前神经元重吸收,增加了突触中的多巴胺含量。它还能刺激多巴胺和去甲肾上腺素释放到突触中。最后,它在刺激后增加了多巴胺释放的量,提高了刺激的重要性。与安非他命不同,芬坎法明不抑制单胺氧化酶酶的活性,因此相对更安全。一些实验还表明,阿片受体在芬坎法明的活性中发挥作用,因为低剂量可以引起矛盾的镇静作用,且该药物的一些效果可以被纳洛酮阻断。
Fencamfamine acts as an indirect dopamine agonist. It releases dopamine by a similar mechanism to amphetamines, but is 10x less potent than dexamphetamine at producing this effect. The drug seems to inhibit the dopamine transporter (DAT) that removes dopamine from the synapses. This inhibition of DAT blocks the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine into the presynaptic neuron, increasing the amount of dopamine in the synapse. It also stimulates the release of dopamine and norepinephrine into the synapse. Finally, it increases the magnitude of dopamine release after a stimulus, increasing the salience of stimulus. Also unlike amphetamines, fencamfamine does not inhibit the action of monoamine oxidase enzymes and so is somewhat safer. Some experiments also suggest a role for opioid receptors in the activity of fencamfamine, as low doses can cause paradoxical sedation, and some effects of the drug are blocked by naloxone.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)