二氯乙醚 | 111-44-4
中文名称
二氯乙醚
中文别名
双(2-氯乙基)醚;二氯乙基醚;2-氯乙醚;2,2'-二氯二乙醚;2-氯乙基醚;2,2"-二氯乙醚;二氯二乙醚;β,β'-二氯二乙醚;β,β'-二氯代二乙醚;对称二氯二乙基醚;β,β-二氯二乙醚;2,2-二氯乙基醚
英文名称
3-oxa-1,5-dichloropentane
英文别名
bis-(2-chloroethyl) ether;1-chloro-2-(2-chloroethoxy)ethane;2-chloroethyl ether;2,2'-dichlorodiethyl ether;dichloroethyl ether;chloromethylmethyl ether;dichlorodiethyl ether;Bis(2-chloroethyl) ether
CAS
111-44-4
化学式
C4H8Cl2O
mdl
MFCD00000975
分子量
143.013
InChiKey
ZNSMNVMLTJELDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−47 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:65-67 °C15 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:1.22 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:131 °F
-
溶解度:水中的溶解度为0.01克/升
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: TWA 5 ppm (30 mg/m3), STEL 10 ppm, IDLH 100 ppm; OSHA PEL: C 15 ppm (90 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 30 mg/m3, STEL 60 mg/m3.
-
介电常数:20.789999999999999
-
LogP:1.12-1.56 at 20℃
-
物理描述:2,2'-dichlorodiethyl ether appears as a clear colorless liquid with a sweet pleasant or nauseating odor. Flash point 131°F. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Toxic by inhalation and skin absorption. Used in cleaning compounds, paints, textile finishing, and as a general solvent.
-
颜色/状态:COLORLESS, CLEAR LIQ
-
气味:PUNGENT
-
蒸汽密度:4.93 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1.55 mm Hg @ 25 °C
-
自燃温度:369 °C (696 °F)
-
分解:WHEN HEATED TO DECOMP, EMITS HIGHLY TOXIC FUMES OF /HYDROGEN CHLORIDE/.
-
粘度:2.0653 cP @ 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:NOT VERY CORROSIVE TO IRON, MILD STEEL, OR ALUMINUM.
-
燃烧热:(EST) -4180 CAL/G
-
汽化热:79.5 CAL/G
-
表面张力:37.9 DYNES/CM @ 19 °C
-
气味阈值:Odor detection in water= 3.60x10+2 ppm, purity not specified.
-
折光率:INDEX OF REFRACTION: 1.451 @ 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:945.9;948;951.52;948;954;954;948;965.4;956.6;956
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.3
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:9.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
MALE RATS GIVEN SINGLE ORAL DOSE OF BIS(2-CHLOROETHYL)ETHER, TWO METABOLITES WERE IDENTIFIED IN URINE SAMPLES: THIODIGLYCOLIC ACID (TDGA) & 2-CHLOROETHYL BETA-D-GLUCURONIC ACID.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
雄性大鼠单次口服给予了40毫克/千克的14C标记的双(2-氯乙基)醚(BCEE)。在给予14C标记的双(2-氯乙基)醚后,尿液中收集到的总14C中,约有75%是硫代二甘酸。BCEE的较小代谢物包括(2-氯乙氧基)乙酸(5%)和N-乙酰-S-(2-(2-氯乙氧基)乙基)-L-半胱氨酸(7%)。
MALE RATS WERE GIVEN A SINGLE ORAL DOSE OF 40 MG/KG (14)C-LABELED BIS(2-CHLOROETHYL) ETHER (BCEE). THIODIGLYCOLIC ACID ACCOUNTED FOR APPROX 75% OF THE TOTAL URINARY (14)C COLLECTED AFTER THE (1-(14)C)BIS(2-CHLOROETHYL) ETHER DOSE. LESSER METABOLITES OF BCEE WERE (2-CHLOROETHOXY)ACETIC ACID (5%), AND N-ACETYL-S-(2-(2-CHLOROETHOXY)ETHYL)-L-CYSTEINE (7%).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Either 40 umole or 160 umole DCEE was injected into male Wistar rats and the metabolites, thiodiglycolic acid (TdGA) and hydroxyethyl mercapturic acid (HEMA), were determined in the 24 hr urine specimens. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
... 在进一步的步骤中,进行了吸入实验,以确定雄性Wistar大鼠在暴露于10、50、100和500 ppm DCEE 8小时后,两种代谢物的尿液排泄情况...。
... In a further step, inhalation experiments were performed to determine urinary excretion of the two metabolites after an 8 hr exposure of male Wistar rats to 10, 50, 100, and 500 ppm DCEE ... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
BCEE通过吸入暴露、口服给药以及皮肤接触而被吸收。BCEE在体内分布,但最高水平见于肝脏、肾脏和小肠,而在肺、脾和肌肉中则水平较低。BCEE被广泛代谢为硫代二甘酸(TDGA)、2-氯乙氧基乙酸(CEAA)和N-乙酰-S-[2-(2-氯乙氧基)乙基]-L-半胱氨酸,其中TDGA是主要的最终产物。较小量的BCEE通过氧化或在不断裂醚的情况下对氯原子进行取代而代谢。口服给药的大约80%的BCEE在48小时内以TDGA的形式排出。较小量通过粪便或呼出气体排出,只有极小部分剂量残留在体内。这表明BCEE有效地排出,并且它在组织中有较低的积累倾向。(L183, A129)
BCEE is absorbed following inhalation exposure, oral administration, as well as contact to the skin. BCEE is distributed through the body, but highest levels are found in the liver, kidney and small intestine, while much lower levels are found in lung, spleen and muscle. BCEE is extensively metabolized to thiodiglycolic acid (TDGA), 2-chloroethoxyacetic acid (CEAA), and N-acetyl-S-[2-(2-chloroethoxy)ethyl]-L-cysteine, with TDGA being the principal endproduct. Smaller amounts of BCEE are metabolized by oxidation or substitution at a chlorine without ether cleavage. Approximately 80% of BCEE administered orally is excreted as TDGA within 48 hours. Smaller amounts are excreted in feces or expired air and only a very small fraction of the dose remains in the body. This indicates that BCEE is effectively excreted, and that it has a low tendency to accumulate in tissues. (L183, A129)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
BCEE /双(2-氯乙基)醚/在人体内的动力学和代谢的定量信息是不可用的。...有限数据显示,通过吸入或灌胃给大鼠施用的放射性BCEE能够迅速被吸收。...BCEE在大鼠体内易于被代谢。主要代谢物是硫代二甘酸...BCEE在大鼠和恒河猴体内快速消除。...BCEE通过口服、吸入或皮肤接触途径具有急性毒性。...实验室动物通过吸入高浓度单一剂量...导致眼部刺激以及肺部充血、水肿和出血。...一般来说,在体外进行诱变试验时得到了阳性结果。.../在一项研究中/与未暴露的对照组相比,肝细胞瘤(良性和恶性肿瘤的组合)的发生率显著增加。...其他在大鼠和小鼠中使用口服灌胃、皮下或腹腔注射和皮肤涂敷的有限研究未能证实这些发现。...短期暴露后,发现BCEE对人类的眼睛和鼻腔通道有刺激性...尚未报告有关长期暴露于BCEE影响的研究。...实验室动物的所有长期研究都没有足够的质量,无法提供关于BCEE致癌潜力或长期暴露于该物质产生的毒理学效果的定量信息。
Quantitative information on the kinetics and metabolism of BCEE /bis(2-chloroethyl) ether/... in humans is not available. ... Limited data show that radioactive BCEE administered to rats by inhalation or gavage is rapidly absorbed. ... BCEE is readily metabolized in rats. The principal metabolite is thiodiglycolic acid ... BCEE is eliminated quickly in both rats and rhesus monkeys. ... BCEE is acutely toxic by the oral, inhalation or dermal routes of exposure. ... Exposure of laboratory animals by inhalation to high single concentrations ... resulted in eye irritation as well as congestion, edema, and hemorrhage in the lungs. ... In general, positive results were obtained when ... tested for mutagenicity in vitro. ... /In one study/ there was a significant increase in the incidence of hepatomas (combined benign hepatomas and malignant tumors) compared to unexposed controls. ... Other limited studies in rats and mice using oral gavage, subcutaneous or intraperitoneal injection and skin painting failed to confirm these findings. ... BCEE was found to be irritating to the eyes and nasal passages of humans ... following short term exposure. No epidemiological studies on the effects of long term exposure to BCEE have been reported. ... None of the long term studies in laboratory animals is of sufficient quality to provide quantitative information on either the potential of BCEE to cause cancer or the toxicological effects produced by long term exposure to this substance.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
BCEE is extremely meabolized, with thiodiglycolic acid (TDGA) being the principal endproduct. The pathway leading to TDGA formation is uncertain, but probably involves oxidative cleavage of the ether bond to yield chloroacetaldehyde and 2-chloroethanol. (L183)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
癌症分类:B2组可能的人类致癌物
Cancer Classification: Group B2 Probable Human Carcinogen
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
分类:B2;可能的人类致癌物。分类依据:在两种小鼠品系中观察到阳性致癌性结果,并有致突变性证据。人类致癌性数据:无。
CLASSIFICATION: B2; probable human carcinogen. BASIS FOR CLASSIFICATION: Positive carcinogenicity results in two strains of mice and evidence of mutagenicity. HUMAN CARCINOGENICITY DATA: None.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence for the carcinogenicity of bis(2-chloroethyl)ether in humans. There is limited evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of bis(2-chloroethyl)ether. Overall evaluation: Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity in humans (Group 3).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
雄性大鼠单次口服给予了40毫克/千克的14C标记的双(2-氯乙基)醚(BCEE)。在48小时内监测了14CO2的呼出和尿液中14C的排泄。半衰期消除一半剂量所需的时间为12小时,对于1-(14C)BCEE。呼出的14CO2占剂量的11.5%,尿液中的14C占64.7%,粪便中发现了2.4%。
MALE RATS WERE GIVEN A SINGLE ORAL DOSE OF 40 MG/KG (14)C-LABELED BIS(2-CHLOROETHYL) ETHER (BCEE). EXCRETION OF (14)CARBON DIOXIDE AND URINARY (14)C FOLLOWED FOR 48 HR. THE TIME REQUIRED TO ELIMINATE ONE HALF OF THE DOSE WAS 12 HR FOR (1-(14)C)BCEE. EXPIRED (14)CARBON DIOXIDE ACCOUNTED FOR 11.5% OF THE DOSE, URINARY (14)C ACCOUNTED FOR 64.7%, AND 2.4% WAS FOUND IN THE FECES.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
40微摩尔或160微摩尔的DCEE被注射到雄性Wistar大鼠中,并在24小时尿液样本中测定了代谢物硫代二甘酸(TdGA)和羟乙基巯基尿酸(HEMA)的含量。代谢物分析显示,在摄入DCEE后,羟甲基巯基尿酸的排泄量远低于硫代二甘酸的排泄量。
Either 40 umole or 160 umole DCEE was injected into male Wistar rats and the metabolites, thiodiglycolic acid (TdGA) and hydroxyethyl mercapturic acid (HEMA), were determined in the 24 hr urine specimens. ... Analysis of the metabolites showed that hydroxymethyl mercapturic acid excretion was much lower than the excretion of thiodiglycolic acid following the uptake of DCEE ... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 5 ppm (30 mg/m3), STEL: 10 ppm (60 mg/m3) [skin]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:100 ppm
-
危险品标志:T+
-
安全说明:S27,S28,S28A,S36/37,S45,S7/9
-
危险类别码:R26/27/28,R10,R40
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29091900
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1916 6.1/PG 2
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:KN0875000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:储存时应注意以下事项:存放在阴凉、干燥且通风良好的库房中,远离火源和热源,并避免阳光直射。包装需密封,以防受潮。与氧化剂、酸类及食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用可能产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区域应配备泄露应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61594 |
| CAS: | 111-44-4 |
| 中文名称: | 二氯乙醚 |
| 英文名称: | dichloroethyl ether;bis-(2-chloroethyl)ether |
| 别 名: | β,β'-二氯代二乙醚;2,2’-二氯乙醚 |
| 分子式: | C 4 H 8 Cl 2 O;ClCH 2 CH 2 OCH 2 CH 2 |
| 分子量: | 143.01 |
| 熔 点: | -52℃ 沸点:178.5℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.22(2 |
| 蒸汽压: | 55℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,可混溶于乙醇、醚、多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 带有辣味和水果味的无色透明液体 |
| 危险标记: | 14(有毒品) |
| 用 途: | 用作溶剂、土壤熏蒸杀虫剂,也用于有机合成和制涂料 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:接触本品对眼睛、呼吸道粘膜有明显刺激作用,并有难以忍受的感觉,发生咳嗽、恶心、呕吐。动物实验本品有麻醉和强烈的刺激作用。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
急性毒性:LD50110mg/kg(大鼠经口);140mg/kg(小鼠经口)
致突变性:微生物致突变:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌1mL/皿(2小时)。
致癌性:IARC致癌性评论:动物阳性。
危险特性:遇明火、高热易燃。受热或遇水分解放热,放出有毒的腐蚀性烟气。燃烧分解时,放出有毒的刺激性氯化物烟气。与氧化剂接触会猛烈反应。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化物。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法《水和废水标准检验方法》19版译文,江苏省监测中心
空气中的测定:样品用活性炭吸附后,经二硫化碳洗脱,再用气相色谱法测定(NIOSH法)
水中的测定:样品用二氯甲烷萃取,再卤化物特效检测器的气相色谱法分析(EPA611法)或用色谱联用仪测定(EPA625法)
5.环境标准:
前苏联 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 2mg/m3
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火泊。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿消防防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物。尽可能切断泄漏源,防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用砂土或其它不燃材料吸附或吸收。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。用泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
废弃物处置方法:建议用焚烧法处置。废料同其他燃料混合后再焚烧,燃烧要充分、防止生成光气。焚烧炉排气中的卤化氢通过酸洗涤器除去。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,必须佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴空气呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
身体防护:穿透气型防毒服。
手防护:戴防化学品手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。
眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:饮足量湿水,催吐,就医。
灭火方法:消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服。灭火剂:二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。
制备方法与用途
化学性质
无色液体,气味与乙醚相似,具有刺激性。易溶于乙醇和乙醚,微溶于水。
用途
用作橡胶、树脂等的溶剂;也可作为气相色谱固定液及脂肪、石蜡、油类等的溶剂和干洗剂;性质稳定,适用于脂肪、油、蜡、橡胶、焦油、沥青、树脂、乙基纤维等的溶剂,并可用作土壤的杀虫剂。此外,还用于有机合成和制涂料。
类别
农药
毒性分级
高毒
急性毒性
口服 - 大鼠 LD50: 75 毫克/公斤;口服 - 小鼠 LD50: 209 毫克/公斤
刺激数据
皮肤接触 - 兔子,500 毫克,轻度刺激;眼睛接触 - 兔子,100 毫克,重度刺激
爆炸物危险特性
与空气混合可爆
可燃性危险特性
可燃;燃烧产生有毒氯化物气体
储运特性
库房需通风、低温干燥,并与食品原料分开存放和运输
灭火剂
干粉、泡沫
职业标准
时间加权平均容许浓度 (TWA): 0.5 毫克/立方米;短时间暴露极限 (STEL): 1.0 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-氯乙氧基乙醇 2-(2-Chloroethoxy)ethanol 628-89-7 C4H9ClO2 124.567 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-氯乙氧基乙醇 2-(2-Chloroethoxy)ethanol 628-89-7 C4H9ClO2 124.567 1-溴-2-(2-氯-乙氧基)-乙烷 2-bromo-2’-chlorodiethyl ether 51070-66-7 C4H8BrClO 187.464 —— 2-(2-chloro-ethoxy)-ethanethiol 76331-21-0 C4H9ClOS 140.634 1-(2-氯乙氧基)-2-甲氧基乙烷 1-chloro-2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethane 52808-36-3 C5H11ClO2 138.594 2-氯乙基乙烯基醚 2-chloroetyl vinyl ether 110-75-8 C4H7ClO 106.552
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Cretcher; Koch; Pittenger, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1925, vol. 47, p. 1174摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种二氯乙醚和2-氯乙氧基乙醇的合成方法摘要:本发明公开了一种二氯乙醚和2‑氯乙氧基乙醇的合成方法,属于有机合成领域。该方法包括:将摩尔比为0.8‑1.5:0.3二甘醇和催化剂加入双口烧瓶内,并使双口烧瓶的两个瓶口分别接分液漏斗和冷凝管;利用分液漏斗向双口烧瓶内滴加混合酸,在130℃‑170℃下进行反应,在反应过程中,利用冷凝管收集冷凝液;对冷凝液进行蒸馏,得到二氯乙醚;对双口烧瓶内剩余的液体进行抽滤,得到2‑氯乙氧基乙醇,其中,混合酸包括:质量比为25‑35:1的浓盐酸与浓硫酸。本发明实施例提供的合成方法不仅能够同时合成得到二氯乙醚和2‑氯乙氧基乙醇,而且,该方法反应简单可控、反应条件温和,原料安全且易得,使得两者的合成更加安全可控,成本更加低廉。公开号:CN109721474A
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:FR789405摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
基于咪唑、苯并咪唑及其衍生物的冠醚型离子液体申请人:晟合众新型材料科技(上海)有限公司公开号:CN109824695A公开(公告)日:2019-05-31本发明公开了基于咪唑、苯并咪唑及其衍生物的冠醚型离子液体,所述冠醚型离子液体中阳离子为咪唑、苯并咪唑及其衍生物,阴离子包括中性或碱性的单核阴离子、多核阴离子;所述单核阴离子包括Cl‑、Br‑、BF4‑、PF6‑、CF3COO‑、CF3SO2‑、(CF3SO2)N‑、OH‑,所述多核阴离子包括AlCl4‑、FeCl3‑、CuCl3‑、AuCl4‑;离子液体在一些反应中具有反应速率快、转化率高、反应的选择性高、催化体系可循环重复使用等优点;此外离子液体在溶剂萃取、物质的分离和纯化、废旧高分子化合物的回收、燃料电池和太阳能电池、工业废气中二氧化碳的提取、地质样品的溶解、核燃料和核废料的分离与处理等方面也显示出潜在的应用前景。
-
HETEROBICYCLIC COMPOUNDS申请人:Amgen Inc.公开号:US20130225552A1公开(公告)日:2013-08-29Heterobicyclic compounds of Formula (I): or a pharmaceutically-acceptable salt, tautomer, or stereoisomer thereof, as defined in the specification, and compositions containing them, and processes for preparing such compounds. Provided herein also are methods of treating disorders or diseases treatable by inhibition of PDE10, such as obesity, non-insulin dependent diabetes, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, Huntington's Disease, and the like.
-
2-OXO-2- (2-PHENYL-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-INDOLIZIN-3-YL) -ACETAMIDE DERIVATIVES AND RELATED COMPOUNDS AS ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS申请人:Payne Lloyd James公开号:US20110009390A1公开(公告)日:2011-01-13The invention provides compounds of formula (I), and pharmaceutically and agriculturally acceptable salts thereof: wherein: R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A1, L1 and n are as defined herein. These compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts are useful in the manufacture of medicaments for use in the prevention or treatment of a fungal disease. Compounds of formula (I), and agriculturally acceptable salts thereof, may also be used as agricultural fungicides.该发明提供了式(I)的化合物,以及其在药学和农业上可接受的盐:其中:R1、R2、R3、R4、R5、R6、R7、R8、A1、L1和n如本文所定义。这些化合物及其药学上可接受的盐在制造用于预防或治疗真菌病的药物方面是有用的。式(I)的化合物及其在农业上可接受的盐也可用作农业杀菌剂。
表征谱图
-
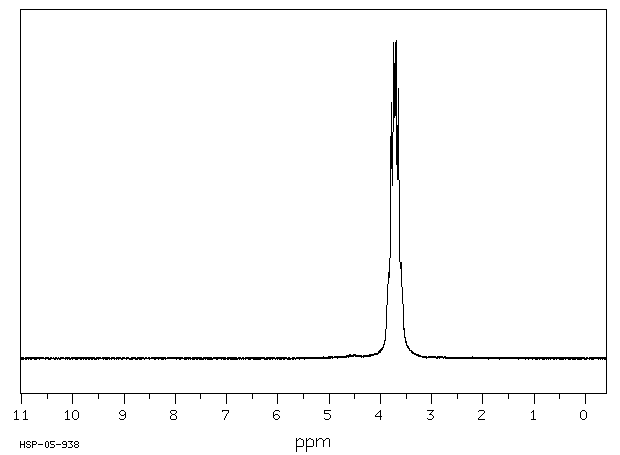
氢谱1HNMR
-
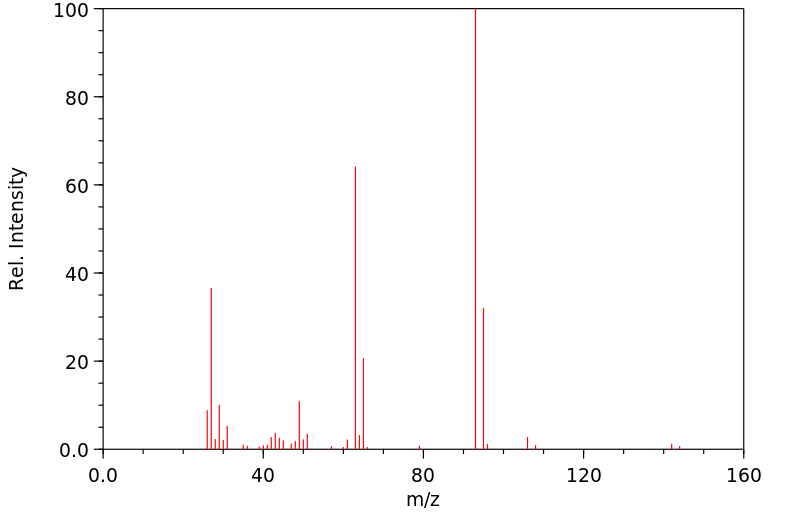
质谱MS
-
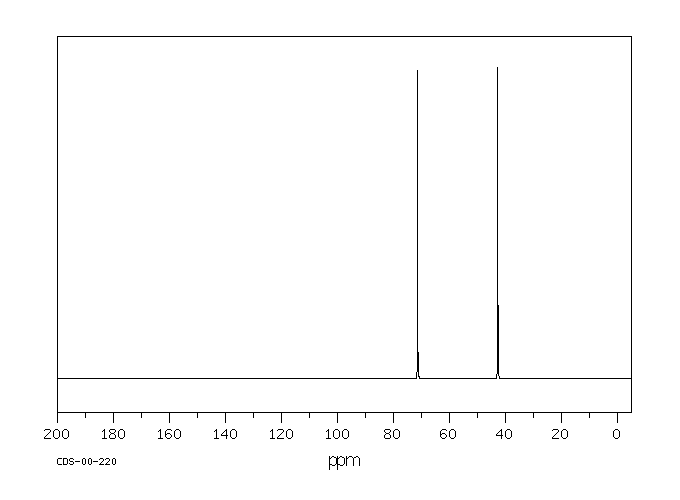
碳谱13CNMR
-
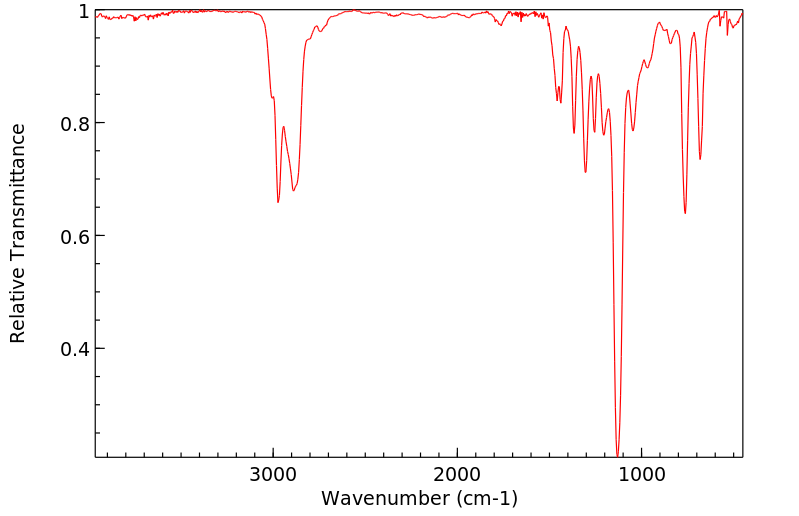
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷