二甲胺 | 124-40-3
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−93 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:7 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.89 g/mL at 25 °C
-
蒸气密度:1.55 (vs air)
-
闪点:60 °F
-
溶解度:very soluble in water (163 g/100 g water at 40°C); soluble in ethanol, ethyl ether, and many organic solvents
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 10 ppm (~18 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); IDLH 2000 ppm (NIOSH).
-
介电常数:6.3(0℃)
-
LogP:-0.274 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Colorless gas with an ammonia- or fish-like odor. [Note: A liquid below 44°F. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas.]
-
颜色/状态:Colorless gas
-
气味:... Ammonia or fish-like odor ...
-
蒸汽密度:1.6 (USCG, 1999) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1520 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.77X10-5 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:6.54e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
基本性质:二甲胺具有弱碱性,能与无机酸生成易溶于水的盐类。其蒸气与空气混合可形成爆炸性混合物,爆炸极限为2.8%-14.4%,闪点低,应避免日光直射和远离火源。它对铜、铜合金、铝、锡、锌等金属有腐蚀作用。
-
- 水溶液呈碱性,能与无机酸、有机酸及酸性芳香族硝基化合物生成熔点较高的盐类。也能与重金属化合物形成络合物。
- 与酰氯、酸酐等发生酰基化反应,生成N-取代酰胺;与脂肪族羧酸形成的盐经脱水后也生成N-取代酰胺;与磺酰氯或芳香族磺酰氯反应生成相应的N-取代磺酰胺。
- 与卤代烃、醇、酚或胺盐等烃基化试剂作用,氮上的氢原子可被烃基取代。
- 能与氰酸、二硫化碳、腈、环氧物等发生加成反应。
- 仲胺能与脂肪族或芳香族醛反应脱水生成Schiff碱;在碱性溶液中与甲醛反应生成双(二烷基氨基)甲烷。或者通过Mannich反应(即二甲胺盐酸盐、甲醛与含有活性氢的化合物反应),形成活性氢被二甲氨基甲基取代的化合物。
- 在碳酸钾存在下,仲胺能与醛反应生成二叔胺,并经蒸馏得到α,β-不饱和胺(即烯胺)。
- 仲胺对酸性高锰酸钾较为稳定,在碱性高锰酸钾中容易被氧化;与过硫酸、过氧化氢或有机过氧酸作用时,会生成胺的含氧化合物,例如与过氧化氢作用生成二烷基羟基胺。经氧化苯甲酸作用后,则生成邻苯甲酸衍生物。
- 与亚硝酸反应可生成亚硝基胺。
- 可以与Grignard试剂发生反应生成烃类物质。
- 在420~440℃下,二甲胺会热裂解产生甲胺、甲烷和氢等。在紫外光照射下亦会发生分解,生成甲烷及其他高分子物质。
-
二甲胺溶液对皮肤和黏膜有强烈的刺激作用,长时间接触高浓度蒸气可能导致皮肤炎症、结膜炎、失明及窒息等症状。嗅觉阈值为165mg/m³,根据TJ 36-79的规定,车间空气中最高允许浓度为10mg/m³。大鼠经口的半数致死量(LD₅₀)约为698mg/kg,而兔静脉注射的半数致死量则高达4000mg/kg。
-
稳定性:二甲胺相对稳定。
-
禁配物:强氧化剂、酸类及卤素。
-
聚合危害:不会发生聚合反应。
-
-
自燃温度:752 °F (400 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions: Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx).
-
粘度:1.7 mPa.s at 15.5 °C /40% Dimethylamine aqueous solution/
-
腐蚀性:Liquid dimethylamine will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings
-
燃烧热:-1743.5 kJ/mol at 25 °C /liquid/; 1768.9 kJ/mol at 25 °C /gas/
-
汽化热:25.05 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:26.34 mN/m at 25 °C
-
电离电位:8.24 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.00076 [ppm]; Odor Threshold High: 1.6 [ppm]; Odor threshold from AIHA
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.350 at 17 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = 10.732 at 25 °C (conjugate acid)
-
相对蒸发率:Greater than 1 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:434 ;425
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.2
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:12
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 10 ppm (18 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:500 ppm
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S29,S3,S36/37/39,S39,S45
-
危险类别码:R37/38,R12,R41,R20
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2921110010
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2924 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:IP8750000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05,GHS07
-
危险性描述:H220,H280,H315,H318,H332,H335,H412
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P261,P273,P280,P305 + P351 + P338,P410 + P403
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风的易燃气体专用库房。 - 远离火种、热源,库温不宜超过30℃。 - 保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂、酸类、卤素分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备。
SDS
| |
| |
| |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | |
| 健康危害: | 本品对眼和呼吸道有强烈的刺激作用。皮肤接触液态二甲胺可引起坏死,眼睛接触可引起角膜损伤、混浊。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品易燃,具强刺激性。 |
| |
| 皮肤接触: | |
| 眼睛接触: | |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: |
| |
| 危险特性: | 易燃,与空气混合能形成爆炸性混合物。遇热源和明火有燃烧爆炸的危险。与氧化剂接触猛烈反应。气体比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇火源会着火回燃。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | |
| 灭火方法: |
| |
| 应急处理: |
| |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,加强通风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(全面罩),穿防静电工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。防止气体泄漏到工作场所空气中。避免与氧化剂、酸类、卤素接触。在传送过程中,钢瓶和容器必须接地和跨接,防止产生静电。搬运时轻装轻卸,防止钢瓶及附件破损。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。库温不宜超过 30 ℃ 。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂、酸类、卤素分开存放,切忌混储。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备。 |
| |
| 职业接触限值 | |
| 中国 MAC(mg/m3) : | 10 |
| 前苏联 MAC(mg/m3) : | 1 |
| TLVTN : | OSHA 10ppm,18mg/m3; ACGIH 5ppm,9.2mg/m3 |
| TLVWN : | ACGIH 15ppm,27.6mg/m3 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,加强通风。提供安全淋浴和洗眼设备。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度超标时,佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(全面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴氧气呼吸器或空气呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 呼吸系统防护中已作防护。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防静电工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴橡胶手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作完毕,淋浴更衣。 |
| |
| 主要成分: | 纯品 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色气体,高浓度的带有氨味,低浓度的有烂鱼味。 |
| pH : | |
| 熔点 ( ℃ ) : | -92.2 |
| 沸点 ( ℃ ) : | 6.9 |
| 0.68 | |
| 相对蒸气密度 ( 空气 =1) : | 1.55 |
| 饱和蒸气压 (kPa) : | 202.65(10 ℃ ) |
| 燃烧热 (kJ/mol) : | 1741.8 |
| 临界温度 ( ℃ ) : | 164.5 |
| 临界压力 (MPa) : | 5.31 |
| -0.38 | |
| 闪点 ( ℃ ) : | -17.8 |
| 引燃温度 ( ℃ ) : | 400 |
| 爆炸上限 %(V/V) : | 2.8 |
| 爆炸下限 %(V/V) : | 14.4 |
| 溶解性: | |
| 主要用途: | 用于有机合成及沉淀氢氧化锌等。 |
| 其它理化性质: |
| |
| 稳定性: | |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、酸类、卤素。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | |
| 分解产物: |
| |
| 急性毒性: | LD50 :无资料 LC50 : 8354mg/m3 , 6 小时 ( 大鼠吸入 ) |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | 家兔经眼: 50mg/5 分钟,眼睛刺激。 |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| |
| |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 处置前应参阅国家和地方有关法规。建议用焚烧法处置。焚烧炉排出的氮氧化物通过洗涤器除去。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 21044 |
| UN&, lt;, /SPAN> 编号: | 1032 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | O52 |
| 包装方法: | 钢质气瓶;安瓿瓶外普通木箱;罐车(充装系数 0.55 吨 / 立方米)。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 本品铁路运输时限使用耐压液化气企业自备罐车装运,装运前需报有关部门批准。铁路非罐装运输时应严格按照铁道部《危险货物运输规则》中的危险货物配装表进行配装。采用刚瓶运输时必须戴好钢瓶上的安全帽。钢瓶一般平放,并应将瓶口朝同一方向,不可交叉;高度不得超过车辆的防护栏板,并用三角木垫卡牢,防止滚动。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。装运该物品的车辆排气管必须配备阻火装置,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具装卸。严禁与氧化剂、酸类、卤素、食用化学品等混装混运。夏季应早晚运输,防止日光曝晒。中途停留时应远离火种、热源。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶,禁止在居民区和人口稠密区停留。铁路运输时要禁止溜放。 |
| |
| 法规信息 |
| |
| 参考文献: | |
| 填表时间: | |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | |
| MSDS 修改日期: | |
制备方法与用途
DMA,又称二甲胺,是一种有机化合物。它在常温下为无色易燃气体或液体,在高浓度或压缩液化时具有氨的气味;低浓度时则带有鱼油般的恶臭。该物质易溶于水,并能溶解于乙醇和乙醚中。DMA有毒性。
理化性质二甲胺在常温下为气体,具有明显的氨味。其熔点为-96℃,沸点为7.4℃;液态时的密度约为0.680 g/cm³。该物质易溶于水,并能溶解于乙醇和乙醚中。此外,二甲胺还容易燃烧,并表现出一定的弱碱性特性,与盐酸反应可生成有一定熔点的盐酸盐[(CH3)2NH·HCl](熔点为171℃)。
制法二甲胺可通过将甲醇与氨以特定比例混合,在一定温度和压力下,使用活性氧化铝作为催化剂进行合成。经过热交换、冷凝、脱氨、萃取、脱水及分离过程后可获得成品二甲胺。此外,也可通过甲醇氨化法生产:在425℃的反应温度和2.45 MPa的压力条件下,以α-Al₂O₃作为催化剂进行气相催化反应,生成一甲胺、二甲胺与三甲胺混合物;再通过加压精馏分离出单一组分的产品。相关化学方程式如下:
- CH₃OH + NH₃ → CH₃NH₂ + H₂O
- 2CH₃OH + NH₃ → (CH₃)₂NH + 2H₂O
- 3CH₃OH + NH₃ → (CH₃)₃N + 3H₂O
二甲胺广泛用作生产药物、染料、农药、皮革去毛剂、橡胶硫化促进剂、火箭推进剂等的原料。它还作为农药的重要中间体,用于制备多种杀虫剂和除草剂;另外,在橡胶工业中作为主要的硫化促进剂;同时在医药领域用于抗菌素的生产;纺织工业则将其用作溶剂;此外,二甲胺还可用于有机合成中的各种化学反应。
生产方法将甲醇与氨按照一定比例混合,并在特定温度和压力条件下利用活性氧化铝作为催化剂进行合成,最终经热交换、冷凝、脱氨、萃取、脱水及分离等步骤得到纯净的二甲胺。具体生产流程与一甲胺类似。
安全特性DMA属于有害气体且具有高毒性。急性毒性测试显示,通过口服途径对大鼠和小鼠的半致死量分别为698 mg/kg 和316 mg/kg。眼睛接触50 mg/5分钟兔子实验表明,该物质具有刺激性。与空气混合后遇明火或受热可引发爆炸;此外,在遇到明火、高温及氧化剂时易燃并产生有毒的氮氧化物烟雾。
储运特性应将二甲胺存放在通风干燥且低温环境下,并与其他氧化剂和酸类分开存放。灭火时宜采用雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳或四氯化碳以及干粉灭火器;其职业暴露限值为TWA 9 mg/m³ 和 STEL 18 mg/m³。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Preparation of bis-dialkylamino phosphonous anhydrides摘要:公开号:US02671109A1
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Application of the WATR Technique for Water Suppression in 1H NMR Spectroscopy in Determination of The Kinetics of Hydrolysis of Neostigmine Bromide in Aqueous Solution摘要:氨基氯化铵和胍基氯化铵均用于利用“T2弛豫水衰减”(WATR)技术在80兆赫1H核磁共振谱中抑制水信号。在80兆赫下,磷酸盐缓冲液对抑制效果的影响在一系列pH值下进行了研究。发现在存在0.1摩尔磷酸盐缓冲液和1摩尔胍基氯化铵的条件下,80兆赫下水质子的自旋-自旋弛豫时间在pH 7.3时达到最小值;因此,这些条件被选择用于后续使用WATR技术研究新斯的明溴化物水解动力学。该方法被发现非常适用于研究这种代表性酰胺的水解过程。DOI:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1993.tb05598.x
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:KR20240069725A摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
Ammonia–dimethylchloramine system: Kinetic approach in an aqueous medium and comparison with the mechanism involving liquid ammonia作者:J. Stephan、V. Pasquet、M. Elkhatib、V. Goutelle、H. DelaluDOI:10.1002/kin.20312日期:2008.6medium. Dimethylchloramine prepared in a pure state undergoes dehydrohalogenation in an alkaline medium: the principal products formed are N-methylmethanimine, 1,3,5-trimethylhexahydrotriazine, formaldehyde, and methylamine. The kinetics of this reaction was studied by UV, GC, and HPLC as a function of temperature, initial concentrations of sodium hydroxide, and chlorinated derivative. The reaction is of在对液氨中的氨-二甲基氯胺系统进行了详尽的研究之后,比较该系统在液氨中的反应性与相同系统在水性介质中的反应性是很有趣的。以纯态制备的二甲基氯胺在碱性介质中进行脱卤化氢:形成的主要产物是 N-甲基甲亚胺、1,3,5-三甲基六氢三嗪、甲醛和甲胺。该反应的动力学通过 UV、GC 和 HPLC 作为温度、氢氧化钠初始浓度和氯化衍生物的函数进行了研究。该反应是二级反应,遵循 E2 机理(k1 = 4.2 × 10-5 M-1 s-1,ΔH○# = 82 kJ mol-1,ΔS○# = -59 J mol-1 K-1 )。二甲基氯胺氧化不对称二甲基肼涉及两个连续的过程。第一步遵循关于卤胺和肼的一级定律,导致形成氨基氮烯中间体 (k2 = 150 × 10-5 M-1 s-1)。第二步对应于在 pH 13) 下将氨基氮烯转化为甲醛二甲腙。该反应遵循一阶定律 (k3 = 23.5 × 10-5 s-1)。二甲基氯胺-氨相互作用对应于
-
[EN] IMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF FAAH<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS IMIDAZOLE UTILES COMME INHIBITEURS DE LA FAAH申请人:MERCK & CO INC公开号:WO2009152025A1公开(公告)日:2009-12-17The present invention is directed to certain imidazole derivatives which are useful as inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzeimer Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
-
Asymmetric Synthesis and Absolute Configuration Assignment of a New Type of Bedaquiline Analogue作者:Chang-Jiang Qiao、Xiao-Kui Wang、Fei Xie、Wu Zhong、Song LiDOI:10.3390/molecules201219846日期:——Bedaquiline is the first FDA-approved new chemical entity to fight multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in the last forty years. Our group replaced the quinoline ring with a naphthalene ring, leading to a new type of triarylbutanol skeleton. An asymmetric synthetic route was established for our bedaquiline analogues, and the goal of assigning their absolute configurations was achieved by comparison of experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism spectra, and was confirmed by the combined use of circular dichroism and NMR spectroscopy.
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
Nucleic acid related compounds. 47. Synthesis and biological activities of pyrimidine and purine "acyclic" nucleoside analogs作者:Morris J. Robins、Peter W. Hatfield、Jan Balzarini、Erik De ClercqDOI:10.1021/jm00377a018日期:1984.11Various acyclic, i.e., (2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl and (2-acetoxyethoxy)methyl, analogues of pyrimidine and purine nucleosides have been prepared and evaluated for their antiviral, antimetabolic, and cytotoxic properties. All of the pyrimidine analogues, including (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]uracil (12) and its O-acetyl derivative (13), were virtually devoid of antiviral, cytotoxic
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
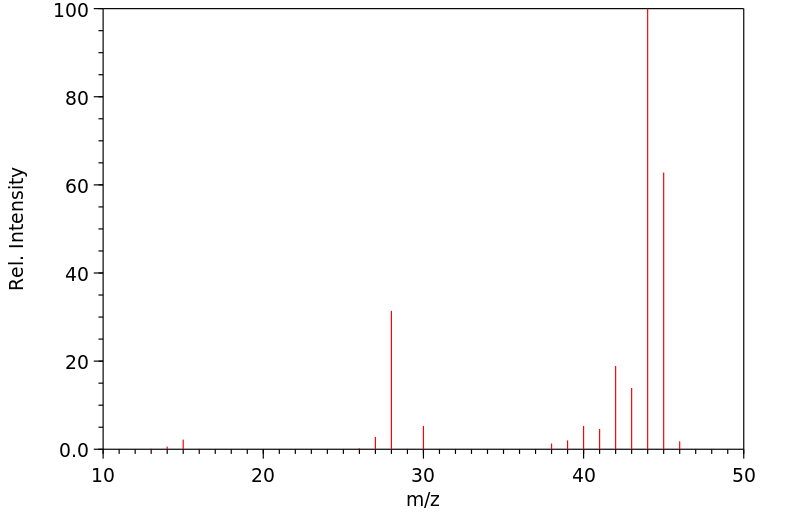
质谱MS
-
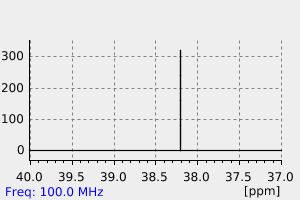
碳谱13CNMR
-
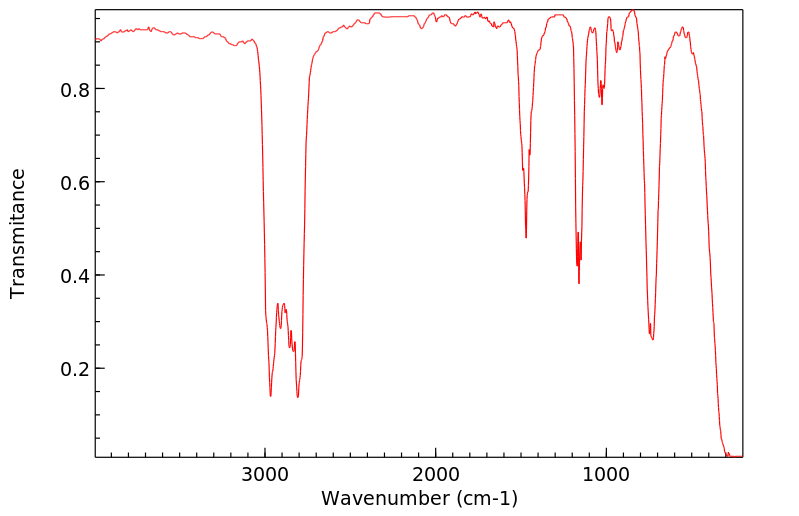
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息