庚基-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 | 78617-12-6
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:74-75℃
-
稳定性/保质期:
远离氧化物。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.8
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:8
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:99.4
-
氢给体数:4
-
氢受体数:6
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29400000
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P280,P301+P312,P302+P352,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:-20℃保存。
SDS
制备方法与用途
n-Heptyl-β-D-glucopyranoside 是一种非离子型表面活性剂,可用于溶解膜结合蛋白(保持其天然状态),以及制备脂质体。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-2-癸氧基-6-(羟基甲基)四氢吡喃-3,4,5-三醇 n-decyl β-D-glucopyranoside 58846-77-8 C16H32O6 320.426 壬基-Β-D-葡萄吡喃糖甙 (2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-2-Hydroxymethyl-6-nonyloxy-tetrahydro-pyran-3,4,5-triol 69984-73-2 C15H30O6 306.4 n-辛基-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 n-octyl β-D-glucopyranoside 29836-26-8 C14H28O6 292.373 戊基BETA-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 pentyl β-D-glucoside 66957-71-9 C11H22O6 250.292 己基β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 n-hexyl-β-D-glucopyranoside 59080-45-4 C12H24O6 264.319 丁基葡糖苷 n-butyl β-D-glucopyranoside 5391-18-4 C10H20O6 236.265 丙基 BETA-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Propyl-β-D-glucopyranosid 34384-77-5 C9H18O6 222.238 纤维素二糖 Cellobiose 16462-44-5 C12H22O11 342.3 D-葡萄糖 D-glu 2280-44-6 C6H12O6 180.158 可得然胶 β-D-glucose 492-61-5 C6H12O6 180.158 蔗糖 Sucrose 57-50-1 C12H22O11 342.3 β-D-葡萄糖五乙酸酯 β-D-glucose pentaacetate 604-69-3 C16H22O11 390.344 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 n-辛基-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 n-octyl β-D-glucopyranoside 29836-26-8 C14H28O6 292.373 (2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-2-癸氧基-6-(羟基甲基)四氢吡喃-3,4,5-三醇 n-decyl β-D-glucopyranoside 58846-77-8 C16H32O6 320.426 壬基-Β-D-葡萄吡喃糖甙 (2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-2-Hydroxymethyl-6-nonyloxy-tetrahydro-pyran-3,4,5-triol 69984-73-2 C15H30O6 306.4 戊基BETA-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 pentyl β-D-glucoside 66957-71-9 C11H22O6 250.292 己基β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 n-hexyl-β-D-glucopyranoside 59080-45-4 C12H24O6 264.319 丁基葡糖苷 n-butyl β-D-glucopyranoside 5391-18-4 C10H20O6 236.265 丙基 BETA-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Propyl-β-D-glucopyranosid 34384-77-5 C9H18O6 222.238 可得然胶 β-D-glucose 492-61-5 C6H12O6 180.158
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Significantly Improved Equilibrium Yield of Long-Chain Alkyl Glucosides via Reverse Hydrolysis in a Water-Poor System Using Cross-Linked Almond Meal as a Cheap and Robust Biocatalyst摘要:An array of ten beta-D-glueopyranosides with varied alkyl chain lengths were enzymatically synthesized. It was found that for longer alkyl chains a lower initial rate and final yield of glucoside was obtained except for methyl glucoside because of the severe toxicity of methanol to the enzyme. From a thermodynamics point of view, the equilibrium constant and Gibbs free energy variation of the glucoside syntheses were systematically investigated. To improve the final yields of the glucosides containing long alkyl chains the equilibrium of the enzymatic glucoside synthesis was altered. The equilibrium yield of decyl beta-D-glucoside increased from 1.9% to 6.1% when the water content was reduced from 10% to 5% (v/v) using tert-butanol as a cosolvent and 0.10 mol/L of glucose as a substrate. As for the other longer alkyl chain glucosides, heptyl beta-D-glucoside was found to have significant surface activity as well.DOI:10.1016/s1872-2067(11)60333-1
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Significantly Improved Equilibrium Yield of Long-Chain Alkyl Glucosides via Reverse Hydrolysis in a Water-Poor System Using Cross-Linked Almond Meal as a Cheap and Robust Biocatalyst摘要:An array of ten beta-D-glueopyranosides with varied alkyl chain lengths were enzymatically synthesized. It was found that for longer alkyl chains a lower initial rate and final yield of glucoside was obtained except for methyl glucoside because of the severe toxicity of methanol to the enzyme. From a thermodynamics point of view, the equilibrium constant and Gibbs free energy variation of the glucoside syntheses were systematically investigated. To improve the final yields of the glucosides containing long alkyl chains the equilibrium of the enzymatic glucoside synthesis was altered. The equilibrium yield of decyl beta-D-glucoside increased from 1.9% to 6.1% when the water content was reduced from 10% to 5% (v/v) using tert-butanol as a cosolvent and 0.10 mol/L of glucose as a substrate. As for the other longer alkyl chain glucosides, heptyl beta-D-glucoside was found to have significant surface activity as well.DOI:10.1016/s1872-2067(11)60333-1
-
作为试剂:描述:磷酸单硝基苯基酯 在 protein tyrosine phosphatase from apple pathogen Erwinia amylovora 、 sodium chloride 、 庚基-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 作用下, 以 aq. buffer 为溶剂, 生成 对硝基苯酚参考文献:名称:Determination and Kinetic Characterization of a New Potential Inhibitor for AmsI Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase from the Apple Pathogen Erwinia amylovora摘要:
Erwinia amylovora is a Gram-negative bacterium, responsible for the fire blight disease in Rosaceae plants. Its virulence is correlated with the production of an exopolysaccharide (EPS) called amylovoran, which protects the bacterium from the surrounding environment and helps its diffusion inside the host. Amylovoran biosynthesis relies on the expression of twelve genes clustered in the ams operon. One of these genes, amsI, encodes for a Low Molecular Weight Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (LMW-PTP) called EaAmsI, which plays a key role in the regulation of the EPS production pathway. For this reason, EaAmsI was chosen in this work as a target for the development of new antibacterial agents against E. amylovora. To achieve this aim, a set of programs (DOCK6, OpenEye FRED) was selected to perform a virtual screening using a database of ca. 700 molecules. The six best-scoring compounds identified were tested in in vitro assays. A complete inhibition kinetic characterization carried out on the most promising molecule (n-Heptyl β-D-glucopyranoside, N7G) showed an inhibition constant of 7.8 ± 0.6 µM. This study represents an initial step towards the development of new EaAmsI inhibitors able to act as antibacterial agents against E. amylovora infections.
DOI:10.3390/molecules28237774
文献信息
-
PROCESS FOR STRAIGHTENING KERATIN FIBRES WITH A HEATING MEANS AND DENATURING AGENTS申请人:Philippe Michel公开号:US20100028280A1公开(公告)日:2010-02-04The invention relates to a process for straightening keratin fibres, comprising: (i) a step in which a straightening composition containing at least two denaturing agents is applied to the keratin fibres, (ii) a step in which the temperature of the keratin fibres is raised, using a heating means, to a temperature of between 110 and 250° C.该发明涉及一种直发角蛋白纤维的拉直过程,包括:(i)将至少两种变性剂含有的拉直组合物涂抹到角蛋白纤维上的步骤,(ii)使用加热装置将角蛋白纤维的温度升高至110至250°C的步骤。
-
Simple Synthesis of .BETA.-D-Glycopyranosides Using .BETA.-Glycosidase from Almonds作者:Katsumi Kurashima、Mikio Fujii、Yoshiteru Ida、Hiroyuki AkitaDOI:10.1248/cpb.52.270日期:——Enzymatic glycosidation of twenty-one kinds of alcohols (n-hepanol, n-octanol, 2-phenylethanol, 3-phenylpropanol, 4-phenylbutanol, 5-phenylpentanol, 6-phenylhexanol, furfury alcohol, 2-pyridinemethanol, isobutanol, isopentanol, p-methoxycinnamylalcohol) including secondary alcohols (isopropanol, cyclohexanol, 1-phenylethanol) and 1,ω-alkanediols (1,5-pentanediol, 1,6-hexanediol, 1,7-heptanediol, 1,8-octanediol, 1,9-nonanediol), salicyl alcohol and 4-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside (5) using β-glucosidase from almonds stereoselectively gave the corresponding β-D-glucopyranosides in moderate yield.
-
POLYMER STABILIZER申请人:KIMURA Yoshikazu公开号:US20100179253A1公开(公告)日:2010-07-15A polymer stabilizer comprising the following alkoxy compound: the alkoxy compound: a compound obtained by alkoxylating at least one hydroxyl group contained in a compound of the following formula (1) containing one formyl group or carbonyl group and (n− 1 ) hydroxyl groups in the molecule with an alkyl group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms: C n H 2n O n (1) (wherein, n represents an integer of 3 or more).一种聚合物稳定剂,包含以下烷氧基化合物:所述烷氧基化合物是通过将含有以下通式(1)中的一个甲酰基或羰基以及分子中(n-1)个羟基的化合物中的至少一个羟基进行烷氧基化而得到的化合物,其中烷基团含有1至12个碳原子:CnH2nOn(1)(其中,n代表3或以上的整数)。
-
A Solanum torvum GH3 β-glucosidase expressed in Pichia pastoris catalyzes the hydrolysis of furostanol glycoside作者:Rungarun Suthangkornkul、Pornpisut Sriworanun、Hiroyuki Nakai、Masayuki Okuyama、Jisnuson Svasti、Atsuo Kimura、Saengchan Senapin、Dumrongkiet ArthanDOI:10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.03.015日期:2016.7glucosyl hydrolase 1 (GH1) or 3 (GH3) families. Previously, a β-glucosidase (torvosidase) was purified from Solanum torvum leaves that specifically catalyzed hydrolysis of two furostanol 26-O-β-glucosides, torvosides A and H. Furostanol glycoside 26-O-β-glucosides have been reported as natural substrates of some plant GH1 enzymes. However, torvosidase was classified as a GH3 β-glucosidase, but could植物 β-葡萄糖苷酶通常是葡萄糖基水解酶 1 (GH1) 或 3 (GH3) 家族的成员。以前,一种 β-葡萄糖苷酶(torvosidase)是从 Solanum torvum 叶子中纯化出来的,它专门催化两种呋喃甾醇 26-O-β-葡萄糖苷、torvosides A 和 H 的水解。 糠醇糖苷 26-O-β-葡萄糖苷已被报道为天然底物一些植物GH1酶。然而,torvosidase 被归类为 GH3 β-葡萄糖苷酶,但不能水解 GH3 酶的天然底物 β-寡糖苷。在这里,通过 cDNA 末端快速扩增方法分离了编码 S. torvum β-葡萄糖苷酶 (SBgl3) 的全长 cDNA。1887bp 的 ORF 编码 629 个氨基酸,与其他植物 GH3 β-葡萄糖苷酶具有高度同源性。LC-MS/MS 确定的纯化天然 SBgl3 的内部肽序列与 SBgl3 cDNA 的推导氨基酸序列匹配,表明它编码天然酶。带有多组氨酸标签
-
Preparation of alkyl α- and β-d-glucopyranosides, thermotropic properties and X-ray analysis作者:Volker Adasch、Bettina Hoffmann、Wolfgang Milius、Gerhard Platz、Gundula VossDOI:10.1016/s0008-6215(98)00302-4日期:1998.12Monohydrates of heptyl to decyl α- d -glucopyranosides as obtained from product mixtures of the Fischer glucosylation were crystallized from water at the Krafft point. The results of the single-crystal X-ray analysis of anhydrous α anomers and their monohydrates provide for a better understanding of crystal formation and stability of their hydrates. The preparation of alkyl β- d -glucopyranosides—without
表征谱图
-
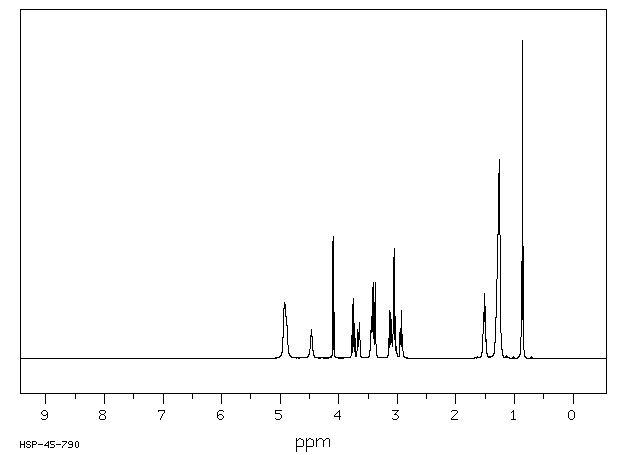
氢谱1HNMR
-
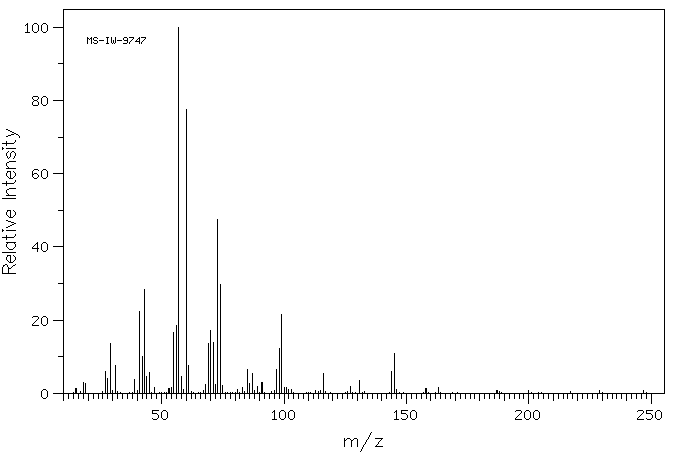
质谱MS
-
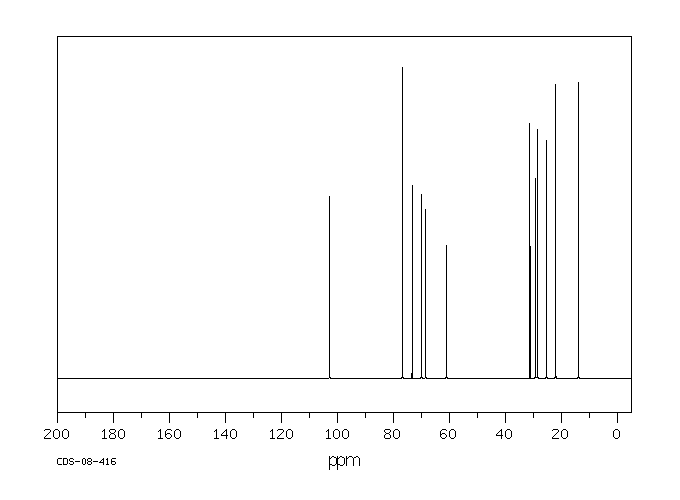
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息