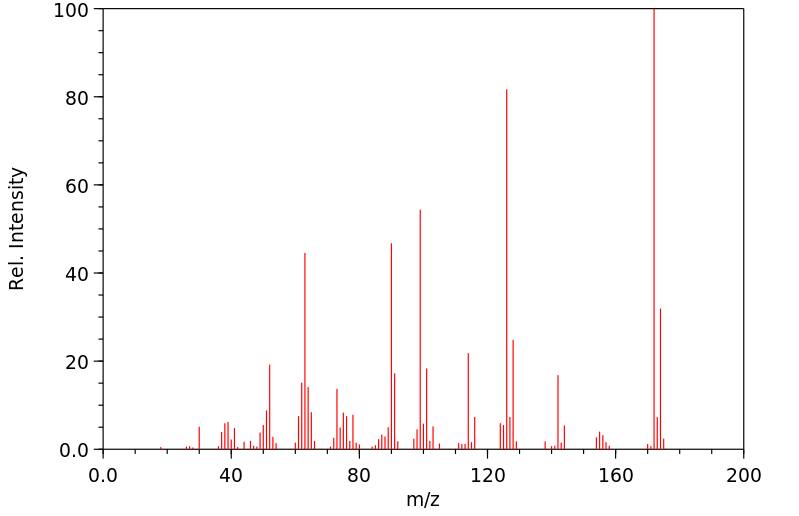
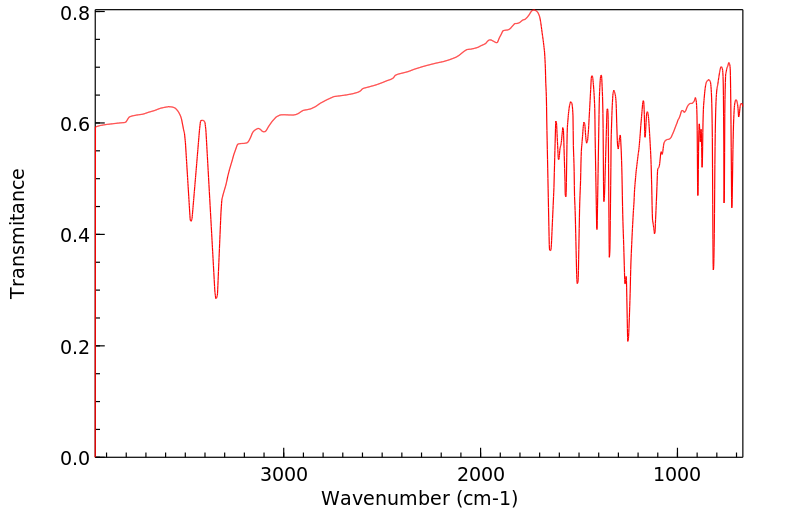
代谢
14C标记的4-氯-2-硝基苯胺(CNA)在雄性F344大鼠体内的处置和代谢进行了研究,研究包括口服或静脉(iv)给药。发现CNA的胃肠道吸收几乎是完全的,并且在研究的剂量范围内(0.788-78.8微摩尔/千克)不受剂量的影响。无论是口服还是静脉给药后,CNA迅速分布到全身组织,并未表现出对任何特定组织的明显亲和力。[14C]CNA通过代谢和尿液排泄迅速清除,在粪便中也有少量的排泄。在大鼠体内,CNA的全身半衰期大约为1小时,3天内体内的放射性活性几乎完全清除。已知的致癌物和CNA的潜在代谢物,4-氯邻苯二胺,在给予CNA后的大鼠组织或排泄物中未被检测到。大约70%的剂量以CNA单一代谢物的硫酸盐结合物形式出现在尿液中。剩余的剂量以七种额外代谢物和少量母体化合物的形式被排泄。CNA衍生的放射性活性几乎不具有生物积累的潜力,并且没有证据表明在研究的剂量范围内CNA的吸收、分布、代谢或排泄机制会饱和。
The disposition and metabolism of 14C-labeled 4-chloro-2-nitroaniline (CNA) was studied in male F344 rats following oral or intravenous (iv) administration. The gastrointestinal absorption of CNA was found to be near complete and was not affected by the dose in the range studied (0.788-78.8 mumol/kg). Following either oral or iv administration, CNA was rapidly distributed throughout the tissues and showed no marked affinity for any particular tissue. [14C]CNA was rapidly cleared by metabolism and excretion in urine and to a lesser extent in feces. The whole-body half-life of CNA in the rat was approximately 1 hr, and clearance of radioactivity from the body was near complete in 3 d. The known carcinogen and potential metabolite of CNA, 4-chloro-o-phenylenediamine, was not detected in rat tissues or excreta following administration of CNA. Approximately 70% of the dose was detected in urine as a sulfate conjugate of a single metabolite of CNA. The remainder of the dose was excreted in the form of seven additional metabolites and a trace of the parent compound. CNA-derived radioactivity had little potential for bioaccumulation, and there was no evidence for saturation of any mechanism involved in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion of CNA in the dose range studied.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)