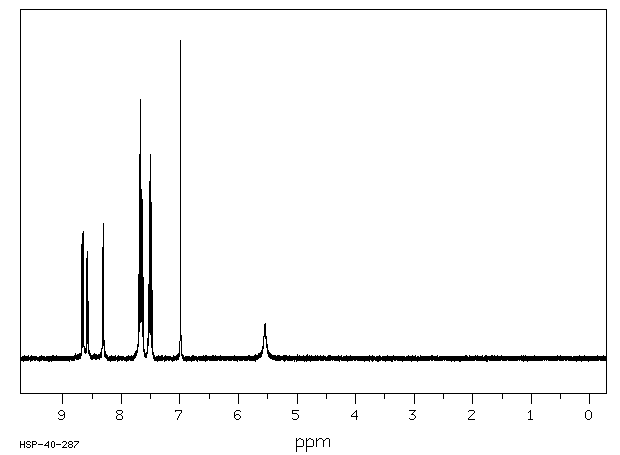
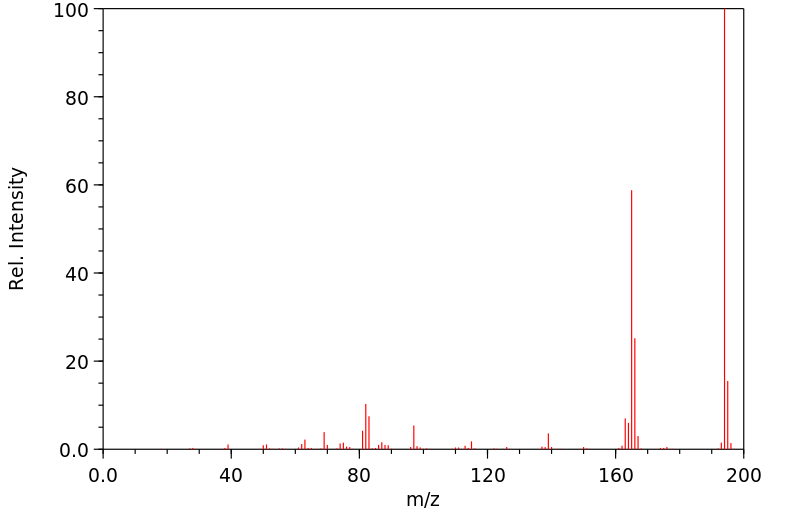
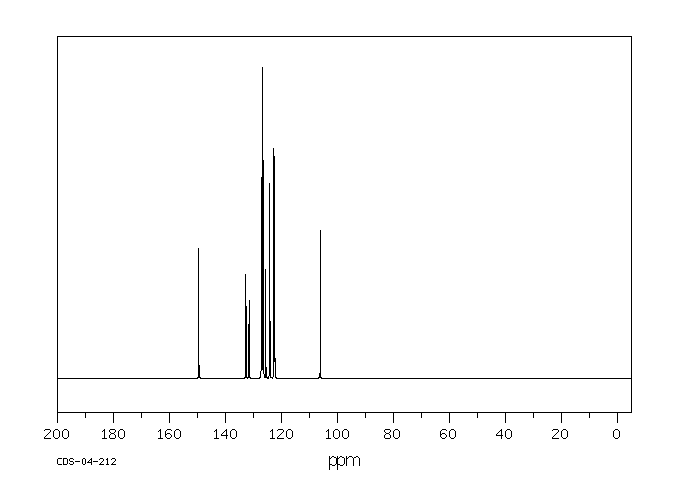
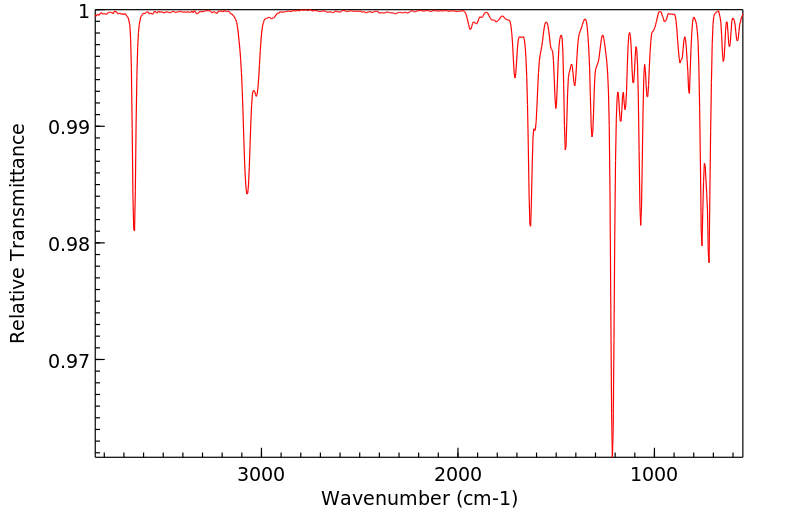
毒理性
9-phenanthrol 是一种最近被识别的瞬时受体电位黑色素(TRPM)4通道的抑制剂,这是一种由 Ca(2+) 激活的非选择性阳离子通道,其作用机制尚未确定。9-phenanthrol 通过抑制 TRPM4 电流调节多种生理过程。9-phenanthrol 调节膀胱和脑动脉平滑肌的收缩,影响神经元和心脏的自发活动,并减少脂多糖诱导的细胞死亡。9-phenanthrol 对抗缺血再灌注损伤具有心脏保护作用,并减少缺血性中风损伤。(A15462) 目前最特异的 TRPM4 通道抑制剂是 9-phenanthrol,它消除了小鼠心室由缺氧和复氧诱导的心律失常。TRPM4 与多种生理功能有关,如防止 Ca2+ 过载,调节细胞内 ATP 和活性氧种类的水平,以及细胞死亡。神经元中的 TRPM4 通过介导细胞死亡,有助于炎症诱导的神经退行性变,这与 9-phenanthrol 的心脏保护作用相对应。由缺血/再灌注(I/R)引起的损伤是由 TPRM4 依赖的细胞死亡引起的,而 9-phenanthorol 通过阻断这一途径诱导心脏保护作用。(A15463)
9-phenanthrol is a recently identified inhibitor of the transient receptor potential melastatin (TRPM) 4 channel, a Ca(2+) -activated non-selective cation channel whose mechanism of action remains to be determined. 9-phenanthrol modulates a variety of physiological processes through TRPM4 current inhibition. 9-Phenanthrol modulates smooth muscle contraction in bladder and cerebral arteries, affects spontaneous activity in neurons and in the heart, and reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced cell death. 9-phenanthrol exerts cardioprotective effects against ischaemia-reperfusion injuries and reduces ischaemic stroke injuries. (A15462) The most specific inhibitor of TRPM4 channels currently available is 9-phenanthrol, which abolishes arrhythmias induced by hypoxia and reoxygenation in the mouse ventricle. TRPM4 has been linked to diverse physiological functions such as protection against Ca2+ overload, regulating the levels of intracellular ATP and reactive oxygen species, and cell death. TRPM4 in neurons contributes toward inflammation-induced neurodegeneration by mediating cell death, which corresponds to the cardioprotective effect of 9-phenanthrol. Damage induced by ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) was caused by TPRM4-dependent cell death and that 9-phenanthorol induces cardioprotection by blocking this pathway. (A15463)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)