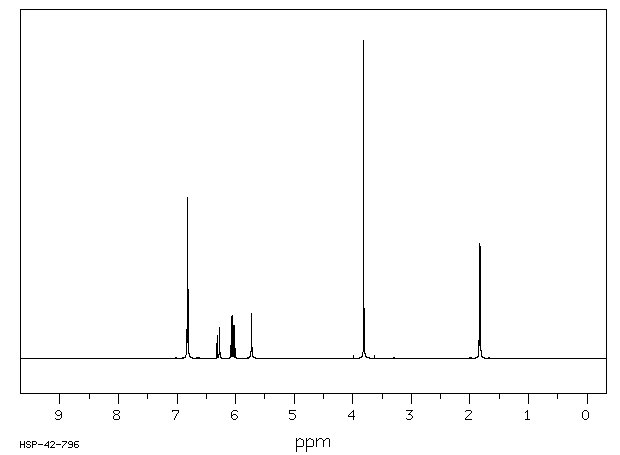
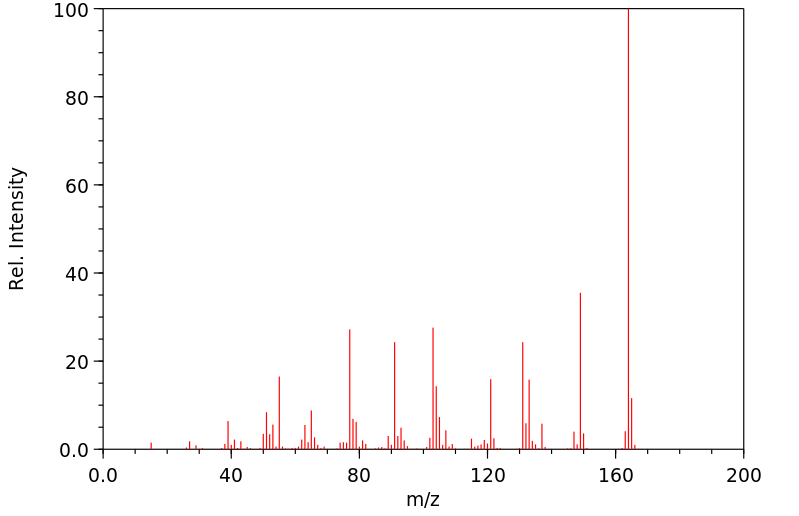
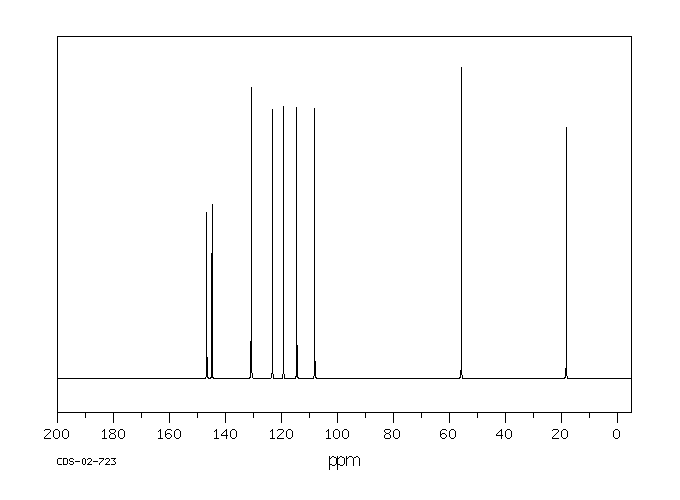
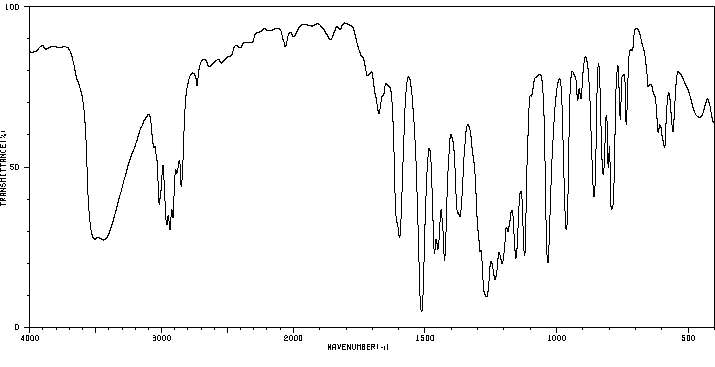
代谢
在口服给予(14)C-异丁子香酚(156 mg/kg,50 uCi/kg)单次剂量后,72小时内超过85%的给药剂量主要以硫酸盐或葡萄糖醛酸代谢物的形式通过尿液排出。大约10%在粪便中回收,不到0.1%以CO(2)或呼出的有机物形式回收。在任何分析的时间点,血液中均未检测到母体异丁子香酚。静脉给药(15.6 mg/kg,100 uCi/kg)后,异丁子香酚迅速从血液中消失。半衰期为12分钟,Cl(s)为1.9 L/min/kg。排泄特性与口服给药相似。在72小时内,所选组织中残留的总放射性物质量不到口服或静脉给药剂量的0.25%。这些研究的结果表明,异丁子香酚被迅速代谢,并且主要以母体化合物的第二阶段结合物形式通过尿液排出。
Following a single oral dose of (14)C-isoeugenol (156 mg/kg, 50 uCi/kg), greater than 85% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine predominantly as sulfate or glucuronide metabolites by 72 hr. Approximately 10% was recovered in the feces, and less than 0.1% was recovered as CO(2) or expired organics. No parent isoeugenol was detected in the blood at any of the time points analyzed. Following iv administration (15.6 mg/kg, 100 uCi/kg), isoeugenol disappeared rapidly from the blood. The half life was 12 min and the Cl(s) was 1.9 L/min/kg. Excretion characteristics were similar to those of oral administration. The total amount of radioactivity remaining in selected tissues by 72 hr was less than 0.25% of the dose following either oral or intravenous administration. Results of these studies show that isoeugenol is rapidly metabolized and is excreted predominantly in the urine as phase II conjugates of the parent compound.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)