丙烯醛 | 107-02-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-88 °C
-
沸点:52.5 °C
-
密度:0.8075 g/cm3(Temp: 50 °C)
-
物理描述:Acrolein, stabilized appears as a colorless to yellow volatile liquid with a disagreeable choking odor. Flash point below 0°F. Initially irritating to the eyes and mucous membranes. Very toxic by inhalation. Less dense than water (7.0 lb / gal). Vapors heavier than air. Used to make other chemicals, plastics, and as a herbicide. Rate of onset: Immediate Persistence: Minutes to hour Odor threshold: 1 ppm Source/use/other hazard: Herbicide; tox and corrosive fumes.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless or yellowish liquid
-
气味:Extremely sharp; extremely acrid, pungent, burnt sweet; hot fat
-
闪点:-29 °C (-20 °F) - closed cup
-
溶解度:In water, 2.11X10+5 mg/L at 20 °C
-
蒸汽密度:1.94 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:274 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.22e-04 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:1.99e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
化学性质:丙烯醛兼有双键和醛基,表现出两种官能团的典型反应。其双键在酸或碱催化下可与醇、硫醇、水、胺、有机酸及无机酸等物质发生加成反应;而醛基则可在温和酸性条件下与醇或多羟基物质缩合生成缩醛。这两种官能团相互作用,赋予丙烯醛独特的性质。
-
本品为一种极毒且强刺激性的液体,强烈刺激眼睛和呼吸道黏膜,可能导致眼结膜炎、喉炎、支气管炎;高浓度蒸气可引起肺炎、肺出血、肺水肿及呼吸困难。误服会导致严重肠胃病和肺出血等。亦可通过皮肤吸收中毒。小鼠皮下注射的半数致死量为30毫克/千克,工作场所空气中最高容许浓度为0.25毫克/立方米。操作人员应佩戴防护口罩。
-
丙烯醛是一种极毒且具有高度刺激性的液体,在空气中的最高允许浓度为0.3毫克/立方米。直接接触会损伤眼睛和呼吸道,是一种强效的催泪毒气。吸入会引起肠胃不适、肺充血及水肿。
-
稳定性:丙烯醛相对稳定(参考资料[26])。
-
避免接触条件:受热、光照和与空气接触。
-
聚合危害:存在聚合风险。
-
-
自燃温度:428 °F (220 °C); unstable
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides.
-
粘度:0.35 cP at 20 °C
-
腐蚀性:Non-corrosive to iron & steel at room temperature
-
燃烧热:-12,500 BTU/lb = -6,950 cal/g = -290X10+5 J/kg
-
汽化热:216 BTU/lb = 120 cal/g = 5.02X10+5 J/kg
-
表面张力:24 dynes/cm = 0.024 N/m at 20 °C
-
电离电位:10.13 eV
-
聚合:Violent polymerization reaction on contact with strong acid, strong base, weak acid conditions (e.g., nitrous fumes, sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide), thiourea, or dimethylamine.
-
气味阈值:Air: 0.16 uL/L; Water: 0.11 mg/L; Odor safety class D; D= 10-50% of attentive persons can detect TLV concn in the air
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4017 at 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:462;470;469;463;463;463;464;469;465;467.7;473.1;453.7
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:17.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1
-
安全说明:S23,S26,S28,S36/37/39,S45,S61
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1092 6.1/PG 1
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2912190030
-
危险类别:6.1
-
危险品标志:F
-
危险类别码:R24/25,R26,R50,R11,R34
-
RTECS号:AS1050000
-
包装等级:I
-
储存条件:1. **储存注意事项**:应储存在阴凉、通风良好的专用库房内,实行“双人收发、双人保管”制度。远离火种和热源,库温不宜超过29℃。包装需密封,避免与空气接触。应与氧化剂、还原剂、酸类、碱类及食用化学品分开存放,严禁混储。不宜大量储存或久存。采用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 2. **丙烯醛的光热反应**:在光照、加热或存在微量杂质的情况下,丙烯醛会迅速聚合并释放大量热量,存在爆炸风险。与无机酸、碱或胺类接触时也会高度发热。为防止此类情况发生,建议将无机酸、碱与丙烯醛接触前加入缓冲溶液(冰醋酸84%,照相级对苯二酚8%,无水碳酸钠8%)。贮运设备及管道阀门必须十分洁净,并用惰性气体彻底清洗。按危险品规定进行储存和运输。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 31024 |
| CAS: | 107-02-8 |
| 中文名称: | 丙烯醛 |
| 英文名称: | acrolein;allylaldehyde |
| 别 名: | 烯丙醛 |
| 分子式: | C 3 H 4 O;CH 2 CHCHO |
| 分子量: | 56.06 |
| 熔 点: | -87.7℃ 沸点:52.5℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)0.84; |
| 蒸汽压: | -26℃ |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水,易溶于醇、丙酮等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 不稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色或淡黄色液体,有恶臭 |
| 危险标记: | 7(低闪点易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 为合成树脂工业的重要原料之一,也大量用于有机合成与药物合成 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:本品有强烈刺激性。吸入蒸气损害呼吸道,出现咽喉炎、胸部压迫感、支气管炎;大量吸入可致肺炎、肺水肿,尚可出现休克、肾炎及心力衰竭。可致死。液体及蒸气损害眼睛;皮肤接触可致灼伤。口服引起口腔及胃刺激或灼伤。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属高毒类。
急性毒性:LD 50 46mg/kg(大鼠经口);562mg/kg(兔经皮);LC 50 300mg/m 3 ,1/2小时(大鼠吸入)人吸入2.3mg/m 3 ×5分钟,不能忍受;人吸入153ppm×10分钟,最小致死浓度;人经口5mg/kg最小致死剂量。
刺激性:家兔经眼:1mg,重度刺激。家兔经皮:5mg,重度刺激。
亚急性和慢性毒性:大鼠持续接触本品浓度低至4.8mg/m 3 ,40小时后,其肝脏的碱性磷酸酶活性升高。
致突变性:微生物致突变性:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌20nL/皿。微粒体致突变:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌50µl/皿。
生殖毒性:大鼠静脉最低中毒剂量(TDL 0 ):6mg/kg(孕后用药9天),胚泡植入后死亡率升高。
致癌性:IARC致癌性评论:动物为不肯定性反应。
危险特性:其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热极易燃烧爆炸。受热分解释出高毒蒸气。在空气中久置后能生成具有爆炸性的过氧化物。与酸类、碱类、氨、胺类、二氧化硫、硫脲、金属盐类、氧化剂等猛烈反应。在火场高温下能发生聚合放热,使容器破裂。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳。
3.现场应急监测方法:
检气管法《化工企业空气中有害物质测定方法》,化学工业出版社
4.实验室监测方法:
| 监测方法 | 来源 | 类别 |
| 气相色谱法 | HJ/T39-1999 | 固定污染源排气 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《水质分析大全》张宏陶等主编 | 水质 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《固体废弃物试验与分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译 | 固体废弃物 |
| 4-已基间苯二酚分光光度法 | 《空气和废气监测分析方法》国家环保局编 | 空气和废气 |
5.环境标准:
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.3mg/m 3 |
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 居住区大气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.10mg/m 3 (一次值) |
| 中国(GB16297-1996) | 大气污染物综合排放标准 | ①最高允许排放浓度(mg/m 3 ): 16(表2);20(表1) ②最高允许排放速率(kg/h): 二级0.52~11(表2);0.61~13(表1) 三级0.78~17(表2);0.92~20(表1) ③无组织排放监控浓度限值(mg/m 3 ): 0.40(表2);0.50(表1) |
| 中国(GB11607-89) | 渔业水质标准 | 0.02mg/L |
| 中国(GB5048-92) | 农田灌溉水质标准 | 0.5mg/L(水作、旱作、蔬菜) |
| 中国(待颁布) | 饮用水源中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.1mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 0.48~4.1mg/m 3 |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并立即进行隔离,小泄漏时隔离150米,大泄漏时隔离300米,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防毒服。不要直接接触泄漏物。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用活性面料或其它惰性材料吸收。也可以用大量水冲洗,洗水稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。用防爆泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,必须佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(全面罩)。
眼睛防护:呼吸系统防护中已作防护。
身体防护:穿防静电工作服。
手防护:戴橡胶手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去被污染的衣着,用大量流动清水冲洗,至少15分钟。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水彻底冲洗至少15分钟。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者用水漱口,给饮牛奶或蛋清。就医。
灭火方法:消防人员须戴好防毒面具,在安全距离以外,在上风向灭火。灭火剂:在抗溶性泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。用水灭火无效。
制备方法与用途
-
实验室制法:将甘油与硫酸氢钾或硫酸镁、硼酸及三氧化铝在215~235 ℃共热,将反应生成的丙烯醛气体蒸出并经冷凝收集,得粗品。然后将粗品加入10%磷酸氢钠溶液中调pH值至6,进行分馏,收集50~75 ℃馏分,即得丙烯醛精品。投料比(mol):甘油:硫酸氢钾:硫酸钾=1:0.5:0.026。
-
工业制法:目前主要采用丙烯催化空气氧化法。将丙烯、空气和水蒸气按一定比例混合后与催化剂一起送入固定床反应器,在0.1~0.2 MPa、350~450 ℃下进行反应,接触时间0.8 s,反应释放的热量回收用以蒸汽的生产。反应生成的气体混合物用水急冷,从急冷塔出来的尾气放空前经过洗涤。从急冷塔塔底出来的有机液进汽提塔,汽提出丙烯醛和其他轻组分,然后用蒸馏法从粗丙烯醛中除去水和乙醛。反应式:投料比(mol)丙烯:空气:水蒸气=1:10:2。
-
乙醛和甲醛在催化剂作用下,经气相催化缩合制得丙烯醛。或者在催化剂的作用下,将丙烯用空气氧化制丙烯醛,副产物为乙酸、乙醛、丙烯酸和二氧化碳。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 巴豆醛 (E)-But-2-enal 123-73-9 C4H6O 70.091 (E)-丁-2-烯二醛 butenedial 2363-83-9 C4H4O2 84.0746 2-甲基丙烯醛 2-methylpropenal 78-85-3 C4H6O 70.091 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丁烯酮 methyl vinyl ketone 78-94-4 C4H6O 70.091 2,4-戊二烯醛 2,4-pentadienal 764-40-9 C5H6O 82.102 丙烯酰胺 2-propenamide 79-06-1 C3H5NO 71.0788
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:钼酸铋催化剂上丙烯醛氨氧化为丙烯腈摘要:目前的工作涉及使用中孔钼酸铋催化剂将绿色起源的丙烯醛转化为丙烯腈的潜在重要过程。通过N 2物理吸附,X射线衍射和在各种条件下,不同温度,接触时间和反应物摩尔比下的催化试验,表征氨氧化催化剂。结果表明,催化活性与比表面积成比例,这取决于钼酸铋相和气体进料中氧气的浓度。催化剂的选择性仅取决于反应温度。在350–400°C下获得的ACN选择性为100%,在450°C下降至97%。DOI:10.1016/j.apcata.2016.03.030
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Simons, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1926, vol. 48, p. 1992摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:使用Grubbs催化剂通过复分解反应合成α,β-不饱和醛和腈摘要:使用格鲁布斯的催化剂,在缺电子的烯烃(即丙烯醛,巴豆醛,甲基丙烯醛和丙烯腈)与各种不同的1 -烯烃,包括1-癸烯,1-辛烯,1-己烯和2-烯丙氧基-6-甲基庚烷。后者特别受关注,因为它以前没有在交叉复分解反应中用作底物,并允许获得有价值的中间体以合成新的香料。大多数反应对所需的CM产物具有良好的选择性(≥90%)。对丙烯醛与1-癸烯的交叉复分解进行了详细的优化和机理研究。已经尝试使用离子液体来再循环催化剂。DOI:10.1016/j.apcata.2014.08.032
文献信息
-
Synthesis and Preliminary Biological Evaluation of Two Fluoroolefin Analogs of Largazole Inspired by the Structural Similarity of the Side Chain Unit in Psammaplin A作者:Bingbing Zhang、Guangsheng Shan、Yinying Zheng、Xiaolin Yu、Zhu-Wei Ruan、Yang Li、Xinsheng LeiDOI:10.3390/md17060333日期:——Largazole and the amide moiety in Psammaplin A, and thus designed and synthesized two novel fluoro olefin analogs of Largazole. The preliminary biological assays showed that the fluoro analogs possessed comparable Class I HDAC inhibitory effects, indicating that this kind of modification on the side chain of Largazole was tolerable.
-
Sterically Demanding Oxidative Amidation of α-Substituted Malononitriles with Amines Using O<sub>2</sub>作者:Jing Li、Martin J. Lear、Yujiro HayashiDOI:10.1002/anie.201603399日期:2016.7.25An efficient amidation method between readily available 1,1-dicyanoalkanes and either chiral or nonchiral amines was realized simply with molecular oxygen and a carbonate base. This oxidative protocol can be applied to both sterically and electronically challenging substrates in a highly chemoselective, practical, and rapid manner. The use of cyclopropyl and thioether substrates support the radical
-
Synthesis of (-)-Δ<sup>9</sup>-<i>trans</i>-Tetrahydrocannabinol: Stereocontrol via Mo-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation Reaction作者:Barry M. Trost、Kalindi DograDOI:10.1021/ol063022k日期:2007.3.1[reaction: see text] Delta9-THC is synthesized in enantiomericaly pure form, where all of the stereochemistry is derived from the molybdenum-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation reaction of the extremely sterically congested bis-ortho-substituted cinnamyl carbonate in high regio- and enantioselectivity.
-
<i>tert-</i> Butyl Iodide Mediated Reductive Fischer Indolization of Conjugated Hydrazones作者:Yuta Ito、Masafumi Ueda、Norihiko Takeda、Okiko MiyataDOI:10.1002/chem.201504010日期:2016.2.18available N‐aryl conjugated hydrazones with tert‐butyl iodide has been developed. In this reaction, tert‐butyl iodide is used as anhydrous HI source, and the generated HI acts as a Brønsted acid and a reducing agent. This operationally simple method allows access to various indole derivatives. Furthermore, the procedure can be applied to the synthesis of biologically active compounds.
-
New cyclic phosphonium salts derived from the reaction of phosphine-aldehydes with acid作者:Alexandre A. Mikhailine、Paraskevi O. Lagaditis、Peter E. Sues、Alan J. Lough、Robert H. MorrisDOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2010.04.016日期:2010.6Various cyclic phosphonium structures are formed in high yield by the deprotection of unstable phosphine-aldehydes in acidic solution. When there is a methylene spacer between the phosphine and the aldehyde, a phosphonium ion [PHR2CH2CH(OEt)2]Br2, R=iPrOH, Et is obtained. Reaction of these phosphonium salts with water produces the dimers [–PR2CH2CH(OH)–]2[Br]2 R = iPr, Et. When there is an ethylene通过将不稳定的膦醛在酸性溶液中脱保护,可以高产率形成各种环状结构。当在膦和醛之间存在亚甲基间隔基时,获得ion离子[PHR 2 CH 2 CH(OEt)2 ] Br 2,R = iPrOH,Et。这些phospho盐与水反应生成二聚体[–PR 2 CH 2 CH(OH)–] 2 [Br] 2 R = i Pr,Et。如PPh 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH(OCH 2 CH 2O),一种具有16元环[-PPh 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH(OH)–] 4 [Cl] 4的显着四聚体,在盐酸溶液中形成为一种非对映异构体。HCl与受保护的膦醛与丙烯间隔基(PPh 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH(OCH 2 CH 2 O))的反应导致形成单体phospho盐[–PPh 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2具有5元环的CH(OH)–] Cl。使用X射线衍射实验确定了不同环类型的固态结构。
表征谱图
-
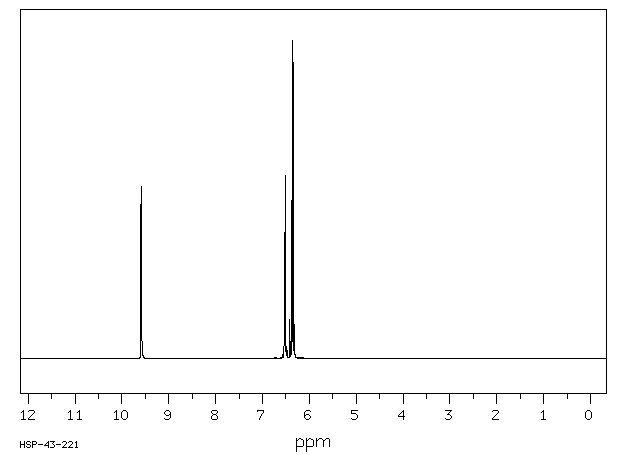
氢谱1HNMR
-
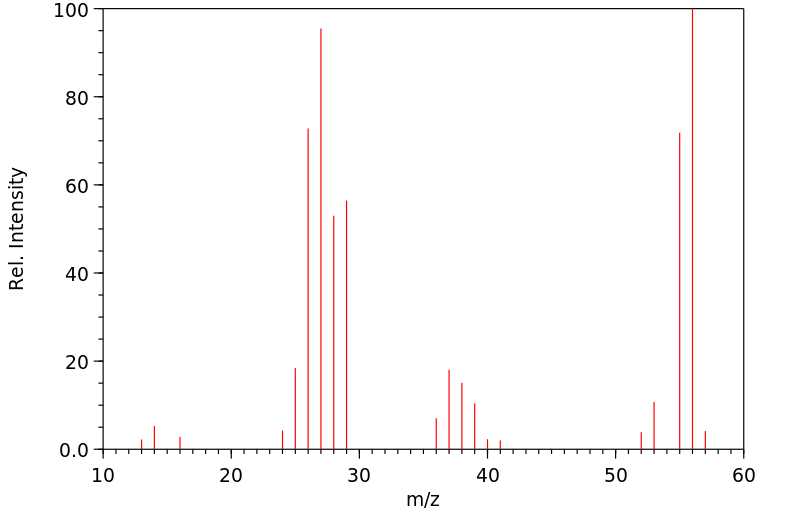
质谱MS
-
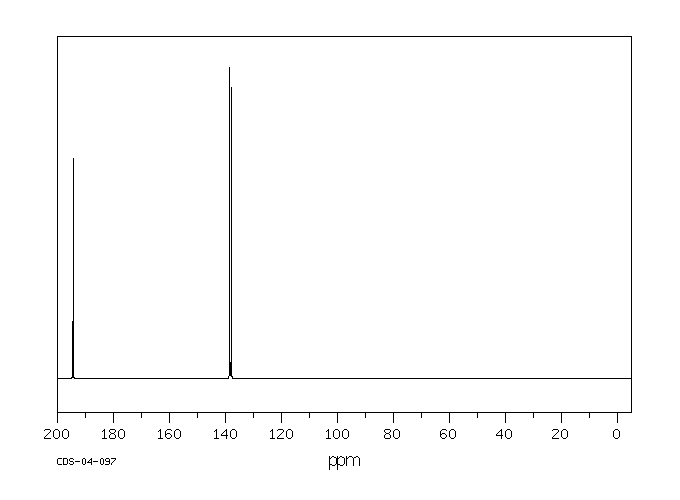
碳谱13CNMR
-
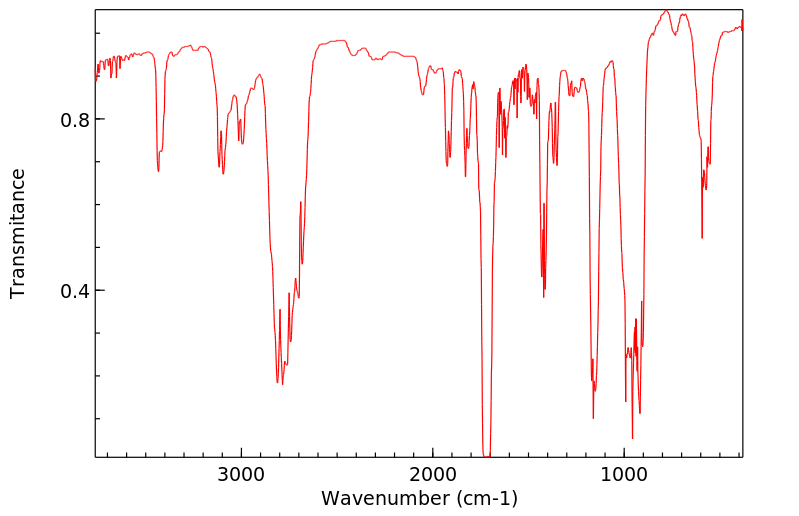
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息