麦草畏 | 1918-00-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:112-116 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:316.96°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.57
-
闪点:2 °C
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
最大波长(λmax):223nm(lit.)
-
LogP:2.210
-
物理描述:Dicamba is a white solid dissolved in a liquid carrier. The carrier is water emulsifiable. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since it is a liquid it can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams. It can cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption and/or ingestion. It is used as a herbicide.
-
颜色/状态:Crystals from pentane
-
气味:Odorless (reference grade)
-
蒸汽密度:7.62 (USCG, 1999) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1.25X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
如果按照规格正确使用和储存,则不会发生分解,也不存在已知的危险反应。请避免与氧化剂接触。
-
自燃温度:Not Applicable. Not flammable. (USCG, 1999)
-
分解:Decomposes below boiling point at 200 °C.
-
腐蚀性:Mild to noncorrosive
-
气味阈值:/SRP: Air/ 250.8 PPM
-
解离常数:pKa = 1.97
-
碰撞截面:157.21 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: stepped-field]
-
保留指数:1617;1657.6
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.2
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.125
-
拓扑面积:46.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S36,S61
-
危险类别码:R22,R52/53,R41
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2918990024
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3077 9/PG 3
-
RTECS号:DG7525000
-
储存条件:密封,在2°C至-8°C下保存
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 3,6-二氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸;麦草畏 |
| 化学品英文名称: | 3,6-Dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid;Dicamba |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 1918-00-9 |
| 分子式: | C 8 H 6 Cl 2 O 3 |
| 分子量: | 221.04 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:3,6-二氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸;麦草畏 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第8.1类 酸性腐蚀品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 摄入有毒。有报道可致突变。加热可释放出有毒的氯烟雾。 |
| 环境危害: | 对环境有危害,对水体可造成污染。 |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用流动清水冲洗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 饮足量温水,催吐。洗胃,导泄。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。其粉体与空气可形成爆炸性混合物, 当达到一定浓度时, 遇火星会发生爆炸。受高热分解产生有毒的腐蚀性烟气。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 雾状水、泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | 尽可能将容器从火场移至空旷处。 |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 150 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴防尘口罩,穿一般作业工作服。不要直接接触泄漏物。小量泄漏:避免扬尘,小心扫起,收集于干燥、洁净、有盖的容器中。大量泄漏:收集回收或运至废物处理场所处置。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,局部排风。防止粉尘释放到车间空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩,戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿透气型防毒服,戴防化学品手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与氧化剂接触。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。包装密封。应与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中粉尘浓度较高时,建议佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿透气型防毒服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作场所禁止吸烟、进食和饮水,饭前要洗手。工作完毕,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色晶体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 114~116 |
| 沸点(℃): | 无资料 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.57(25℃) |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 无资料 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 0.000499 |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | 无资料 |
| 临界温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 临界压力(MPa): | 无资料 |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | 无资料 |
| 闪点(℃): | 150 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 分子式: | C 8 H 6 Cl 2 O 3 |
| 分子量: | 221.04 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 难溶于水,溶于乙醇、异丙醇、丙酮、甲苯、二氯甲烷、二恶烷。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作农用除草剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | 属低毒类 LD50:1879~2740mg/kg(大鼠经口);>2000mg/kg(兔经皮) LC50:>200mg/m3(大鼠吸入) |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | 对蜜蜂无害。 |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 建议用焚烧法处置。在能利用的地方重复使用容器或在规定场所掩埋。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61890 |
| UN编号: | 2765 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | 塑料袋或二层牛皮纸袋外全开口或中开口钢桶;两层塑料袋或一层塑料袋外麻袋、塑料编织袋、乳胶布袋;塑料袋外复合塑料编织袋(聚丙烯三合一袋、聚乙烯三合一袋、聚丙烯二合一袋、聚乙烯二合一袋);塑料袋或二层牛皮纸袋外普通木箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶、复合塑料瓶或铝瓶外普通木箱;塑料瓶、两层塑料袋或两层牛皮纸袋(内或外套以塑料袋)外瓦楞纸箱。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 铁路运输时包装所用的麻袋、塑料编织袋、复合塑料编织袋的强度应符合国家标准要求。运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与酸类、氧化剂、食品及食品添加剂混运。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶,勿在居民区和人口稠密区停留。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定;常用危险化学品的分类及标志 (GB 13690-92)将该物质划为第6.1 类毒害品。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 5 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
毒性
原药对大鼠急性经口LD50为1879~2740mg/kg,家兔急性经皮LD50>2000mg/kg;大鼠急性吸入LC50>200mg/kg。对家兔眼睛有刺激和腐蚀作用,对家兔皮肤有中等刺激性。家兔亚急性经皮无作用剂量为500mg/kg,而大鼠2年饲喂试验的无作用剂量为每天25mg/kg,狗则为1.25mg/kg。在实验条件下未观察到致畸、致癌或致突变效应。虹鳟鱼的LC50值为28mg/L(96小时),青鳃翻车鱼的LC50值为23mg/L(96小时)。
化学性质
纯品为白色结晶,熔点114~116℃,闪点150℃,在200℃时分解,相对密度1.57 (25℃),蒸汽压0.5Pa (100℃)。在25℃时的溶解度如下:乙醇922g/L、异丙醇760g/L、丙酮810g/L、甲苯130g/L、二氯甲烷260g/L、二噁烷1180g/L和水6.5g/L。麦草畏与其他物质相混性良好,贮存稳定,具有抗氧化及抗水解能力。
用途
作为安息香酸系除草剂(苯甲酸类),麦草畏具有内吸传导作用,对一年生和多年生阔叶杂草有显著防效。用于小麦、玉米、谷子、水稻等禾本科作物防除猪殃殃、荞麦蔓、藜、牛繁缕、大巢菜、播娘莴、苍耳、薄朔草、田旋花、刺儿菜、问荆和鲤肠等杂草,一般使用48%水剂3~4.5mL/100m2(有效成分1.44~2g/100m2)。麦草畏杀草谱较窄,对某些抗性杂草效果不佳,并且对小麦的安全性较小,常与2,4-滴丁酯或2甲4氯胺盐混用。
用途
作为植物发芽后的除草剂,通常与其他苯氧羧酸类除草剂或其他除草剂混合加工成混剂,用于谷物地除草。
用途
对小麦、玉米等作物中的一年生和多年生阔叶杂草有显著效果。叶面或土壤除草剂,通过植株叶片和根部的传导,用于防除芦笋、玉米、高粱、小麦、甘蔗等作物田中的杂草,也可用于防除耕作区的木本灌木丛。通常单用或几个苯氧羧酸类除草剂混用,也可与其他类型的除草剂混用。
生产方法
以1,2,4-三氯苯、甲醇、二氧化碳和硫酸二甲酯为主要原料合成麦草畏。
生产方法
由1,2,4-三氯苯与甲醇/氢氧化钠反应制得2,5-二氯苯酚。然后在一定压力下与二氧化碳反应生成2-羟基-3,6-二氯苯甲酸,再通过硫酸二甲酯合成麦草畏。
类别
农药
毒性分级
中毒
急性毒性
口服-大鼠LD50: 1039 毫克/公斤; 口服-小鼠LD50: 1190 毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性
明火可燃;受热分解产生有毒氯化物气体
储运特性
库房需通风、低温干燥,与食品原料分开储存和运输
灭火剂
砂土、干粉、泡沫
职业标准
STEL 1 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 增糖酯 dicamba methyl ester 6597-78-0 C9H8Cl2O3 235.067 3,6-二氯水杨酸 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid 3401-80-7 C7H4Cl2O3 207.013 —— dicamba 4-methoxyphenol ester 1430102-93-4 C15H12Cl2O4 327.164 —— 2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde 27164-08-5 C8H6Cl2O2 205.04 —— dicamba 4-methoxyphenacylmethyl ester 1430102-82-1 C17H14Cl2O5 369.201 麦草畏2-羟基吡啶酯 dicamba 2-hydroxypyridine ester 1430102-86-5 C13H9Cl2NO3 298.125 —— dicamba 4-butoxyphenacylmethyl ester 1430102-83-2 C20H20Cl2O5 411.282 —— dicamba maleic hydrazide diester 1430102-87-6 C20H12Cl4N2O6 518.137 —— 5-bromo-3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid —— C7H3BrCl2O3 285.909 3,6-二氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸氯 3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoyl chloride 10411-85-5 C8H5Cl3O2 239.485 —— 3',6'-dichloro-2'-methoxyacetophenone 73239-05-1 C9H8Cl2O2 219.067 —— dicamba 2-nitrobenzyl ester 1430102-79-6 C16H13Cl2NO5 370.189 —— 1,4-dichloro-2-methoxy-3-methylbenzene —— C8H8Cl2O 191.057 5-溴-3-氯-2-羟基苯甲酸 5-bromo-3-chlorosalicylic acid 2200-85-3 C7H4BrClO3 251.464 —— 2-(3-oxopropyl)-6-dicambyl-2,3-dihydro-3-pyridazinone 1430102-98-9 C15H12Cl2N2O5 371.177 —— 2-(2-cyanoethyl)-6-dicambyl-3(2H)-pyridazinone 1430102-99-0 C15H11Cl2N3O4 368.176 —— 2-(3-oxobutyl)-6-dicambyl-2,3-dihydro-3-pyridazinone 1430102-97-8 C16H14Cl2N2O5 385.204 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 增糖酯 dicamba methyl ester 6597-78-0 C9H8Cl2O3 235.067 3,6-二氯水杨酸 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid 3401-80-7 C7H4Cl2O3 207.013 —— 3-Chlorobenzyl 3,6-Dichloro-2-methoxybenzoate 101191-06-4 C15H11Cl3O3 345.61 3,6-二氯-2-甲氧基苄醇 (3,6-dichloro-2-metoxyphenyl)methanol 4849-12-1 C8H8Cl2O2 207.056 —— 2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde 27164-08-5 C8H6Cl2O2 205.04 —— dicamba 4-methoxyphenacylmethyl ester 1430102-82-1 C17H14Cl2O5 369.201 —— dicamba 4-butoxyphenacylmethyl ester 1430102-83-2 C20H20Cl2O5 411.282 —— 3,6-Dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid,pentafluorobenzyl ester —— C15H7Cl2F5O3 401.1 —— dicamba 2-(2-nitrobenzoxy)ethanol ester 1430102-81-0 C17H15Cl2NO6 400.215 3,6-二氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸氯 3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoyl chloride 10411-85-5 C8H5Cl3O2 239.485 —— dicamba bromoxynil ester 1430102-91-2 C15H7Br2Cl2NO3 479.939 3,6-二氯-2-羟基苯甲醛 3,6-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde 27164-09-6 C7H4Cl2O2 191.014 —— 2-Hydroxy-3,6-dichlorbenzylalkohol 56025-06-0 C7H6Cl2O2 193.029 —— dicamba phthalhydrazide diester 1430102-88-7 C24H14Cl4N2O6 568.197 —— dicamba 6-nitroveratryl alcohol ester 1430102-78-5 C17H15Cl2NO7 416.215 —— 3,6-dichloro-N-(4-ethoxy-phenyl)-2-methoxy-benzamide —— C16H15Cl2NO3 340.206 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Degradation of benomyl, picloram, and dicamba in a conical apparatus by zero-valent iron powder摘要:Reduction of some pesticides (benomyl, picloram, and dicamba) was studied in an aerobic batch conical pilot system to investigate the disappearance of these pesticides on contact with iron powder (20 g/l, 325-mesh). Aqueous buffered solutions of the compounds were added to the system followed by zero-valent iron powder (ZVIP), and the decline in the pesticide concentrations was monitored over time. HPLC analyses show a complete disappearance of picloram (1.20 mg/l) after 20 min of reaction. Benomyl (1.00 mg/l) and dicamba (1.25 mg/l) disappear after 25 and 40 min, respectively. The t(50) values ranged From 3 to 5.5 min, and were about slightly less than the t(1/2) values reported when the log of the relative HPLC peak area was plotted versus time, where the relative peak area was calculated by dividing the measured peak area by the initial peak area. Pathways for the degradation of the studied pesticides by ZVIP are proposed. (C) 2001 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/s0045-6535(00)00184-3
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:制备3,6-二氯-2-羟基苯甲酸的新方法,这是合成除草剂麦草畏的倒数第二个中间体摘要:草甘膦[ N-(膦酰基甲基)甘氨酸]是一种广谱的芽后除草剂,是全球使用最广泛的农用化学品之一。在过去的30年中,抗草甘膦的杂草得到了发展,这对种植者和农作物科学家构成了巨大的挑战,导致农作物产量降低和成本增加。3,6-二氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸(麦草畏)是XtendiMax®的活性成分,XtendiMax®是拜耳作物科学公司开发的用于控制阔叶杂草(包括抗草甘膦的物种)的独立除草剂。3,6-二氯-2-羟基苯甲酸(3,6-DCSA)是麦草畏合成中的倒数第二个中间体。现有的麦草畏制造路线利用高温高压Kolbe-Schmitt羧化反应制备3,6-DCSA。这封信中描述的是一种新的非柯尔布-施密特流程,该流程准备3,DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.03.024
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:Rieske非血红素铁单加氧酶催化的O-去甲基化涉及饱和C–H键的困难氧化摘要:麦草畏单加氧酶(DMO)催化麦草畏(3,6-二氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸酯)的O-去甲基化反应,生成3,6-二氯水杨酸酯和甲醛。最近的晶体学研究表明,DMO催化了麦草畏甲基内部饱和CH键的富挑战性氧化,形成半缩醛中间体。通过我们开发两种新的独立技术,可以检验该假设。作为允许使用18 O 2跟随反应产物的新方法,亚硫酸氢盐用于将新形成的18 O-甲醛捕获在稳定的加合物羟基甲烷磺酸盐(HMS –)中,从而阻止了甲醛中18 O与甲醛的快速交换。16水中有O。第二种技术利用恶臭假单胞菌甲醛脱氢酶的独特特性,可将18 O-甲醛快速转化为稳定且易于检测的18 O-甲酸。使用这两种新技术进行的实验为DMO催化的麦草畏甲基氧化提供了令人信服的证据,从而验证了DMO [和香草酸单加氧酶(一种相关的Rieske非血红素铁单加氧酶)]的机理,该机理涉及到饱和C– H键。DOI:10.1021/cb400154a
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE AND 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO))MÉTHYL]-N-(TÉTRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE ET DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO)MÉTHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'HERBICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG公开号:WO2021013969A1公开(公告)日:2021-01-28The present invention related to compounds of Formula (I): or an agronomically acceptable salt thereof, wherein Q, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are as described herein. The invention further relates to compositions comprising said compounds, to methods of controlling weeds using said compositions, and to the use of compounds of Formula (I) as a herbicide.本发明涉及以下式(I)的化合物或其农业上可接受的盐,其中Q、R2、R3、R4、R5和R6如本文所述。该发明还涉及包含所述化合物的组合物,使用这些组合物控制杂草的方法,以及将式(I)的化合物用作除草剂的用途。
-
HERBICIDAL AND FUNGICIDAL 5-OXY-SUBSTITUTED 3-PHENYLISOXAZOLINE-5-CARBOXAMIDES AND 5-OXY-SUBSTITUTED 3-PHENYLISOXAZOLINE-5-THIOAMIDES申请人:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG公开号:US20150245616A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03Herbicidally and fungicidally active 5-oxy-substituted 3-phenylisoxazoline-5-carboxamides and 5-oxy-substituted 3-phenylisoxazoline-5-thioamides of the formula (I) are described. In this formula (I), X, X 2 to X 6 , R 1 to R 4 are radicals such as hydrogen, halogen and organic radicals such as substituted alkyl. A is a bond or a divalent unit. Y is a chalcogen.
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
表征谱图
-
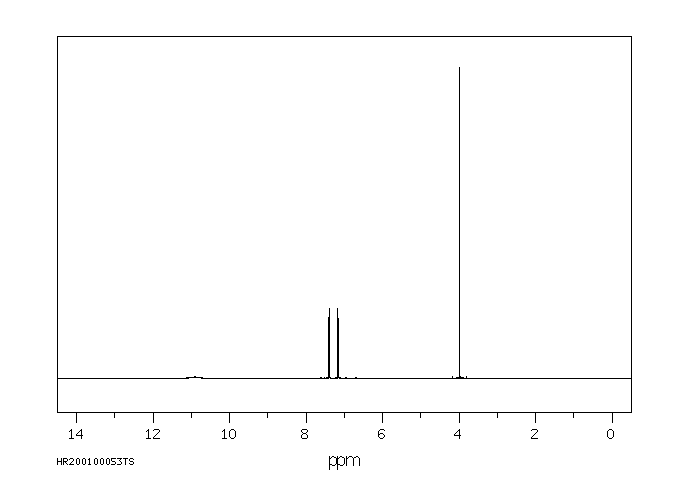
氢谱1HNMR
-
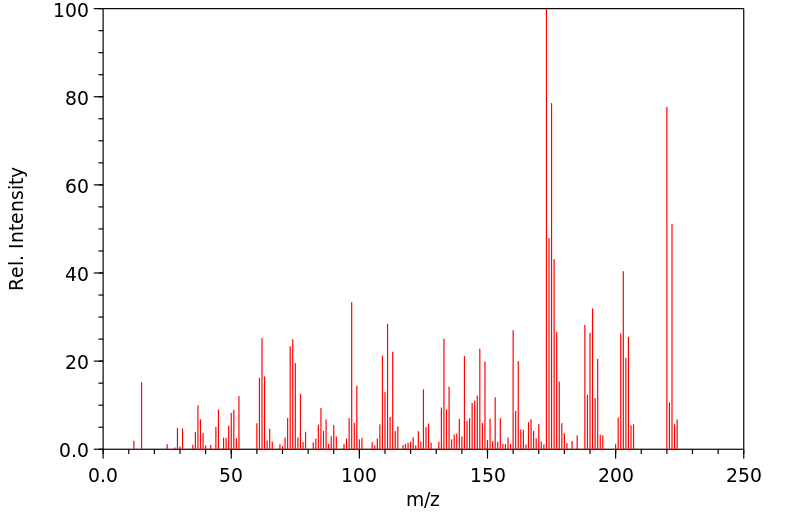
质谱MS
-
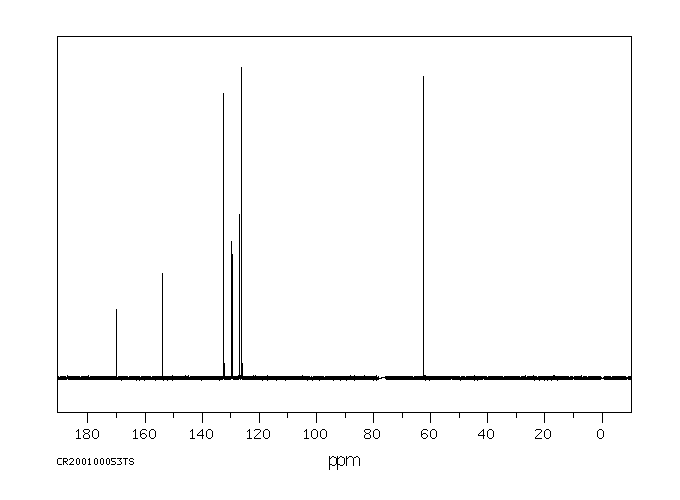
碳谱13CNMR
-
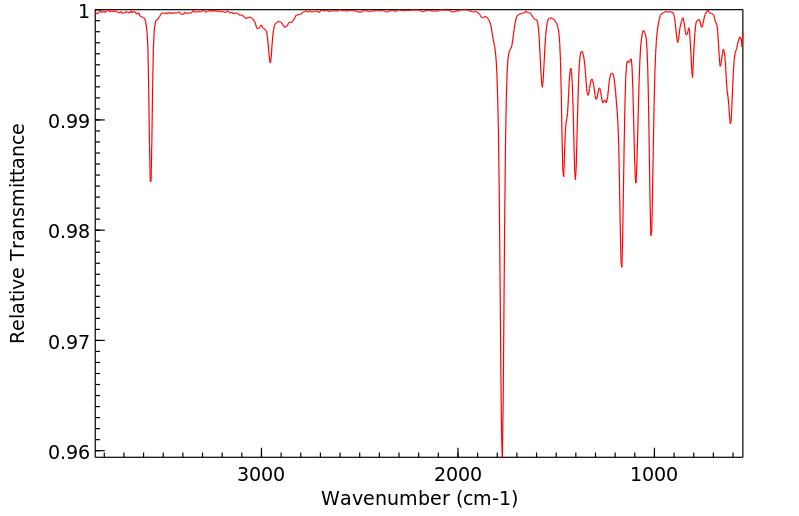
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息