呋喃妥因 | 67-20-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:268°C
-
沸点:380.75°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.5824 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:在DMF中的溶解度为50mg/mL
-
最大波长(λmax):358nm(MeOH)(lit.)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.5
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.12
-
拓扑面积:121
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:6
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S22,S36/37,S45
-
危险类别码:R22,R42/43
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2933990090
-
危险品运输编号:2811
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
RTECS号:MU2800000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS07,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H302,H317,H334
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P280,P342 + P311
SDS
制备方法与用途
呋喃妥因又名呋喃坦丁、呋喃坦啶、硝呋妥因或硝基呋喃妥因,化学名为1-[[(5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene]amino]-2,4-imidazolidinedione。这是一种合成抗菌药,其抗菌谱较广,对大多数革兰氏阳性菌及阴性菌均有抗菌作用,如金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、白色葡萄球菌和化脓性链球菌等。临床常用于治疗由敏感细菌引起的泌尿系统感染,例如急性单纯性下尿路感染(包括肾盂肾炎、膀胱炎)以及前列腺炎。
适应症该药物主要用于对其敏感的大肠埃希菌、肠球菌属、葡萄球菌属及克雷伯菌属、肠杆菌属等细菌引起的急性单纯性下尿路感染;也可用于预防尿路感染。
药理作用呋喃妥因抗菌谱广,其作用机制是通过干扰细菌的氧化还原酶活性来阻断其正常代谢。对葡萄球菌、肠球菌、大肠埃希杆菌、奈瑟球菌(如淋球菌)、枯草杆菌、志贺菌及沙门菌等有良好的抗菌效果;对变形杆菌、克雷伯杆菌、肠杆菌属和沙雷杆菌的作用较弱,对铜绿假单胞菌无效。通常微生物对抗生素不易产生耐药性,但近年来耐药菌株有所增多,必要时可与其他药物(如TMP)联合使用以提高疗效。
药物相互作用- 与可能导致溶血的药物合用,可能会增加溶血反应。
- 丙磺舒或苯磺唑酮均可抑制呋喃妥因的肾小管分泌,导致其血药浓度增高、半衰期延长,而尿中排出量则减少,从而影响疗效。
- 与制酸剂合用会降低本品的吸收。
- 不可与萘啶酸或诺氟沙星合用,因为两者之间存在拮抗作用。
将盐酸和纯化水加入反渗透膜反应装置内,升温至60℃~70℃,随后加入5-硝基糠醛二乙酯并维持80℃~85℃的温度直到完全水解。接着加入催化剂和适量氯化钠固体,再加入预热至60℃~70℃的氨基乙内酰脲,并加压。在90℃~95℃下回流保温40分钟~60分钟后将反应产物用纯化水洗涤至pH为6.0~8.0,甩出干料并将所得呋喃妥因用90℃~95℃流动的纯化水洗一定时间后得到成品。
化学性质橙黄色针状结晶。熔点270-272℃(分解)。在100ml下列溶剂中可溶解的毫克数:水19.0,95%乙醇51.0,丙酮510,DMF8000。几乎不溶于氯仿。无臭,味苦。
用途该品是一种优良的抗菌药物,口服吸收迅速而完全,尿中排出量可达40-50%,常用于治疗各种敏感细菌引起的尿路感染,尤其是由大肠杆菌引起急性尿路感染时疗效较好。
生产方法呋喃妥因可通过以下步骤制备:水合肼与尿素缩合生成氨基脲,再与丙酮缩合得到丙酮缩氨基脲。然后与氯乙酸乙酯环合成丙酮缩乙内酰脲,并经水解后与5-硝基糠醛二乙酸酯缩合而得。
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1-[(2-furanylmethylene)amino]-2,4-imidazolidinedione 777-34-4 C8H7N3O3 193.162
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Radioiodination and bioevaluation of nitrofurantoin for urinary tract imaging摘要:呋喃妥因 (NF) 通过亲电取代反应用碘 125 进行标记。研究了影响 125I-NF 放射化学产率的一些因素,如 NF 浓度、氯胺-T (CAT) 浓度、反应混合物的 pH、反应时间、温度和反应介质。通过在 DMF 中使用 3.7MBq Na125I、1mM CAT、1mM NF,在 pH 2 和 60°C 下 5 分钟内获得 125I-NF 的最大产率 (90%)。 125I-NF比活度达到33.3MBq/0.2mmol,通过高压液相色谱将125I-NF完全分离纯化。正常小鼠中的生物分布表明放射性碘化 NF 适合尿路成像。版权所有 © 2012 约翰·威利父子有限公司DOI:10.1002/jlcr.2942
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种呋喃妥因的合成方法摘要:本发明提供了一种呋喃妥因的合成方法,以盐酸氨基海因为底物,并与5‑硝基呋喃醛二乙酯反应后得1‑[[(5‑硝基‑2‑呋喃基)亚甲基]氨基]‑2,4‑咪唑烷二酮粗品;然后将1‑[[(5‑硝基‑2‑呋喃基)亚甲基]氨基]‑2,4‑咪唑烷二酮粗品与N,N‑二甲基甲酰胺按照比例混合后,室温下搅拌40~60分钟,压滤处理后得滤液,滤液至于结晶锅内搅拌30分钟并滴加纯化水,然后甩滤得滤饼,对滤饼进行提纯后,即得呋喃妥因。该呋喃妥因的合成方法,不需要使用酸酐,因此克服了现有技术中产生大量氮氧化物气体的缺陷,并降低了合成难度;同时,该合成方法也显著的降低了最终制得的呋喃妥因中的杂质含量,从而使得该合成方法能够适用于工业化量产。公开号:CN108440511A
文献信息
-
Eflornithine Prodrugs, Conjugates and Salts, and Methods of Use Thereof申请人:Xu Feng公开号:US20100120727A1公开(公告)日:2010-05-13In one aspect, the present invention provides a composition of a covalent conjugate of an eflornithine analog with an anti-inflammatory drug. In another aspect, the present invention provides a composition of an eflornithine prodrug. In another aspect, the present invention provides a composition of an eflornithine or its derivatives aspirin salt. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods for treating or preventing cancer using the conjugates or salts of eflornithine analogs or eflornithine prodrugs.
-
[EN] METALLOENZYME INHIBITOR COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS INHIBITEURS DE MÉTALLOENZYMES
-
[EN] DERIVATIVES OF AMANITA TOXINS AND THEIR CONJUGATION TO A CELL BINDING MOLECULE<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TOXINES D'AMANITES ET LEUR CONJUGAISON À UNE MOLÉCULE DE LIAISON CELLULAIRE申请人:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH CO LTD公开号:WO2017046658A1公开(公告)日:2017-03-23Derivatives of Amernita toxins of Formula (I), wherein, formula (a) R 1, R 2, R 3, R 4, R 5, R 6, R 7, R 8, R 9, R 10, X, L, m, n and Q are defined herein. The preparation of the derivatives. The therapeutic use of the derivatives in the targeted treatment of cancers, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases.
-
[EN] A CONJUGATE OF A CYTOTOXIC AGENT TO A CELL BINDING MOLECULE WITH BRANCHED LINKERS<br/>[FR] CONJUGUÉ D'UN AGENT CYTOTOXIQUE À UNE MOLÉCULE DE LIAISON CELLULAIRE AVEC DES LIEURS RAMIFIÉS申请人:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH CO LTD公开号:WO2020257998A1公开(公告)日:2020-12-30Provided is a conjugation of cytotoxic drug to a cell-binding molecule with a side-chain linker. It provides side-chain linkage methods of making a conjugate of a cytotoxic molecule to a cell-binding ligand, as well as methods of using the conjugate in targeted treatment of cancer, infection and immunological disorders.提供了一种将细胞毒性药物与一个侧链连接分子结合的共轭物。它提供了制备细胞毒性分子与细胞结合配体的共轭物的侧链连接方法,以及在靶向治疗癌症、感染和免疫性疾病中使用该共轭物的方法。
-
[EN] CROSS-LINKED PYRROLOBENZODIAZEPINE DIMER (PBD) DERIVATIVE AND ITS CONJUGATES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉ DE DIMÈRE DE PYRROLOBENZODIAZÉPINE RÉTICULÉ (PBD) ET SES CONJUGUÉS申请人:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH CO LTD公开号:WO2020006722A1公开(公告)日:2020-01-09A novel cross-linked cytotoxic agents, pyrrolobenzo-diazepine dimer (PBD) derivatives, and their conjugates to a cell-binding molecule, a method for preparation of the conjugates and the therapeutic use of the conjugates.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
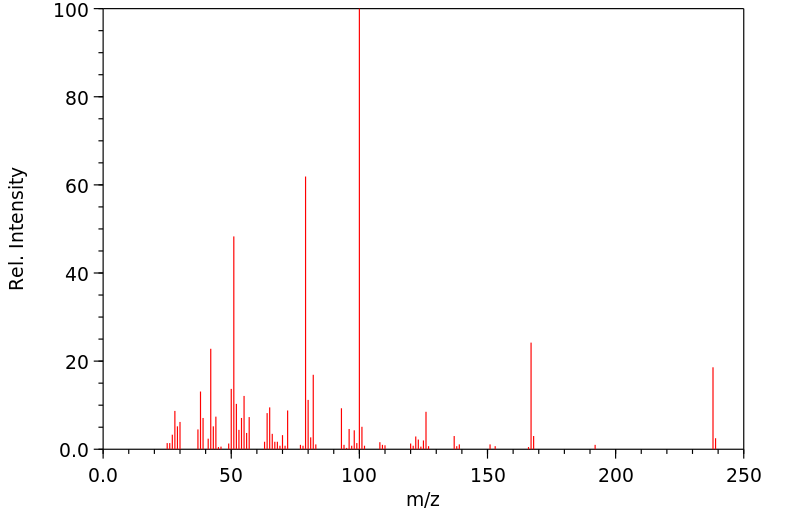
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
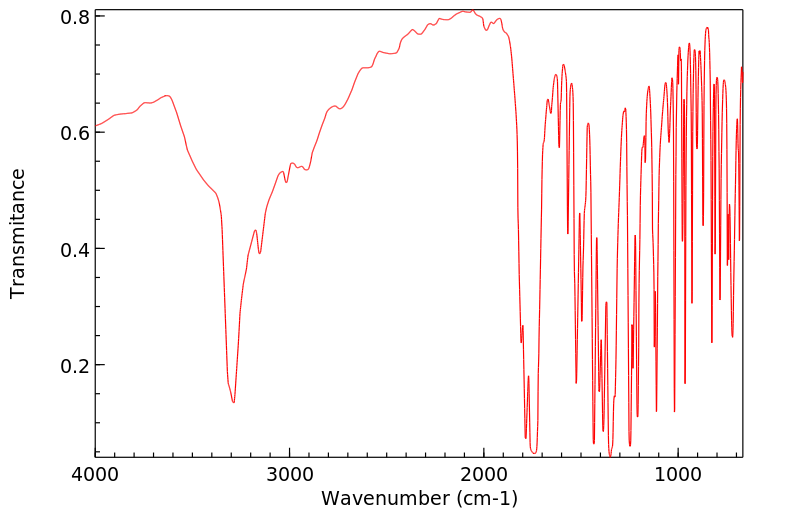
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息