毒理性
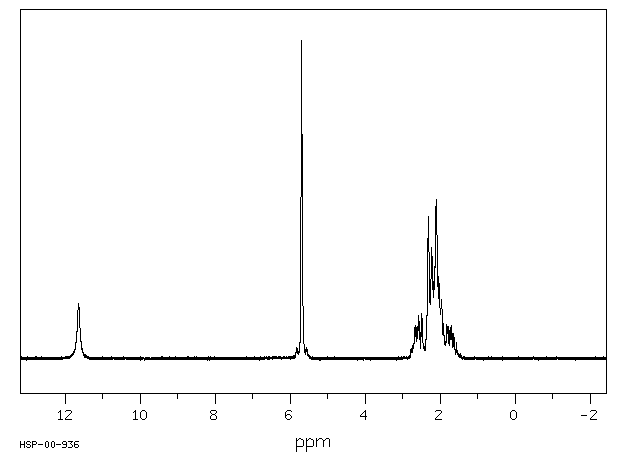
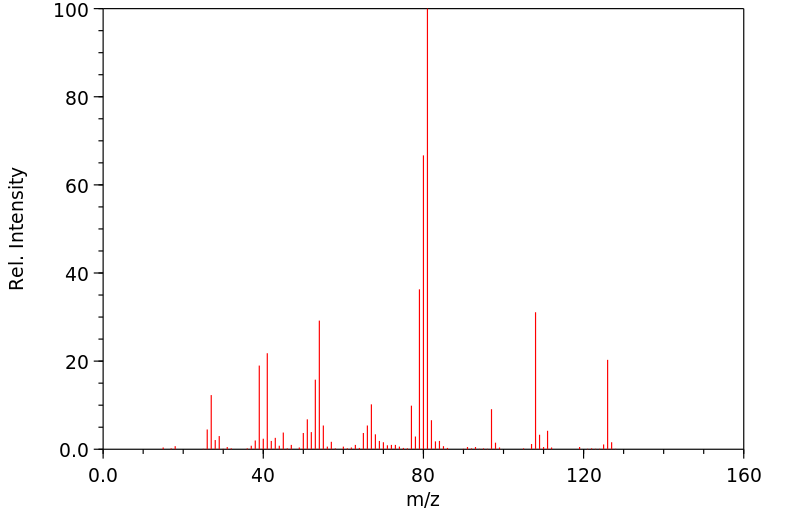
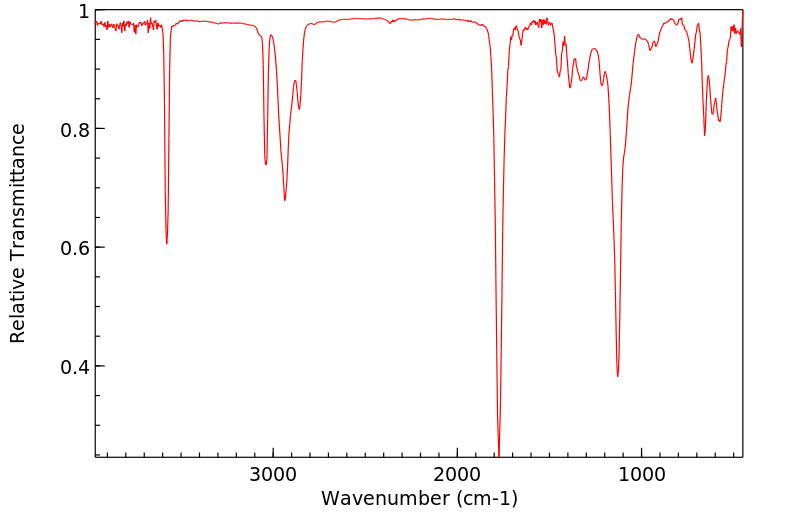
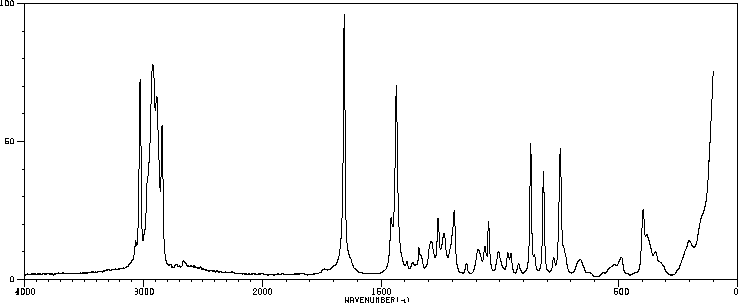
鉴別和使用:环烷酸是粘稠的液体,颜色从淡黄色到深琥珀色不等。环烷酸是从石油馏分中回收的自然存在的环脂肪族羧酸的混合物。商业环烷酸以不同纯度等级销售。产生的环烷酸中有超过三分之二用于制造金属盐,其中最大量的用于铜萘酸盐,在木材防腐剂工业中消耗。一个不断增长的市场是在木材和纺织品防腐剂中。环烷酸的另一个市场应用是在轮胎工业中。在润滑油脂和脂的极高压力添加剂、腐蚀抑制剂、乳化剂和消泡剂、化学中间体中的有限用途。人类暴露和毒性:环烷酸诱导暴露的H295R细胞产生雌二醇和孕酮,并降低睾酮的产生。暴露于环烷酸导致肾上腺皮质激素受体上调,CYP1A1上调。结果表明,这些碳氢污染物具有干扰甾体生成这一极其重要过程的潜力。人类的致死口服剂量大约为1升。动物研究:在给予环烷酸(分别为10毫克/千克,静脉注射,5-15毫克/千克,肌肉注射)的狗和兔子中,对红白细胞和血小板的生成有显著影响,对血小板形成的影响更大。在急性测试中,成年雌性大鼠单次口服给予环烷酸的剂量为3、30或300毫克/千克体重,而成年雄性大鼠给予300毫克/千克。在高剂量组中,两性的食物消耗暂时受到抑制。组织病理学检查发现,高剂量组两性的胆周炎发病率显著,提示急性肝毒性效应。其他组织学病变包括高剂量雄性大鼠的大脑出血,以及雌性大鼠的心脏周围动脉坏死和纤维化。在亚慢性测试中,将环烷酸以0.6、6或60毫克/千克的剂量口服给予大鼠,每周5天,持续90天。结果再次提示肝脏是一个潜在的目标器官。高剂量组的相对肝脏重量比对照组高出35%。生物化学分析显示,高剂量大鼠的血淀粉酶(比对照组高30%)和低胆固醇血症(比对照组低43%)。在高剂量组中,有42%的动物观察到过量的肝糖原积累。这些结果表明,在最坏暴露条件下,野生动物暴露于环烷酸不太可能产生急性毒性,但反复暴露可能对健康产生不利影响。通过 Ames 致突变性试验,环烷酸不具有致突变性。生态毒性研究:环烷酸对哺乳动物的毒性很小,但对鱼类、细菌和破坏木材的昆虫有毒。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Naphthenic acids are viscous liquids with colors range from pale yellows to dark amber. Naphthenic acids are mixtures of naturally occurring cycloaliphatic carboxylic acids recovered from petroleum distillates. Commercial naphthenic acids are sold in various grades of purity. More than two-thirds of the naphthenic acid produced is used to make metal salts, with the largest volume being used for copper naphthenate, consumed in the wood preservative industry. An expanding market is in wood and textile preservatives. Another market application naphthenic acid is in the tire industry. Limited use in extreme pressure additives for lubricating oils and greases, corrosion inhibitors, emulsifiers and defoamers, chemical intermediates. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Naphthenic acids induced the production of both estradiol and progesterone in exposed H295R cells, and decreased the production of testosterone. Exposure to naphthenic acids caused an up-regulation of adrenocorticotropic hormone receptor, and up-regulation of CYP1A1. The results indicated that these hydrocarbon pollutants have the potential to disrupt the vitally important process of steroidogenesis. The lethal oral dose for humans is approximately 1 L. ANIMAL STUDIES: In dogs and rabbits that received naphthenic acids (10 mg/kg, intravenously, and 5-15 mg/kg, intramuscularly, respectively), a notable effect was observed on hemopoiesis of both the red and white cells and a greater effect was observed on platelet formation. In acute tests, adult female rats were given single po dosages of naphthenic acids at either 3, 30, or 300 mg per kg body weight (mg/kg), while adult male rats received 300 mg/kg. Food consumption was temporarily suppressed in the high-dose groups of both sexes. Histopathology revealed a significant incidence of pericholangitis in the high-dose group of both sexes, suggesting hepatotoxicity as an acute effect. Other histological lesions included brain hemorrhage in high-dose males, and cardiac periarteriolar necrosis and fibrosis in female rats. In subchronic tests, naphthenic acids were po administered to rats at 0.6, 6, or 60 mg/kg, 5 days per week for 90 days. Results again suggested the liver as a potential target organ. The relative liver weight in the high-dose group was 35% higher than in controls. Biochemical analysis revealed elevated blood amylase (30% above controls) and hypocholesterolemia (43% below controls) in high-dose rats. Excessive hepatic glycogen accumulation was observed in 42% of animals in this group. These results indicate that, under worst-case exposure conditions, acute toxicity is unlikely in wild mammals exposed to naphthenic acids, but repeated exposure may have adverse health effects. Naphthenic acid is nonmutagenic by the Ames mutagenicity test. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: Naphthenic acids are only slightly toxic to mammals but are toxic to fish, bacteria, and wood-destroying insects.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)