Boc-D-天冬酰胺 | 75647-01-7
中文名称
Boc-D-天冬酰胺
中文别名
BOC-D-天冬酰胺;叔丁氧羰基-D-天冬酰胺;N-叔丁氧羰基-D-天冬酰胺;Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺;Boc-D-Asn-OH;N-BOC-D-天冬酰胺
英文名称
N-t-butyloxycarbonyl-D-asparagine
英文别名
N-Boc-D-asparagine;Boc-D-asparagine;Boc-D-Asn;(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-D-asparagine;(2R)-4-amino-2-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)-4-oxo-butanoic acid;(2R)-4-amino-2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]-4-oxobutanoic acid
CAS
75647-01-7
化学式
C9H16N2O5
mdl
——
分子量
232.236
InChiKey
FYYSQDHBALBGHX-RXMQYKEDSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:165-169 °C
-
比旋光度:9 º (c=1, DMF)
-
沸点:374.39°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.2896 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:溶于二甲基甲酰胺
-
稳定性/保质期:
在指定条件下稳定,远离氧化物。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.6
-
重原子数:16
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.67
-
拓扑面积:119
-
氢给体数:3
-
氢受体数:5
安全信息
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S24/25
-
危险类别码:R25
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2924199090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:存放在密封容器内,并置于阴凉、干燥处。
SDS
Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺
修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
Nα-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-D-asparagine
产品名称:
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺
百分比: >98.0%(LC)(T)
CAS编码: 75647-01-7
俗名: Nα-Boc-D-asparagine , Boc-D-Asn-OH
分子式: C9H16N2O5
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 二甲基甲酰胺
Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
Nα-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-D-asparagine
产品名称:
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺
百分比: >98.0%(LC)(T)
CAS编码: 75647-01-7
俗名: Nα-Boc-D-asparagine , Boc-D-Asn-OH
分子式: C9H16N2O5
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 二甲基甲酰胺
Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
Nα-(叔丁氧羰基)-D-天冬酰胺 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-叔丁氧羰基-D-天冬氨酸对硝基苯酯 N-butyloxycarbonyl-D-asparagine p-nitrophenyl ester 104199-82-8 C15H19N3O7 353.332 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— benzyl (2R)-4-amino-2-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)-4-oxo-butanoate 130539-03-6 C16H22N2O5 322.361 —— tert-butyl (S)-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-3-yl)carbamate 124842-29-1 C9H14N2O4 214.221 —— tert-butyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-3-yl)carbamate 1822518-66-0 C9H14N2O4 214.221 —— (R)-3-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione —— C9H14N2O4 214.221 —— O-benzyl N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-D-asparaginate 1428095-72-0 C16H20N2O6 336.345 —— BOC-D-asparagine diphenylmethyl ester 88147-56-2 C22H26N2O5 398.459 N2,N3-二叔丁氧羰基-D-2,3-二氨基丙酸二环己胺盐 (R)-2,3-bis-tert-butoxycarbonylaminopropionic acid 159652-30-9 C13H24N2O6 304.343 丁氧羰基-D-二氨基二酸羟基 (R)-2-tert-butoxycarbonyl-3-aminopropionic acid 76387-70-7 C8H16N2O4 204.226 —— 3-amino-2-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)propanoic acid 159002-17-2 C8H16N2O4 204.226 N-叔丁氧羰基-D-天冬氨酸对硝基苯酯 N-butyloxycarbonyl-D-asparagine p-nitrophenyl ester 104199-82-8 C15H19N3O7 353.332
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:[EN] CONJUGATES AND METHODS OF USING THE SAME
[FR] CONJUGUÉS ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION摘要:公开号:WO2020037009A8 -
作为产物:描述:N-叔丁氧羰基-D-天冬氨酸对硝基苯酯 在 Ac-IHIHIQI-NH2 、 zinc(II) chloride 作用下, 以 aq. buffer 为溶剂, 反应 24.0h, 生成 Boc-D-天冬酰胺参考文献:名称:主动组装淀粉样蛋白催化剂的底物特异性摘要:在 Zn2+ 存在下,发现催化性淀粉样蛋白形成肽 Ac-IHIHIQI-NH2 在自组装过程中对疏水性对硝基苯酯底物表现出增强的选择性。与底物对硝基苯乙酸盐相反,后者在完全原纤维状态下被 Ac-IHIHIQI-NH2 更有效地水解,疏水底物 Z-L-Phe-ONp 以大于 11-的二级速率常数转化当催化剂积极组装时,它会增加数倍。在这种条件下,Z-L-Phe-ONp 的水解速度比亲水性更强且更不稳定的 Boc-L-Asn-ONp 酯的水解速度更快。组装时,催化剂对 Z-Phe-ONp 的 L-对映体也表现出更高的选择性。DOI:10.1002/bip.23003
文献信息
-
Piperidine derivative and use thereof申请人:Ikeura Yoshinori公开号:US20060142337A1公开(公告)日:2006-06-29The present invention provides a compound represented by the formula: wherein Ar is an aryl group optionally having substituents, R is a C 1-6 alkyl group, R 1 is a hydrogen atom, a hydrocarbon group optionally having substituents, an acyl group or a heterocyclic group optionally having substituents, X is an oxygen atom or an imino group optionally having substituents, ring A is a piperidine ring optionally further having substituents, and ring B is a benzene ring having substituents, or a salt thereof, and an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of lower urinary tract abnormality and the like, which contains the compound.
-
Amino Acid Conjugates of Lithocholic Acid As Antagonists of the EphA2 Receptor作者:Matteo Incerti、Massimiliano Tognolini、Simonetta Russo、Daniele Pala、Carmine Giorgio、Iftiin Hassan-Mohamed、Roberta Noberini、Elena B. Pasquale、Paola Vicini、Silvia Piersanti、Silvia Rivara、Elisabetta Barocelli、Marco Mor、Alessio LodolaDOI:10.1021/jm301890k日期:2013.4.11Structure–activity relationships indicate that the presence of a lipophilic amino acid side chain is fundamental to achieve good potencies. The l-Trp derivative (20, PCM126) was the most potent antagonist of the series disrupting EphA2–ephrinA1 interaction and blocking EphA2 phosphorylation in prostate cancer cells at low μM concentrations, thus being significantly more potent than LCA. Compound 20 is amongEph 受体-ephrin 系统是开发新型抗血管生成药物的新兴目标。我们最近发现石胆酸 (LCA) 是一种能够阻断癌细胞中依赖 EphA2 信号的小分子,这表明其 (5β)-cholan-24-oic 酸支架可用作模板来设计新一代改进的EphA2 拮抗剂。在这里,我们报告了通过将其羧基与不同的 α-氨基酸共轭而获得的一组扩展 LCA 衍生物的设计和合成。构效关系表明亲脂性氨基酸侧链的存在是实现良好效力的基础。的升-Trp衍生物(20, PCM126) 是该系列中最有效的拮抗剂,可在低 μM 浓度下破坏 EphA2-ephrinA1 相互作用并阻断前列腺癌细胞中的 EphA2 磷酸化,因此比 LCA 更有效。化合物20是 EphA2 受体最有效的小分子拮抗剂之一。
-
[EN] ASPARAGINE DERIVATIVES AND METHODS OF USING SAME<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'ASPARAGINE ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION申请人:SENDA BIOSCIENCES INC公开号:WO2021252640A1公开(公告)日:2021-12-16The present disclosure relates to compounds of formulas (A) and (I), pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and solvates of any of the foregoing, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, methods of preparing the same, intermediate compounds useful for preparing the same, and methods for treating or prophylaxis of diseases, in particular cancer, such as colorectal cancer, using the same.本公开涉及式(A)和(I)的化合物,其药学上可接受的盐,以及任何上述化合物的溶剂化合物,包括相同的药物组合物,制备相同的方法,用于制备相同的中间化合物,以及使用相同的方法治疗或预防疾病,特别是癌症,如结直肠癌。
-
Kinase inhibitor compounds申请人:Liang Congxin公开号:US20090076005A1公开(公告)日:2009-03-19The invention relates to compounds, compositions comprising the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compound compositions. The compounds, compositions, and methods described herein can be used for the therapeutic modulation of kinase-mediated processes, and treatment of disease and disease symptoms, particularly those mediated by certain kinase enzymes.这项发明涉及化合物、包含这些化合物的组合物,以及使用这些化合物和化合物组合物的方法。本文描述的化合物、组合物和方法可用于治疗激酶介导的过程,并治疗疾病和疾病症状,特别是那些由特定激酶酶介导的症状。
-
Amino Acid Derivatives as Palmitoylethanolamide Prodrugs: Synthesis, In Vitro Metabolism and In Vivo Plasma Profile in Rats作者:Federica Vacondio、Michele Bassi、Claudia Silva、Riccardo Castelli、Caterina Carmi、Laura Scalvini、Alessio Lodola、Valentina Vivo、Lisa Flammini、Elisabetta Barocelli、Marco Mor、Silvia RivaraDOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0128699日期:——Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) has antinflammatory and antinociceptive properties widely exploited in veterinary and human medicine, despite its poor pharmacokinetics. Looking for prodrugs that could progressively release PEA to maintain effective plasma concentrations, we prepared carbonates, esters and carbamates at the hydroxyl group of PEA. Chemical stability (pH 7.4) and stability in rat plasma and liver homogenate were evaluated by in vitro assays. Carbonates and carbamates resulted too labile and too resistant in plasma, respectively. Ester derivatives, prepared by conjugating PEA with various amino acids, allowed to modulate the kinetics of PEA release in plasma and stability in liver homogenate. L-Val-PEA, with suitable PEA release in plasma, and D-Val-PEA, with high resistance to hepatic degradation, were orally administered to rats and plasma levels of prodrugs and PEA were measured at different time points. Both prodrugs showed significant release of PEA, but provided lower plasma concentrations than those obtained with equimolar doses of PEA. Amino-acid esters of PEA are a promising class to develop prodrugs, even if they need further chemical optimization.棕榈酰乙醇胺(PEA)具有抗炎和镇痛特性,在兽医和人类医学中得到广泛应用,尽管其药代动力学特性不佳。为了寻找能够逐步释放PEA以维持有效血浆浓度的前药,我们制备了在PEA的羟基上的碳酸盐、酯和氨基甲酸酯。通过体外试验评估了这些化合物的化学稳定性(pH 7.4)以及在鼠血浆和肝匀浆中的稳定性。碳酸盐和氨基甲酸酯在血浆中分别表现出过于不稳定和过于稳定。通过将PEA与各种氨基酸结合制备的酯衍生物,能够在血浆中调节PEA的释放动力学并在肝匀浆中稳定存在。L-Val-PEA在血浆中具有适当的PEA释放,而D-Val-PEA对肝脏降解具有较高的抵抗性,两者均通过口服给予大鼠,并在不同时间点测量了血浆中前药和PEA的水平。两种前药均显示了显著的PEA释放,但提供的血浆浓度低于等摩尔剂量的PEA。PEA的氨基酸酯类是一类有前景的前药开发类别,尽管它们需要进一步的化学优化。
表征谱图
-
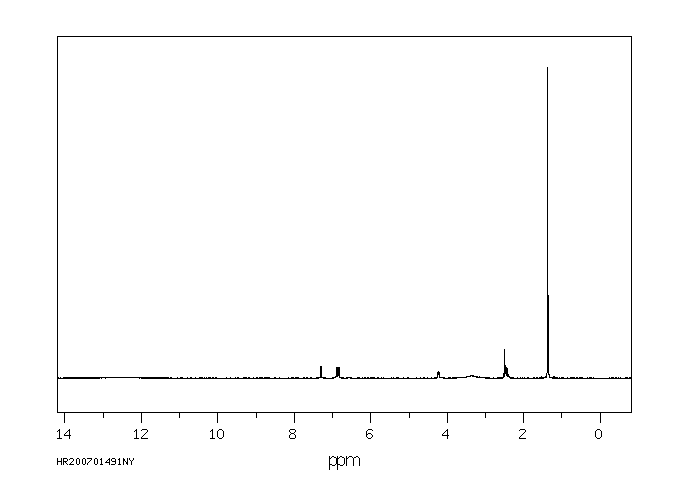
氢谱1HNMR
-
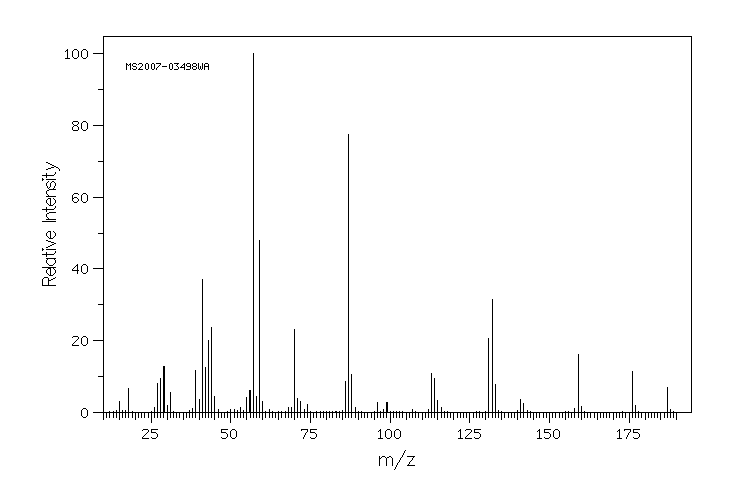
质谱MS
-
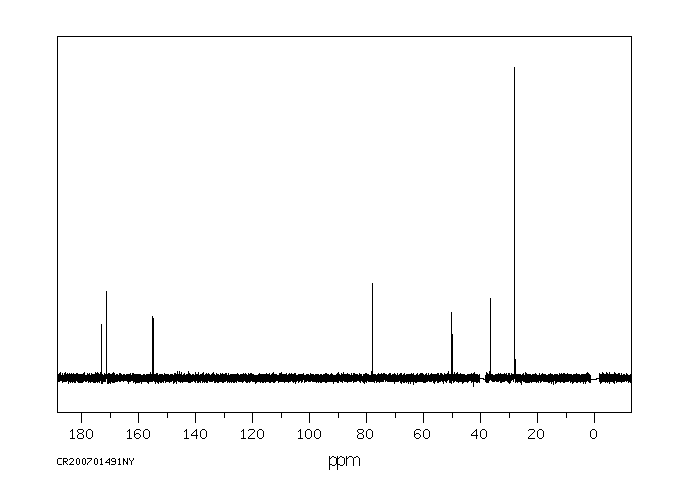
碳谱13CNMR
-
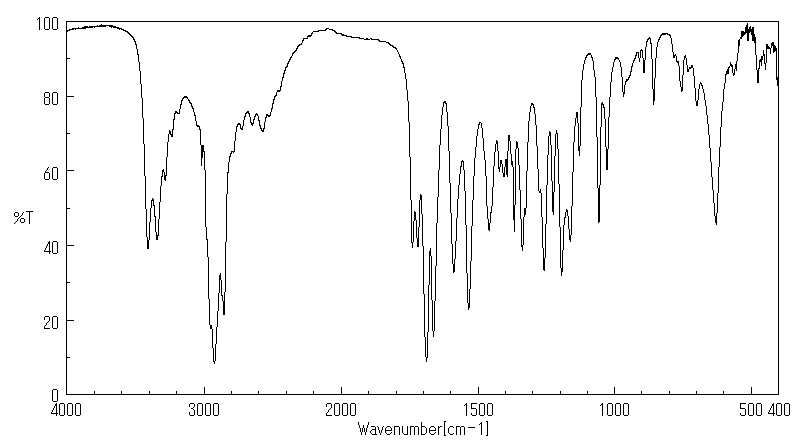
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸