1-苯基丙-1-胺 | 2941-20-0
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:116°C (estimate)
-
沸点:204 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.938 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:170 °F
-
保留指数:1128
-
稳定性/保质期:
常温常压下稳定。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.7
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.333
-
拓扑面积:26
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
危险等级:IRRITANT
-
危险品标志:C
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R22,R34
-
WGK Germany:3
-
RTECS号:DP4907000
-
海关编码:2921499090
-
包装等级:II
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2735 8/PG 2
SDS
: α-EthylbenzylAMine
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
易燃液体 (类别4)
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
皮肤腐蚀 (类别1B)
严重的眼损伤 (类别1)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
危害类型象形图
信号词 危险
危险申明
H227 可燃液体
H302 吞咽有害。
H314 造成严重皮肤灼伤和眼损伤。
警告申明
预防
P210 远离热源/火花/明火/热表面。- 禁止吸烟。
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P280 戴防护手套/ 穿防护服/ 戴防护眼罩/ 戴防护面具。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P301 + P330 + P331 如误吞咽:漱口。不要诱导呕吐。
P303 + P361 + P353 如皮肤(或头发)沾染:立即去除/ 脱掉所有沾染的衣服。用水清洗皮肤/
淋浴。
P304 + P340 如果吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如进入眼睛:用水小心清洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取出,取出
隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
P310 立即呼救解毒中心或医生。
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P363 沾染的衣服清洗后方可重新使用。
P370 + P378 火灾时: 用干的砂子,干的化学品或耐醇性的泡沫来灭火。
储存
P403 + P235 存放在通风良好的地方。保持低温。
P405 存放处须加锁。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C9H13N
分子式
: 135.21 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
α-EthylbenzylAMine
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 2941-20-0
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
在皮肤接触的情况下
立即脱掉污染的衣服和鞋子。 用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
如果误服
禁止催吐。 切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
该物质对粘膜组织和上呼吸道、眼睛和皮肤破坏巨大。, 痉挛,发炎,咽喉肿痛, 痉挛,发炎,支气管炎, 肺炎,
肺水肿, 灼伤感:, 咳嗽, 喘息, 喉炎, 呼吸短促, 头痛, 恶心
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
小(起始)火时,使用媒介物如“乙醇”泡沫、干化学品或二氧化碳。大火时,尽可能使用水灭火。使用大量(
洪水般的)水以喷雾状应用;水柱可能是无效的。用大量水降温所有受影响的容器。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
水喷雾可用来冷却未打开的容器。
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 移去所有火源。
将人员撤离到安全区域。 防范蒸汽积累达到可爆炸的浓度,蒸汽能在低洼处积聚。
6.2 环境预防措施
在确保安全的条件下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
用防电真空清洁器或湿的刷子将溢出物收集起来并放置到容器中去,根据当地规定处理(见第13部分)。
存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止吸入蒸汽和烟雾。
切勿靠近火源。-严禁烟火。采取防静电生成的措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
打开了的容器必须仔细重新封口并保持竖放位置以防止泄漏。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据工业卫生和安全使用规则来操作。 休息以前和工作结束时洗手。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
紧密装配的防护眼镜请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 液体
颜色: 无色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
204 °C - lit.
g) 闪点
77 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
0.938 g/cm3 在 25 °C
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
辛醇--水的分配系数的对数值: 2.079
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
热,火焰和火花。
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂强氧化剂, 强酸
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞诱变
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 该物质对组织、粘膜和上呼吸道破坏力强
摄入 误吞对人体有害。 引致灼伤。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 引起皮肤烧伤。
眼睛 引起眼睛烧伤。
接触后的征兆和症状
该物质对粘膜组织和上呼吸道、眼睛和皮肤破坏巨大。, 痉挛,发炎,咽喉肿痛, 痉挛,发炎,支气管炎, 肺炎,
肺水肿, 灼伤感:, 咳嗽, 喘息, 喉炎, 呼吸短促, 头痛, 恶心
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: DP4907000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
此易爆炸产品可以在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: 2735 国际海运危规: 2735 国际空运危规: 2735
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: AMINES, LIQUID, CORROSIVE, N.O.S. (α-EthylbenzylAMine)
国际海运危规: AMINES, LIQUID, CORROSIVE, N.O.S. (α-EthylbenzylAMine)
国际空运危规: AMines, liquid, corrOSiVE, n.o.s. (α-EthylbenzylAMine)
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: 8 国际海运危规: 8 国际空运危规: 8
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: II 国际海运危规: II 国际空运危规: II
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任,。更多使用条款,参见发票或包
装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (S)-(-)-1-苯丙胺 (R)-1-phenylpropylamine 3789-59-1 C9H13N 135.209 R(+)-alpha-甲基苄胺 (R)-1-phenyl-ethyl-amine 3886-69-9 C8H11N 121.182 α-苯乙胺 rac-methylbenzylamine 618-36-0 C8H11N 121.182 N-(1-苯基丙基)甲酰胺 N-(1-phenylpropyl)formamide 83834-93-9 C10H13NO 163.219 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (R)-(+)-1-苯丙胺 1-phenylpropylamine 3082-64-2 C9H13N 135.209 (S)-(-)-1-苯丙胺 (R)-1-phenylpropylamine 3789-59-1 C9H13N 135.209 N-甲基-1-苯基丙胺 methamphetamine 7713-71-5 C10H15N 149.236 —— (S)-N-Methyl-1-phenylpropylamine 20218-56-8 C10H15N 149.236 达泊西汀杂质12 α-ethyl-N,N-dimethylbenzenemethanamine 3330-05-0 C11H17N 163.263 —— (S)-N-(1-phenylpropyl)formamide 87858-37-5 C10H13NO 163.219 N-(1-苯基丙基)甲酰胺 N-(1-phenylpropyl)formamide 83834-93-9 C10H13NO 163.219 1-异硫氰基丙基苯 (1-isothiocyanatopropyl)benzene 4426-82-8 C10H11NS 177.27 —— N-(1-phenylpropan-1-yl)octane-1-amine 93811-44-0 C17H29N 247.424 N-(1-苯基丙基)乙酰胺 N-(1-phenylpropyl)acetamide 2698-79-5 C11H15NO 177.246 —— (R)-N-(1-phenylpropyl)acetamide —— C11H15NO 177.246 —— 1,1'-azobis(1-phenylpropane) —— C18H22N2 266.386 —— (S)-N-(1-phenylpropyl)acetamide 20306-86-9 C11H15NO 177.246 —— N-(1-Phenyl-propyl)-thioharnstoff 99171-39-8 C10H14N2S 194.301 —— (+/-)-(1-phenyl-propyl)-urea 32774-42-8 C10H14N2O 178.234 —— (1S,1'S)-bis(1-phenylpropyl)amine 40636-61-1 C18H23N 253.387 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:SO2F2 介导的伯胺和叔胺氧化与 30% H2O2 水溶液摘要:描述了使用 SO 2 F 2 /H 2 O 2 /碱系统对伯胺和叔胺进行高效和选择性氧化。苯胺转化为相应的偶氮苯,而伯苄胺转化为腈,仲苄胺重排为酰胺。对于叔胺底物喹啉、异喹啉和吡啶,它们的氧化产物是相应的N-氧化物。反应条件非常温和,仅涉及 SO 2 F 2、胺类、30% H 2 O 2水溶液溶液和无机碱在室温下。一个独特的优点是该氧化系统仅由廉价的无机化合物组成,而没有使用任何金属和有机化合物。DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2021.153457
-
作为产物:描述:苯丙酮 在 titanium(IV) isopropylate 、 氯化铵 、 三乙胺 、 sodium tetrahydroborate 作用下, 以 乙醇 为溶剂, 反应 17.0h, 以92%的产率得到1-苯基丙-1-胺参考文献:名称:Selective Monoalkylation of Ammonia: A High Throughput Synthesis of Primary Amines摘要:初级胺通过与烷基和芳基酮的高度选择性单烷基化反应,使用四异丙氧化钛和硼氢钠获得,产率良好至优异。DOI:10.1055/s-1999-2946
-
作为试剂:描述:1-phenylbutyl acetate 在 4 A molecular sieve 、 lipase B (Candida antarctica, Novozym 435) 、 1-苯基丙-1-胺 作用下, 以 1,4-二氧六环 为溶剂, 反应 163.0h, 生成 (R)-(+)-1-苯基-1-丁醇 、 (S)-(-)-1-苯基-1-丁醇 、 (S)-1-phenylbutyl acetate 、 (R)-1-phenylbutyl acetate参考文献:名称:(±)-1-Phenylbutan-1-ol 的 CALB 催化氨基分解动力学拆分:胺在酒精拆分中的作用研究摘要:(±)-1-phenylbutan-1-ol [(±)-1] 通过使用 (±)-1-苯乙胺 [( ±)-3] 作为亲核试剂比相应的 CALB 催化的 (±)-1 与乙酸乙烯酯的酯交换反应 (E = 19) 更慢但对映选择性更高 (E = 50)。在 (±)-1 的酯交换反应中使用三乙胺和乙酰苯胺作为添加剂提高了对映体比(分别为 E = 43 和 38),因此表明胺的基本特性及其结构性质可能是造成这种情况的原因对于在酯交换反应和氨解反应之间观察到的对映选择性差异。我们还使用不同的手性和非手性胺对 (±)-2 进行了氨解。对映体比率值随所用胺的不同而显着变化,但酶始终对底物的 R-对映体具有更高的选择性。在所有测试的胺中,(±)-1-phenylpropan-1-amine [(±)-5] 是首选的亲核试剂。(±)-2 的每个对映异构体的转化率分析表明,脂肪酶在氨解反应中表现出的选择性差异是由于底物DOI:10.1002/1615-4169(200108)343:6/7<646::aid-adsc646>3.0.co;2-a
文献信息
-
SYNTHESIS OF NOVEL INTERMEDIATE(S) FOR PREPARING RIVASTIGMINE申请人:Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd.公开号:US20200095195A1公开(公告)日:2020-03-26The present invention relates to novel intermediate(s), which are useful for the preparation of Rivastigmine compound of formula (I) and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts. The present invention further relates to the processes for the preparation of such novel intermediate(s) and preparation of Rivastigmine using such novel intermediate(s).本发明涉及新型中间体,该中间体对于制备化合物Rivastigmine的公式(I)及其药用可接受的盐是有用的。本发明还涉及制备这种新型中间体的方法以及使用这种新型中间体制备Rivastigmine的方法。
-
Cyclohexylamine oxidase as a useful biocatalyst for the kinetic resolution and dereacemization of amines作者:Hannes Leisch、Stephan Grosse、Hiroaki Iwaki、Yoshie Hasegawa、Peter C.K. LauDOI:10.1139/v11-086日期:2012.1
The biocatalytic performance of a cloned cyclohexylamine oxidase derived from Brevibacterium oxydans IH-35A towards structurally different amines was investigated. Cycloalkyl primary amines, alkyl aryl amines, and α-carbon-substituted aliphatic amines were identified as suitable substrates for the biocatalyst based on an activity assay. Kinetic resolutions of several amines by either recombinant whole cells or crude enzyme extracts prepared therefrom gave enantiomerically pure (R)-amines besides the corresponding ketones. When cyclohexylamine oxidase in combination with a borane–ammonia complex as reducing agent was applied to the deracemization of several substrates, excellent enantiomeric ratios (>99:1) and good isolated yields (62%–75%) of the corresponding (R)-amines were obtained.
-
Reductive Amination of Ketonic Compounds Catalyzed by Cp*Ir(III) Complexes Bearing a Picolinamidato Ligand作者:Kouichi Tanaka、Takashi Miki、Kunihiko Murata、Ayumi Yamaguchi、Yoshihito Kayaki、Shigeki Kuwata、Takao Ikariya、Masahito WatanabeDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.9b01565日期:2019.9.6Cp*Ir complexes bearing a 2-picolinamide moiety serve as effective catalysts for the direct reductive amination of ketonic compounds to give primary amines under transfer hydrogenation conditions using ammonium formate as both the nitrogen and hydrogen source. The clean and operationally simple transformation proceeds with a substrate to catalyst molar ratio (S/C) of up to 20,000 at relatively low
-
Primary Amines by Transfer Hydrogenative Reductive Amination of Ketones by Using Cyclometalated Ir<sup>III</sup>Catalysts作者:Dinesh Talwar、Noemí Poyatos Salguero、Craig M. Robertson、Jianliang XiaoDOI:10.1002/chem.201303541日期:2014.1.3Cyclometalated iridium complexes are found to be versatile catalysts for the direct reductive amination (DRA) of carbonyls to give primary amines under transfer‐hydrogenation conditions with ammonium formate as both the nitrogen and hydrogen source. These complexes are easy to synthesise and their ligands can be easily tuned. The activity and chemoselectivity of the catalyst towards primary amines
-
Chemoselective reductive alkylation of ammonia with carbonyl compounds: synthesis of primary and symmetrical secondary amines作者:Bruhaspathy Miriyala、Sukanta Bhattacharyya、John S WilliamsonDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2003.12.024日期:2004.2efficient, general procedure for highly chemoselective reductive mono-alkylation of ammonia with ketones is reported. Treatment of ketones with ammonia in ethanol and titanium(IV) isopropoxide, followed by in situ sodium borohydride reduction, and a straightforward workup afforded primary amines in good to excellent yields. Reductive alkylation of ammonia with aldehydes, on the other hand, afforded the corresponding
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
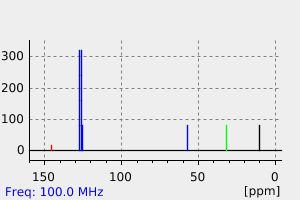
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息