2-甲基菲 | 2531-84-2
中文名称
2-甲基菲
中文别名
——
英文名称
2-methylphenathrene
英文别名
2-Methylphenanthrene
CAS
2531-84-2
化学式
C15H12
mdl
——
分子量
192.26
InChiKey
KANLOADZXMMCQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
物理描述:2-methylphenanthrene is a white crystalline solid. (NTP, 1992)
-
沸点:311 to 320 °F at 3 mm Hg (NTP, 1992)
-
熔点:58.0 °C
-
溶解度:less than 1 mg/mL at 68° F (NTP, 1992)
-
保留指数:1884;1909.3;1865;1945;1945;1875;1875;1915.2;1945;316.4;319.5;320.2;320.3
-
稳定性/保质期:
存在于烟气中。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5.2
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.07
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2902909090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 3-甲基菲 3-methylphenathrene 832-71-3 C15H12 192.26 9-甲基菲 9-methylphenanthrene 883-20-5 C15H12 192.26 1-甲基菲 1-methylphenanthrene 832-69-9 C15H12 192.26 (氯甲基)萘 1-Chloromethylnaphthalene 86-52-2 C11H9Cl 176.645 1-羟基-3-甲基菲 1-hydroxy-3-methylphenanthrene 168777-08-0 C15H12O 208.26 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 3-甲基菲 3-methylphenathrene 832-71-3 C15H12 192.26 1-甲基菲 1-methylphenanthrene 832-69-9 C15H12 192.26 9-甲基菲 9-methylphenanthrene 883-20-5 C15H12 192.26 2-羟甲基菲 2-Hydroxymethyl-phenanthren 2606-54-4 C15H12O 208.26 —— trans-2-Styrylphenanthren 30750-44-8 C22H16 280.369 菲 phenanthrene 85-01-8 C14H10 178.233
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:337.氨基氧基衍生物。第五部分.2-取代的4,6-二氨基-1,2-二氢-1-羟基-1,3,5-三嗪的一些O-醚摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9650001829
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:The Dehydration of Beta-Phenylethyl-3-methylcyclohexanol-1摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01291a015
文献信息
-
Reaction of Benzyne with Styrene Oxide: Insertion of Arynes into a C-O Bond of Epoxides作者:Diego Peña、Sandra Beltrán-Rodil、Enrique GuitiánDOI:10.1055/s-2007-977460日期:——Benzyne inserts into one of the C-O bonds of styrene -oxide to form a dihydrobenzofuran as the major product together with five other reaction products. A detailed study of the reaction mixture clarified an intriguing forty-year-old personal communication from Stiles and Haag.
-
Intramolecular carbonyl-ene reactions in the synthesis of peri-oxygenated hydroaromatics作者:Shyam Basak、Dipakranjan MalDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2016.02.033日期:2016.4Suzuki coupling of 2-formylphenylboronic acids, are shown to provide cycloalkylidene ene products under acidic conditions. Susceptibility of the products to aromatization is manoeuvred by varying the reaction conditions and catalysts including binol-derived Brønsted acid catalysts. A peri-effect is identified as a controlling factor for the aromatizations. Several oxidative transformations of an ene product
-
Straightforward synthesis of phenanthrenes from styrenes and arenes作者:Hu Li、Ke-Han He、Jia Liu、Bi-Qin Wang、Ke-Qing Zhao、Ping Hu、Zhang-Jie ShiDOI:10.1039/c2cc33100d日期:——Semi-one-pot synthesis of phenanthrenes from styrenes and arenes was developed through cross-dehydrogenative coupling. A sequence of Heck-type coupling and photo-cyclization were involved and a variety of functionalities were tolerated. This method provides an effective and practical protocol towards the synthesis of substituted phenanthrenes.
-
Construction of Phenanthrenes and Chrysenes from β-Bromovinylarenes via Aryne Diels–Alder Reaction/Aromatization作者:Vikram Singh、Ram Subhawan Verma、Anil K. Khatana、Bhoopendra TiwariDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.9b01644日期:2019.11.1A highly efficient transition-metal-free general method for the synthesis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons like phenanthrenes and chrysenes (and tetraphene) from β-bromovinylarenes and arynes has been developed. The reactions proceed via an aryne Diels-Alder (ADA) reaction, followed by a facile aromatization. This is the first report on direct construction of chrysenes (and tetraphene) using the
-
Efficiencies of photoinduced electron-transfer reactions: role of the Marcus inverted region in return electron transfer within geminate radical-ion pairs作者:Ian R. Gould、Deniz Ege、Jacques E. Moser、Samir FaridDOI:10.1021/ja00167a027日期:1990.5step is conversion of the electronic energy of an excited state into chemical energy retained in the form of a redox (geminate radical-ion) pair (A + D A'-/D'+). In polar solvents, separation of the geminate pair occurs with formation of free radical ions in solution. The quantum yields of product formation, from reactions of either the free ions, or of the geminate pair, are often low, however, due在光致电子转移过程中,主要步骤是将激发态的电子能转化为以氧化还原(成对自由基-离子)对 (A + D A'-/D'+) 形式保留的化学能。在极性溶剂中,随着溶液中自由基离子的形成,双对的分离发生。由自由离子或成对反应形成的产物的量子产率通常很低,但是,由于返回电子转移反应 (A'-/D'+ - A + D),一种能量-与离子对的有用反应竞争的浪费步骤。本研究旨在研究控制这些返回电子转移反应速率的参数。在室温下,通过简单的芳烃供体在乙腈中对氰蒽的第一激发单线态进行电子转移猝灭后形成的离子对,测量自由基离子形成的量子产率。自由离子产率由分离速率和返回电子转移速率之间的竞争决定。通过假设分离速率恒定,可以得到返回电子转移过程的速率。发现这些高度放热的返回电子转移反应 (-AG,, = 2-3 eV) 强烈依赖于反应放热。随着放热性的增加,电子转移速率显示出显着降低(在该 AG 范围内,大约为 2
表征谱图
-
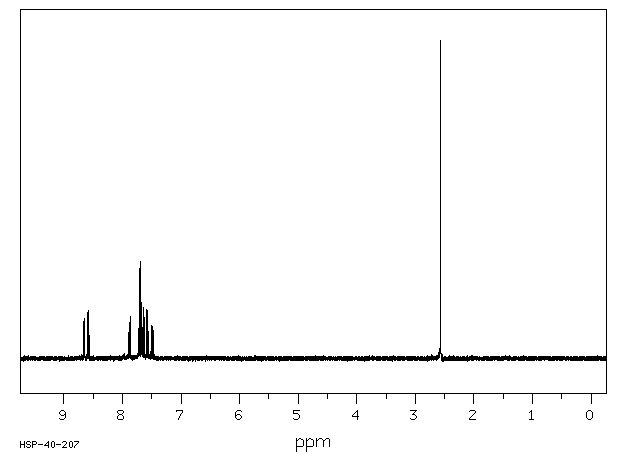
氢谱1HNMR
-
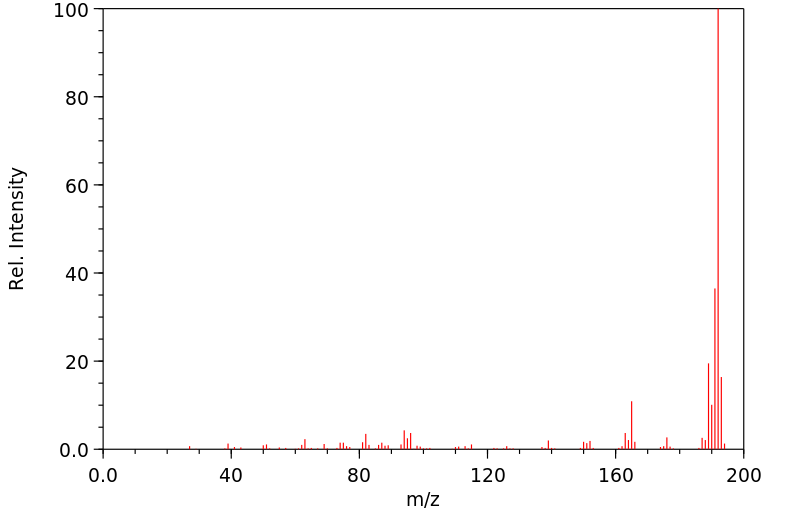
质谱MS
-
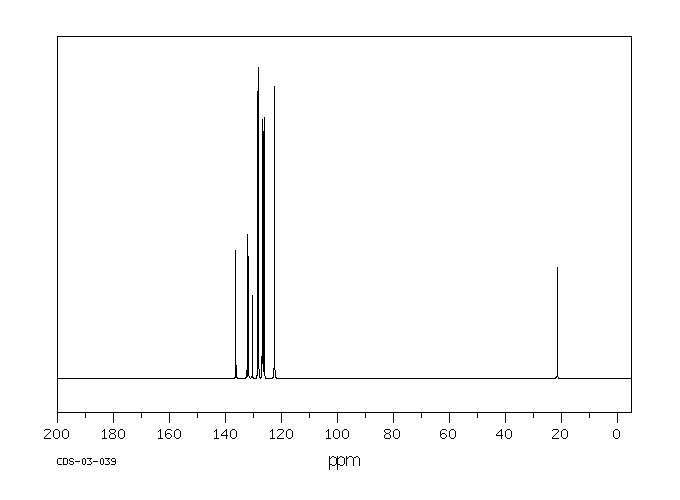
碳谱13CNMR
-
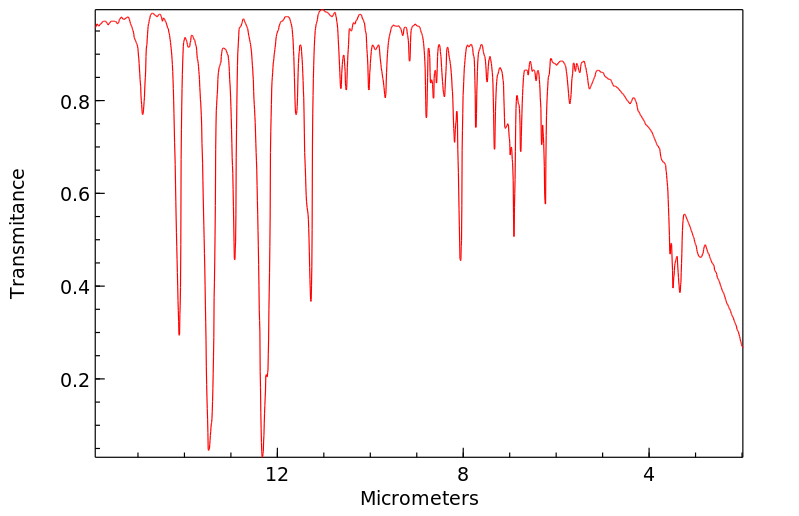
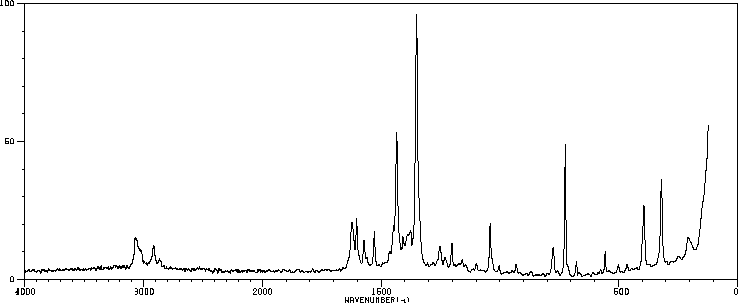
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(R)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-6,6''-二-9-菲基-1,1''-螺双[1H-茚]-7,7''-二醇
(6,6)-苯基-C61己酸甲酯
高雌二醇
马兜铃酸钠
马兜铃酸盐
马兜铃酸C
马兜铃酸B
马兜铃酸(1:1MIXTUREOFARISTOLOCHICACIDIANDARISTOLOCHICACIDII)
马兜铃酸 Ia
马兜铃酸 IVa
马兜铃酸
颜料黑32
颜料红179
颜料红178
颜料红149
颜料红123
顺式-菲-1,2-二醇-3,4-环氧化物
顺式-苯并(a)屈-11,12-二醇-13,14-环氧化物
雷公藤酚A
镁二(1,4,5,6,7,16,17,18,19,19,20,20-十二氯六环[14.2.1.14,7.02,15.03,8.09,14]二十-5,9,11,13,17-五烯-11-磺酸酯)
钩大青酮
钩大青酮
钙(2+)12-羟基十八烷酸酯
酒石酸布托诺啡
那布扶林
还原红32
足球烯
贝那他汀B
贝母兰素
萘并[2,3-b]荧蒽
萘并[2,1-e][1]苯并二硫杂环戊烷
萘并[2,1-C:7,8-C']二菲
萘并[1,2-e][2]苯并呋喃-1,3-二酮
萘并[1,2-b]屈
萘并[1,2-a]蒽
萘并[1,2-B]菲-6-醇
萘二(六氯环戊二烯)加合物
萘,8-溴-1,2,3-三(1,1-二甲基乙基)-6-甲基-
菲醌单缩氨基硫脲
菲醌
菲并[9,10]呋喃
菲并[9,10-e]醋菲烯
菲并[4,5-bcd]噻吩
菲并[4,5-bcd]呋喃-3-醇
菲并[4,3-d]-1,3-二噁唑-5-羧酸,10-羟基-9-甲氧基-6-硝基-
菲并[3,2-b]噻吩
菲并[2,1-d]噻唑
菲并[2'',1'',10'':4,5,6;7'',8'',9'':4',5',6']二异喹啉并[2,1-a:2',1'-a']二萘嵌间二氮杂苯-8,13-二酮
菲并(3,4-b)噻吩
菲并(1,2-b)噻吩