4-氧代戊酸戊酯 | 20279-49-6
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:259.0±13.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:0.96357 g/cm3
-
保留指数:1325
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.5
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:8
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.8
-
拓扑面积:43.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
海关编码:2918300090
SDS
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Levulinic Acid. V. The 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazones of Certain of its Alkyl Esters摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01335a076
-
作为产物:描述:pentyl 5-diazo-4-oxo-pentanoate 在 copper acetylacetonate 、 三正丁基氢锡 作用下, 以 苯 为溶剂, 反应 5.0h, 以76%的产率得到4-氧代戊酸戊酯参考文献:名称:氢化三丁基锡存在下的重氮分解。还原α-重氮羰基化合物摘要:在Cu(acac)2催化或光化学条件下,Bu 3 SnH可以将一系列α-重氮羰基化合物的重氮基还原为相应的CH 2基。详细研究了该反应的机理,并讨论了可能的反应途径。DOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(00)00678-5
文献信息
-
Processes and intermediates useful for preparing integrase inhibitor compounds申请人:Evans W. Jared公开号:US20080039487A1公开(公告)日:2008-02-14The invention provides processes and intermediates useful for preparing integrase inhibiting compounds.本发明提供了用于制备整合酶抑制化合物的工艺和中间体。
-
通过调控含水量制备乙酰丙酸烷基酯的方法申请人:中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所公开号:CN110963914B公开(公告)日:2022-12-09
-
Silica-supported sulfonic acids as recyclable catalyst for esterification of levulinic acid with stoichiometric amounts of alcohols作者:Raimondo Maggi、N Raveendran Shiju、Veronica Santacroce、Giovanni Maestri、Franca Bigi、Gadi RothenbergDOI:10.3762/bjoc.12.207日期:——
Converting biomass into value-added chemicals holds the key to sustainable long-term carbon resource management. In this context, levulinic acid, which is easily obtained from cellulose, is valuable since it can be transformed into a variety of industrially relevant fine chemicals. Here we present a simple protocol for the selective esterification of levulinic acid using solid acid catalysts. Silica supported sulfonic acid catalysts operate under mild conditions and give good conversion and selectivity with stoichiometric amounts of alcohols. The sulfonic acid groups are tethered to the support using organic tethers. These tethers may help in preventing the deactivation of the active sites in the presence of water.
-
Preparation of levulinic acid esters and formic acid esters from biomass and olefins; compositons prepared thereby; and uses of the compositions as fuel additives申请人:——公开号:US20030233011A1公开(公告)日:2003-12-18This invention relates to a process for producing a mixture of levulinic acid esters and formic acid esters from biomass and olefins, and the composition prepared therefrom. This invention also relates to usage of the mixture of these esters as fuel and as fuel additives for gasoline fuel, diesel fuel, and biofuel.
-
Catalytic Synthesis of Levulinate Esters over Zirconia and its Modified Forms Coated on Honeycomb Monoliths: Green Synthesis作者:Reena Saritha Serrao、S.Z. Mohamed Shamshuddin、Joyce D'souzaDOI:10.14233/ajchem.2019.22102日期:2019.8.10
A series of solid acid catalysts such as ZrO2, Mo(VI)/ZrO2 and W(VI)/ZrO2 have been coated on honeycomb monoliths as well as synthesized in the powder forms and used as catalytic materials for synthesis of ethyl levulinate from levulinic acid and ethanol. These solid acids were characterized by BET, NH3-TPD/n-butyl amine back titration, FTIR, PXRD and SEM techniques. Effects of various reaction parameters towards the reaction performance were studied. The performance of the catalyst was tested based on nature of the catalyst (honeycomb coated or powder form), reaction time (1 to 5 h), molar ratio (1:1 to 1:12 levulinic acid to ethanol) and reusability of the catalytic material. An excellent yield (86-88 %) of ethyl levulinate was obtained under optimized conditions. An attempt is made to correlate the activity of the catalysts in this esterification reaction with their surface characteristics. The honeycomb monoliths coated with zirconia and its modified forms were found to be ecofriendly, cost-effective and reusable catalytic materials compared to their powder forms.
一系列固体酸催化剂,如ZrO2、Mo(VI)/ZrO2和W(VI)/ZrO2,已经涂覆在蜂窝状单体上,并以粉末形式合成并用作从戊酸和乙醇合成乙基左旋檸檬酸酯的催化材料。这些固体酸通过BET、NH3-TPD/n-丁基胺反滴定、FTIR、PXRD和SEM技术进行表征。研究了各种反应参数对反应性能的影响。催化剂的性能是基于催化剂的性质(蜂窝涂层或粉末形式)、反应时间(1至5小时)、摩尔比(1:1至1:12戊酸与乙醇)和催化材料的可重复使用性进行测试的。在优化条件下获得了优异的乙基左旋檸檬酸酯产率(86-88%)。试图将催化剂在酯化反应中的活性与其表面特性相关联。发现用氧化锆及其改性形式涂覆的蜂窝单体是环保、成本效益高且可重复使用的催化材料,与它们的粉末形式相比。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
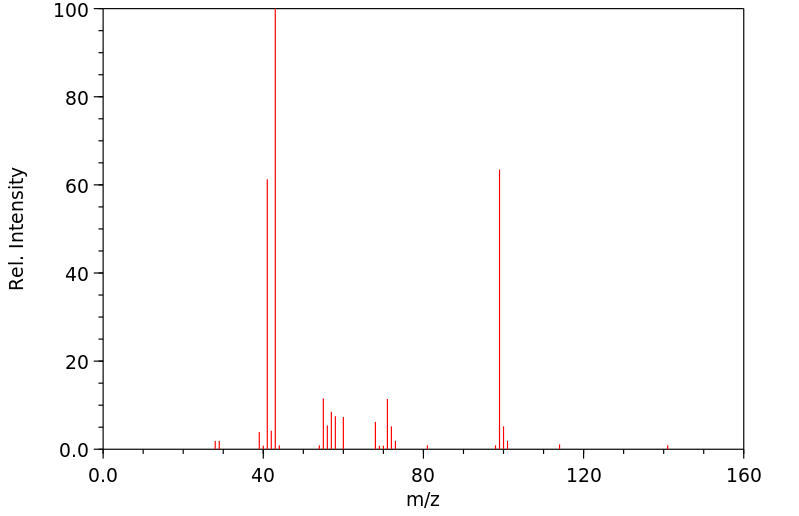
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息