邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯 | 85-68-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:370°C
-
密度:1.1 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:10.8 (vs air)
-
闪点:>230 °F
-
溶解度:二甲基亚砜:100 mg/ml(320.14 mM)
-
LogP:4.84 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Butyl benzyl phthalate appears as a clear colorless liquid with a mild odor. Primary hazard is to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Easily penetrates the soil to contaminate groundwater and nearby waterways.
-
颜色/状态:Clear, oil liquid
-
气味:Slight odor
-
味道:Bitter
-
熔点:-35 °C
-
蒸汽密度:10.8 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:8.25X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
与大多数树脂有良好的相容性,具有较强的溶剂化作用。
-
自燃温度:425 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition, it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
燃烧热:-14,550 BTU/LB= -8,090 CAL/G= -338X10+5 JOULES/KG
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.535-1.540 at 25 °C/D
-
保留指数:2327;2271;2290.6;2287;2287;2290;2290;2327
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.9
-
重原子数:23
-
可旋转键数:9
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.263
-
拓扑面积:52.6
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:9
-
危险品标志:T,N
-
安全说明:S45,S53,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R62,R50/53,R61
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29173400
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3082 9/PG 3
-
危险类别:9
-
RTECS号:TH9990000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H360Df,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P273,P308 + P313,P501
-
储存条件:密封于4℃、干燥且避光的环境中保存。应存放在室内通风干燥的地方,确保容器密封以防止水分侵入。本产品易燃,请远离火源,并避免与氧化剂或爆炸性物质共同储存。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 酞酸苄基丁酯;邻苯二甲酸苄基丁基酯 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Benzyl butyl phthalate;Butyl benzyl phthalate |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 85-68-7 |
| 分子式: | C 19 H 20 O 4 |
| 分子量: | 312.39 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:酞酸苄基丁酯;邻苯二甲酸苄基丁基酯 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 吸入、摄入或经皮肤吸收后对身体有害。对眼睛、皮肤和粘膜有刺激作用。 |
| 环境危害: | 对环境有危害。 |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。与氧化剂可发生反应。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服,在上风向灭火。尽可能将容器从火场移至空旷处。喷水保持火场容器冷却,直至灭火结束。处在火场中的容器若已变色或从安全泄压装置中产生声音,必须马上撤离。灭火剂:雾状水、二氧化碳、干粉。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 199 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 240 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。用砂土、干燥石灰或苏打灰混合,收集于一个密闭的容器中,运至废物处理场所。用水刷洗泄漏污染区,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,局部排风。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩),戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。在清除液体和蒸气前不能进行焊接、切割等作业。避免产生烟雾。避免与氧化剂、碱类接触。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂、碱类分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 可能接触其蒸气时,应该佩戴防毒口罩。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,建议佩戴防毒面具。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿相应的防护服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作后,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 透明油状液体,微具芳香味。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | <-35 |
| 沸点(℃): | 370 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.116(25℃) |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 10.8 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 199 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 240 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 19 H 20 O 4 |
| 分子量: | 312.39 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于多数有机溶剂。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作聚氯乙烯、氯乙烯共聚物、纤维素树脂、天然橡胶和合成橡胶的增塑剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强碱。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:2330mg/kg(大鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 建议用焚烧法处置。在能利用的地方重复使用容器或在规定场所掩埋。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。保持容器密封。防止阳光曝晒。应与碱类、氧化剂等分开存放。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。操作现场不得吸烟、饮水、进食。分装和搬运作业要注意个人防护。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 6 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯是一种透明的油状液体,带有轻微的芳香气味。它具有强大的溶剂能力,并且在散发泡性能、耐油抽出性方面表现优异。此外,该物质还表现出良好的抗污染性和低挥发性,拥有低水抽出性及抗迁移性,塑化速度快。
应用邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯是一种性能优良的外增塑剂,在塑料制品加工成型工艺中得到广泛应用。它能够改善树脂的塑性和流动性,并溶解有机颜料,使成品具有良好的透明度和光滑表面。
生物活性Butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP, 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, butyl phenylmethyl eSTer) 是一种邻苯二甲酸酯类物质,已被确认为有毒物质,并常作为增塑剂添加到塑料制品中。体外研究表明,Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) 会诱导侧群体(S1PR3)细胞中的组蛋白修饰,但不会对非侧群体(non-SP)细胞产生相同效果。
化学性质邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯是一种无色透明的油状液体,带有轻微芳香气味。该物质不溶于水,但能溶解在大多数有机溶剂中,并且与多种树脂有良好的相容性,具有很强的溶剂化能力。
用途邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯主要用作增塑剂,常用于聚氯乙烯、氯乙烯共聚物、纤维素树脂、天然和合成橡胶等材料。它具有强大的溶解能力和良好的耐污染性、快速的塑化速度以及大填充容量,适用于制作薄膜、板材及管材等塑料制品,并能赋予成品优良的透明性和光滑表面。
生产方法通过将苯酐与丁醇进行酯化反应制得邻苯二甲酸单丁酯[131-70-4],随后在碳酸钠的存在下与氯化苄进行第二次酯化。经过液碱中和、水洗及减压蒸馏处理后即可得到目标产物。每吨原料消耗为:苯酐(98%)560公斤、丁醇290公斤、氯化苄620公斤、碳酸钠320公斤。
类别易燃液体
毒性分级中毒
-
急性毒性
- 大鼠口服 LD50: 2330 毫克/公斤
- 小鼠口服 LD50: 4170 毫克/公斤
与氧化剂激烈反应
可燃性危险特性遇明火、高温或强氧化剂、酸较易燃;燃烧时排放刺激烟雾
储运特性- 包装完整,轻装轻放
- 库房通风良好,远离明火和高温环境
- 与氧化剂及酸类物质分开存放
泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉
职业标准- 时间加权平均容许浓度 (TWA): 3 毫克/公斤
- 短时间接触极限 (STEL): 5 毫克/公斤
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 Dibutyl phthalate 84-74-2 C16H22O4 278.348 邻苯二甲酸单丁酯 phthalic acid monobutyl ester 131-70-4 C12H14O4 222.241 苯酐 phthalic anhydride 85-44-9 C8H4O3 148.118 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— phthalic acid benzyl ester-decyl ester 1252-12-6 C25H32O4 396.527 —— phthalic acid benzyl ester-(6-methyl-heptyl ester) —— C23H28O4 368.473 2-乙基己基苄基邻苯二甲酸酯 benzyl 2-ethylhexyl phthalate 18750-05-5 C23H28O4 368.473 邻苯二甲酸单丁酯 phthalic acid monobutyl ester 131-70-4 C12H14O4 222.241 邻苯二甲酸二辛酯 Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate 82208-43-3 C24H38O4 390.563 邻苯二甲酸丁基酯2-乙基己基酯 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid 1-butyl 2-ethylhexyl ester 85-69-8 C20H30O4 334.456
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:利用邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯精馏低沸物制备乙酸苄 酯的方法摘要:本发明公开了一种利用邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯精馏低沸物制备乙酸苄酯的方法,该方法包括以下步骤:1)将邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯精馏低沸物、醋酸、第一催化剂和带水剂投入反应器中,升温至90~130℃回流反应并分水,直至分相器无水分出;2)再向反应器中加入醋酸酐和第二催化剂,继续升温至130~160℃回流反应,气相色谱跟踪,待反应物料中残留的苄基丁基醚小于0.2%时停止加热;3)将反应所得产物进行减压精馏除去杂质,再用重量百分含量为15~25%的碳酸钠溶液洗至中性,然后经水洗、精馏得到成品乙酯苄酯。实践证明,该方法操作简便、效率高、生产成本低、适于工业化生产。公开号:CN104003871B
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Butyl esters of phthalic acid摘要:公开号:US01554032A1
文献信息
-
[EN] HEMI-AMINAL ETHERS AND THIOETHERS OF N-ALKENYL CYCLIC COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] ÉTHERS ET THIOÉTHERS HÉMIAMINAUX DE COMPOSÉS CYCLIQUES N-ALCÉNYLIQUES申请人:ISP INVESTMENTS INC公开号:WO2014116560A1公开(公告)日:2014-07-31Described herein are hemi-aminal ethers and thioethers of N-alkenyl cyclic compounds that may be produced through a reaction comprising: (A) at least one first reactant represented by a structure (I), wherein X is a functionalized or unfunctionalized C1-C5 alkylene group optionally having one or more heteroatoms, and each R1, R2, and R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and functionalized and unfunctionalized alkyl groups optionally having one or more heteroatoms, and (B) at least one second reactant having at least one hydroxyl moiety or thiol moiety. The hemi-aminal ethers and thioethers of N-alkenyl cyclic compounds may comprise a polymerizable moiety, in which case they may be left as-is or used to create homopolymers or non-homopolymers, or they may not comprise a polymerizable moiety. A wide variety of formulations may be created using the hemi-aminal ethers and thioethers of N-alkenyl cyclic compounds, including personal care, oilfield, and construction formulations.
-
METHODS OF TREATING A BLOOD VESSEL申请人:Kerber Charles W.公开号:US20090137981A1公开(公告)日:2009-05-28Described herein are methods for treating a blood vessel. In an embodiment, the method of treating a blood vessel comprises providing at least one manipulable tool in a blood vessel, depositing a non-solid polymerizable material into a deposition area of the vessel, wherein the polymerizable liquid hardens over time upon contact with blood in the blood vessel, and altering the shape of the polymerizable material while it hardens by manipulating the tool.描述了治疗血管的方法。在一个实施例中,治疗血管的方法包括在血管中提供至少一个可操作的工具,将非固体聚合材料沉积到血管的沉积区,其中聚合液体在与血管中的血液接触后随时间硬化,并通过操作工具在材料硬化时改变其形状。
-
BITTER TASTE MODIFIERS INCLUDING SUBSTITUTED 1-BENZYL-3-(1-(ISOXAZOL-4-YLMETHYL)-1H-PYRAZOL-4-YL)IMIDAZOLIDINE-2,4-DIONES AND COMPOSITIONS THEREOF申请人:SENOMYX, INC.公开号:US20160376263A1公开(公告)日:2016-12-29The present invention includes compounds and compositions known to modify the perception of bitter taste, and combinations of said compositions and compounds with additional compositions, compounds, and products. Exemplary compositions comprise one or more of the following: cooling agents; inactive drug ingredients; active pharmaceutical ingredients; food additives or foodstuffs; flavorants, or flavor enhancers; food or beverage products; bitter compounds; sweeteners; bitterants; sour flavorants; salty flavorants; umami flavorants; plant or animal products; compounds known to be used in pet care products; compounds known to be used in personal care products; compounds known to be used in home products; pharmaceutical preparations; topical preparations; cannabis-derived or cannabis-related products; compounds known to be used in oral care products; beverages; scents, perfumes, or odorants; compounds known to be used in consumer products; silicone compounds; abrasives; surfactants; warming agents; smoking articles; fats, oils, or emulsions; and/or probiotic bacteria or supplements.本发明涵盖已知用于改变苦味感知的化合物和组合物,以及所述组合物和化合物与额外的组合物、化合物和产品的组合。示例组合物包括以下一种或多种:冷却剂;无活性药物成分;活性药用成分;食品添加剂或食品;调味剂或调味增强剂;食品或饮料产品;苦味化合物;甜味剂;苦味剂;酸味调味剂;咸味调味剂;鲜味调味剂;植物或动物产品;已知用于宠物护理产品中的化合物;已知用于个人护理产品中的化合物;已知用于家用产品中的化合物;制药制剂;局部制剂;大麻衍生或与大麻相关的产品;已知用于口腔护理产品中的化合物;饮料;香味、香水或除臭剂;已知用于消费品中的化合物;硅化合物;磨料;表面活性剂;发热剂;吸烟物品;脂肪、油脂或乳化剂;和/或益生菌或补充剂。
-
Heterocylic fluoroalkenyl thioethers and the use thereof as pesticides (IV)申请人:——公开号:US20030187259A1公开(公告)日:2003-10-02The present invention relates to novel heterocyclic fluoroalkenyl thioethers of the formula (I) 1 in which m represents integers from 3 to 10, n represents 0, 1 or 2 and Het represents the following, in each case optionally substituted, groupings: 2 and to processes for their preparation and to their use as pesticides.
-
Use of riboflavin and flavin derivatives as chitinase inhibitors
表征谱图
-
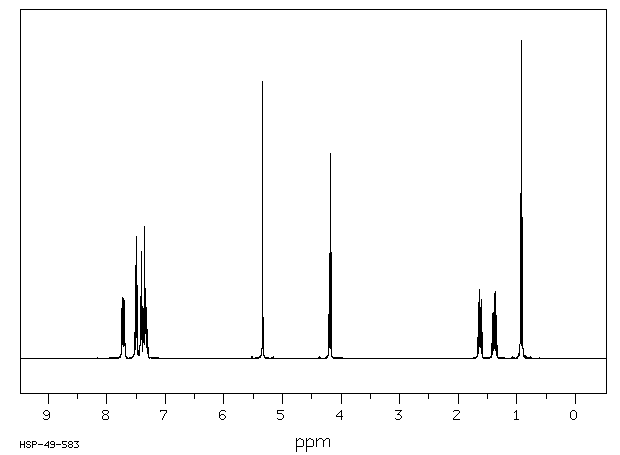
氢谱1HNMR
-
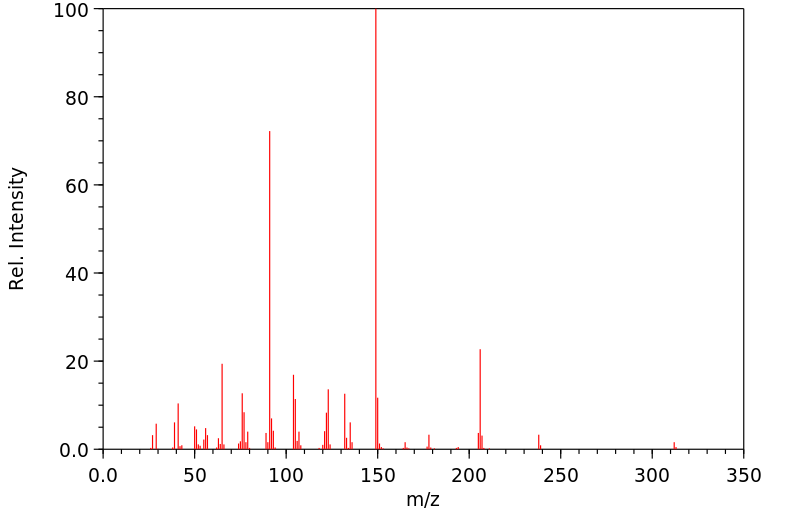
质谱MS
-
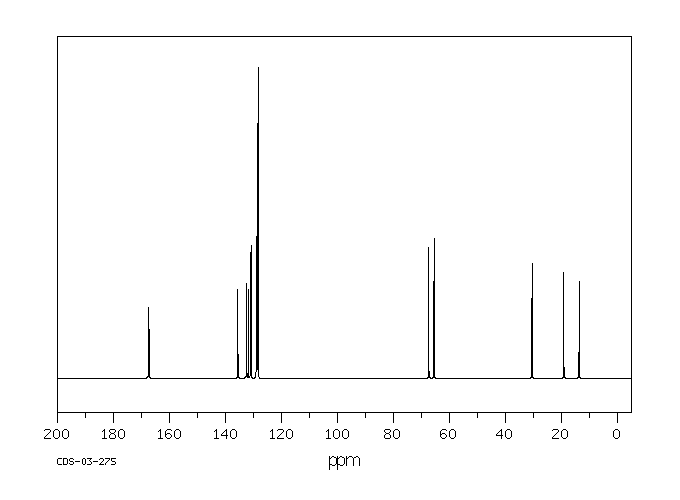
碳谱13CNMR
-
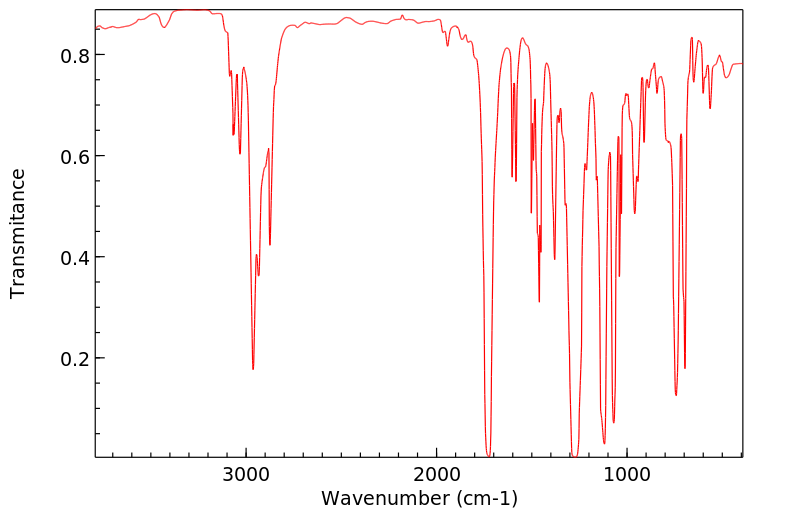
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息