N-叔丁基-α-(4-吡啶基-1-氧)硝酮 | 66893-81-0
中文名称
N-叔丁基-α-(4-吡啶基-1-氧)硝酮
中文别名
Alpha-(4-吡啶基-1-氧)-N-叔丁基硝基酮;N-叔丁基-α-(4-吡啶基)-硝酮N'-氧化物;α-(4-吡啶基-1-氧)-N-叔丁基硝基酮;N-(4-吡啶基亚甲基)-叔丁胺N,N'-二氧化物;α-(4-吡啶基N-氧化物)-N-叔丁基硝酮;A-(4-吡啶基-1-氧)-N-叔丁基硝基酮
英文名称
N-(4-pyridylmethylene)-t-butylamine N,N'-dioxide
英文别名
2-methyl-N-(4-pyridinemethylidene)propan-2-amine N,N'-dioxide;N,N'-Dioxide-2-methyl-N-(4-pyridinylmethylene)-2-propanamine;α-(4-pyridyl N–oxide)-N-tert-butylnitrone;α-4-pyridyl-N-tert-butylnitrone α-1-oxide;α-(4-pyridyl, 1-oxide)-N-tert-butylnitrone;α-[4-pyridyl N-oxide]-N-tert-butyl nitrone;tert-butyl-[(1-oxidopyridin-4-ylidene)methyl]-oxoazanium
CAS
66893-81-0
化学式
C10H14N2O2
mdl
——
分子量
194.233
InChiKey
RNRMWTCECDHNQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:183-185 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:330.68°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.1444 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:水中的溶解度:10mg/mL,澄清,无色至淡黄色
-
稳定性/保质期:
常温常压下稳定,远离氧化剂。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.7
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.4
-
拓扑面积:46.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
海关编码:2933399090
-
安全说明:S22,S24/25
-
WGK Germany:3
-
储存条件:存放在密封容器内,并置于阴凉、干燥处。请确保存储地点远离氧化剂。
SDS
1.1 产品标识符
: α-(4-Pyridyl N-oxide)-N-tert-butylnitrone
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
N-tert-Butyl-α-(4-pyridyl)nitrone N′-oxide
N-(4-Pyridylmethylene)-tert-butylamine N,N′-dioxide
POBN
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
根据全球协调系统(GHS)的规定,不是危险物质或混合物。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: N-tert-Butyl-α-(4-pyridyl)nitrone N′-oxide
别名
N-(4-Pyridylmethylene)-tert-butylamine N,N′-dioxide
POBN
: C10H14N2O2
分子式
: 194.23 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
1,1-Dimethyl-N-(4-pyridylmethylene)ethylamine N,N'-dioxide
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 66893-81-0
EC-编号 266-512-3
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。
6.2 环境预防措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
扫掉和铲掉。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
常规的工业卫生操作。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所来选择人体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 结晶
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/熔点范围: 183 - 185 °C - lit.
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞诱变
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表保证此产品的性质。
公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任,。更多使用条款,参见发票或包
装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
: α-(4-Pyridyl N-oxide)-N-tert-butylnitrone
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
N-tert-Butyl-α-(4-pyridyl)nitrone N′-oxide
N-(4-Pyridylmethylene)-tert-butylamine N,N′-dioxide
POBN
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
根据全球协调系统(GHS)的规定,不是危险物质或混合物。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: N-tert-Butyl-α-(4-pyridyl)nitrone N′-oxide
别名
N-(4-Pyridylmethylene)-tert-butylamine N,N′-dioxide
POBN
: C10H14N2O2
分子式
: 194.23 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
1,1-Dimethyl-N-(4-pyridylmethylene)ethylamine N,N'-dioxide
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 66893-81-0
EC-编号 266-512-3
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。
6.2 环境预防措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
扫掉和铲掉。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
常规的工业卫生操作。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所来选择人体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 结晶
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/熔点范围: 183 - 185 °C - lit.
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞诱变
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表保证此产品的性质。
公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任,。更多使用条款,参见发票或包
装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
POBN(4-POBN)是一种亲水性的自旋陷阱,可以穿透细胞膜,并常用于检测自由基加合物。
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Spin trapping of hydroxyl radical in the troposphere for determination by electron spin resonance and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry摘要:DOI:10.1021/ac00251a015
-
作为产物:描述:4-吡啶醛 N-氧化物 、 N-叔丁基羟胺 以35%的产率得到N-叔丁基-α-(4-吡啶基-1-氧)硝酮参考文献:名称:Spin trapping of hydroxyl radical in the troposphere for determination by electron spin resonance and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry摘要:DOI:10.1021/ac00251a015
-
作为试剂:描述:乙醇 、 astaxanthin diferulate 在 N-叔丁基-α-(4-吡啶基-1-氧)硝酮 、 iron(II) chloride tetrahydrate 、 双氧水 作用下, 以 水 为溶剂, 反应 0.02h, 生成 、参考文献:名称:Astaxanthin diferulate as a bifunctional antioxidant摘要:Astaxanthin when esterified with ferulic acid is better singlet oxygen quencher with k(2) = (1.58 +/- 0.1) 10(10) L mol(-1)s(-1) in ethanol at 25 degrees C compared with astaxanthin with k(2) = (1.12 +/- 0.01) 10(9) L mol(-1)s(-1). The ferulate moiety in the astaxanthin diester is a better radical scavenger than free ferulic acid as seen from the rate constant of scavenging of 1-hydroxyethyl radicals in ethanol at 25 degrees C with a second-order rate constant of (1.68. 0.1) 10(8) L mol(-1)s(-1) compared with (1.60. 0.03) 10(7) L mol(-1)s(-1) for the astaxanthin: ferulic acid mixture, 1:2 equivalents. The mutual enhancement of antioxidant activity for the newly synthetized astaxanthin diferulate becoming a bifunctional antioxidant is rationalized according to a two-dimensional classification plot for electron donation and electron acceptance capability.DOI:10.3109/10715762.2014.982112
文献信息
-
Radical Trifluoromethoxylation of Arenes Triggered by a Visible‐Light‐Mediated N−O Bond Redox Fragmentation作者:Benson J. Jelier、Pascal F. Tripet、Ewa Pietrasiak、Ivan Franzoni、Gunnar Jeschke、Antonio TogniDOI:10.1002/anie.201806296日期:2018.10.15method enables non‐directed functionalization of C−H bonds on a range of substrates, providing access to aryl trifluoromethyl ethers. This light‐driven process is distinctly different from conventional procedures and occurs through an OCF3 radical mechanism mediated by a photoredox catalyst, which triggers an N−O bond fragmentation. The pyridinium‐based trifluoromethoxylation reagent is bench‐stable and
-
REGENERATION OF VITAMIN E FROM α-CHROMANOXYL RADICAL BY GLUTATHIONE AND VITAMIN C作者:Etsuo Niki、Jyunichi Tsuchiya、Ritsuko Tanimura、Yoshio KamiyaDOI:10.1246/cl.1982.789日期:1982.6.5α-Chromanoxyl radical formed by the interaction of α-tocopherol (vitamin E) with alkoxyl radical or DPPH was found by electron spin resonance spectroscopy to react with glutathione and vitamin C to regenerate α-tocopherol.
-
MASS SPECTROMETRIC DETERMINATION OF SPIN ADDUCTS IN SPIN TRAPPING TECHNIQUE作者:Hironori Suezawa、Kazuhisa Abe、Minoru Hirota、Tetsuo IshiiDOI:10.1246/cl.1981.1049日期:1981.7.5The GC/MS(MC) technique was shown to be applicable to identify various kinds of free radicals trapped by α-aryl N-t-butyl nitrones. When spin adducts are unstable under the conditions for measurement, they were trimethylsilylated on the nitroxyl oxygen atom, which makes GC/MS measurement possible.
-
Substituent Effect on the Rate of the Hydroxyl and Phenyl Radical Spin Trapping with Nitrones作者:Yoshimi Sueishi、Chiharu Yoshioka、Claudio Olea-Azar、Lester A. Reinke、Yashige KotakeDOI:10.1246/bcsj.75.2043日期:2002.9and spin trapping was performed in benzene. Spin trapping rate constants were calculated using EPR signal intensity ratios for the DMPO spin adducts vs PBN-type spin adducts. The rate constants were strongly dependent on the kind of substituent in the spin trap; the magnitude of the substituent effect was also dependent on the kind of free radicals trapped, i.e., hydroxyl or phenyl radicals. For exampleα-苯基-Nt-丁基硝酮(PBN,N-亚苄基-叔丁胺 N-氧化物)及其类似物的羟基和苯基自由基自旋捕获率使用竞争性捕获方法确定。在选定的自旋阱和 5,5-二甲基-吡咯啉 N-氧化物 (DMPO) 存在下,使用紫外线光解从水中的过氧化氢生成羟基自由基。四苯基铅紫外光解产生苯基自由基,在苯中进行自旋捕获。使用 DMPO 自旋加合物与 PBN 型自旋加合物的 EPR 信号强度比计算自旋捕获速率常数。速率常数强烈依赖于自旋阱中取代基的种类;取代基效应的大小还取决于被捕获的自由基的种类,即羟基或苯基自由基。例如,在苯基自由基捕获中,羟基取代的PBNs中的自旋俘获率遵循Hammett方程,而在羟基自由基俘获中没有这种相关性。羟基取代...
-
Chitosan as an antioxidant alternative to sulphites in oenology: EPR investigation of inhibitory mechanisms作者:Antonio Castro Marín、Marcel Culcasi、Mathieu Cassien、Pierre Stocker、Sophie Thétiot-Laurent、Bertrand Robillard、Fabio Chinnici、Sylvia PietriDOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.155日期:2019.7Pre-incubation with 2 g/L chitosan followed by filtration had a better effect than adding 50 mg/L sulphur dioxide to the experimental Chardonnay wine on the release of 4-POBN adducts after 6 days of incubation with 100 μM iron(II). In a relevant photooxidative system acetaldehyde formation was significantly reduced after 6 days of incubation. Parallel EPR tests were performed to assess the importance通过电子顺磁共振(EPR)研究了两种商业上不溶的壳聚糖(一种被批准用于酿酒)在模型酒和不含亚硫酸盐的白葡萄酒中对氧化降解的功效。两种化合物在不同剂量下均显着抑制α-(4-吡啶基-1-氧化物)-N - t的形成正常葡萄酒储存条件下的丁基丁基亚硝基(4-POBN)-1-羟乙基加合物。与100μM铁(II)孵育6天后,与2 g / L脱乙酰壳多糖进行预温育然后过滤比将50 mg / L二氧化硫添加到实验霞多丽酒中对4-POBN加合物的释放有更好的效果。在相关的光氧化系统中,孵育6天后乙醛的形成显着减少。进行了并行的EPR测试,以评估金属螯合(铁和铜)相对于直接清除羟基自由基对壳聚糖的影响的重要性。本数据支持使用生物相容性壳聚糖作为更健康的补充和/或替代二氧化硫对抗白葡萄酒氧化变质的潜力。
表征谱图
-
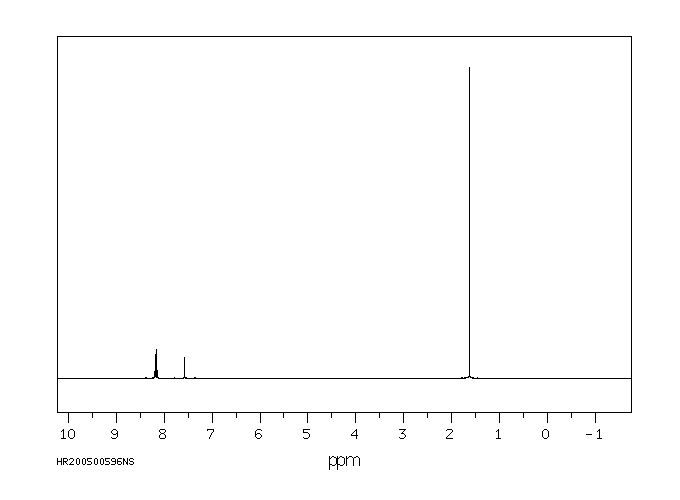
氢谱1HNMR
-
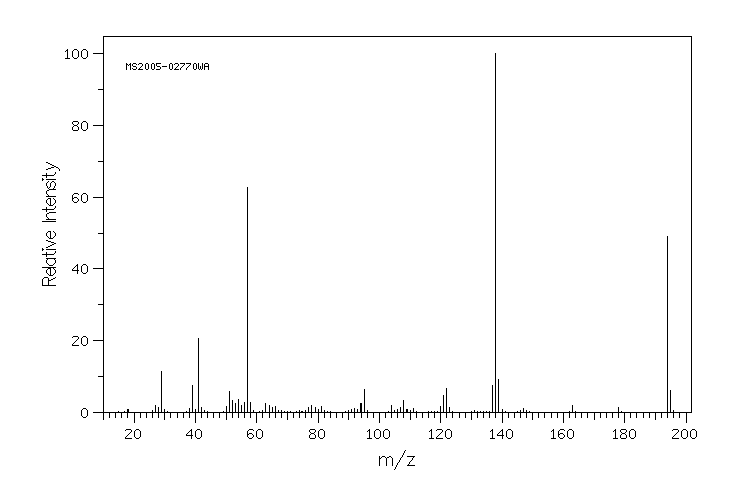
质谱MS
-
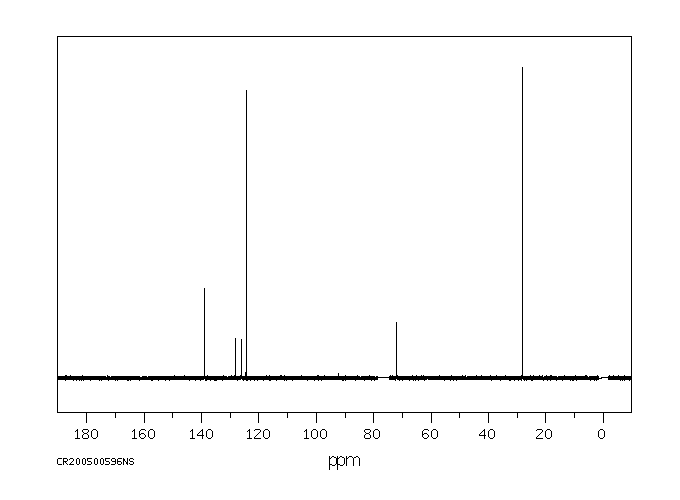
碳谱13CNMR
-
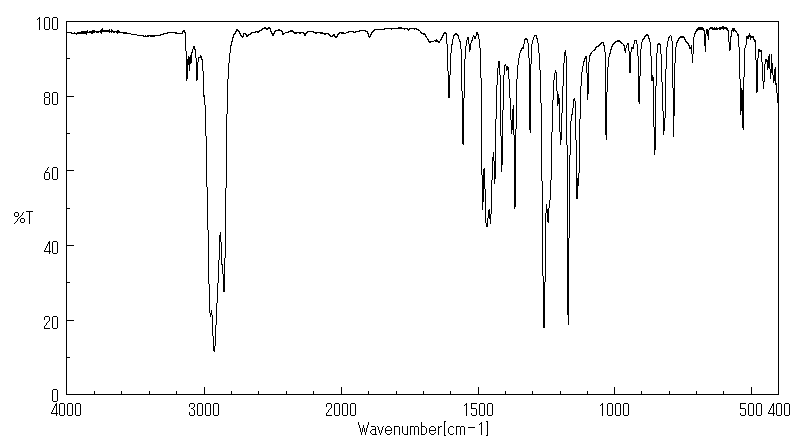
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-氨氯地平-d4
(R,S)-可替宁N-氧化物-甲基-d3
(R)-(+)-2,2'',6,6''-四甲氧基-4,4''-双(二苯基膦基)-3,3''-联吡啶(1,5-环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-N'-亚硝基尼古丁
(R)-DRF053二盐酸盐
(5E)-5-[(2,5-二甲基-1-吡啶-3-基-吡咯-3-基)亚甲基]-2-亚磺酰基-1,3-噻唑烷-4-酮
(5-溴-3-吡啶基)[4-(1-吡咯烷基)-1-哌啶基]甲酮
(5-氨基-6-氰基-7-甲基[1,2]噻唑并[4,5-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺)
(2S,2'S)-(-)-[N,N'-双(2-吡啶基甲基]-2,2'-联吡咯烷双(乙腈)铁(II)六氟锑酸盐
(2S)-2-[[[9-丙-2-基-6-[(4-吡啶-2-基苯基)甲基氨基]嘌呤-2-基]氨基]丁-1-醇
(2R,2''R)-(+)-[N,N''-双(2-吡啶基甲基)]-2,2''-联吡咯烷四盐酸盐
(1'R,2'S)-尼古丁1,1'-Di-N-氧化物
黄色素-37
麦斯明-D4
麦司明
麝香吡啶
鲁非罗尼
鲁卡他胺
高氯酸N-甲基甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸,吡啶
高奎宁酸
马来酸溴苯那敏
马来酸氯苯那敏-D6
马来酸左氨氯地平
顺式-双(异硫氰基)(2,2'-联吡啶基-4,4'-二羧基)(4,4'-二-壬基-2'-联吡啶基)钌(II)
顺式-二氯二(4-氯吡啶)铂
顺式-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯铬氯化物
顺式-1-(4-甲氧基苄基)-3-羟基-5-(3-吡啶)-2-吡咯烷酮
顺-双(2,2-二吡啶)二氯化钌(II) 水合物
顺-双(2,2'-二吡啶基)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
顺-二氯二(吡啶)铂(II)
顺-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
韦德伊斯试剂
非那吡啶
非洛地平杂质C
非洛地平
非戈替尼
非布索坦杂质66
非尼拉朵
非尼拉敏
雷索替丁
阿雷地平
阿瑞洛莫
阿扎那韦中间体
阿培利司N-6
阿伐曲波帕杂质40
间硝苯地平
间-硝苯地平
镉,二碘四(4-甲基吡啶)-
锌,二溴二[4-吡啶羧硫代酸(2-吡啶基亚甲基)酰肼]-