甘氨酰-DL-甲硫氨酸 | 1999-34-4
中文名称
甘氨酰-DL-甲硫氨酸
中文别名
甘氨酰-DL-蛋氨酸
英文名称
glycylmethionine
英文别名
2-[(2-azaniumylacetyl)amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoate
CAS
1999-34-4
化学式
C7H14N2O3S
mdl
——
分子量
206.266
InChiKey
PFMUCCYYAAFKTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:203-205 °C (decomp)
-
沸点:493.7±45.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.267±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
物理描述:Solid
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-3.1
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.71
-
拓扑面积:118
-
氢给体数:3
-
氢受体数:5
安全信息
-
WGK Germany:3
-
储存条件:-20°C
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:甘氨酰-DL-甲硫氨酸 以 水 为溶剂, 生成 glycyl-DL-methioninatocytosinepalladium(II)参考文献:名称:Crystal and molecular structure of chloroglycyl-dl-methioninatopalladium(II) monohydrate and its interaction with guanosine, cytidine and cytosine摘要:The crystal and molecular structure of the parent complex, chloroglycol-DL-methionatopalladium(II) monohydrate has been determined by X-ray diffraction analysis. Palladium has a square planar disposition in the complex and the deprotonated peptide moiety acts as a terdentate ligand and binds through N, O and S. The fourth coordination position on the metal ion is occupied by the chloride ion. The structure involves an extensive network of hydrogen bonds. Mixed ligand complexes of chloroglycl-DL-methionatopalladium(II) monohydrate with guanosine, cytosine and cytidine were synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, conductivity measurements. IR and H-1 NMR spectral studies. In the case of guanosine, the metal coordinating site is N(7) whereas in cytosine and cytidine it is N(3).DOI:10.1016/s0277-5387(00)83324-0
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:New Amine-masking Groups for Peptide Synthesis摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01574a029
文献信息
-
Effective Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity of Methyl Maleopimarate Imides作者:Ilshat Maratovich Sakhautdinov、Rauilya Nadirovna Malikova、Diana Valievna Khasanova、Liana Fanzilevna Zainullina、Vener Absatarovich Vakhitov、Alexander Nikolaevich Lobov、Yuliya Venerovna Vakhitova、Marat Sabirovich YunusovDOI:10.2174/1570178615666180212154722日期:2018.8.8two-fold excess of amines and ultrasonic influence increased yield of target products and reduced reaction time. The structures of the products were proved by two-dimensional correlation spectra of HSQC, HMBC, COSY, NOESY. A new efficient method for the synthesis of a large group of hybrid potentially biologically active compounds by condensation of methyl maleopimarate with various amines (glycine, β-alanine现代生物化学的一个持续存在的问题是寻找基于具有各种抗癌活性并且同时对整个生物体正常细胞影响很小的具有不同药效基团的天然加合物合成新杂合化合物的方法。 在DMSO中用不同的胺处理从松香中得到的马来酸甲酯MMP,通过60分钟的热缩合和30分钟的超声(US)处理缩合得到马来酸酰亚胺。所有合成的化合物(包括母体化合物-马来酸和MMP)都在HEK293(人类胚胎肾细胞)和Jurkat细胞(人类T细胞淋巴母细胞样细胞系)中进行了体外细胞毒性MTT分析。通过开发的方法,获得了一系列新的马来酰亚胺。发现使用两倍过量的胺和超声影响增加了目标产物的产率并缩短了反应时间。通过HSQC,HMBC,COSY,NOESY的二维相关光谱证明了产物的结构。 一种新的有效方法,可通过马来酸马来酸甲酯与各种胺(甘氨酸,β-丙氨酸,γ-氨基丁酸,氨基己酸,α-丙氨酸,β-苯基-α-开发了在二甲基亚砜(DMSO)中超声作用下的丙
-
Oxidation of methionine residue in Gly-Met dipeptide induced by [Au(en)Cl2]+ and influence of the chelated ligand on the rate of this redox process作者:Biljana Đ. Glišić、Miloš I. Djuran、Zorka D. Stanić、Snežana RajkovićDOI:10.1007/s13404-013-0108-7日期:2014.5same process with previously investigated [AuCl4]− complex. Difference in the oxidation rate of Gly-Met between these two complexes was attributed to the presence of chelated ethylenediamine ligand in [Au(en)Cl2]+. The finding that the oxidation of sulfur-containing peptides and proteins can be inhibited by structural modifications of gold(III) complexes introducing polydentate nitrogen-containing ligands光谱(1H NMR 和 UV-vis)和电化学 (CV) 技术已用于研究 Gly-Met 二肽与具有双齿配位乙二胺 (en) 配体的 [Au(en)Cl2]+ 配合物的反应。所研究反应的最终产物是 Gly-Met 亚砜,它是通过用 [Au(en)Cl2]+ 氧化甲硫氨酸残基形成的。Gly-Met亚砜的形成通过两个步骤进行,包括甲硫氨酸残基的硫醚硫原子的单齿配位和从Au(III)释放en配体。为了研究 pH 值和 Cl− 浓度对氧化还原过程的影响,反应在 KCl 溶液中进行,浓度范围为 0.01 至 0.50 M,pH 值范围为 2.00-5.00。获得的动力学数据表明,与使用先前研究的 [AuCl4]- 复合物的相同过程相比,Gly-Met 中甲硫氨酸残基的氧化要慢 200 倍。这两种复合物之间 Gly-Met 氧化速率的差异归因于 [Au(en)Cl2]+ 中螯合乙二胺配体的存在。通过引入多齿含氮配体的金
-
Compositions for use in golf balls申请人:Bulpett A. David公开号:US20050245652A1公开(公告)日:2005-11-03A golf ball comprises a core, an outer cover layer, and, optionally, an intermediate layer disposed between the core and the outer cover layer. The outer cover layer may comprise a polyurethane or polyurea composition. At least one portion of the golf ball comprises a composition that enhances physical properties and/or performance characteristics (e.g., coefficient of restitution) of the golf ball. Preferably, the coefficient of restitution of the core is 0.8 or greater.
-
COMPOSITIONS FOR USE IN GOLF BALLS申请人:Sullivan Michael J.公开号:US20080227567A1公开(公告)日:2008-09-18A golf ball comprises a core, an outer cover layer, and, optionally, an intermediate layer disposed between the core and the outer cover layer. The outer cover layer may comprise a polyurethane or polyurea composition. At least one portion of the golf ball comprises a composition that enhances physical properties and/or performance characteristics (e.g., coefficient of restitution) of the golf ball. Preferably, the coefficient of restitution of the core is 0.8 or greater.
-
Compositions for Use in Golf Balls申请人:Bulpett David A.公开号:US20080176678A1公开(公告)日:2008-07-24A golf ball comprising a core and at least one layer disposed about the core, wherein at least one of the core or the layer is formed from a composition comprising a base polymer, a crosslink initiator, and an additive comprising an aromatic iodonium compound or an aromatic iodonium salt.
表征谱图
-
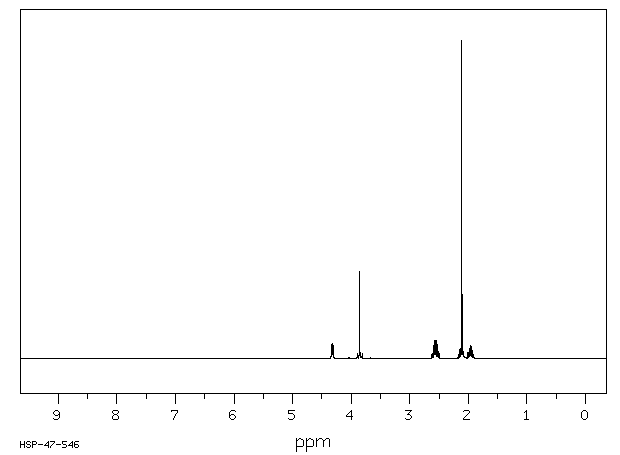
氢谱1HNMR
-
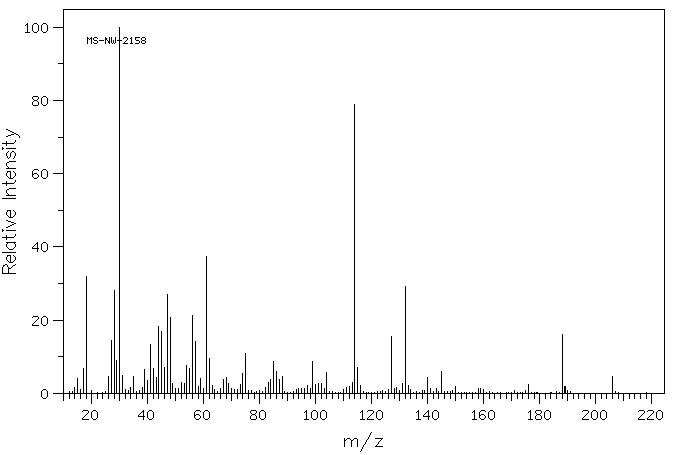
质谱MS
-
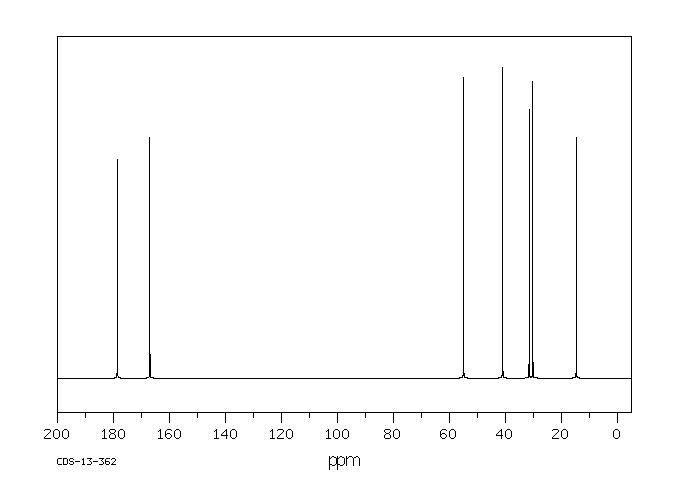
碳谱13CNMR
-
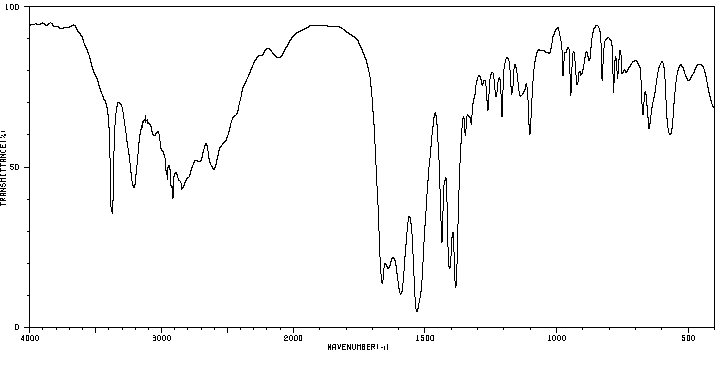
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸