丙烯酸羟乙酯 | 818-61-1
中文名称
丙烯酸羟乙酯
中文别名
丙烯酸羟基乙酯;N-丙烯酰基乙醇胺;乙二醇单丙烯酸酯;2-羟基乙基丙烯酸酯;乙二醇丙烯酸脂;丙烯酸-2-羟乙酯;丙烯酸-2-羟乙基酯;丙烯酸-2-羟基乙酯;丙烯酸-β-羟乙酯;HEA
英文名称
2-hydroxyethyl acrylate
英文别名
hydroxyethyl acrylate;2-hydroxylethyl acrylate;HEA;2-hydroxyethyl prop-2-enoate
CAS
818-61-1
化学式
C5H8O3
mdl
MFCD00002865
分子量
116.117
InChiKey
OMIGHNLMNHATMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-60 °C
-
沸点:90-92 °C12 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:1.106 g/mL at 20 °C
-
蒸气密度:>1 (vs air)
-
闪点:209 °F
-
暴露限值:ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3
-
LogP:-0.17 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Hydroxyethylacrylate appears as a clear colorless liquid. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. Corrosive to tissue. May polymerize exothermically if heated or contaminated. If the polymerization takes place inside a container, the container may rupture violently. Used to make plastics.
-
颜色/状态:Liquid
-
气味:Sweet pleasant odor
-
溶解度:In water, miscible /1X10+6 mg/L/ at 25 °C
-
蒸汽密度:Vapors heavier than air
-
蒸汽压力:0.0523 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
在常温常压下稳定,需避免与氧化物、热源、光(特别是紫外线)及自由基引发剂接触。
-
本品具有一定的毒性。实验表明,大鼠经口摄入0.1克/千克即显示出致死效应;吸入后会有明显的刺激作用。皮肤接触引起的刺激较为轻微,但对眼睛的伤害较大。操作时应佩戴防护眼镜。
-
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions. - Carbon oxides
-
粘度:5.2 mm²/s at 15 °C
-
腐蚀性:Corrosive to tissue
-
燃烧热:-10,800 Btu/lb = -6,000cal/g = -250X10+5 J/kg (est)
-
表面张力:Liquid surface tension: 28 dynes/cm = 0.028 N/m at 20 °C (est)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4482 at 25 °C
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.2
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.4
-
拓扑面积:46.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
毒理性
识别和使用:2-羟基乙基丙烯酸酯(HEA)是一种液体。HEA主要用于作为聚合物的共聚单体或在制造化学中间体时的化学反应物。在聚合物制造中,HEA可以与丙烯酸、丙烯酸酯、甲基丙烯酸酯、醋酸乙烯酯、氯乙烯、偏二氯乙烯、苯乙烯、丁二烯等进行共聚。与HEA反应的共反应物包括芳香族和脂肪族异氰酸酯、酐和环氧树脂。使用HEA制造的聚合物和化学中间体在汽车顶层涂料、建筑涂料、光固化树脂和粘合剂等领域有应用。HEA的衍生物曾作为实验性治疗进行测试。人体研究:在暴露浓度为3 ppm(名义值)及以上时,观察到眼睛和鼻子的刺激。刺激的严重程度随浓度增加而加剧,在10 ppm时可以忍受几分钟。对(甲基)丙烯酸酯进行15年贴片测试的经验总结显示,在440名有(甲基)丙烯酸酯暴露史的病人中,最常见的阳性测试反应是2-羟基乙基丙烯酸酯(9.6%)。动物研究:未稀释的HEA对皮肤有严重刺激作用。几项研究表明,未稀释的HEA对眼睛有严重刺激作用并可能造成损害。大鼠对HEA的吸入数据显示,7小时暴露于264 ppm(1250 mg/m³)没有致死效应。吸入暴露于333至394 ppm,分别为4或8小时,引起了刺激并处于致死阈值区域。在500 ppm及以上暴露时,接近100%的致死率被观察到。评估HEA急性皮肤毒性的关键研究使用了家兔,并应用了未稀释的测试材料。在塑料封闭绷带下,对家兔施以63、130、160、200或250 mg/kg体重的局部剂量,持续24小时。所有处理的动物都出现了明显的皮肤红斑和水肿,一些动物观察到轻微到中度的皮肤坏死。毒性临床体征包括嗜睡、活动减少、食欲减退,在250 mg/kg体重时,只有快速浅表呼吸。评估HEA急性口服毒性的关键研究是通过灌胃给四组大鼠分别施以266.7、400、600和900 mg/kg体重的10%溶液。动物在给药后观察了14天。各剂量水平下的死亡率为0/4、0/4、3/4和4/4。临床体征包括活动减少、粗糙毛发、呼吸困难、肌肉无力、死亡的动物出现胃肠道出血。纯净物质可能会烧伤口腔、喉咙和胃肠道的组织。在小鼠局部淋巴结试验中报告了阳性反应,表明HEA具有皮肤致敏性。在大鼠的慢性吸入研究中,5或0.5 ppm的处理组没有显示出显著慢性毒性或致癌效应的迹象(雄性和雌性大鼠每天暴露于HEA 6小时,每周5天,持续18个月)。HEA没有改变狗或大鼠的睾丸或子宫的组织病理学(狗饮食中最高达0.4%,大鼠最高达150 mg/kg体重/天)。在大鼠发育研究中,没有观察到与治疗相关的植入数量增加、胚胎/胎儿死亡率或胎儿畸形。在大鼠测试中,HEA的神经毒性潜力似乎最小。HEA在有无代谢活化的情况下对沙门氏菌属伤寒杆菌均不具有诱变性。生态毒性研究:使用瓦堡试验,HEA被认为对适应的污泥不具有毒性。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: 2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA) is a liquid. HEA is used mainly either as a co-monomer in the manufacture of polymers or as a chemical reactant in the manufacture of chemical intermediates. In the manufacture of polymers, HEA can be co-polymerized with acrylic acid, acrylates, methacrylates, vinyl acetate, vinyl chloride, vinylidene chloride, styrene, butadiene, and the like. Co-reactants with HEA include aromatic and aliphatic isocyanates, anhydrides, and epoxides. The polymers and chemical intermediates made with HEA find applications in automotive top coatings, architectural coatings, photocure resins, and adhesives. Derivatives of HEA had been tested as experimental therapy. HUMAN STUDIES: Irritation of eyes and nose was observed at exposure concentrations of 3 ppm (nominal) and higher. The severity of irritation increased with concentration and could be tolerated for several minutes at 10 ppm. A summary of 15 years of experience of patch testing to (meth)acrylates presented the results in 440 patients with a history of exposures to (meth)acrylates. The most frequent positive test reactions were seen with 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (9.6%). ANIMAL STUDIES: Undiluted HEA is severely irritating to the skin. Several studies have shown that undiluted HEA is severely irritating and can damage the eye. Inhalation data available for rats on HEA indicate that a 7 hour exposure of 264 ppm (1250 mg/cu m) had no lethal effect. Inhalation exposures to 333 to 394 ppm for 4 or 8 hours respectively caused irritation and were in the threshold area for lethality. At exposures at 500 ppm and above, close to 100% lethality was observed. The key study evaluating the acute dermal toxicity of HEA used rabbits and applied undiluted test material. Topical doses of 63, 130, 160, 200 or, 250 mg/kg bw were applied for 24 hours under a plastic occlusive bandage. Marked erythema and edema of the skin was seen in all treated animals and slight to moderate necrosis of the skin was observed in some animals. Clinical signs of toxicity were lethargy, decreased activity, loss of appetite and at 250 mg/kg bw only, rapid shallow breathing. The key study evaluating the acute oral toxicity of HEA administered as a 10% solution by gavage to groups of four rats at doses of 266.7, 400, 600, and 900 mg/kg bw. The animals were observed for 14 days post-dosing. The mortality was 0/4, 0/4, 3/4, and 4/4 at each dose level, respectively. Clinical signs included hypoactivity, rough fur, labored breathing, muscle weakness, GI tract hemorrhage in the animals that died. Neat material may burn the tissues of the mouth, throat and gastrointestinal tract. Positive responses have been reported in mice in the local lymph node assay indicating HEA dermal sensitization. There was no indication of significant chronic toxicity or a carcinogenic effect in either the 5 or 0.5 ppm treatment groups in rats in a chronic inhalation study (male and female were exposed to HEA 6 hours per day, 5 days/week for 18 months). HEA did not alter the histopathology of the testes or uterus in either dogs or rats (dogs up to 0.4% in the diet, rats up to 150 mg/kg bw/day). There were no treatment-related increases in the number of implants, embryo/fetal mortality, or fetal malformations observed in developmental study in rats. Neurotoxic potential of HEA appears to be minimal when tested in rats. HEA was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium with or without metabolic activation. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: Using the Warburg test, HEA was judged non-toxic to adapted sewage sludge.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过吸入其蒸汽、通过皮肤接触以及摄入进入人体。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation of its vapour, through the skin and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
咳嗽。喉咙痛。灼热感。呼吸困难。
Cough. Sore throat. Burning sensation. Laboured breathing.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
可能会被吸收!红色。疼痛。
MAY BE ABSORBED! Redness. Pain.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
红肿。疼痛。视力模糊。
Redness. Pain. Blurred vision.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
吸收、分配和排泄
2-羟基乙基丙烯酸酯(HEA)在一项研究中进行了评估,该研究检查了雄性Fischer 344大鼠通过口服、腹腔注射、皮肤和吸入途径暴露下的代谢和排泄情况... 对于口服和腹腔注射暴露途径,大鼠(每种剂量水平/暴露途径四只动物)单次接受了2.5或50毫克/千克体重的(14)C-HEA剂量。对于吸入暴露,六只大鼠在仅有头部的吸入室中暴露于目标浓度为8 ppm的(14)C-HEA,持续六小时。对于皮肤暴露,四只大鼠以50毫克/千克的剂量接受了(14)C-HEA处理。观察到的尿液代谢物在途径之间没有定性差异,表明HEA的代谢命运没有明显的途径依赖性差异。研究结果表明,一旦化学物质在体内系统性地可用,它就会被迅速代谢,并以呼出空气中的CO2或尿液代谢物的形式从体内排出,每条途径大约有相等百分比的管理/暴露剂量被消除。放射性消除的半衰期大约为尿液14小时和 17小时。尽管标签与母体HEA无关,但血浆中放射性消除的半衰期大约为26小时。HEA的代谢数据与其他丙烯酸酯的研究信息一致,其中酯功能的水解是主要的代谢途径。类比乙基丙烯酸酯和丙烯酸,预计HEA的一个次要代谢途径将与谷胱甘肽结合,产生的巯基酸衍生物通过尿液排出。
2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA) has been evaluated in a study that examined metabolism and excretion in male Fischer 344 rat using oral, intraperitoneal, dermal and inhalation routes of exposure ... For the oral and intraperitoneal routes of exposure the rats (four animals/dose level/route of exposure) received a single dose of (14)C-HEA at 2.5 or 50 mg/kg bw. For the inhalation exposure, six rats were exposed to a target concentration of 8 ppm (14)C-HEA for six hours in a head only inhalation chamber. For the dermal exposure, four rats were treated with (14)C-HEA at a dose of 50 mg/kg. No qualitative differences in urinary metabolites between routes were observed, indicating no marked route-dependent differences in the metabolic fate of HEA. The results of the study indicate that once the chemical becomes systemically available it is rapidly metabolized and eliminated from the body as either CO2 in the expired air or urinary metabolites with approximately equal percentage of administered/exposed dose eliminated by each route. The half-lives of elimination of radioactivity were approximately 14 hours for urine and 17 hours for CO2. The halflife of elimination of radioactivity from plasma was approximately 26 hours although the label was not associated with parent HEA. The available metabolic data on HEA is consistent with information on studies with other acrylates where hydrolysis of the ester functionality is the primary metabolic pathway. By analogy with ethyl acrylate and acrylic acid, it is expected that a minor metabolic pathway for HEA will be via conjugation with glutathione with the resulting mercapturic acid derivatives being excreted in the urine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
HEA的代谢和排泄已经在雄性Fischer 344大鼠中进行了研究,使用了口服、腹腔注射、皮肤和吸入等暴露途径... 对于口服和腹腔注射暴露途径,大鼠(每剂量水平/暴露途径4只动物)接受了单次剂量为2.5或50 mg/kg体重的HEA(大约15-20微居里)。对于吸入暴露,六只大鼠在一个仅头部吸入的实验舱中以8 ppm的目标浓度暴露于(14)C HEA,持续6小时。对于皮肤暴露,4只大鼠以12.5 mg/kg体重的剂量接受了(14)C HEA的处理。不同暴露途径之间在尿液代谢物上没有观察到定性差异,表明HEA的代谢命运没有明显的途径依赖性差异。研究结果表明,一旦化学物质在体内系统性地可用,它就会被迅速代谢并从体内排出,作为呼出空气中的CO2或尿液代谢物。关于HEA的代谢数据与具有其他丙烯酸酯类物质的物质的信息一致,其中酯功能的水解是主要的代谢途径。类似于乙基丙烯酸和丙烯酸,预计HEA的一个次要代谢途径是通过与谷胱甘肽结合,形成的巯基酸衍生物通过尿液排出。对于口服和腹腔注射途径(2.5 mg/kg体重),在给药后48小时内,35-36%的给药剂量以(14) 的形式呼出,43-47%的剂量通过尿液排出。在50 mg/kg体重时,40-45%的剂量以(14) 的形式呼出,33-36%的剂量通过尿液排出。经皮肤给药后,在给药后48小时内吸收了66%的剂量,剩余的33%与给药部位相关。吸收的剂量中有27%以HEA的代谢物形式通过尿液排出,27%以(14) 的形式通过呼出空气排出。对于吸入途径,48小时内通过尿液排出了吸收剂量的39%,41%以(14) 的形式呼出。对于所有途径,9-16%的剂量在组织和尸体中被发现,而在粪便中不到3%。
The metabolism and excretion of HEA has been examined in male Fischer 344 rat using oral, intraperitoneal, dermal and inhalation routes of exposure ... For the oral and intraperitoneal routes of exposure the rats (4 animals/dose level/route of exposure) received a single dose of 2.5 or 50 mg/kg bw (approx 15-20 uCi). For the inhalation exposure six rats were exposed to a target concentration of 8 ppm (14)C HEA for 6 hours in a head only inhalation chamber. For the dermal exposure 4 rats were treated with (14)C HEA at a dose of 12.5 mg/kg bw. No qualitative differences in urinary metabolites between routes were observed, indicating no marked route-dependent differences in the metabolic fate of HEA. The results of the study indicate that once the chemical becomes systemically available it is rapidly metabolized and eliminated from the body as either CO2 in the expired air or urinary metabolites. The available metabolic data on HEA is consistent with information on substances with other acrylates where hydrolysis of the ester functionality is the primary metabolic pathway. By analogy with ethyl acrylate and acrylic acid it is expected that a minor metabolic pathway for HEA will be via conjugation with glutathione with the resulting mercapturic acid derivatives being excreted in the urine. For the oral and intraperitoneal routes (2.5 mg/kg bw) 35-36% of the administered dose was expired as (14)CO2 and 43-47% of the dose excreted via the urine by 48 hours post-dosing. At 50 mg/kg bw 40-45% of the dose was expired as (14)CO2 and 33-36% of the dose was excreted in the urine. Following dermal administration 66% of the dose was absorbed within 48 hours of the application with remaining 33% being associated with the application site. Of the absorbed dose 27% was excreted in the urine as metabolites of HEA and 27% was excreted in the expired air as (14)CO2. For inhalation 39% of the absorbed dose was eliminated in the urine by 48 hr and 41% was expired as (14)CO2. For all routes, 9-16% was found in the tissues and carcass and less than 3% in the feces.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在给Fisher 344雄性大鼠口服给药(14)C-HEA后,给药的放射活性的91%至95%在尿液中、二氧化碳、粪便、组织、尸体、挥发性有机物和最终笼子清洗中被回收。在2.5 mg (14)C-HEA/kg体重这种低剂量下,口服给药途径大约有43-47%的剂量通过尿液排出,这是主要的消除途径,而有35-36%的剂量以(14)CO2的形式呼出,组织和尸体占剂量的9-13%。给药的放射活性中不到1.5%在粪便中被回收,不到1%在最终的笼子清洗中被发现。剂量中不到0.2%以挥发性有机物的形式在呼出的空气中回收。
在50 mg/kg (14)C-HEA/kg体重这种较高剂量下,口服给药途径有33-36%的剂量通过尿液排出,而有40-45%的剂量以(14) 的形式呼出。在这个较高剂量下,主要的消除途径从尿液途径转变为以呼出(14) 作为主要的消除途径。与2.5 mg/kg剂量一样,组织和尸体占剂量的10-13%,回收的放射活性中不到0.6%在最终的笼子清洗中,不到0.1%以挥发性有机物的形式在呼出的空气中回收,不到2.5%的剂量在粪便中被回收。
口服给药后,剂量的0.3-1.5%在给药后15分钟内就以(14) 的形式呼出。 排泄的峰值发生在4-8小时收集间隔期间或之前。在口服给药2.5 mg/kg后12小时,剂量的31-32%以(14) 的形式呼出。在50 mg/kg口服给药后相同的收集间隔期间,剂量的41%以(14) 的形式呼出。(14)C-HEA来源的(14) 呼出似乎遵循一级动力学作为双相过程,除了经皮给药后。口服给药后,通过尿液排出的总放射活性的92%以上在前12小时收集间隔期间被排出。
Following oral administration of (14)C-HEA to Fisher 344 male rats, between 91 and 95% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine, CO2, feces, tissues and carcass, volatile organics and final cage wash. At the low dose of 2.5 mg (14)C-HEA/kg body weight, for the oral route of administration, approximately 43-47 % of the dose was eliminated in the urine, the primary elimination route, whereas 35-36% of the dose was expired as (14)CO2, and the tissues and carcass accounted for between 9-13 % of the dose. Less than 1.5% of the administered dose of radioactivity was recovered in the feces and less than 1% was found in the final cage wash. Less than 0.2% of the dose was recovered as volatile organics in the expired air. At the higher dose of 50 mg/kg (14)C-HEA/kg body weight, for the oral route of administration, 33-36% of the dose was eliminated in the urine, whereas 40-45% of the dose was expired as (14)CO2. At this higher dose there was a shift from the urinary pathway as the primary route of elimination to the exhalation of (14)CO2 as the primary route of elimination. As with the 2.5 mg/kg dose, the tissues and carcass accounted for 10-13% of the dose and less than 0.6% of the recovered radioactivity was in the final cage wash, less than 0.1% was recovered as volatile organics in the expired air and less than 2.5% of the dose was recovered in the feces. Following the oral route of administration, 0.3-1.5% of the dose was expired as (14)CO2 as early as 15 minutes post-dosing. The peak of CO2 excretion occurred during or before the 4-8 hr collection interval. By 12 hr post-dosing with 2.5 mg/kg for the oral route of administration, 31-32 of the dose was expired as (14)CO2. For this same collection interval following 50 mg/kg oral administration, 41 of the dose was expired as (14)CO2. The exhalation of (14)CO2 derived from (14)C-HEA appeared to follow first-order kinetics as a biphasic process, except following dermal administration. Following oral administration, greater than 92% of the total radioactivity excreted via the urine was excreted during the first 12 hr collection interval.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:8
-
危险品标志:T,N
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39,S36/39,S45,S61
-
危险类别码:R24,R43,R20/22,R34,R50
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2916129000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2927 6.1/PG 2
-
危险类别:8
-
RTECS号:AT1750000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS05,GHS06,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H302,H311,H314,H317,H400
-
危险性防范说明:P273,P280,P303 + P361 + P353,P304 + P340 + P310,P305 + P351 + P338,P333 + P313
-
储存条件:储存时应保持在干燥的惰性气体中,并确保容器密封。存放于阴凉、干燥的地方。 该物质采用镀锌铁桶包装,应储存在阴凉通风处。仓库需专用,不得与其他物品混放。注意防火安全,在储存和运输前应加入阻聚剂。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 丙烯酸-2-羟乙酯;乙二醇单丙烯酸酯 |
| 化学品英文名称: | 2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate;Acrylic acid-2-hydroxyethyl ester |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 818-61-1 |
| 分子式: | C 5 H 8 O 3 |
| 分子量: | 116.13 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:丙烯酸-2-羟乙酯;乙二醇单丙烯酸酯 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 吸入、摄入或经皮肤吸收后均会中毒。对眼睛和皮肤有刺激作用。遇热分解释出有腐蚀性的烟雾。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品易燃,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。与强氧化剂接触可发生化学反应。容易自聚,聚合反应随着温度的上升而急骤加剧。若遇高热,容器内压增大,有开裂和爆炸的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | 消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服,在上风向灭火。 |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 98 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。用砂土、干燥石灰或苏打灰混合,收集于一个密闭的容器中,运至废物处理场所。也可以用大量水冲洗,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,局部排风。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩),戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防静电工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。在清除液体和蒸气前不能进行焊接、切割等作业。避免产生烟雾。避免与氧化剂、酸类、碱类接触。容器与传送设备要接地,防止产生静电。灌装时应控制流速,且有接地装置,防止静电积聚。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。库温不宜超过30℃。保持容器密封,严禁与空气接触。应与氧化剂、酸类、碱类分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,加强通风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度超标时,必须佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,应该佩戴空气呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防静电工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴橡胶手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色透明液体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | <-70 |
| 沸点(℃): | 210 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.1098 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 98 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 5 H 8 O 3 |
| 分子量: | 116.13 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水、普通溶剂。 |
| 主要用途: | 用于制备热固性涂料、粘结剂、纤维处理剂、润滑油添加剂及共聚物改性剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 不稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强酸、强碱。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 能发生 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:无资料 LC50:无资料 |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | 家兔经皮:开放性刺激试验, 500mg,中度刺激。家兔经眼:20mg/24 小时,中度刺激。 |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 建议用焚烧法处置。在能利用的地方重复使用容器或在规定场所掩埋。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | 无资料。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与氧化剂、酸类、碱类、食用化学品等混装混运。运输车船必须彻底清洗、消毒,否则不得装运其它物品。船运时,配装位置应远离卧室、厨房,并与机舱、电源、火源等部位隔离。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 5 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
丙烯酸羟乙酯的应用
丙烯酸羟乙酯在油脂工业用作润滑油洗涤的添加剂,在电子工业中则作为电子显微镜的脱水剂。在纺织工业,它用于制造织物胶粘剂。此外,其在分析化学中用作化学试剂,并且还被用作水溶性的包埋剂等。
化学性质丙烯酸羟乙酯是一种无色液体,熔点为-70℃,沸点为90-92℃(1.6kPa),74-75℃(667Pa)。其相对密度为1.1098(20/4℃),折射率为1.4469,闪点(开杯)为104℃,粘度为5.34mPa·s(25℃)。该液体与水混溶,并可溶解于一般有机溶剂。商品中通常含有阻聚剂氢醌一甲基醚,浓度约为400ppm。
用途该产品可以与丙烯酸及其酯类、丙烯醛、丙烯腈、丙烯酰胺、甲基丙烯腈、氯乙烯、苯乙烯等许多单体共聚。所得产物可用于处理纤维,以提高纤维的耐水性、耐溶剂性、防皱性和防水性;还用于制造性能优良的热固性涂料和合成橡胶,并用作润滑油添加剂。在粘合剂方面,与乙烯基单体共聚可改善其粘接强度。此外,在纸加工方面,丙烯酸羟乙酯可用于制备涂层用的丙烯酸乳液,以提高其耐水性和强度。
辐射固化体系中的应用丙烯酸羟乙酯亦可用作辐射固化体系中的活性稀释剂和交联剂,也可以作为树脂交联剂、塑料及橡胶改性剂。
生产方法丙烯酸与环氧乙烷在催化剂及阻聚剂的存在下进行加成反应,生成粗成品后,通过脱气和蒸馏步骤获得最终产品。生产消耗定额为:每吨原料需要710kg的丙烯酸和485kg的环氧乙烷。
安全信息上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2-(vinyloxy)ethyl acrylate 41440-38-4 C7H10O3 142.155 —— methylene-bis(oxyethyl acrylate) —— C11H16O6 244.244 丙烯酸甲酯(MA) acrylic acid methyl ester 96-33-3 C4H6O2 86.0904 —— hydroxy-ethyl acrylate 13331-72-1 C5H8O3 116.117 丙烯酸丁酯 acrylic acid n-butyl ester 141-32-2 C7H12O2 128.171 丙烯酸丁酯 acrylic acid n-butyl ester 141-32-2 C7H12O2 128.171 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-乙酰氧基乙基丙-2-烯酸酯 2-acetoxyethyl acrylate 55231-03-3 C7H10O4 158.154 —— methylene-bis(oxyethyl acrylate) —— C11H16O6 244.244 甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate 868-77-9 C6H10O3 130.144 —— acryloxyacetaldehyde 150753-10-9 C5H6O3 114.101 2-((氯甲酰基)氧基)乙基丙烯酸酯 acryloyloxyethyl chloroformate 41892-42-6 C6H7ClO4 178.572 —— 2-hydroxyethyl 2-iodoacrylate 1422263-06-6 C5H7IO3 242.013 —— Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) but-2-enedioate 45125-84-6 C8H12O6 204.18 —— acrylic acid 2-ethoxycarbonyloxy-ethyl ester 17650-45-2 C8H12O5 188.18 —— 2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl methacrylate 69040-48-8 C9H12O4 184.192 2-丙烯酰基氧基乙氧基三甲基硅烷 2-(trimethylsilyloxy)ethyl acrylate 18269-99-3 C8H16O3Si 188.299 丙烯酸丁酯 acrylic acid n-butyl ester 141-32-2 C7H12O2 128.171 丙烯酸氰乙酯 acrylic acid 2-cyano-ethyl ester 106-71-8 C6H7NO2 125.127 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:丙烯酸羟乙酯 在 三乙胺 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 29.0h, 生成 2-[3-[Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]propanoyloxy]ethyl 2-bromo-2-methylpropanoate参考文献:名称:Synthesis of Well-Defined Y-Shaped Zwitterionic Block Copolymers via Atom-Transfer Radical Polymerization摘要:A series of well-defined Y-shaped (AB(2)-type) zwitterionic block copolymers were synthesized by atom-transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). First, a bishydroxy-functional ATRP initiator was synthesized by esterification of 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate with 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide, followed by Michael addition using excess diethanolamine. 2-(Diethylamino)ethyl methacrylate (DEA) was polymerized via ATRP using this bishydroxy-functional initiator. The bromine end groups of PDEA were then quantitatively removed by radical chain transfer using excess N,N,N',N",N"-pentamethyldiethylenetri-amine (PMDETA). Esterification of the omega-bishydroxyl end groups using excess 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide afforded a PDEA-based omega-bifunctional macroinitiator [PDEA-(Br)(2)]. A series of Y-shaped zwitterionic PDEA-(PSEMA)(2) [PSEMA poly(succinyloxyethyl methacrylate)] block copolymers were synthesized via ATRP of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) using this PDEA-(Br)(2) macroinitiator, followed by reacting the HEMA hydroxyl groups with succinic anhydride. The 'schizophrenic' micellization character of these Y-shaped zwitterionic block copolymers in aqueous solution was confirmed by H-1 NMR spectroscopy, aqueous electrophoresis, and dynamic light-scattering studies.DOI:10.1021/ma048511j
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Process for preparing hydroxyalkyl acrylates and methacrylates摘要:公开号:US02877264A1
-
作为试剂:描述:2-羟基苯硫酚 、 硫代磷酸三(4-苯基异氰酸酯) 在 丙烯酸羟乙酯 作用下, 以 乙酸丁酯 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以83%的产率得到2-[[4-Bis[4-(phenylsulfanylcarbonylamino)phenoxy]phosphinothioyloxyphenyl]carbamoyloxy]ethyl prop-2-enoate参考文献:名称:一种高折射率树脂及其应用摘要:本发明涉及一种高折射率树脂,所述树脂具有如下通式:。本发明的树脂折射率较高,达到1.58以上,可以用于光学薄膜材料的硬化涂层中,能够提高聚酯薄膜的折射率。公开号:CN105418674A
文献信息
-
磷酸酯类交联剂及其制备方法、磷酸酯基交联凝胶聚合物电解质及其制备方法和应用
-
含氮磷一元醇或多元醇及其制备方法
-
Adamantyl Antiestrogens with Novel Side Chains Reveal a Spectrum of Activities in Suppressing Estrogen Receptor Mediated Activities in Breast Cancer Cells作者:Jian Min、Valeria Sanabria Guillen、Abhishek Sharma、Yuechao Zhao、Yvonne Ziegler、Ping Gong、Christopher G. Mayne、Sathish Srinivasan、Sung Hoon Kim、Kathryn E. Carlson、Kendall W. Nettles、Benita S. Katzenellenbogen、John A. KatzenellenbogenDOI:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00585日期:2017.7.27To search for new antiestrogens more effective in treating breast cancers, we explored alternatives to the acrylic acid side chain used in many antiestrogens. To facilitate our search, we used a simple adamantyl ligand core that by avoiding stereochemical issues enabled rapid synthesis of acrylate ketone, ester, and amide analogs. All compounds were high affinity estrogen receptor α (ERα) ligands but为了寻找在乳腺癌中更有效的新型抗雌激素,我们探索了许多抗雌激素中丙烯酸侧链的替代物。为了方便我们的搜索,我们使用了一个简单的金刚烷基配体核心,该核心通过避免立体化学问题而实现了丙烯酸酯,酯和酰胺类似物的快速合成。所有化合物均为高亲和力雌激素受体α(ERα)配体,但作为抗增殖剂和ERα下调剂表现出一系列功效和功效。具有微小结构变化的化合物之间的活性差异很大,但抗增殖和ERα下调的功效通常相互平行。一些具有侧链极性基团的化合物具有特别高的亲和力。次生羧酰胺具有最佳的细胞活性,3-羟丙基酰胺在抑制细胞增殖和基因表达方面与氟维司群一样有效。这项研究基于简单的金刚烷基核心结构以及针对细胞拮抗剂活性进行了优化的丙烯酸酯侧链,生产出了结构新颖的抗雌激素药。
-
ASYMMETRIC BIFUNCTIONAL SILYL MONOMERS AND PARTICLES THEREOF AS PRODRUGS AND DELIVERY VEHICLES FOR PHARMACEUTICAL, CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL AGENTS申请人:The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill公开号:US20170021030A1公开(公告)日:2017-01-26Asymmetric bifunctional silyl (ABS) monomers comprising covalently linked pharmaceutical, chemical and biological agents are described. These agents can also be covalently bound via the silyl group to delivery vehicles for delivering the agents to desired targets or areas. Also described are delivery vehicles which contain ABS monomers comprising covalently linked agents and to vehicles that are covalently linked to the ABS monomers. The silyl modifications described herein can modify properties of the agents and vehicles, thereby providing desired solubility, stability, hydrophobicity and targeting.
-
ArNMeCH(SiMe<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>: a useful precursor of formal α-aminoalkyl diradicals in visible-light-mediated homo- and hetero-diaddition with alkenes作者:Shunfa Liu、Yufan Yang、Lu Gao、Zhenlei SongDOI:10.1039/d0cc02277b日期:——ArNMeCH(SiMe3)2 has been developed as a useful precursor of a formal α-aminoalkyl diradical in Ru(bpy)3Cl2-catalzyed addition with alkenes under visible-light-mediated photoredox conditions. This approach leads to homo-diaddition with two identical alkenes in one-pot, or hetero-diaddition with two different alkenes via a sequential operation.ArNMeCH(SiMe 3)2被开发为在可见光-介导的光氧化还原条件下,Ru(bpy)3 Cl 2-催化加成烯烃的形式α-氨基烷基双自由基的有用前体。该方法导致在一个反应釜中具有两个相同烯烃的均二价加成,或通过顺序操作导致具有两个不同烯烃的异二价加成。
表征谱图
-
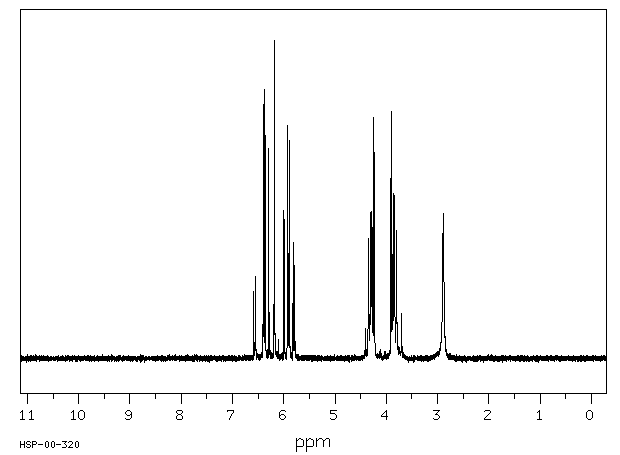
氢谱1HNMR
-
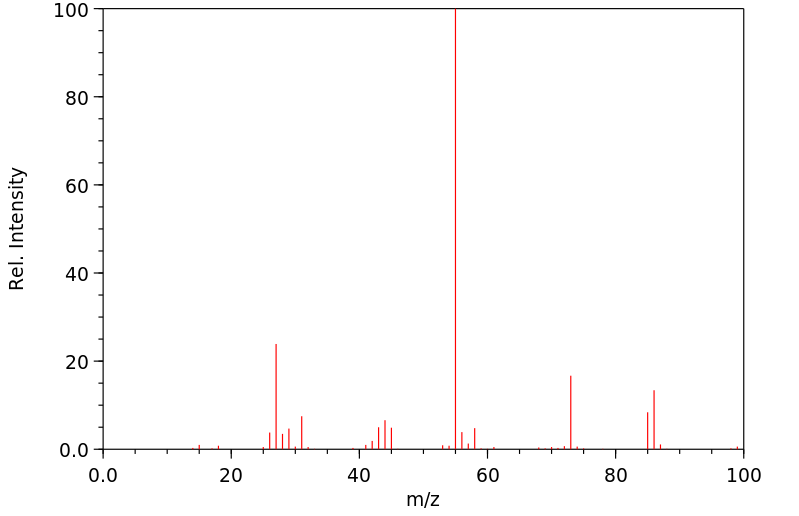
质谱MS
-
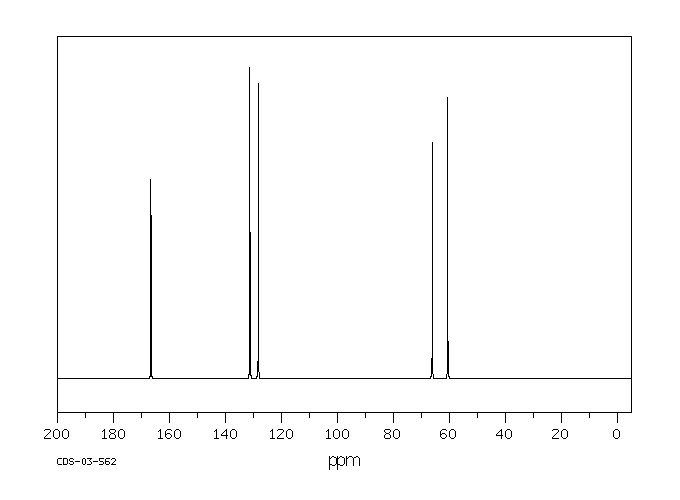
碳谱13CNMR
-
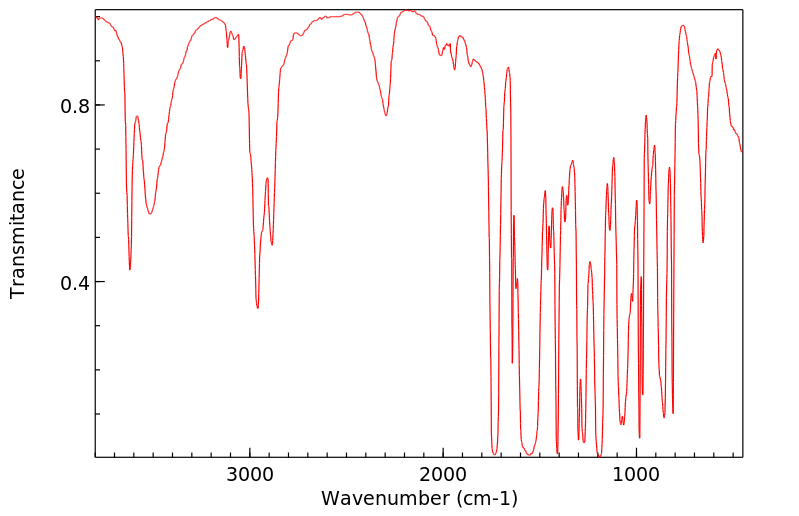
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸