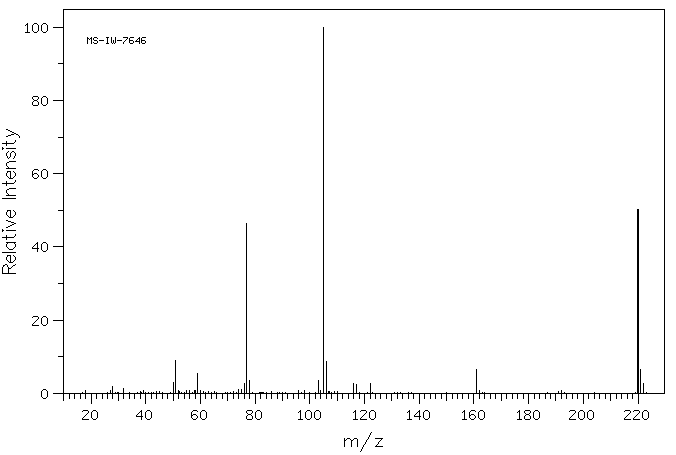
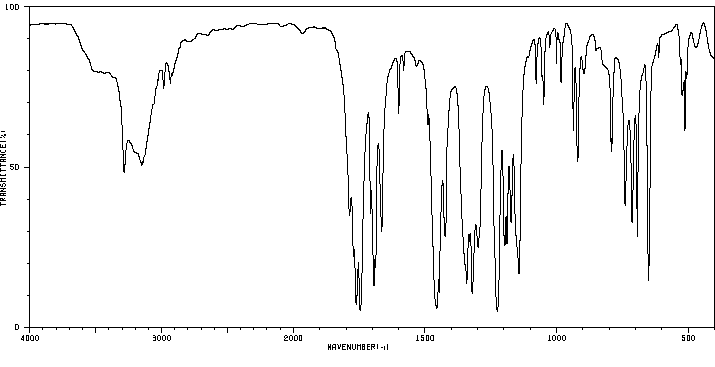
1-苯甲酰基-2-硫代-4-咪唑烷酮 | 577-47-9
中文名称
1-苯甲酰基-2-硫代-4-咪唑烷酮
中文别名
——
英文名称
1-benzoyl-2-thioxo-imidazolidin-4-one
英文别名
1-Benzoyl-2-thiohydantoin;1-benzoyl-2-sulfanylideneimidazolidin-4-one
CAS
577-47-9
化学式
C10H8N2O2S
mdl
MFCD00451759
分子量
220.252
InChiKey
YTMVOQHVLQJLML-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.2
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.1
-
拓扑面积:81.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:A New Glycociamidine Ring Precursor: Syntheses of (Z)-Hymenialdisine, (Z)-2-Debromohymenialdisine, and (±)-endo-2-Debromohymenialdisine摘要:[GRAPHICS]The synthesis of the C-1,H-5 marine sponge alkaloids, (Z)-hymenialdisine and (Z)-2-debromohymenialdisine, is described. A key step was the condensation between aldisine or its monobromo derivative and a new, efficient imidazolinone-based glycociamidine precursor. In the first case, the main product turned out to be the unprecedented (+/-)-endo-2-debromohymenialdisine.DOI:10.1021/ol052266m
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:刚性双(磺酰基)乙烯作为不对称催化的有效迈克尔受体:在季乙内酰脲的对映选择性合成中的应用摘要:开发了乙内酰脲替代物II与“刚性化”亚乙烯基双(砜)试剂的催化、对映和非对映选择性加成,从而克服了常用的 β-取代乙烯基砜无法反应的问题。加合物通过水解和还原脱磺酰化过程转化为富含对映体的 5,5-二取代乙内酰脲,为最终的生物测定提供新结构。还提供了使观察到的反应性和立体选择性趋势合理化的密度泛函理论研究。DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.2c02403
文献信息
-
Thiohydantoins. XI Kinetic Studies of the Alkaline Hydrolysis of 1-Acyl-2-thiohydantoins作者:Wayne I. Congdon、John T. EdwardDOI:10.1139/v72-598日期:1972.12.1
1-Acyl-2-thiohydantoins ionize in alkaline solution (pK ∼ 7). In solutions more alkaline than pH > 11 they are rapidly hydrolyzed to 2-thiohydantoin and a carboxylic acid, by attack of a hydroxide ion on the conjugate base of the 1-acyl-2-thiohydantoin. Possible mechanisms to accord with the entropy of activation, which is less negative than usual for base-catalyzed amide hydrolyses, are discussed. 1-Benzoyl-2-thiohydantoin hydrolyzes more rapidly than 1-acetyl-2-thiohydantoin, possibly because the ground state of the former molecule is destabilized by steric effects.
-
Swan, Australian Journal of Scientific Research, Series A: Physical Sciences, 1952, vol. 5, p. 728,732作者:SwanDOI:——日期:——
-
1015. Thiohydantoins. Part II. Alkaline hydrolyses作者:J. T. Edward、S. NielsenDOI:10.1039/jr9570005080日期:——
-
Johnson; Hill; Bailey, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1915, vol. 37, p. 2415作者:Johnson、Hill、BaileyDOI:——日期:——
-
Johnson; Nicolet, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1911, vol. 33, p. 1976作者:Johnson、NicoletDOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸