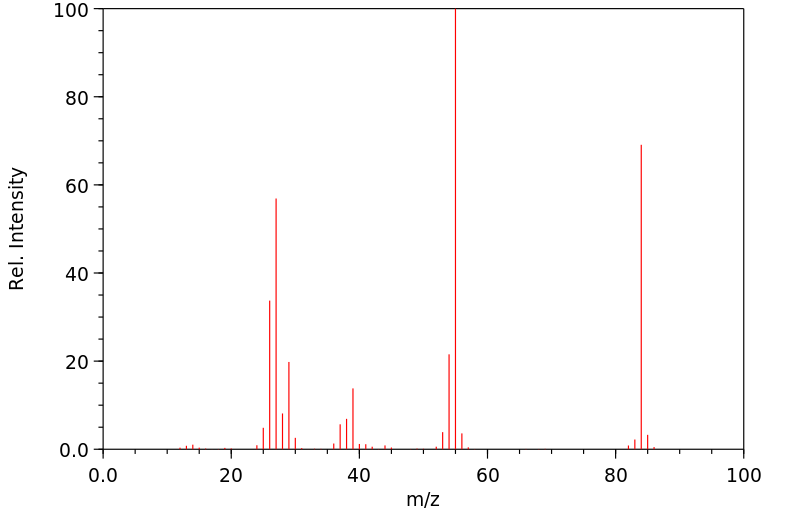
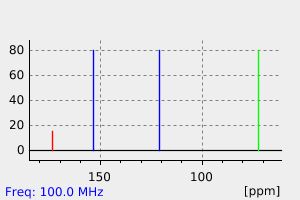
毒理性
识别和使用:2(5H)-呋喃酮是一种内源性饱腹物质,能够抑制食欲和/或食物摄入。实验动物模型显示,2-呋喃酮作为治疗肥胖和自身免疫疾病的药物具有前景。人类暴露和毒性:2-呋喃酮和2-吡咯酮在细胞中诱导细胞DNA损伤和拓扑异构酶I-和拓扑异构酶II-DNA复合物的形成。这两种内酯在人类细胞系中具有细胞毒性:在A549肺癌细胞中的浓度低于MRC5非恶性肺纤维细胞。这些结果提示2-呋喃酮和2-吡咯酮可能具有抗癌和DNA损伤活性。动物毒性研究:为了研究2-呋喃酮对食物摄入的影响,将Wistar大鼠进行各种应用。腹膜内给药剂量为30至100 mg/kg时,食物摄入量呈剂量依赖性下降,但饮水模式和运动活动没有显著影响。2-呋喃酮经胃内给药和第三脑室给药也剂量依赖性地减少了食物摄入。在其他研究中,测试了2-呋喃酮对猕猴进食行为的影响。将套管植入三只成年雄性猕猴的第三脑室。在不同的日子,于食物呈现前五分钟,通过脑室内给药不同剂量的2-呋喃酮。产生显著饱腹效果的 有效剂量是20.0 mg,而10.6 mg产生轻微效果,25.0 mg产生严重效果。这项研究表明,猕猴和大鼠中存在2-呋喃酮饱腹机制。2-呋喃酮(5 mg/kg)的腹膜内注射促进了小鼠的空间表现。此外,2-呋喃酮还抑制了Lewis大鼠实验性变态反应脑炎的临床症状[通过髓鞘碱性蛋白(MBP)免疫诱导],这是人类多发性硬化的模型。MBP免疫后,MBP的迟发型超敏反应在2-呋喃酮处理的大鼠中也有所减少。这些结果表明,2-呋喃酮不仅是一种强大的饱腹物质,而且还是记忆促进和免疫功能的调节剂。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: 2(5H)-Furanone is an endogenous satiety substance which suppresses appetite and/or food intake. Experimental animal models show promise for therapeutic use of 2-furanone as medication for treatment of obesity and autoimmune diseases. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: 2-furanone and 2-pyrone induce cellular DNA damage and the formation of topoisomerase I- and topoisomerase II-DNA complexes in cells. Both lactones were cytotoxic in human cell lines: in A549 lung cancer cells at lower concentrations than in MRC5 non-malignant lung fibroblasts. These results suggest possible anticancer and DNA-damaging activities for 2-furanone and 2-pyrone. ANIMAL TOXICITY STUDIES: To study the effect of 2-furanone on food intake, Wistar rats were subjected to various applications. Intraperitoneal administration in doses of 30 to 100 mg/kg decreased food intake dose-dependently, but drinking patterns and locomotor activity were not significantly affected. Administration of 2-furanone intragastrically, and intra-third cerebroventricularly also dose-dependently reduced food intake. In other studies effect on feeding behavior of Rhesus monkey was tested. The cannula was implanted in the third ventricle of three adult male Rhesus monkeys. Various doses of 2-furanone were administered intracerebroventricularly on different days five minutes prior to presentation of food. The effective dose for inducing significant satiety effect was 20.0 mg, while 10.6 mg induced a mild and 25.0 mg a severe effect. This study is suggestive of the presence of 2-furanone satiety mechanism in monkeys and rats. The intraperitoneal injection of 2-furanone (5 mg/kg) facilitated the spatial performance in mice. In addition, 2-furanone also suppresses the clinical symptoms of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats [induced by immunization with a myelin basic protein (MBP)], a model for human multiple sclerosis. After immunization with MBP, the delayed-type hypersensitivity response to MBP is also reduced in 2-furanone-treated rats. These results indicate that 2-furanone is not only a powerful satiety substance, but also effective as a memory facilitation and a modulator of immune functions.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)