烯丙基辛基醚 | 3295-97-4
中文名称
烯丙基辛基醚
中文别名
烯丙基正辛基醚
英文名称
allyl octyl ether
英文别名
1-(allyloxy)octane;Allyl n-octyl ether;1-prop-2-enoxyoctane
CAS
3295-97-4
化学式
C11H22O
mdl
MFCD00015294
分子量
170.295
InChiKey
IELYMBBIHQDONA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:206 °C
-
密度:0.81
-
稳定性/保质期:
常温常压下稳定,密度为0.81 g/mL(25/4 ℃),沸点为206 ºC。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.1
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:9
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.818
-
拓扑面积:9.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
海关编码:2909199090
-
储存条件:常温、避光、通风干燥处,密封保存。
SDS
烯丙基正辛基醚 修改号码:6
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Allyl n-Octyl Ether
修改号码: 6
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第4级
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 可燃液体
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 远离明火/热表面。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
烯丙基正辛基醚 修改号码:6
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 烯丙基正辛基醚
百分比: >95.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 3295-97-4
分子式: C11H22O
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离明火和热表面。
采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 使用封闭系统,通风。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
存放于惰性气体环境中。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
气敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
烯丙基正辛基醚 修改号码:6
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 206 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.81
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 明火
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
烯丙基正辛基醚 修改号码:6
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Allyl n-Octyl Ether
修改号码: 6
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第4级
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 可燃液体
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 远离明火/热表面。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
烯丙基正辛基醚 修改号码:6
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 烯丙基正辛基醚
百分比: >95.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 3295-97-4
分子式: C11H22O
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离明火和热表面。
采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 使用封闭系统,通风。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
存放于惰性气体环境中。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
气敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
烯丙基正辛基醚 修改号码:6
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 206 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.81
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 明火
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
烯丙基正辛基醚 修改号码:6
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Highly practical iron-catalyzed C–O cleavage reactions摘要:在乙基镁氯的存在下,容易用铁催化剂切断各种烯丙基、肉桂基和苄基的C–O键。该方法操作简单(用二甲苯–四氢呋喃,在室温下反应1小时),所需催化剂用量低(1 mol% FeCl2),并且对卤素、酯、胺、醚和烯烃具有耐受性。烯丙基部分转化为挥发性烃,省去了繁琐的产品分离步骤。DOI:10.1039/c3cy00266g
-
作为产物:描述:(2S)-2-(octoxymethyl)thiirane 以99%的产率得到参考文献:名称:Gesson J. P., Jacquesy J. C., Rambaud D., Tetrahedron, 49 (1993) N 11, S 2239-2248摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Solid State Polymerization Process for Polyester with Phosphinic Acid Compounds申请人:Odorisio Paul公开号:US20130035451A1公开(公告)日:2013-02-07Disclosed are phosphinic acid compounds of formula I, II or III where R 1 and R 1 ′ are for instance straight or branched C 1 -C 50 alkyl, R 2 is for instance straight or branched C 22 -C 50 alkyl, R 3 and R 3 ′ are for instance straight or branched C 1 -C 50 alkyl, R 4 is for instance straight or branched C 1 -C 50 alkylene and m is from 2 to 100. Also disclosed are polyester compositions comprising the compounds of formula I, II and III.
-
A mild and rapid regeneration of alcohols from their allylic ethers by chlorotrimethylsilane/sodium iodide
-
Vinyl polymerization versus [1,3] O to C rearrangement in the ruthenium-catalyzed reactions of vinyl ethers with hydrosilanes作者:Nari-aki Harada、Takashi Nishikata、Hideo NagashimaDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2012.02.025日期:2012.4reaction does not give the polyvinyl ether but results in [1,3] O to C rearrangement to give the corresponding aldehyde, RCH2CHO in moderate to good yields. The rearrangement selectively proceeds when vinyl ethers having α-substituents are used as the starting materials to give the corresponding ketones in high yields. With catalytic amounts of hydrosilanes, the rearrangement gives ketones or aldehydes selectively
-
Graphite-Catalyzed Acylative Cleavage of Ethers with Acyl Halides作者:Yoshitada Suzuki、Masayuki Matsushima、Mitsuo KodomariDOI:10.1246/cl.1998.319日期:1998.4Graphite is found to catalyze acylative cleavage of ethers such as benzylic, allylic, tert-butylic and cyclic ethers with acyl halides to give the corresponding esters in good to excellent yields. Benzylic ether was cleaved chemoselectively, when a variety of other functional groups was present, to produce the corresponding ester along with benzyl halide.
-
Zeolite-Promoted Benzylation of Alcohols作者:Makoto Onaka、Motomitsu Kawai、Yusuke IzumiDOI:10.1246/bcsj.59.1761日期:1986.6Zeolite-promoted benzylation of alcohols with benzyl chloride has been investigated. By use of a series of cation-exchanged zeolites, which have the same crystalline structure but different acid and base properties, it is confirmed that the cooperative function of acid sites and base sites of zeolite is required for the effective benzylation of alcohols although both acid and base strengths are low. It is also found that alcohols show different reactivities in zeolite from those in solution depending on their molecular structures because the benzylation is promoted inside the narrow cavities of zeolite.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
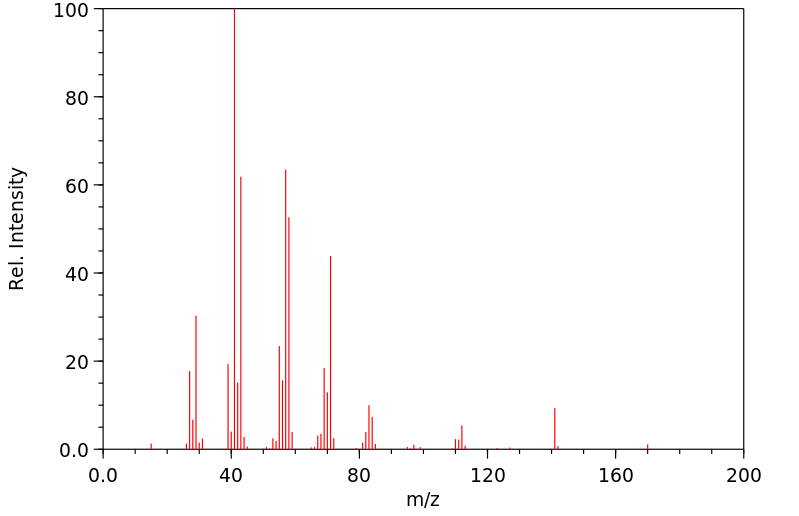
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
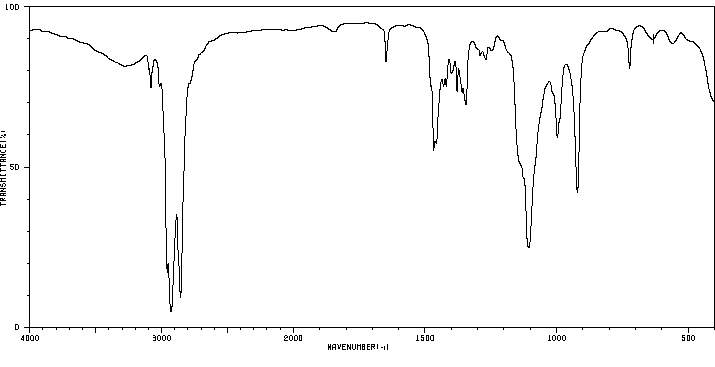
红外IR
-
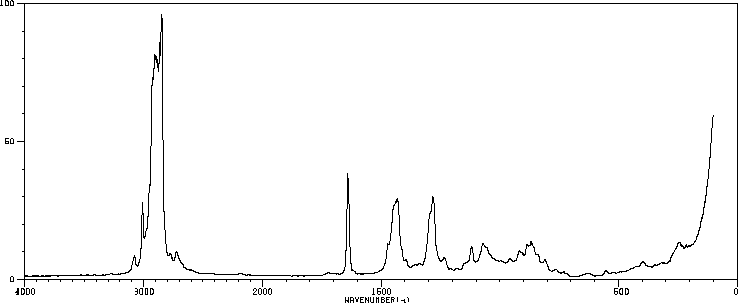
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷