美雄酮 | 72-63-9
物质功能分类
分子结构分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:165-166 °C
-
沸点:381.66°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.0597 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:-2℃
-
溶解度:乙腈:1mg/mL;乙醇:1mg/mL;甲醇:1mg/mL
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:Crystals from acetone and ether
-
气味:ODORLESS
-
蒸汽压力:1.2X10-8 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
旋光度:Specific optical rotation: 0 at 26 °C/D (1.15%, chloroform)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.6
-
重原子数:22
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.75
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:F,T
-
安全说明:S45,S53
-
危险类别码:R60,R61,R11,R19,R38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2942000000
-
危险品运输编号:3249
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
RTECS号:BV8000000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:2-8°C
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 17b-羟基-17a-甲基-1,4-雄甾二烯-3-酮
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
MethandrOStenolone
Methandienone
Dianabol
1-Dehydro-17α-methyltestOSterone
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
根据化学品全球统一分类与标签制度(GHS)的规定,不是危险物质或混合物。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: MethandrOStenolone
别名
Methandienone
Dianabol
1-Dehydro-17α-methyltestOSterone
: C20H28O2
分子式
: 300.44 g/mol
分子量
无
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
某些类固醇表明有致癌或畸胎生成效应, 据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
建议的贮存温度: 2 - 8 °C
对光线敏感
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
常规的工业卫生操作。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所来选择人体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 结晶
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 164 - 166 °C
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
无数据资料
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - > 1,000 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
细胞突变性-体内试验 - 老鼠 - 经口
显性致死实验
致癌性
致癌性 - 人 - 雄性 - 经口
肿瘤发生:符合RTECS标准的致癌性。 肝脏:肿瘤
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
致畸性 - 大鼠 - 经口
父体效应:睾丸、附睾、输精管。 父体效应:其他对男性的影响。
致畸性 - 大鼠 - 经口
母体效应:卵巢、输卵管。 母体效应:子宫、宫颈、阴道。
致畸性 - 大鼠 - 皮下的
母体效应:卵巢、输卵管。 母体效应:子宫、宫颈、阴道。 对生殖的影响:其他生殖力相关检测。
致畸性 - 人 - 雄性 - 经口
父体效应:精子发生(包括遗传物质、精子形态、活力和数量)。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
某些类固醇表明有致癌或畸胎生成效应, 据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: BV8000000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
美雄酮是甲睾酮的去氢衍生物,其蛋白同化作用与丙酸酯睾酮相似,但雄性激素活性仅为后者的百分之一。此药物能够促进蛋白质合成,抑制异生过程,维持正氮平衡,从而增加食欲、肌肉量和体重;它还能促使钙磷在骨组织中沉积,加速骨细胞间质形成及骨钙化,加速骨折愈合与创伤修复,并降低血胆固醇水平,改善脂质代谢。尽管美雄酮曾被滥用于体育竞赛,但因长期或大剂量使用可能导致多种副作用,如骨骼增重、水钠潴留、皮肤血供增加等,甚至可能诱发肝癌及良性肝细胞腺瘤,已于1976年被列入国际奥委会禁用兴奋剂名单。目前禁止使用的蛋白同化制剂共有31种。
性状美雄酮为白色或类白色的结晶性粉末,无特殊气味,不溶于水而易溶于乙醇和氯仿,微溶于乙醚。

药理作用- 促进蛋白质合成,抑制异生过程,维持正氮平衡,增进食欲、肌肉生长及体重增加。
- 加速钙磷沉积于骨组织,促进骨细胞间质形成,加速骨钙化和骨成长。
- 促进组织新生与肉芽生成,加快创伤修复与溃疡愈合。
- 降低血胆固醇水平,改善脂质代谢。
适用于蛋白质合成不足或分解增多的情况,如慢性消耗性疾病、严重感染、创伤、烧伤造成的负氮平衡状态、恶性肿瘤、骨质疏松症、小儿发育不良、侏儒症、骨折难愈合及高胆固醇血症等。此信息由Chemicalbook的侍艳编辑整理(2015-11-17)。
用法用量成人初期可每日服用10~30毫克,分2~3次口服;病情改善后调整为每天5~10毫克维持剂量,治疗周期4~8周为一个疗程。重复使用时需间隔1~2个月。老年人应酌情减量,儿童每公斤体重日剂量为0.05毫克。为了提高疗效,建议同时补充适量蛋白质、糖分和维生素。
不良反应常见的不良反应包括胃肠道不适(如恶心、呕吐等),长期大量使用可能导致骨骼增重、水钠滞留、皮肤血流增加、低钙血症及骨质硬化等症状。女性使用者可能出现轻微的男性化表现,比如痤疮、多毛症状、声音变得粗犷、阴蒂增大和月经紊乱等。此外,肝功能方面可能出现黄疸或肝功能障碍。
禁忌证- 对美雄酮过敏者禁用。
- 肝脏功能不全患者禁用。
- 孕妇以及治疗期间可能怀孕的女性禁止使用。
- 前列腺癌、肾病、高血压及前列腺增生疑诊者禁用。
- 使用过程中应定期检测肝功能状况。
- 老年人用药量需适当减少。
- 为了增强疗效,应补充适量的蛋白质、糖分和维生素等营养物质。
与羟基保泰松同用时,后者血药浓度可能会升高。
剂型常见的剂型为片剂:1毫克/片,2.5毫克/片,5毫克/片。
制备方法用途
作为雄激素及同化激素类药物使用。适用于慢性消耗性疾病、小儿发育不良、骨质疏松症和高血脂等病症治疗。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 17-甲睾酮 17-methyltestosterone 58-18-4 C20H30O2 302.457 雄甾-1,4-二烯-3,17-二酮 Androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione 897-06-3 C19H24O2 284.398 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 17α-hydroxy-17β-methylandrosta-1,4-dien-3-one 33526-40-8 C20H28O2 300.441 —— (3aα,8aα,8bβ)-dodecahydro-5aβ,6α-dimethyl-6β-hydroxy-2'-methyl-as-indacene-3(R)-spiro-(2',5'-cyclohexadienone) —— C20H28O2 300.441 —— 11α,17β-dihydroxy-17α-methylandrost-1,4-dien-3-one 25356-68-7 C20H28O3 316.441 —— (8S,9S,10R,11S,13S,14S,17S)-11,17-dihydroxy-10,13,17-trimethyl-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one 22204-44-0 C20H28O3 316.441 17Alpha-甲基-17Β-羟基雄甾-1,4,6-三烯-3-酮 17β-Hydroxy-3-oxo-17α-methyl-Δ1,4,6-androstatrien 28816-02-6 C20H26O2 298.425 —— metandienone,TMS —— C23H36O2Si 372.623 —— (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-10,13,17-Trimethyl-17-trimethylsilanyloxy-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one 73024-97-2 C23H36O2Si 372.623 6β-羟基美雄酮 6β,17β-dihydroxy-17α-methyl-1,4-androstadien-3-one 33526-41-9 C20H28O3 316.441 17-甲睾酮 17-methyltestosterone 58-18-4 C20H30O2 302.457 —— metanedienone-17-sulfate 119888-55-0 C20H28O5S 380.505 17a-甲基-1,5-雄甾二烯-3b,17b-二醇 17α-Methyl-androsta-1,5-dien-3β,17β-diol 2694-98-6 C20H30O2 302.457 —— 17,17-dimethyl-18-norandrosta-1,4,13(14)-trien-3-one 77702-25-1 C20H26O 282.426 —— 17α-methylandrost-4-ene-3β,17β-diol 571-03-9 C20H32O2 304.473 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Torrini; Romeo, Farmaco, Edizione Scientifica, 1980, vol. 35, # 8, p. 681 - 683摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Gewinnung von 1; 4-Bisdehydro-3-oxo-steroiden。ÜberSteroide,139。摘要:描述了一种方法,该方法使得能够仅在一个化学步骤中从环A中饱和的3-氧-甾族化合物或从αβ-单不饱和的3-酮中特别生产1,4-双脱氢-3-氧-甾族化合物。脱氢剂是二氧化硒,溶剂是叔醇,优选含有一些酸。DOI:10.1002/hlca.19560390314
文献信息
-
Photocontrolled Cobalt Catalysis for Selective Hydroboration of α,β‐Unsaturated Ketones作者:Frédéric Beltran、Enrico Bergamaschi、Ignacio Funes‐Ardoiz、Christopher J. TeskeyDOI:10.1002/ange.202009893日期:2020.11.16In this way, we bias the reaction down two divergent pathways, giving contrasting products in the catalytic hydroboration of α,β‐unsaturated ketones. This includes direct access to previously elusive cyclic enolborates, via 1,4‐selective hydroboration, providing a straightforward and stereoselective route to rare syn‐aldol products in one‐pot. DFT calculations and mechanistic experiments confirm two
-
COMBINATION THERAPY OF A HIF-2-ALPHA INHIBITOR AND AN IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC AGENT AND USES THEREOF申请人:PELOTON THERAPEUTICS, INC.公开号:US20180140569A1公开(公告)日:2018-05-24The present invention provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating proliferative disorders. The method involves step of administering to said subject a HIF-2alpha inhibitor and an immunotherapeutic agent.本发明提供了治疗增殖性疾病的方法和药物组合物。该方法涉及向所述受试者施用HIF-2alpha抑制剂和免疫治疗药物的步骤。
-
[EN] 5-HT2C RECEPTOR AGONISTS AND COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS OF USE<br/>[FR] AGONISTES DE RÉCEPTEUR 5-HT2C ET COMPOSITIONS ET PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION申请人:ARENA PHARM INC公开号:WO2017023679A1公开(公告)日:2017-02-09Provided in some embodiments are compounds of Formula A, as defined herein, that modulate the activity of 5-HT2C receptor. Also provided in some embodiments are methods, such as, for weight management, inducing satiety, and decreasing food intake, and for preventing and treating obesity, antipsychotic-induced weight gain, type 2 diabetes, Prader-Willi syndrome, tobacco/nicotine dependence, drug addiction, alcohol addiction, pathological gambling, reward deficiency syndrome, and sex addiction), obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorders and impulse control disorders (including nail-biting and onychophagia), sleep disorders (including insomnia, fragmented sleep architecture, and disturbances of slow-wave sleep), urinary incontinence, psychiatric disorders (including schizophrenia, anorexia nervosa, and bulimia nervosa), Alzheimer disease, sexual dysfunction, erectile dysfunction, epilepsy, movement disorders (including parkinsonism and antipsychotic-induced movement disorder), hypertension, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity-related renal disease, and sleep apnea.在某些实施例中提供了一些符合本文所定义的A式化合物,其调节5-HT2C受体的活性。在某些实施例中还提供了一些方法,例如用于体重管理、诱导饱腹感、减少食物摄入,以及预防和治疗肥胖、抗精神病药物引起的体重增加、2型糖尿病、普拉德-威利综合征、烟草/尼古丁依赖、药物成瘾、酒精成瘾、病理性赌博、奖赏缺乏综合征和性成瘾,强迫症谱系障碍和冲动控制障碍(包括咬指甲和咬甲症),睡眠障碍(包括失眠、睡眠结构碎裂和慢波睡眠紊乱),尿失禁,精神障碍(包括精神分裂症、厌食症和暴食症),阿尔茨海默病,性功能障碍,勃起功能障碍,癫痫,运动障碍(包括帕金森病和抗精神病药物引起的运动障碍),高血压,血脂异常,非酒精性脂肪肝病,肥胖相关肾脏疾病和睡眠呼吸暂停症。
-
Iridium-catalysed highly selective reduction–elimination of steroidal 4-en-3-ones to 3,5-dienes in water作者:Jide Li、Weiping Tang、Demin Ren、Jiaxi Xu、Zhanhui YangDOI:10.1039/c9gc00654k日期:——Steroidal 3,5-diene is an important structural motif in steroid drugs. In this report, an iridium-catalyzed reduction–elimination of readily available steroidal 4-en-3-ones is realized to prepare steroidal 3,5-dienes. At a low catalyst loading (S/C = 200), heating 4-en-3-ones in a water-mixed organic solvent with formic acid without inert atmosphere protection afforded the desired 3,5-dienes in moderate甾类3,5-二烯是类固醇药物中的重要结构基序。在该报告中,实现了铱催化的现成甾体4-en-3-ones的还原-消除反应,从而制备了甾体3,5-二烯。在低催化剂负荷下(S / C= 200),在与甲酸混合的水混合有机溶剂中加热4-en-3-one,而没有惰性气氛保护,以中等至优异的产率得到所需的3,5-二烯。在克级制备中,使用重结晶代替柱色谱法纯化产物。具有出色的功能耐受性和区域选择性。链烷醇(伯,仲和叔),酯(甲酸酯除外),甲苯磺酸酯和酮(内环或外环)等结构部分不受影响。出人意料的是,消除还原仅发生在A环4环3合1处。另外,双环4-en-3-ones也是可行的底物。证明了甾体3,5-二烯的合成应用。当DCO发生时,我们的方法还可以导致甾体3,5-二烯-3-d(> 99%D-掺入)2 D和D 2 O一起使用。
-
[EN] BENZIMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE BENZIMIDAZOLE ET LEURS UTILISATIONS申请人:PELOTON THERAPEUTICS INC公开号:WO2015175845A1公开(公告)日:2015-11-19Benzimidazole derivatives of Formula I, that modulate the activity of ACSS2 are disclosed for therapeutic use. The fused imidazole ring of the compounds disclosed has a diarylmethyl or diarylmethanol moiety attached at the 2-position and the compounds have at least one other substituent at the 5 or 6 position of the benzimidazole. Also disclosed are methods of using the benzimidazole compounds for the treatment of diseases or disorders, such as cancer.
表征谱图
-
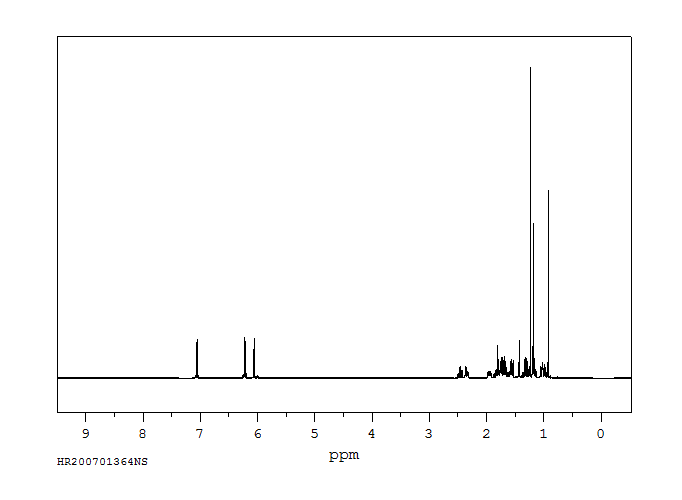
氢谱1HNMR
-
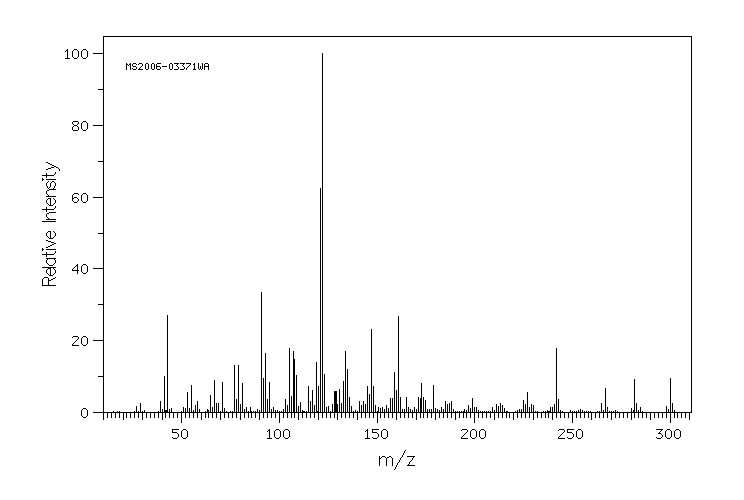
质谱MS
-
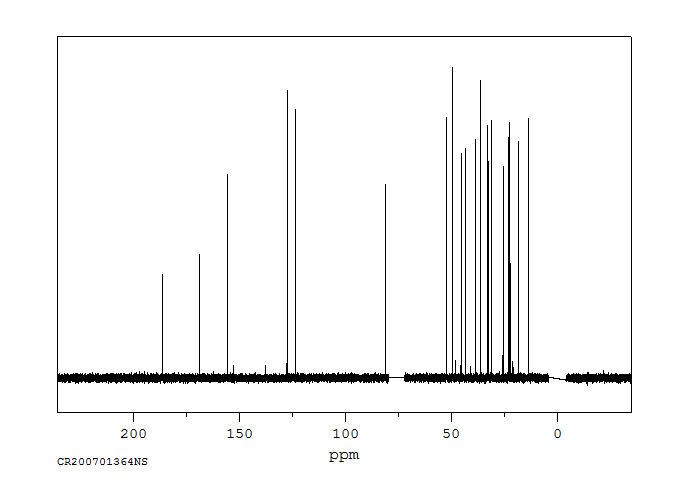
碳谱13CNMR
-
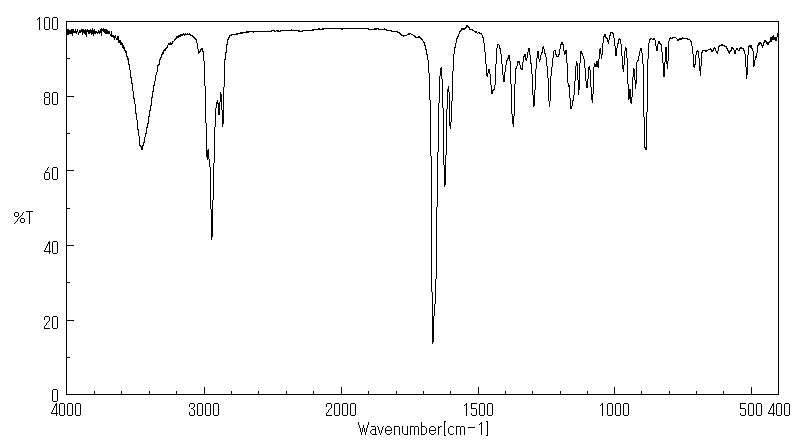
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息