9-methyl-Δ5(10)-octalin-1-ol-6-one | 4242-00-6
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
9-methyl-Δ5(10)-octalin-1-ol-6-one
英文别名
5-hydroxy-4a-methyl-4,4a,5,6,7,8-hexahydronaphthalen-2(3H)-one;(±)-4a,5-cis-(5-hydroxy-4a-methyl-4,4 a,5,6,7,8-hexahydronaphthalen-2(3H)-one);5-hydroxy-4a-methyl-3,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydronaphthalen-2-one
CAS
4242-00-6
化学式
C11H16O2
mdl
——
分子量
180.247
InChiKey
KLAHBFOZHSNBDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:47-56 °C
-
沸点:328.2±31.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.11±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.9
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.73
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 8a-methyl-2,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-naphthalen-1-ol 13304-34-2 C11H18O 166.263 1,6-萘二醇,1,2,3,4,6,7,8,8a-八氢-8a-甲基- 8a-methyl-2,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-naphthalene-1,6-diol 100052-83-3 C11H18O2 182.263 9-甲基-delta-5(10)-辛-1,6-二酮 Wieland-Miescher ketone 20007-72-1 C11H14O2 178.231 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (4aS,5S)-4,4a,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-5-hydroxy-4a-methylnaphthalen-2(3H)-one —— C11H16O2 180.247 —— (R)-1,2,3,4,8,8a-hexahydro-1β-hydroxy-8aβ-methyl-6-(7H)-naphthalenone 34996-06-0 C11H16O2 180.247 —— 5-(methoxymethoxy)-4a-methyl-4,4a,5,6,7,8-hexahydronaphthalen-2(3H)-one 1242641-78-6 C13H20O3 224.3 —— (±)-8a,1-cis-(8a-methyl-6-oxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalen-1-yl acetate) 36927-82-9 C13H18O3 222.284 9-甲基-delta-5(10)-辛-1,6-二酮 Wieland-Miescher ketone 20007-72-1 C11H14O2 178.231 (S)-(+)-3,4,8,8a-四氢-8a-甲基-1,6-(2H,7H)-萘醌 (S)-8a-methyl-3,4,8,8a-tetrahydro-2H,7H-naphthalene-1,6-dione 33878-99-8 C11H14O2 178.231
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:9-methyl-Δ5(10)-octalin-1-ol-6-one 在 盐酸 、 Pd/SrCO3 、 乙醚 、 乙醇 作用下, 生成 (+/-)(4aΞ)-2ξ-(4-Methoxy-phenyl)-4a-methyl-5ξ-((Ξ)-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-(4ar,8ac)-decahydro-[2ξ]naphthol参考文献:名称:男性性激素的类似物摘要:描述了顺式和反式-6-(4'-氧代环己烯基)-9-甲基十氢-1-醇的合成,其可以被视为D-高-睾丸激素的类似物。DOI:10.1016/0040-4020(58)88055-2
-
作为产物:描述:9-甲基-delta-5(10)-辛-1,6-二酮 在 sodium tetrahydroborate 、 溶剂黄146 作用下, 以 乙醇 为溶剂, 生成 9-methyl-Δ5(10)-octalin-1-ol-6-one参考文献:名称:Dowex 50WX4-100:醇四氢吡喃化的高效催化剂摘要:摘要 已发现离子交换树脂 Dowex 50WX4-100 在环境条件下可有效催化多种醇与 2,3-二氢-4H 吡喃 (DHP) 和二氯甲烷的保护反应。DOI:10.1080/00397910902774059
文献信息
-
CONTRACEPTIVE AGENTS申请人:Blanco Gustavo公开号:US20140005132A1公开(公告)日:2014-01-02The invention provides compounds of formula I, II, III, or IV: wherein R 1 to R 11 , X, and Y have any of the values defined in the specification. The compounds inhibit Na, K-ATPase α4 and are useful as contraceptive agents.这项发明提供了式I、II、III或IV的化合物: 其中R1至R11、X和Y具有规范中定义的任何值。这些化合物抑制Na、K-ATPase α4,并可用作避孕剂。
-
Discovery of New Carbonyl Reductases Using Functional Metagenomics and Applications in Biocatalysis作者:Sophie A. Newgas、Jack W. E. Jeffries、Thomas S. Moody、John M. Ward、Helen C. HailesDOI:10.1002/adsc.202100199日期:2021.6.21Enzyme discovery for use in the manufacture of chemicals, requiring high stereoselectivities, continues to be an important avenue of research. Here, a sequence directed metagenomics approach is described to identify short chain carbonyl reductases. PCR from a metagenomic template generated 37 enzymes, with an average 25% sequence identity, twelve of which showed interesting activities in initial screens用于化学品制造的酶发现需要高立体选择性,仍然是一个重要的研究途径。在这里,描述了一种序列定向宏基因组学方法来识别短链羰基还原酶。宏基因组模板的 PCR 产生了 37 种酶,平均序列同一性为 25%,其中 12 种酶在初始筛选中显示出有趣的活性。然后,针对 21 种底物(包括在生物催化还原中具有挑战性的体积较大的底物)对六种生产力最高的酶进行了测试。选择两种酶与维兰德米歇尔酮进行进一步研究。值得注意的是,酶 SDR-17 当与辅因子回收系统共表达时,以 89% 和 99% ee的优异分离产率产生反(4a R ,5 S ) 异构体。这些结果证明了序列定向宏基因组学方法用于鉴定具有低相似性的多个同源序列的可行性,该方法可以产生适用于工业生物催化的高度立体选择性酶。
-
Metal-assisted reactions—12作者:Brendan J. Hussey、Robert A.W. Johnstone、Peter Boehm、Ian D. EntwistleDOI:10.1016/0040-4020(82)80090-2日期:1982.1Zinc bis-tetrahydroborate forms a solid complex with dimethylformamide (DMF) of composition, Zn(BH4)2 1.5DMF. Unlike zinc bis-tetrahydroborate itself, the complex with DMF can be stored as a solid at room temperature. Ketones and aldehydes are reduced to the corresponding alcohols by the complex but the mechanism of reduction appears to be different from that using zinc bis-tetrahydroborate itself双-四氢硼酸锌与组成为Zn(BH 4)2 1.5DMF的二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)形成固体络合物。与双-四氢硼酸锌本身不同,与DMF形成的络合物可以在室温下以固体形式存储。酮和醛是由复杂的还原为相应的醇,但减少的机制似乎是从该使用锌不同双-tetrahydroborate本身和其他tetrahydroborates在仅一个氢化物当量为每BH 4 -使用单位而不是四个。此外,尽管饱和脂族酮迅速还原成醇,但芳族酮反应要慢得多,而α,β-不饱和酮反应得很慢,因此该络合物对于不同种类的酮似乎具有选择性还原的潜力。同样明显的是,双-四氢硼酸锌/ DMF络合物还原位阻饱和酮的速度比未受阻酮的还原速度慢得多。可以在溶液中制备类似的双-四氢硼酸镉/ DMF络合物,并与锌络合物类似地与酮反应。
-
Oxidation of alkenes to enones using -butyl hydroperoxide in the presence of chromium carbonyl catalysts作者:Anthony J. Pearson、Yong-Shin Chen、Shih-Ying Hsu、Tapan RayDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)80121-0日期:1984.1Treatment of alkenes with t-butyl hydroperoxide in the presence of Cr(CO)6 or Cr(CO)x (CH3CN)y species results in oxidation of allylic methylene groups to give α,β-unsaturated ketones, in the presence of certain alcohols, and in moderate to excellent yields.
-
Total syntheses of the sesquiterpenes β-corymbolol and corymbolone作者:Helena M.C. Ferraz、Antonio J.C. Souza、Beatriz S.M. Tenius、Graziela G. BiancoDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2006.07.026日期:2006.9The first total synthesis of racemic corymbolone, an eudesmane sesquiterpene isolated from Cyperus species used in traditional medicine to treat many diseases, is reported. In the developed sequence, the immediate precursor of corymbolone is the diol β-corymbolol, an epimer at C1 of the natural α-corymbolol. Thus, starting from the readily available Wieland–Miescher Ketone, the title compounds were据报道,外消旋Corymbolone是从香蒲属植物中分离得到的一种大叶倍半萜烯,它是传统药物中的首个全合成药物,可用于治疗多种疾病。在已开发的序列中,Corymbolone的直接前体是二醇β-Corymbolol,它是天然α-Corymbolol在C 1处的差向异构体。因此,从现成的Wieland-Miescher Ketone开始,标题化合物分别在大约11和12个步骤中获得。总产率为3%。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
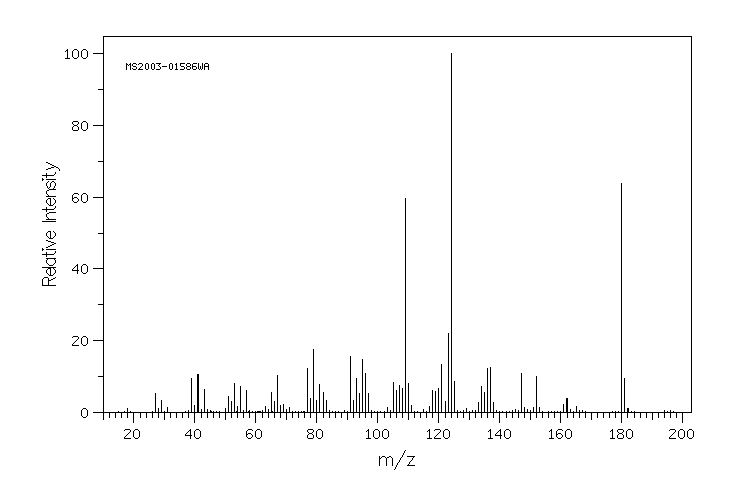
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
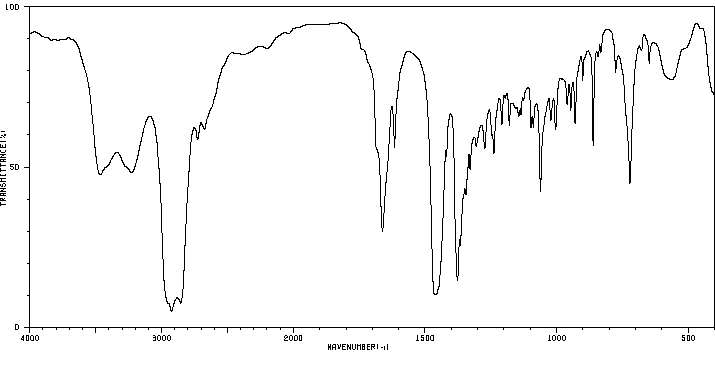
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷